オハイオ州
座標: 北緯40度30分 西経82度30分 / 北緯40.5度 西経82.5度
- オハイオ州
- State of Ohio
-


(州旗) (州章) - 州の愛称: トチノキの州
The Buckeye State - 州のモットー: 神の御側にあれば為せざることなし
With God, all things are possible 
-
州都 コロンバス[1][2] 最大の都市 コロンバス 州知事 マイク・デワイン
(共和党)公用語 英語(事実上)
法的指定なし面積
- 総計
- 陸地
- 水域全米第34位
116,096 km²
106,156 km²
10,040 km² (8.7%)人口(2020年)
- 総計
- 人口密度全米第7位
11,799,448人
111.2人/km²合衆国加入
- 順番
- 加入年月日
17番目
1803年3月1日[3]時間帯 UTC -5
DST -4緯度 北緯38°24' - 41°59' 経度 西経80°31' - 84°49' 東西の幅 355 km 南北の長さ 355 km 標高
-最高標高
-平均標高
-最低標高
472 m
260 m
139 m略称 (ISO 3166-2:US) US-OHウェブサイト オハイオ州政府 上院議員 シェロッド・ブラウン
J・D・ヴァンス
オハイオ州︵オハイオしゅう、英: State of Ohio、略号: OH.[4], O.[4]︶は、アメリカ合衆国中西部の北東にある州。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第34位、人口では第7位である。州の北はミシガン州とエリー湖、東はペンシルベニア州、南はケンタッキー州とウェストバージニア州、西はインディアナ州に接している。州都および2020年度の国勢調査での人口最大都市はコロンバス市である。州旗は全米の中で唯一、長方形でない、燕尾旗を採用している。漢字表記は阿海阿。
オハイオ州は1803年3月1日に、北西部領土から分かれて合衆国17番目の州に昇格した[3][5]。独立宣言に加わった13植民地ではないが、北東部はコネチカット州の西部保留地だった。
州名の由来[編集]
オハイオとは、インディアンのイロコイ族の言葉で、﹁美しい川﹂ないし﹁偉大な川﹂という意味である ohi-yo’ から派生した[6][7][8]。
州名の由来については他にも異論があるが、昔から州内に自生するトチノキに因んで "Buckeye State" と呼ばれており、州民も﹁バッカイ﹂と呼ばれている[9]。

イロコイ族が17世紀半ばのビーバー戦争で征服した地域、オハイオ川流 域の上中流ではほとんど人が住まなくなった[12]。赤色はイロコイ族の元々の領土
紀元前100年ごろ、オハイオではアデナ文化にホープウェル文化が加わった。その特徴ある文化の遺物が発見されたM・C・ホープウェル大尉が所有する農園に因んでこの名が付けられた[13]。ホープウェル文化の人々はアデナ文化の場合と同様にマウンドを造った。その複雑で大きく、技術的に洗練された土盛り工作物を現在のマリエッタ、ニューアーク、サークルビルで見ることができる[13]。しかし、ホープウェル文化は西暦600年ごろにオハイオ・バレーから消えた。その人々に代わった民族についてはほとんど知られていない[14]。研究によってフォート・エンシェント人とウィットルジーフォーカス人という2つの特徴ある前史文化が示されてきた[14]。どちらもおそらく、ヨーロッパ人との接触で広まった伝染病によって人口が激減し、17世紀には消失したと考えられている。インディアンはヨーロッパ由来の病気に免疫が無かった。フォートエンシェント人は﹁ショーニー族の先祖であるか、少なくともショーニー族がフォートエンシェント人で残っていた者達を吸収した﹂と考える学者もいる[14]。
オハイオ・バレーにいたインディアンは、現在のニューヨーク州中部と西部を地盤にしていたイロコイ族の攻撃的戦術に大きく影響された[15]。17世紀半ばのビーバー戦争の後、イロコイ族はオハイオ地域の大半を狩猟場、さらに重要なことにビーバーの罠猟を行う場と宣言した。17世紀半ばに起きた伝染病の蔓延と戦争によって、17世紀後半までオハイオ地域にはほとんど人が住まなくなった。その後主にアルゴンキン語を話す古代人の子孫が戻ってくるようになった。彼等はアデナ文化、ホープウェル文化さらにミシシッピ文化の人々の子孫である。オハイオ地域の住民は伝染病、戦争、さらにそれに続いた社会的不安定さによってもたらされた破壊のために、多民族、多言語の社会となった。彼等はトウモロコシ、ヒマワリ、豆類などの栽培で生活し、季節による狩猟で補っていた。18世紀までにヨーロッパ人が毛皮交易に入ってくることで、より大きな地球規模経済に入っていくことになった[16]。
有史時代になってオハイオ地域に住んだインディアン部族としては、マイアミ族、ワイアンドット族、デラウェア族、ショーニー族、オタワ族、ミンゴ族、エリー族などがいた[17]。オハイオ地域はインディアン虐殺の舞台にもなった。例えばイエロークリーク虐殺、グナーデンヒュッテン虐殺、ポンティアックの反乱の時の学校虐殺があった[18]。

ローワー・マンハッタンのフェデラル・ホール外にある北西部条例の銘 板
アメリカ合衆国は1787年の北西部条例で北西部領土を創設した[20]。この新領土のなかでは奴隷制度が禁じられた。オハイオ共同会社による開拓地マリエッタの設立で、開拓が始まった。この会社はアメリカ独立戦争退役兵の集団が設立したものだった。オハイオ会社の後に、マイアミ会社︵シムズ・パーチェイスとも呼ばれる︶が南西部を領有し、コネチカット土地会社が現在のオハイオ州北東部にあったコネチカット西部保留地の測量を行い入植させた。
古い北西部領土は当初、それ以前にオハイオ領土やイリノイ領土と呼ばれた地域を含んでいた。オハイオが州昇格の準備を始めると、インディアナ準州が創設され、北西部領土は現在のオハイオ州領域と、ミシガンのロウアー半島東半分、およびアッパー半島東端を含むものになった。
北西部条例の下では、ある領域の人口が6万人に達すると州として昇格が認められると決められていた。1801年12月時点でオハイオの人口はまだ45,000人だったが、アメリカ合衆国議会は、オハイオの人口が急増しており、州昇格への道を歩み始めたと判断した。州昇格の時までに人口は6万人を超えるものと仮定された。さらにレニ・レナペ族インディアンが地域に住んでおり、これに関して現在のオハイオ州にあるマスキンガム川沿い1万エーカー (40 km2) の土地を﹁モラヴィア兄弟団の資産として取っておきこれに与える。...前述兄弟団はインディアンを文明化しキリスト教徒に変える﹂と判断した[21]。

ジェームズ・ガーフィールド、オハイオ州出身のアメリカ合衆国大統領
1803年2月19日、当時の大統領トーマス・ジェファーソンは、オハイオの境界と憲法を承認する法案に署名し、オハイオは17番目のアメリカ合衆国の州に昇格した。当時は、オハイオの正式な州昇格の宣言がなされなかったことから、150年が経過した1953年8月7日に、時の大統領ドワイト・D・アイゼンハワーが署名することによって、改めてオハイオの連邦加盟が1803年3月1日であることが宣言された[22][23]︵現在続いている州昇格宣言という習慣は1812年、18番目のルイジアナ州が最初だった︶。チリコシーにある旧州議会議事堂では州議会特別会期が開催され、州昇格の請願書を馬でワシントンD.C.まで運ぶ議案を承認した。
アメリカ人の進出を避けるために多くのインディアンが西方に移住したが、州内に留まった者もおり、一部は同化した。1830年アンドリュー・ジャクソン大統領の下でアメリカ合衆国政府はインディアン移住を強制し、ミシシッピ川の西にあるインディアン準州に移した。
1835年、オハイオ州はトレド・ストリップを巡って無血の境界戦争であるトレド戦争をミシガン準州との間に演じた。アメリカ合衆国議会が介入し、ミシガンの州昇格を条件に紛争を終わらせた。ミシガンはトレド・ストリップの領有を諦める代わりに、アッパー半島西側3分の2を与えられた。

オハイオ州の歓迎看板、1990年代のスタイル
オハイオ州の地理的な位置づけとその人口で南北戦争のときは重要な役割を演じた。オハイオ川は軍隊と物資の輸送で重要な交通路となり、また州内の鉄道も同様だった。北軍に就いた州で、オハイオ州は人口当たりの兵士派遣数では最大だった。1862年、オハイオ州の部隊が2,000名の犠牲を出すという損失の多かったシャイローの戦いで勝利した後、州内の士気が酷く動揺した[24]。同年後半、ストーンウォール・ジャクソン将軍の指揮する南軍が首都ワシントンD.C.を脅かし、オハイオ州知事デイビッド・トッドは3か月徴兵の条件で5,000人の志願兵を集めた[25]。オハイオ州の歴史家アンドリュー・R・L・ケイトンは、この戦争でほぼ35,000人の州民が死に、﹁3万人ほどの者が残りの人生も戦争の傷跡を持って過ごした﹂と記した[26]。南北戦争の終戦までに北軍のユリシーズ・グラント、ウィリアム・シャーマン、フィリップ・シェリダンという功績の高い3将軍がオハイオ州出身の将軍となった[27][28]。
1912年、チャールズ・B・ガルブレースを議長として憲法制定会議が開催された。その結果は進歩主義時代の関心事を反映したものになった。新憲法は住民発議権と住民投票を導入した。さらに議会発案の州法や憲法修正案について議会が住民に批准を求めることができるようになった。法は一世代で1回見直されるべきだというのがジェファーソン流の原則であり、新憲法では20年毎に住民投票で問題を問うことになった。その問題とは新憲法が必要かどうかということである。この問いは1932年、1952年、1972年、1992年に発せられたが、新憲法が必要とされることは無かった。その代わりに議会に対して数多い憲法修正提案がなされ、その大半は採択された。
オハイオ州から8人のアメリカ合衆国大統領が選ばれており、﹁大統領の母﹂というニックネームはバージニア州と分け合うものである。﹁大統領の近代の母﹂とも言われる[29]。これはバージニア州出身の大統領が合衆国の歴史の初期に偏っているためである。7人の大統領がオハイオ州生まれであり、バージニア州の8人に次いでいる。バージニア州生まれのウィリアム・ハリソンはその人生の大半をオハイオ州で過ごしており、また埋葬されている。ハリソンはオハイオ州ノースベンドにあった義父ジョン・クリーブス・シムズが設立した家族の家で暮らしている間に政歴を積んだ。その他、ユリシーズ・グラント、ラザフォード・ヘイズ、ジェームズ・ガーフィールド、ベンジャミン・ハリソン︵ウィリアム・ハリソンの孫︶、ウィリアム・マッキンリー、ウィリアム・タフト、ウォレン・ハーディングがオハイオ州生まれである。

エリー湖のオハイオ州湖岸
オハイオ州はオハイオ川を州境とするが、川そのものはケンタッキー州とウェストバージニア州に属している。1980年、アメリカ合衆国最高裁判所は、1792年のバージニア州による領土譲渡に関する用語に基づき︵当時のバージニア州には現在のケンタッキー州とウェストバージニア州が含まれていた︶、オハイオ州とケンタッキー州との州境を川の北側低水位標識とするということを確認した[32]。オハイオ州は1792年の低水位標識と現在の高水位標識の間のみが領土となっている。
ミシガン州との境界も変更された。トレド戦争の結果、モーミー川河口の北岸までやや北東に修正された。
オハイオ州の土地の大半は氷河作用を受けた平原であり、北西部のみがグレート・ブラック・スワンプと呼ばれる平坦な地域になっている。北西部と中央部の氷河作用を受けた地域の境界は、まず東と南東に氷河作用アルゲイニー台地と呼ばれるベルト地帯で仕切られ、さらに非氷河作用アルゲイニー台地と呼ばれるもう1つのベルト地帯で仕切られている。大半は起伏が少ないが、非氷河作用アルゲイニー台地だけは岩がちの丘陵と森林になっている。
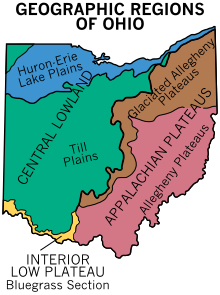
オハイオ州の地勢図
岩の多い南東部4分の1は、ウェストバージニア州のパンハンドル部からシンシナティの郊外部までオハイオ川に沿った外向きの弧を描いており、特徴ある社会経済学的地域となっている。地質的にはウェストバージニア州やペンシルベニア州南西部に類似し、石炭採掘を行った歴史があり、昔は小さな工業地帯となり、特徴ある地域方言は州の他の部分と違っている。1965年、アメリカ合衆国議会はアパラチア地域開発法を成立させ、﹁アパラチア地域の続く貧困と経済不況の拡大に対処する﹂こととした[33]。この法では州内29郡をアパラチア地域と定義した[34]。オハイオ州領土の3分の1は連邦政府が規定するアパラチア地域であり、そこには人口の12.8%︵147万6千人︶しか住んでいない[35]。

オハイオ州図
州内の重要河川としては、カヤホガ川、グレートマイアミ川、モーミー川、マスキンガム川、サイオト川がある。北側の川の水はエリー湖とセントローレンス川を介して北大西洋に排水され、南部の川水はオハイオ川とミシシッピ川を介してメキシコ湾に流れ込んでいる。
オハイオ州の歴史で最悪の自然災害は1913年にグレートマイアミ川で起きた。これはグレート・デイトン洪水と呼ばれ、グレートマイアミ川流域の全体が溢れ、デイトン市の中心事業地区も水に浸かった。その結果、州内さらには国内初の洪水制御土木計画としてマイアミ自然保護地区が創設された[36]。
中西部のグランド湖セントメアリーズは、1820年から1850年の運河建設時代に運河に水を供給するために造られた。この湖は広さが20平方マイル (52 km2) 以上を長年保ち、世界の人工湖として最大だった。オハイオ州の運河建設計画は他州ほど経済的な失敗にはならなかった。デイトンなど幾つかの都市は運河の場所によってその経済成長度が変わっており、1910年まで内陸運河が州内の多くの貨物を運んでいた。
歴史[編集]
主要記事‥オハイオ州の歴史インディアンの時代[編集]
オハイオ・バレーの考古学調査によって、この地域には紀元前13,000年には既に回遊性民族が住んでいたことが示されている[10]。この初期回遊性民族は紀元前1000年までにオハイオから消えたが、その物質文化は次代の人々の文化の基盤となった[10]。紀元前1000年から800年、定住性のアデナ文化が現れた。オハイオ州の歴史家ジョージ・W・クネッパーが主張しているように、この洗練された文化は﹁1902年、チリコシー市に近いトーマス・ワージントンの敷地であるアデナの地で、この文化の遺物が発掘されたので、アデナ文化と名付けられた﹂とされている[11]。アデナ文化の人々は、カボチャ、ヒマワリ、およびおそらくはトウモロコシなどの植物を栽培したので、﹁半恒久的﹂な集落を築くことができた。これらの栽培に加えて狩猟採集によって、より固定され複雑な集落が可能になった[11]。アデナ文化の遺跡の中でも最も壮大なものがオハイオ州アダムズ郡にあるグレート・サーペント・マウンドである[11]。
植民地と独立戦争の時代[編集]
18世紀、フランスが地域の毛皮交易を支配するために交易拠点の体系を作り上げた。1753年、フレンチ・インディアン戦争、ヨーロッパでは七年戦争と呼ばれた戦争でフランスとイギリスが戦った、1763年に結ばれたパリ条約によって、フランスはオハイオを初め、北西部地域の全体をイギリスに割譲した。 しかし1760年代のポンティアックの反乱で、イギリスの軍事支配に警鐘が発せられた[19]。それはアメリカ独立戦争における植民地側の勝利によって終わりを迎えた。1783年のパリ条約により、イギリスはオハイオ領土全ての領有権を新生アメリカ合衆国に譲った。北西部領土[編集]

州昇格以降[編集]


地理[編集]
参照‥オハイオ州の郡一覧、オハイオ州の都市一覧、オハイオ州の村一覧、オハイオ州のタウンシップ一覧、オハイオ州の保護地域 アメリカ合衆国中西部地域の北東角に位置しているオハイオ州は、エリー湖に面していて、接している各州とは主要高速道路によって接続されている。オハイオ州の南部境界はオハイオ川によって区切られ、北部境界の大部分はエリー湖によって画されている。東にはペンシルベニア州、トレド市近くの北西方面でミシガン州、北部はエリー湖の対岸にカナダオンタリオ州、西部でインディアナ州、南部でケンタッキー州、南東部でウェストバージニア州と接している。 オハイオ州の地理的位置づけは経済的な成長と拡張のために重要な資産となってきた。オハイオ州はアメリカ合衆国の中で北東部と中西部を繋いでおり、良く発達した高規格道路を使い大量の貨物が領域内を通って流通されている。国内50州の中で高規格道路のネットワークでは第10位であり、車で1日の範囲内に北アメリカ人口の50%、製造能力の70%が入っている[30]。州の北側がエリー湖の総延長312マイル (502 km) の湖岸線となり[31]、多くの港ができている。 オハイオ州の境界は1802年授権法における境界条項により次のように定義されていた。 東はペンシルベニア州との州境、南はオハイオ川のグレートマイアミ川合流点まで、西は前述グレートマイアミ川合流点からまっすぐ北に引いた線とし、北はミシガン湖最南端を通って東西に引かれた線が前述グレートマイアミ川合流点からまっすぐ北に引いた線と交わる点から、エリー湖とすなわち領土境界と交わる所まで、さらにそこから前述ペンシルベニア州州境までと定義する


国立公園[編集]
●クヤホガバレー国立公園気候[編集]
オハイオ州の気候は湿潤大陸性気候︵ケッペンの気候区分Dfa︶にあり、最南部にあるブルーグラス地域のみが温暖湿潤気候の北端にあたる。またアップランドサウスにも入っている。通常の夏は暑く湿度が高い。冬は概して冷涼から寒冷である。降水量は年間を通じてほどほどである。悪天候は希ではないが、竜巻道と呼ばれる地域にある他州に比べれば竜巻発生個数は少ない。エリー湖南東岸では激しい湖水効果雪が降るのも希ではない、そこはスノーベルトに指定されている。 州内の大半は温帯気候に入っていないが、暖かい地域の植物や動物が州内に入ってきている。例えば、南部に多いブラックジャック・オーク︵Quercus marilandica︶のような木がオハイオ川の直ぐ北、州内最北部でも見られる。他にもタイサンボク︵Magnolia grandiflora︶、ネムノキ︵Albizia julibrissin︶、サルスベリ、さらには時としてニードルパームのような植物がブルーグラス地域の街路、庭、庭園に使われている。これらは温帯から大陸性気候への気候遷移の証拠でもある。しかし州内他地域では同じ植物が繁茂してはいない。この変化は州内を州間高速道路75号線でシンシナティからトレドまで移動したときに分かる。シンシナティで見られるコモンウォール・トカゲは、オハイオ州における温帯性動物の一例である。過去の記録[編集]
過去最高気温は1934年7月21日にガリポリス近くで記録された113°F (45℃) だった[37]。 過去最低気温は1899年2月10日にミリガンで記録された-39°F (-39 ℃) だった[38]。地震[編集]
平均的な住民が感知するような地震は数少ないが、2002年から2007年の間にオハイオ州では30回以上の地震が起こり、1776年以降ではマグニチュード2.0以上の地震が200回以上発生してきた[39]。 オハイオ州の歴史の中で最も強かった地震はシェルビー郡のアンナで起きた地震であり[40]、1937年3月9日のことだった。州西部を震源としマグニチュードは5.4、メルカリ震度階級VIIIだった[41]。 その他の大きな地震としては[42]、1884年9月19日にライマ近くでおきたマグニチュード4.8[43]、1901年5月17日にポーツマス近くで起きたマグニチュード4.2[44]、1986年1月31日にレイク郡レロイ郡区で起きたマグニチュード5.0 があった。最後のものはその後2か月間にマグニチュード 0.5 から 2.4 の余震が13回あった[45][46]。 最近起きた地震では、2011年12月31日午後東部標準時3時5分に起きたものがあった。マグニチュード4.0、震源はヤングスタウンの北西約 4 km(北緯41度7分19.1994秒 西経80度41分2.3994秒 / 北緯41.121999833度 西経80.683999833度)、トランブル郡とマホニング郡の郡境近くだった[47]。 州内の幾つかのカレッジ、大学などの機関にある地震観測所、およびオハイオ州自然資源省地質研究部による調整でできた組織であるオハイオ州地震学ネットワークが[48]、1776年から現在までの地震記録をまとめ、州内で感知された地震の位置などを整理している[49]。人口動勢[編集]
| 人口推移 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 国勢調査 年 |
人口 | 州 順位 |
|
| ||
| 1800年 | 45,365人 | 18 |
| 1810年 | 230,760人 | 13 |
| 1820年 | 581,434人 | 5 |
| 1830年 | 937,903人 | 4 |
| 1840年 | 1,519,467人 | 3 |
| 1850年 | 1,980,329人 | 3 |
| 1860年 | 2,339,511人 | 3 |
| 1870年 | 2,665,260人 | 3 |
| 1880年 | 3,198,062人 | 3 |
| 1890年 | 3,672,329人 | 4 |
| 1900年 | 4,157,545人 | 4 |
| 1910年 | 4,767,121人 | 4 |
| 1920年 | 5,759,394人 | 4 |
| 1930年 | 6,646,697人 | 4 |
| 1940年 | 6,907,612人 | 4 |
| 1950年 | 7,946,627人 | 5 |
| 1960年 | 9,706,397人 | 5 |
| 1970年 | 10,652,017人 | 6 |
| 1980年 | 10,797,630人 | 6 |
| 1990年 | 10,847,115人 | 7 |
| 2000年 | 11,353,140人 | 7 |
| 2010年 | 11,536,504人 | 7 |
| 2020年 | 11,799,448人 | 7 |


オハイオ州の人口は1800年の45,000人を超えたところから、1970年に1,065万人を記録したときまで、10年毎に10%以上の増加を遂げてきた[50]。その後の40年間は成長が鈍化している[51]。2020年の国勢調査では、州人口は11,799,448人で、2010年国勢調査時点︵11,536,504人︶より2.28%の増加となった[52]。オハイオ州の人口増加率の鈍化はアメリカ合衆国全体と歩みを同じくしている。
2000年時点で、オハイオ州の人口重心はモロー郡[53]の郡庁所在地マウントギリアドにあった[54]。1990年の人口重心と比較して約6,346フィート (1,934 m) 南と西にずれた[53]。
2011年時点で州内1歳未満の子供のうち27.6%は少数民族に属している[55]。オハイオ州の人口の6.2%は5歳以下、23.7%は18歳以下、14.1%は65歳以上である。女性は人口の約51.2%である。
2010年時点で、州人口の4.1%︵469,748人︶は外国で生まれたと推計されている。このうちアジア生まれが37.7%、ヨーロッパ生まれが26.4%、ラテンアメリカ生まれが21.4%である。

通学途中のアーミッシュの子供達

オハイオ州での先史時代のインディアンによる巨大墳墓遺跡群

﹁クリーブランド・インディアンス﹂選手の帽子に描かれている﹁ワフー 酋長﹂

マイアミズバーグにあるインディアンの巨大墳墓
同州にはチッペワ族、デラウェア族、エリー族、ホンニアソント族、イリニ族、イロコイ族、キカプー族、マイアミ族、モソペレア族、ニュートラル族、オタワ族、ポタワトミ族、ショーニー族、ワイアンドット族などのインディアン部族は農耕と採集による生活を営んでいた。
先史時代のインディアンたちは、紀元前から同地に巨大な墳墓群を築き、﹁マウンド・ビルダー﹂と呼ばれた。現在も同州には数多くの墳墓遺跡が残っている。
オハイオ州のインディアン部族は、19世紀にアンドリュー・ジャクソン大統領の民族浄化政策である﹁インディアン移住法﹂によってすべて他州に強制移住させられた。強制移住を拒否して同州に残ったインディアン部族は﹁絶滅部族﹂としてアメリカ連邦政府の承認を打ち切られ、保留地︵Reservation︶を没収されており、インディアン部族として存在しないことになっている。唯一、﹁ショーニー族﹂の﹁レムナント・バンド﹂のみが1979年に州政府から﹁州立インディアン部族﹂として認定されている。連邦との条約規定に基づく自治権を得ようと、多数の部族が現在、アメリカ連邦政府に公式承認を要求中である。
インディアン寄宿学校で白人同化教育を受けた、全米の若い世代のインディアンたちが起こしたアメリカインディアン協会は、オハイオ州コロンバスに本部を置く、インディアンの民族権利運動の草分けである。同協会は1911年に、コロンバスで﹁白人のインディアン侵略の始まった日﹂である﹁コロンブス・デー﹂の日に第一回決起大会を開き、﹁インディアンが白人のアメリカを発見した日!﹂というスローガンを掲げた。
オハイオ州に本部を置くプロ野球チーム﹁クリーブランド・インディアンス﹂は、﹁ワフー酋長﹂という、﹁赤い顔をして歯を剥き出して笑うインディアン﹂の﹁インディアン・マスコット﹂を長年使用していた。これに対し、全米のインディアン団体が﹁インディアン民族に対する人種差別である﹂としてその使用撤廃をNCAAならびに球団に要求し続けた結果、クリーブランド・インディアンスは2018年シーズンをもってワフー酋長のロゴの使用を中止した。
オハイオ州は現在、ワシントンD.C.の議会議事堂の彫像ホールに﹁オハイオ州の著名人﹂としてショーニー族の英雄、テクムセの彫像を立てるべきであると合衆国に要望している。現在、ホールに立つインディアンの著名人はサカガウィア、シクウォイア、ワシャキー、サラ・ウィネマッカとポペの五人だけである。
人種及び祖先[編集]
2010年に州内で申告された祖先による構成比は以下の通りだった[56] ●26.5% ドイツ系 ●14.1 アイルランド系 ●9.0% イングランド系 ●7.9% アメリカ人︵特定の民族を祖先と考えない人々︶ ●6.4% イタリア系 ●5.7% スラブ系:(3.8% ポーランド系, 1.2% スロバキア系, 0.7% ロシア系) ●2.5% フランス系 ●1.9% スコットランド系 ●1.7% ハンガリー系 ●1.6% オランダ系 ●1.1% ウェールズ系 ●1.1% スコットランド・アイルランド系 特に北西部の郡の多くではドイツ人を祖先とする住民が最も多いと報告された。 2010年の国勢調査によると、この州の人種的な構成は次の通りだった[57][58]。 ●82.7% 白人︵非ヒスパニック白人 81.1%︶ ●12.2% 黒人 ●1.7% アジア ●0.6% インド系、0.4% 中国系、0.1% フィリピン系、0.1% 韓国系、0.1% ベトナム系、0.1% 日系人 ●0.2% インディアン ●0.03% 太平洋諸島系 ●2.1% 混血 ●3.1% ヒスパニック ●1.5% メキシコ系、0.8% プエルトリコ系、0.1% グァテマラ系、0.1% キューバ系 白人比率は全国平均よりも高い。
宗教[編集]
オハイオ州民の多くはプロテスタントである。バプテスト、メソジスト、ルーテル教会、長老派教会、及びペンテコステ運動が大多数である。他の著名なプロテスタント宗派に、合衆国内最大のアーミッシュの共同体、及びクリーブランド内にあるキリスト連合教会の本部が含まれる。 オハイオ州の宗教別人口構成は‥ ●キリスト教 – 76% ●プロテスタント – 54% ●バプテスト – 15% ●メソジスト – 11% ●ルーテル教会 – 5% ●長老派教会 – 4% ●ペンテコステ運動 – 4% ●キリスト連合教会 – 2% ●アーミッシュ/敬虔主義 – 1% ●他のプロテスタント – 11% ●ローマ・カトリック – 21% ●他のキリスト教 – 1% ●ユダヤ教 - 1.3% ●エホバの証人 - 1% ●イスラム教 - 1% ●ヒンドゥー教 - 0.5%未満 ●仏教 - 0.5%未満 ●モルモン教 - 0.5%未満 ●他の宗教 – 1% ●無宗教 – 17% 2008年のピュー・フォーラム調査に拠れば、州民の55%は宗教が﹁大変重要﹂、30%が﹁幾らか重要﹂、15%は﹁それほど重要でない﹂あるいは﹁全く重要でない﹂と答えていた。また州民の36%は毎週宗教的礼拝に出席し、35%は時々出席し、27%はたまに出席するか、全く出席しないと答えた。インディアン部族[編集]



|
≪アメリカ連邦政府から公認されていない部族・団体≫
|
|
≪アメリカ連邦政府は公認していないが、オハイオ州政府は公認している部族≫
●﹁ショーニー族﹂・﹁レムナント・バンド﹂
インディアン・カジノ[編集]
同州では現在のところ、インディアン部族の運営する﹁インディアン・カジノ﹂は一つもない。 2009年8月18日、オハイオ州投票委員会は、クリーブランド、シンシナティ、コロンバスとトレドの4つの州都市でのカジノ認可のための州憲法改正案を承認した。当時のテッド・ストリックランド州知事は、カジノの24時間営業案に加え、競馬場でのスロットマシン遊戯において18歳を年齢制限とする行政命令に署名した。同州でカジノが合法化されれば、同州にもインディアン・カジノが開設される可能性が拓かれるものと期待されている。主要な都市と町[編集]
参照‥オハイオ州の都市一覧| 順位 | 都市名 | 人口(2020年国勢調査)[52][59] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 市域 | 都市圏 | 広域都市圏 | ||
| 1 | コロンバス市 | 905,748 | 2,138,926 | 2,544,048 |
| 2 | クリーブランド市 | 372,624 | 2,088,251 | 3,633,962 |
| 3 | シンシナティ市 | 309,317 | 2,256,884 | 2,316,022 |
| 4 | トレド市 | 270,871 | 646,604 | 835,489 |
| 5 | アクロン市 | 190,469 | 702,219 | (1) |
| 6 | デイトン市 | 137,644 | 814,049 | 1,088,875 |
| 7 | パーマ市 | 81,146 | (1) | (1) |
| 8 | カントン市 | 70,872 | 401,574 | (1) |
| 9 | ロレイン市 | 65,211 | (1) | (1) |
| 10 | ハミルトン市 | 63,399 | (2) | (2) |
| 11 | ヤングスタウン市 | 60,068 | 541,243 | 643,120 |
| 12 | スプリングフィールド市 | 58,662 | 136,001 | (4) |
| 13 | ケタリング市 | 57,862 | (4) | (4) |
| 14 | エリリア市 | 52,656 | (1) | (1) |
| 15 | カヤホガフォールズ市 | 51,114 | (5) | (1) |
| 16 | ミドルタウン市 | 50,987 | (2) | (2) |
| 17 | レイクウッド市 | 50,942 | (1) | (1) |
| 18 | ニューアーク市 | 49,934 | (3) | (3) |
| 19 | ユークリッド市 | 49,692 | (1) | (1) |
| 20 | ダブリン市 | 49,328 | (3) | (3) |
(3)コロンバス都市圏/広域都市圏、(4)デイトン都市圏/広域都市圏、(5)アクロン都市圏 | ||||
コロンバス市が州都であり、地理的に州の中心に近い。オハイオ州立大学、フランクリン大学、キャピタル大学、オハイオ・ドミニオン大学、ネイションワイド相互保険会社、ヴィクトリアズ・シークレットが所在
大都市圏の中心として機能している都市は以下の通りである。
●アクロン市、アクロン大学とグッドイヤー・タイヤ・アンド・ラバー社が所在
●カントン市、プロフットボール殿堂、マローン大学、ティムケン社が所在
●シンシナティ市、シンシナティ大学、ザビエル大学、シンシナティ美術館、シンシナティ交響楽団、プロクター・アンド・ギャンブル社、クローガー、メイシーズ社、チキータ・ブランズ社、フィフスサード銀行が所在
●クリーブランド市、クリーブランド州立大学、プレイハウス・スクエア・センター、クリーブランド美術館、クリーブランド管弦楽団、ケース・ウェスタン・リザーブ大学、クリーブランド・クリニック、ロックの殿堂、フォレストシティ・エンタープライジーズ、ユニバーシティ・ホスピタルズが所在
●デイトン市、デイトン大学、デイトン・バレー、ライト州立大学、プレミア・ヘルス・パートナーズ、国立アメリカ空軍博物館が所在
●ライマ市、オハイオ州立大学ライマ校、北西オハイオ大学が所在
●マンスフィールド市、オハイオ州立大学マンスフィールド校、ノースセントラル州立カレッジ、マンスフィールド・モータースポーツパークが所在
●スプリングフィールド市、ウィッテンバーグ大学が所在
●スチューベンビル市、フランシスカン大学スチューベンビルが所在
●トレド市、トレド大学、トレド美術館、オーウェンス・コーニング社、オーウェンズ・イリノイが所在
●ヤングスタウン市、ヤングスタウン州立大学、バトラー・アメリカ美術館が所在
シンシナティ都市圏はケンタッキー州とインディアナ州に、スチューベンビル都市圏はウェストバージニア州に、ヤングスタウン都市圏はペンシルベニア州に広がっている。また、ウェストバージニア州のハンティントン都市圏はオハイオ州にもかかっており、アイアントン市が含まれる。
大都市圏の郊外都市として人口の多い都市は次の通りである。
●ボーリンググリーン市 (トレドの郊外)、ボーリンググリーン州立大学が所在
●カヤホガフォールズ市 (クリーブランド/アクロンの郊外)、1939年にローソンが牛乳販売店を開業、後に日本の大手コンビニとなる
●デラウェア市 (コロンバスの郊外)、オハイオ・ウェスリアン大学が所在
●ダブリン市 (コロンバスの郊外)、カーディナル・ヘルス、ウェンディーズが所在
●エリリア市 (クリーブランドの郊外)、インバケア、リッジツールが所在
●ユークリッド市 (クリーブランドの郊外)
●ハミルトン市 (シンシナティの郊外)
●ケタリング市 (デイトンの郊外)
●レイクウッド市 (クリーブランドの郊外)
●ランカスター市 (コロンバスの郊外)
●ロレイン市 (クリーブランドの郊外)
●メアリーズビル市 (コロンバスの郊外)、ホンダ・オブ・アメリカが所在
●メンター市 (クリーブランドの郊外)
●ミドルタウン市 (シンシナティの郊外)、AKスチールが所在
●ニューアーク市 (コロンバスの郊外)、オハイオ州立大学ニューアーク校、ザ・ロンガバーガー・カンパニーが所在
●パーマ市 (クリーブランドの郊外)
●レイノルズバーグ市 (コロンバスの郊外)
小都市圏の中心として機能している主な都市は以下の通りである。
- アセンズ市、オハイオ大学が所在
- チリコシー市、最初の州都、オハイオ大学チリコシー校が所在
- フィンドレー市、フィンドレー大学が所在
- マリオン市、オハイオ州立大学マリオン校が所在
- サンダスキー市、シダーポイント(テーマパーク)、カラハリ・リゾート・アンド・コンベンション・センターが所在
- ウースター市、ウースター大学、オハイオ州立大学農業技術学校、オハイオ農業研究開発センターが所在
- ゼインズビル市、オハイオ大学ゼインズビル校、ゼイン州立カレッジが所在
政府と政治[編集]
詳細は「w:Government of Ohio」を参照

オハイオ州政府は行政府[60]、司法府[61]、立法府[62]の3権で構成されている。

マイク・デワイン
行政府の長がオハイオ州知事である。州知事は、任期4年で州の有権者による選挙により選ばれる。州知事は、州議会が制定した法案に対する拒否権を有している。また、刑事犯に対する恩赦を行う権限を有している。
1991年以降、州知事のポストは共和党により占められていた。2006年の中間選挙で民主党のテッド・ストリックランドが当選したが、2010年の中間選挙で共和党のジョン・ケーシック[63]に敗れた。2011年1月10日、ケーシックが州知事に就任した。
副知事は、知事とペアで立候補し選出される。副知事は知事が不在の場合に代行する[64]。また知事に割り当てられた業務を実行する[65]。
行政府の中で他に州憲法で規定され、選挙で選ばれる役人として、州務長官、州監査官、州財務官および検事総長がいる[60]。
行政府[編集]

近年の州知事[編集]
- ボブ・タフト(1999年1月-2007年1月)
- テッド・ストリックランド(2007年1月-2011年1月)
- ジョン・ケーシック(2011年1月-2019年1月)
- マイク・デワイン(2019年1月-)
立法府[編集]
詳細は「w:Ohio General Assembly」を参照

州議会は、州憲法に基づき、州上院︵Senate︶および州下院︵House of Representatives︶の二院から構成されている[67]。
州上院の定数は33名で、33の小選挙区から一人ずつ選ばれる。現在共和党が23議席、民主党が10議席を占めている。任期は4年で、偶数年に半数ずつ改選される。原則として連続2期までの制限がある。2010年の中間選挙で民主党が2議席を減らした。
州下院の定数は99名で、99の小選挙区から一人ずつ選ばれる[68]。現在共和党が59議席、民主党が40議席を占めている︵1議席は空席︶。任期は2年で全議席が偶数年11月に改選される。原則として連続4期までの制限がある。2010年の中間選挙では民主党が13議席を減らした。
州議会の両院が可決した法案に州知事が署名することにより州法は成立する。州知事が拒否権を行使した法案を再可決するためには、両院それぞれ3/5の特別多数による決議が必要とされる。
司法府[編集]
オハイオ州の司法府は州最高裁判所[69]、地区裁判所[70]、一般訴訟裁判所[71]の3段階がある。州最高裁判所[編集]
アメリカ合衆国の連邦法制度と併せて、州独自の法体系を有している︵オハイオ州法︶。オハイオ州憲法ないしオハイオ州法の解釈については、オハイオ州最高裁判所が連邦法に抵触する場合を除き、最終的な権威を有している。独自の裁量権により控訴裁判所からの控訴案件を審問する。特定の事項については第一審となる権利がある[72]。 州最高裁判所は、州都コロンバスのダウンタウンにあり、サイオト川の河畔に立つ。州最高裁判所は、長官を含め7名の裁判官︵Justice︶で構成されており、任期は6年で、長官は6年ごとに、また、長官を除く6名は2年ごとに2名ずつが選挙により選ばれる。通常は弁護士ないしは下級裁判所の裁判官が選ばれるが、州の最高裁の裁判官となるために、州の司法試験に合格していることが要件とはされていない。日本のキャリアシステムに基づく裁判官とは異なり、弁護士、議員その他の多様なキャリアを有する者が裁判官に選出される。70歳を超える者は、州最高裁の裁判官に立候補することができない。 州最高裁の7名の裁判官のうち6名は共和党員が占めており、2011年から現在まで、州の最高裁長官は、共和党員であるモーリーン・オコナー︵Maureen O'Connor︶がつとめている︵次の改選期は2012年︶。欠員が出た場合を除き裁判官の選挙は偶数年に行われる。その他の州裁判所[編集]
州の高等裁判所︵Appellate Court︶は、州を12に分けて管轄する地区裁判所である。州高等裁判所の裁判官の任期も6年間である。郡一般訴訟裁判所から控訴された案件を審問する。 オハイオ州政府に対する民事訴訟は、州請求裁判所︵State Court of Claims︶にて審理される。 郡一般訴訟裁判所︵County Court of Common Pleas︶が通常民事および刑事事件の第一審を担当する裁判所であり、日本における地方裁判所に相当する。州内各郡に1か所、合計88か所存在する。 その他日本における簡易裁判所に相当する自治体裁判所︵Municipal court︶や郡裁判所︵County Court︶も存在する。連邦裁判所[編集]
連邦控訴裁判所[編集]
オハイオ州は、アメリカ連邦裁判所︵合衆国裁判所︶の控訴裁判所の管轄としては、第6巡回区に属する。連邦地方裁判所[編集]
オハイオ州は、州内を南北に二分して、オハイオ州北地区または南地区連邦地方裁判所がそれぞれ管轄する。政治[編集]
「w:Politics of Ohio」、「w:Political party strength in Ohio」、「w:Ohio Democratic Party」、および「w:Ohio Republican Party」も参照
| 年 | 共和党 | 民主党 |
|---|---|---|
| 2016年 | 51.69% 2,841,005 | 43.56% 2,394,164 |
| 2012年 | 47.60% 2,661,437 | 50.58% 2,827,709 |
| 2008年 | 46.80% 2,677,820 | 51.38% 2,940,044 |
| 2004年 | 50.81% 2,859,768 | 48.71% 2,741,167 |
| 2000年 | 49.97% 2,351,209 | 46.46% 2,186,190 |
| 1996年 | 41.02% 1,859,883 | 47.38% 2,148,222 |
| 1992年 | 38.35% 1,894,310 | 40.18% 1,984,942 |
| 1988年 | 55.00% 2,416,549 | 44.15% 1,939,629 |
| 1984年 | 58.90% 2,678,560 | 40.14% 1,825,440 |
| 1980年 | 51.51% 2,206,545 | 40.91% 1,752,414 |
| 1976年 | 48.65% 2,000,505 | 48.92% 2,011,621 |
| 1972年 | 59.63% 2,441,827 | 38.07% 1,558,889 |
| 1968年 | 45.23% 1,791,014 | 42.95% 1,700,586 |
| 1964年 | 37.06% 1,470,865 | 62.94% 2,498,331 |
| 1960年 | 53.28% 2,217,611 | 46.72% 1,944,248 |
オハイオ州は﹁大統領の母﹂というニックネームがあり、州内で生まれた7人の大統領を送り出してきた[74]。7人共に共和党員である。バージニア州生まれのウィリアム・ハリソンはオハイオ州に住んだホイッグ党員︵共和党の前身︶だった[74]。歴史家のR・ダグラス・ハートは、バージニア州と言えども、﹁全国的な政治にこれほどの足跡を残していない﹂と主張している[75]。雑誌﹁エコノミスト﹂は、﹁この中西部の一画はアメリカのあらゆるものの一端を含んでいる。北東部の一部であり、南部の一部である。都市の一部であり、田園部の一部である。ぎりぎりの貧困の一部であり、景気の良い郊外の一部である。﹂と記した[76]。
2008年時点で州内有権者は民主党支持が強い傾向がある。民主党登録者は推計 2,408,178 人、共和党登録者は推計 1,471,465 人である。2004年では民主党72%、共和党32%だった。有権者総数は 7,937,161 人である。2008年では当時イリノイ州選出アメリカ合衆国上院議員のバラク・オバマが投票総数の51.50%を獲得し、対抗馬であるアリゾナ州出身のジョン・マケインに4.59%の差を付けた[77]。しかしオバマは州内88郡のうち22郡を制しただけだった[78]。
連邦議会への議員選出[編集]
2000年国勢調査によりオハイオ州からのアメリカ合衆国下院議員定数が1人減らされ、18名が選出されている。 2008年の選挙で民主党はアメリカ合衆国下院議員数を3人増やした[79]。アメリカ合衆国上院には民主党のシェロッド・ブラウンと共和党のJ・D・ヴァンスを送り出している[80]。大統領選挙の選挙人[編集]
オハイオ州から選ばれるアメリカ合衆国大統領選挙の選挙人の人数は、全米で538人のうちの20人だった。2010年の国勢調査により、これが2人減らされて18人となり、2012年、2016年、2020年の選挙はこれで行うことになる[81]。産業分布や人種構成が全米平均に近い﹁アメリカの縮図﹂として知られ、選挙の度に共和党・民主党両党に勝利者が変動する﹁スイング・ステート﹂として知られ、1964年から2016年までオハイオ州で勝利した者が大統領に当選しており、﹁オハイオ州を制するものが大統領選を制す﹂と呼ばれる。2000年、2004年の大統領選挙では選挙の帰趨を決する役割を果たした。どちらの年も、小差で共和党のジョージ・W・ブッシュ候補を支持した。2016年でも共和党のドナルド・トランプ候補を支持し当選に一役買っている。しかし、2020年はトランプがオハイオ州で勝利したものの全米ではジョー・バイデンが勝利し大統領当選。1960年のジョン・F・ケネディ以来のオハイオ州で破れながら当選した大統領となった。経済[編集]
詳細は「w:Economy of Ohio」を参照

2010年、雑誌﹁サイトセレクション﹂でオハイオ州は事業に適した州として第2位にランクされた。これは事業活動データベースに基づいている[82]。事業の成長と開発については、この雑誌から3回連続でガバナーズカップ賞を得た[83]。オハイオ州の州内総生産は4,780億米ドルである[84][85]。コロンビア特別区を合わせた51の州と地区の中でオハイオ州の経済規模は第7位である[85]。
小企業・起業家委員会は2009年事業税指数で企業に優しい税制度の第10位にオハイオ州をランク付け、事業税とキャピタルゲイン比率は1.6%で第6位だった[86]。同委員会の小企業生存指数2009年では、友好的な政策の州として第11位だった[87]。ディレクターシップのボードルームガイドでは、事業環境として全体の第13位としており、訴訟環境では第7位にしていた[88]。雑誌フォーブスでは、2009年の調整力ある政府として第8位に位置づけた[89]。USニューズ&ワールド・レポート2010年ランキングに拠れば、州内には国内のトップ115大学のうちの5つがある[90]。同じランキングで2008年には、高校の良さで第8位だった[91]。
2010年5月時点の州内失業率は10.7%であったが、この月は17,000の新たな就職機会が付加された[92][93]。一人当たり収入は34,874米ドルである[85][94]。ムーディーズは2009年の一人当たり収入増加率を1.3%と予測しているが、2007年の4.7%と比べて下がっている[85]。2007年時点で、世帯当たり所得中間値は46,645米ドルであり[95]、人口の13.1%は貧困線以下の暮らしをしている[96]。これは全国平均の13%より僅かに上回っている[96]。雇用情勢は2006年から2016年の間に5%成長すると予測され、純増は290,700人分である[85]。
オハイオ州の州内総生産の中で、製造業が18.3%、金融業も18.3%を占めており、最大の産業分野になっている[85]。中西部では最大のバイオサイエンス分野があり、﹁グリーン﹂経済では国を引っ張っている。プラスティック、ゴム、加工金属、電気機器、電化製品の生産高では国内最大である[97]。州民の約5,212,000人が賃金または給与労働者である[85]。
雇用の面では商業・輸送・公共事業分野が1,010,000 人、すなわち州内総労働者人口の 19.4% を雇用して最大であり、これに医療・教育部門が825,000 人、15.8% で続いている[85]。政府部門が 787,000 人、15.1%、製造業が669,000 人、12.9%、専門職・技術部門が638,000 人、12.2%を雇用している[85]。オハイオ州の製造業は総生産高で50州のうちの第3位である[85]。国内の2008年売上高上位1,000社のうち、59社が州内に本社を置いており、その中にはプロクター・アンド・ギャンブル、グッドイヤー、AKスチール、ティムケン、アバクロンビー&フィッチ、ウェンディーズが入っている[98]。
オハイオ州は独自にオハイオ・ロッタリーという宝くじを発行している41州の1つである[99]。その34年間の歴史で公共教育に155億米ドルを寄付してきた[100]。
主な会社など[編集]
オハイオ州に本拠地のある企業には以下のようなものがある。 ●プロクター・アンド・ギャンブル (P&G) ●ウェンディーズ ●グッドイヤー ●ディボールド ●DHL︵ドイツ系企業だが、在米拠点を州内ウィルミントン市に置いている︶ ●U.Sプレイング・カード社 ●ザ・J. M. スマッカー ︵The J.M. Smucker Co.︶ ●リミテッド・ブランズ ︵Limited Brands︶ ●ザ・ロンガバーガー・カンパニー ︵The Longaberger Company︶ ●スカイライン・チリ ︵Skyline Chili︶ ●グレーターズ ︵Graeter's︶ ●クローガー ●メイシーズ ●チキータ・ブランズ・インターナショナル ●アメリカン・フィナンシャル・グループ ︵American Financial Group︶ ●オーウェンズ・イリノイ ●GE・アビエーション ●GE・ホンダ・エアロ・エンジン ●スミザーズオアシス ●スウェージロックオハイオ州と関係が深い日本企業[編集]
●本田技研工業 - 日本の自動車会社初のアメリカ現地生産工場として1979年に操業開始したメアリーズビル工場の他、州内イースト・リバティ︵East Liberty︶、アンナ︵Anna︶の計三ヶ所にアメリカ法人の工場がある。[5]関連企業も多数州内に存在し、地元住民の雇用を支えている。 ●ファイアストン︵ブリヂストンの子会社︶ - 現地に工場や研究機関があり、地元住民の雇用を支えている。本社はテネシー州ナッシュビル。主な産業など[編集]
19世紀には全米屈指の原油の産出量を誇った (その後ジョン・ロックフェラーがクリーブランド周辺に精製施設を建設し、同市にスタンダード・オイルを設立した)。21世紀初頭にも小規模ながら原油の産出はみられ、原油を産出する32州の中で19位である。60,000程油井があるがほとんどは日産10バレル以下の小規模のものである[101]。 シェールガスのガス井が20,000以上あり、近年同州でも開発ブームが起きている[102]。 北西部には製塩施設がいくつか見られる[103]。交通[編集]
