アロステリック調節因子
薬理学や生化学において、アロステリック調節因子︵アロステリックちょうせついんし、英語: allosteric modulator︶は、受容体に結合してその受容体の刺激に対する反応を変化させる物質群である。ベンゾジアゼピンのように医薬品となるものもある[1]。アロステリック調節因子が結合する部位︵=アロステリック部位︶は、内因性の受容体の作動物質︵別名アゴニスト︶が結合する部位︵=オルソステリック部位︶とは異なる。調節因子と作動物質はどちらも受容体リガンドと呼ぶことが出来る[2]。
アロステリック調節因子には、陽性︵positive︶、陰性︵negative︶、中性︵neutral, silent︶の3つのタイプがある。陽性タイプは作動物質が受容体に結合する確率を高めたり︵親和性︶、受容体を活性化する能力を高めたり︵有効性︶、あるいはその両方により、受容体の反応を増大させる。陰性タイプは作動物質の親和性や有効性を低下させる。中性タイプは作動物質の活性には影響を与えないが、他の調節因子がアロステリック部位に結合するのを阻止することができる。調節因子の中にはアロステリック作動物質として機能するものもある[2]。
﹁アロステリック﹂という言葉は、ギリシャ語に由来する。allosは﹁他の﹂、stereosは﹁固体﹂または﹁形状﹂を意味する。これは﹁他の形﹂と訳すことができ、調節因子によって引き起こされる受容体内の構造変化を示し、調節因子が受容体の機能に影響を与えることを意味している[3]。
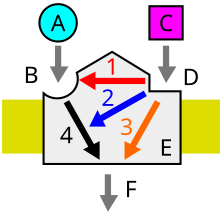
内因性作動物質(A)は、受容体(E)の結合部位(B)に結合する。 アロステリック調節因子(C)はアロステリック部位(D)に結合する。調節因子は、アゴニストの親和性(1)や有効性(2)を増加/減少させる。内因性作動物質は、(1,2)の調整を受けて受容体に影響を与える(4)。調節因子は作動物質として作用し、その効果(3)をもたらすこともある。これら(3,4)を受けて受容体が応答する(F)。
内因性︵オルソステリックな︶作動物質は、通常の結合部位︵オルソステリック部位︶に結合する。アロステリック調節因子はこの部位には結合せず、異なる部位︵アロステリック部位︶に結合する[2]。結合すると、調節因子は一般的に受容体の三次元構造︵即ちコンフォメーション︶を変化させる。これによりオルソステリック部位も変化し、作動物質の結合効果が変化することがある[4]。また、アロステリック調節因子は受容体の正常な構造の一つを安定化させることもできる[5]。
実際のところ、調節の詳細は複雑である。調節因子は、部分作動物質として機能する場合がある。つまり、作動物質を必要とせずに作動物質の効果を得ることができる[6]。また、調節は、異なる作動物質の親和性や有効性に等しく影響しないこともある。同じ作用を持つはずの複数の作動物質が同じ受容体に結合した場合でも、調節因子によっては作動物質が同じように調節されないことがある[4]。
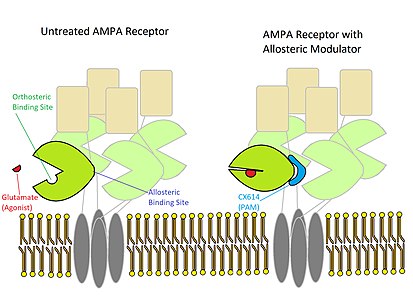
PAMであるCX614は、AMPA受容体のアロステリック部位に結 合し、閉じた構造を安定化させる
調節因子の中には、作動物質が結合した状態での構造変化を安定化させる作用を持つものがある。これにより、受容体が活性状態になる確率が高くなるが、受容体が不活性状態に戻るのを防ぐことはできない。活性状態である確率が高ければ、受容体はより長く作動物質と結合することになる。アニラセタムやCX614で調節されたAMPA受容体は、非活性化の速度が遅くなり、全体的な陽イオン輸送が促進される。これは、アニラセタムやCX614が、グルタミン酸の結合部位を含む貝殻様構造の背面に結合し、AMPA受容体の活性化状態である貝が閉じた構造を安定化させることで達成されると考えられる[5][9]。
概要[編集]
アロステリック調節因子は、受容体に作用する他の物質の親和性や有効性を変化させることができる。調節因子は、受容体に作用する他の物質の親和性と有効性を変化させる[4]。親和性とは、ある物質が受容体に結合する能力のことである。有効性とは、物質が受容体を活性化する能力のことで、受容体の内因性作動物質と比較した場合の割合で与えられる。有効性がゼロの場合、その物質は阻害物質︵別名アンタゴニスト︶と見做される[1]。
分類[編集]
調節因子は、受容体の中で3つの効果を発揮する。1つは、受容体を活性化出来るか出来ないか︵2つの可能性︶である。残りの2つは、アゴニストの親和性と有効性である。これらの効果は、増加するか、減少するか、または影響を受けないままである︵其々3つの可能性︶。これにより、17通りの調節因子の組み合わせが可能となる[4]。中性タイプの調節因子も含めると18通り︵=2×3×3︶となる。 現実的には、これらの組み合わせは、5つの調節因子[4]と1つの中性因子のみに纏められる。 ●陽性アロステリック調節因子︵PAM︶は、作動物質の親和性や有効性を高める作用がある[4]。臨床例としては、GABAA受容体を調節するジアゼパム、アルプラゾラム、クロルジアゼポキシドなどのベンゾジアゼピン系薬剤や、カルシウム感知受容体を調節するシナカルセト等が挙げられる[7]。 ●PAM作動物質は、PAMのように作用するだけでなく、調節する作動物質の有無に拘わらず、作動物質としても作用する[4]。 ●PAM阻害物質は、PAMと同様に作用するが、阻害物質としても機能し、調節する作動物質の効力を低下させる[4]。 ●陰性アロステリック調節因子︵NAM︶は、作動物質の親和性や効力を低下させる[4]。マラビロクは、CCR5を調節する薬剤である。フェノバム、ラセグルラント、ジプラグルラントは実験的なGRM5調節因子である[7]。 ●NAM作動物質は、NAMのように作用するだけでなく、他の作動物質の有無に拘わらず、作動物質としても作用する[4]。 ●中性アロステリック調節因子は、作動物質の活性には影響を与えないが、受容体に結合し、PAMや他の調節因子が同じ受容体に結合するのを防ぎ、その調節を阻害する[4]。中性調節因子は、無作動アロステリック調節因子︵SAM︶[6]や中性アロステリックリガンド︵NAL︶とも呼ばれる。例えば、研究用試薬である5-メチル-2-(フェニルエチニル)ピリジン︵5-MPEP︶はGRM5に結合する[8]。機序[編集]
アロステリック調節因子の結合部位が多彩であることから、アロステリック調節因子は多様な機序で作用する。結合の調節[編集]
アロステリック調節因子の中には、標的となる受容体の構造変化を誘発し、受容体作動物質の結合親和性や有効性を高めるものがある[2]。例えば、ベンゾジアゼピン系やバルビツール酸系の薬剤は、GABAA受容体の陽性アロステリック調節因子である。ジアゼパム等のベンゾジアゼピン系薬剤は、GABAA受容体のイオンチャネルのαサブユニットとγサブユニットの間に結合し、チャネルの開口頻度を増加させるが、各開口の持続時間は増加させない。フェノバルビタールのようなバルビツール酸塩は、βサブユニットと結合し、チャネルの開口部の持続時間を増加させるが、開口部の頻度は増加させない[9]。結合解除の調節[編集]

受容体の感受性低下の予防[編集]
受容体の感受性低下を防ぐことで、全体的なシグナルを増加させることができる。感受性低下とは、作動物質が存在するにもかかわらず、受容体が活性化されない現象である。この現象は、作動物質に繰り返し、あるいは激しく曝されることで起こる場合が多い。この現象を無くしたり減らしたりすることで、受容体全体の活性を高めることが出来る。AMPA受容体は、リガンド結合ドメインの二量体接面が破壊されることで感受性が低下し易い。シクロチアジドは、この接面を安定化させ、感受性低下を遅らせることが明らかになっており、陽性アロステリック調節因子と考えられている[5]。活性型/不活性型構造の安定化[編集]
調節因子は、作動物質の結合に影響を与えずとも、受容体を直接制御することが出来る。結合した受容体の構造を安定化させるのと同様に、この機序で作用する調節因子は、活性状態または不活性状態の構造を安定化させる。これにより、受容体が安定化した状態に留まる確率が高まり、それに応じて受容体の活性を上昇または低下させることが出来る。カルシウム感知受容体はこの一例であり、pHが調節因子となっている。pHが低いと不活性状態の安定性が増し、受容体の感度が低下する。これは、pHの調整に伴う電荷の変化が、不活性化に有利な構造変化を受容体にもたらすからだと推測される[10]。作動物質との相互作用[編集]
部分作動物質および完全作動物質の親和性のみを増加させる調節因子は、より低い作動物質濃度でより早く有効性の最大値に到達させる。即ち、用量反応曲線の上り坂と最大値到達点が低濃度にシフトする[4]。 有効性を増強する調節因子は、部分作動物質の最大効力を上昇させる。完全作動物質の場合は既に受容体を完全に活性化しているので、調節因子は最大効力には影響しないが、反応曲線を低濃度側に多少シフトさせる[4]。- 作動物質濃度[Ago]に対する受容体反応率(%)のグラフ
-
PAMは、親和性を高める場合は初期の応答曲線(実線)を低濃度側にシフトさせ、また、有効性を高める場合は最大応答を増加させる。破線の曲線は、PAM添加後に取り得る曲線の内の2つの例である。矢印は、曲線のシフトのおおよその方向を示している[4]。
-
PAM作動物質は、PAMと同様の働きをするが、それ自体が作動物質である。そのため、修飾する作動物質の濃度が極めて低くとも反応を引き起こすことができる[4]。
-
PAM阻害物質は、作動物質の親和性を高めてその曲線を低濃度側にシフトさせるが、阻害物質として働くため、最大反応を低下させる[4]。
-
NAMは、親和性を低下させる場合は応答曲線を高濃度側にシフトさせ、また、有効性を低下させる場合は最大応答を低下させる。PAMと比較すると、NAMの効果は逆となる[4]。
-
NAM作動物質は、NAMと同様に作用するが、それ自体が作動物質である。そのため、調節する作動物質の濃度が低い領域で反応を引き起こす[4]。
医学的価値[編集]
利点[編集]
内因性作動物質が同じ受容体には、構造が非常によく似たオルソステリック結合部位がある。この部位に変異が生じると、受容体の機能が特に低下する可能性があり、生物にとって有害であるため、進化はこのような変化を好まないことが多い。一方でアロステリック部位は、受容体の機能にとってあまり重要ではないため、関連する受容体間で大きなバリエーションを持つことが多い。これが、オルソステリック薬と比較して、アロステリック薬が非常に特異的である、即ち、非常に限られたタイプの受容体にのみ作用を及ぼすことができる理由である。しかし、このようなアロステリック部位の多様性は生物種間でも起こるので、アロステリック薬の効果は生物種間で大きく異なる[11]。
調節因子の作用は、神経伝達物質のような内因性リガンドに依存するため、受容体を完全にオン/オフすることはできない。このため、同様の作用を持つオルソステリック薬と比較して、過量投与のリスクを低減出来る。また、受容体を飽和させるのに充分な量を安全に服用し、薬効を長持ちさせるという戦略も可能となる[4]。また、タイミングや目的に関係なく作動物質によって常に活性化し続けるのではなく、所定のタイミング︵すなわち、刺激に応じて︶で受容体を活性化することができる[12]。
調節因子は、極一部の組織の反応にのみ影響を与え、薬物の標的を特定の組織のみに絞ることを可能にする。これは、結合出来る全ての受容体に対して均等に作用する傾向にあるオルソステリック薬とは異なる[4]。また、モジュレーターの中には、作動物質のような感受性低下作用を持たないものもある。例えば、ニコチン性アセチルコリン受容体は、オルソステリック薬の存在下ではすぐに感受性が低下するが、PAMの存在下では正常な機能を維持する[13]。
応用[編集]
アロステリック調節因子は、これまで他の医薬品ではコントロールが困難だった多くの症状に有効であることが実証されている。これには以下が含まれる。
●4-nitro-N-(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)benzamide︵VU-29︶のような実験的mGluR5陽性調節剤を用いて、統合失調症に伴う陰性症状を軽減する[14]。
●GABA受容体を陽性に調節して、不安感を軽減する[9]。
●GABA受容体を陽性に調節して、睡眠障害の強度を軽減する[9]。
●ドーパミン受容体を陽性に調節して、大うつ病や統合失調症の抑うつ症状を軽減する。例えば、実験的なD1受容体陽性調節因子であるDETQ、DPTQ、LY3154207等がある[15]。
関連項目[編集]
●アロステリック効果 ●AMPA受容体陽性アロステリック修飾薬 ●GABAA受容体陽性アロステリック修飾薬 ●GABAA受容体陰性アロステリック修飾薬出典[編集]
- ^ a b Rang and Dale's pharmacology (8th ed.). Elsevier. (2016). pp. 6–20. ISBN 978-0-7020-5362-7
- ^ a b c d “International Union of Pharmacology Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification. XXXVIII. Update on terms and symbols in quantitative pharmacology”. Pharmacological Reviews 55 (4): 597–606. (December 2003). doi:10.1124/pr.55.4.4. PMID 14657418.
- ^ Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (5th ed.). W.H. Freeman. (2008). pp. 162. ISBN 978-0-7167-7108-1
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Pharmacology in drug discovery and development: understanding drug response (2nd ed.). Academic Press. (2017). pp. 102–119. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803752-2.00005-3. ISBN 978-0-12-803752-2
- ^ a b c “Mechanism of Positive Allosteric Modulators Acting on AMPA Receptors”. Journal of Neuroscience 25 (39): 9027–9036. (2005-09-28). doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2567-05.2005. ISSN 0270-6474. PMC 6725607. PMID 16192394.
- ^ a b Chemokine receptor oligomerization and allostery. 115. Academic Press. (2013). 4–5. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-394587-7.00009-9. ISBN 978-0-12-394587-7. PMC 4072031. PMID 23415099
- ^ a b “Allosteric modulation of 7 transmembrane spanning receptors: theory, practice, and opportunities for CNS drug discovery”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 55 (4): 1445–64. (February 2012). doi:10.1021/jm201139r. PMC 3349997. PMID 22148748.
- ^ “5 Allosteric Ligands”. Molecular Pharmacology 93 (5): 504–514. (May 2018). doi:10.1124/mol.117.111518. PMID 29514854.
- ^ a b c d Biased signaling in physiology, pharmacology and therapeutics. Elsevier. (2014). pp. 187–189. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-411460-9.00006-9. ISBN 9780124114609
- ^ Principles of bone biology (4th ed.). Elsevier. (2019). pp. 542. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-814841-9.00023-3. ISBN 9780128148419
- ^ “Allosteric Modulator Discovery: From Serendipity to Structure-Based Design”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 62 (14): 6405–6421. (July 2019). doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01749. PMID 30817889.
- ^ “Design and Synthesis of Novel Positive Allosteric Modulators of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors with the Ability To Rescue Auditory Gating Deficit in Mice”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 62 (1): 159–173. (2019-01-10). doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01492. ISSN 1520-4804. PMID 29587480.
- ^ “Positive allosteric modulators as an approach to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-targeted therapeutics: Advantages and limitations”. Biochemical Pharmacology. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors as Therapeutic Targets: Emerging Frontiers in Basic Research and Clinical Science (Satellite to the 2011 Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience) 82 (8): 915–930. (2011-10-15). doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.05.001. ISSN 0006-2952. PMC 3162128. PMID 21575610.
- ^ “mGluR5 Positive Allosteric Modulators Facilitate both Hippocampal LTP and LTD and Enhance Spatial Learning”. Neuropsychopharmacology 34 (9): 2057–2071. (2009). doi:10.1038/npp.2009.30. ISSN 1740-634X. PMC 2884290. PMID 19295507.
- ^ “Positive allosteric modulators of the dopamine D1 receptor: A new mechanism for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders”. Neuropsychotherapeutics. Advances in Pharmacology. 86. (2019). pp. 273–305. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2019.06.001. ISBN 9780128166680. ISSN 1557-8925. PMID 31378255

![PAMは、親和性を高める場合は初期の応答曲線(実線)を低濃度側にシフトさせ、また、有効性を高める場合は最大応答を増加させる。破線の曲線は、PAM添加後に取り得る曲線の内の2つの例である。矢印は、曲線のシフトのおおよその方向を示している[4]。](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/Positive_allosteric_modulator_plot.svg/280px-Positive_allosteric_modulator_plot.svg.png)
![PAM作動物質は、PAMと同様の働きをするが、それ自体が作動物質である。そのため、修飾する作動物質の濃度が極めて低くとも反応を引き起こすことができる[4]。](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0f/Positive_allosteric_modulator_agonist_plot.svg/280px-Positive_allosteric_modulator_agonist_plot.svg.png)
![PAM阻害物質は、作動物質の親和性を高めてその曲線を低濃度側にシフトさせるが、阻害物質として働くため、最大反応を低下させる[4]。](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7e/Positive_allosteric_modulator_antagonist_plot.svg/280px-Positive_allosteric_modulator_antagonist_plot.svg.png)
![NAMは、親和性を低下させる場合は応答曲線を高濃度側にシフトさせ、また、有効性を低下させる場合は最大応答を低下させる。PAMと比較すると、NAMの効果は逆となる[4]。](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ca/Negative_allosteric_modulator_plot.svg/280px-Negative_allosteric_modulator_plot.svg.png)
![NAM作動物質は、NAMと同様に作用するが、それ自体が作動物質である。そのため、調節する作動物質の濃度が低い領域で反応を引き起こす[4]。](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/81/Negative_allosteric_modulator_agonist_plot.svg/280px-Negative_allosteric_modulator_agonist_plot.svg.png)