

| Deep fascia of leg | |
|---|---|
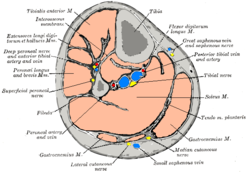
Cross-section through middle of leg.
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia cruris |
| TA98 | A04.7.03.021 |
| TA2 | 2708 |
| FMA | 45206 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The deep fascia of legorcrural fascia forms a complete investment to the muscles, and is fused with the periosteum over the subcutaneous surfaces of the bones.
The deep fascia of the leg is continuous above with the fascia lata (deep fascia of the thigh), and is attached around the knee to the patella, the patellar ligament, the tuberosity and condyles of the tibia, and the head of the fibula.
Behind, it forms the popliteal fascia, covering in the popliteal fossa; here it is strengthened by transverse fibers, and perforated by the small saphenous vein.
It receives an expansion from the tendon of the biceps femoris laterally, and from the tendons of the sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus medially; in front, it blends with the periosteum covering the subcutaneous surface of the tibia, and with that covering the head and malleolus of the fibula; below, it is continuous with the transverse crural and laciniate ligaments.
It is thick and dense in the upper and anterior part of the leg, and gives attachment, by its deep surface, to the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus; but thinner behind, where it covers the gastrocnemius and soleus.
It gives off from its deep surface, on the lateral side of the leg, two strong intermuscular septa, the anterior and posterior peroneal septa, which enclose the fibularis (peroneus) longus and brevis muscles and separate them from the muscles of the anterior and posterior crural regions, and several more slender processes which enclose the individual muscles in each region.
A broad transverse intermuscular septum, called the deep transverse fascia of the leg, intervenes between the superficial and deep posterior crural muscles.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 480 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 480 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iliac region |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Buttocks |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Thigh / compartments |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Leg/ compartments |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Foot |
| ||||||||||||||||
This human musculoskeletal system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |