

| Semimembranosus muscle | |
|---|---|
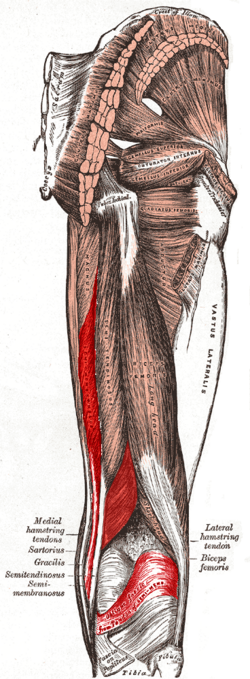
Muscles of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions (semimembranosus labeled at bottom left)
| |
| Details | |
| Origin | Ischial tuberosity |
| Insertion | Medial condyle of tibia |
| Artery | Profunda femoris and gluteal arteries |
| Nerve | Tibial partofsciatic nerve (L5, S1 and S2) |
| Actions | Extensionofhip and flexionofknee |
| Antagonist | Quadriceps muscle and tensor fasciae latae |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus semimembranosus |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.036 |
| TA2 | 2642 |
| FMA | 22438 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The semimembranosus muscle (/ˌsɛmiˌmɛmbrəˈnoʊsəs/) is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles in the thigh. It is so named because it has a flat tendon of origin. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus muscle. It extends the hip joint and flexes the knee joint.

The semimembranosus muscle, so called from its membranous tendon of origin, is situated at the back and medial side of the thigh. It is wider, flatter, and deeper than the semitendinosus (with which it shares very close insertion and attachment points).[1] The muscle overlaps the upper part of the popliteal vessels.
The semimembranosus muscle originates by a thick tendon from the superolateral aspect of the ischial tuberosity.[1] It arises above and medial to the biceps femoris muscle and semitendinosus muscle. The tendon of origin expands into an aponeurosis, which covers the upper part of the anterior surface of the muscle; from this aponeurosis, muscular fibers arise, and converge to another aponeurosis which covers the lower part of the posterior surface of the muscle and contracts into the tendon of insertion.
The semimembranosus muscle inserts on the:
The tendon of insertion gives off certain fibrous expansions: one, of considerable size, passes upward and laterally to be inserted into the posterior lateral condyle of the femur, forming part of the oblique popliteal ligament of the knee-joint; a second is continued downward to the fascia which covers the popliteus muscle; while a few fibers join the medial collateral ligament of the joint and the fascia of the leg.
The semimembranosus is innervated by the tibial part of the sciatic nerve.[1] The sciatic nerve consists of the anterior divisions of ventral nerve roots from L4 through S3. These nerve roots are part of the larger nerve network–the sacral plexus.[2] The tibial part of the sciatic nerve is also responsible for innervation of semitendinosus and the long head of biceps femoris.
The semimembranosus muscle may be reduced or absent, or double, arising mainly from the sacrotuberous ligament and giving a slip to the femur or adductor magnus.
The semimembranosus muscle extends (straightens) the hip joint. It also flexes (bends) the knee joint.[1]
It also helps to medially rotate the knee: the tibia medially rotates on the femur when the knee is flexed. It medially rotates the femur when the hip is extended. The muscle can also aid in counteracting the forward bending at the hip joint.[2]
The semitendinosus muscle may be dry needled.[1]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 479 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 479 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iliac region |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Buttocks |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Thigh / compartments |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Leg/ compartments |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Foot |
| ||||||||||||||||