道路[編集]
国内の東西方向に走る主要幹線道がオハイオ州内を通っている。その中でも20世紀初めに建設された﹁メイン・マーケット・ルート3﹂は1913年に選定され、ニューヨーク市とサンフランシスコ市を繋いで初めて国内を横断する道路となった﹁リンカーン・ハイウェイ﹂の一部になった。オハイオ州内のリンカーン・ハイウェイは、カントン市、マンスフィールド市、ウースター市、ライマ市、バンワート市など多くの都市や町を繋いだ。リンカーン・ハイウェイが州内に入ってきたことで、州の発展に大きな影響を与えた。1926年には番号付き国道体系が整備され、リンカーン・ハイウェイは国道30号線となった。州内には19世紀初めのカンバーランド道路︵ナショナルロード︶もあり、その長さは228マイル (367 km)、現在は国道40号線となっている。 州内には高度に発達した道路と州間高速道路のネットワークがある。主要な東西方向道路として、州間高速道路はコロンバスとデイトンを通り、西側のインディアナ州に通じる70号線、アクロンを通り、東側のペンシルベニア州に通じる76号線、大陸横断道の80号線と90号線︵オハイオ・ターンパイク︶、ウェストバージニア州からシンシナティに通じるアパラチアン・ハイウェイ︵オハイオ州道32号線︶がある。 南北方向道路では、西側のトレドからミシガン州を抜けカナダに向かう州間高速道路75号線、クリーブランドからコロンバスとシンシナティを抜けて南のケンタッキー州に入る71号線、南東側のクリーブランドからアクロン、カントン、ニューフィラデルフィア、マリエッタを抜けてウェストバージニア州に通じる77号線などがある。州間高速道路75号線のシンシナティ・デイトン間は州内で最も交通量が多い区間である。また州都コロンバス市には270号環状線がある。航空[編集]
州内には国際空港が5つ、商業空港が4つ、軍用空港が2つある。5つの国際空港は以下の通りである。 ●クリーブランド・ホプキンス国際空港 (CLE)、コンチネンタル航空のハブ空港 ●ポート・コロンバス国際空港 (CMH) ●デイトン国際空港 (DAY) ●アクロン・フルトン国際空港、貨物と民間用 ●リッケンバッカー国際空港、軍隊と供用、フェデックスの建物がある もう一つの軍用空港はライト・パターソン空軍基地であり、国内最大でもある。他にトレド・イクスプレス空港やアクロン・カントン空港が使われている。 ︵シンシナティの近隣空港であるシンシナティ・ノーザンケンタッキー国際空港(CVG)はケンタッキー州ヘブロンに所在する。︶教育[編集]
オハイオ州の公共教育体系はオハイオ州憲法第6条、およびオハイオ改訂法典第33条に規定されている。基本的には他州に規定される教育体系に類似している。オハイオ州教育委員会が監督するオハイオ州教育省が初等・中等教育を管理している。州全体で約700の教育学区がある。オハイオ州理事会が高等教育機関の調整・援助を行っており、ストリックランド知事の時にオハイオ大学体系の中に再編成された。この体系により年間40万人の学生が学んでおり、国内でも5本の指に入る規模となっている。単科及び総合大学[編集]
●13州立大学 ●ボーリング・グリーン州立大学︵ボーリング・グリーン Bowling Green︶ ●セントラル州立大学︵ウィルバーフォース Wilberforce︶ ●クリーブランド州立大学︵クリーブランド︶ ●ケント州立大学︵ケント Kent︶ ●マイアミ大学︵オックスフォード Oxford︶ ●オハイオ大学 (アセンズ Athens) ●オハイオ州立大学︵コロンバス︶ ●ショーニー州立大学︵ポーツマス Portsmouth︶ ●アクロン大学︵アクロン︶ ●シンシナティ大学︵シンシナティ︶ ●トレド大学︵トレド︶ ●ライト州立大学︵フェアボーン - デイトン郊外︶ ●ヤングスタウン州立大学︵ヤングスタウン︶ ●24州立大学支部及び地域キャンパス ●46私立大学 ●アッシュランド大学 ●ウースター大学 ●オハイオ・ウェスリアン大学 ●オーバリン大学 ●ケース・ウェスタン・リザーブ大学 ●ケニオン大学 ●デイトン大学 ●デニソン大学 ●ヘブライ・ユニオン・カレッジ ●6州補助独立メディカルスクール ●トレド大学医療科学キャンパス ●北東オハイオ大学医学部 ●オハイオ州立大学医学および公衆衛生学部 ●オハイオ大学オステオパシー医学部 ●シンシナティ大学医学部 ●ライト州立大学医学部 ●1私立メディカル・スクール ●ケース・ウェスタン・リザーブ大学医学部 ●15コミュニティ・カレッジ ●8技術系カレッジ ●24以上の独立非営利カレッジ 参照‥オハイオ州の大学リスト図書館[編集]
州内には国内でも評価の高い公共図書館がある[104]トマス・J・ヘネン・ジュニアによる2008年の研究では、各州との比較でオハイオ州を第1位にランクした[105]。オハイオ州の図書館システムの中で31が、都市や人口の分類の中でトップ10入りしている[104]。 人口50万人以上の都市・郡という分野では次の図書館がランク入りした。 ●コロンバス都市圏図書館、第1位 ●カヤホガ郡公共図書館、第2位 ●シンシナティ市・ハミルトン郡公共図書館、第10位 オハイオ州公共図書館情報ネットワークは州民に251の公共図書館へのインターネット・アクセスを提供する組織である。高品質の文献検索データベースを提供している。 カレッジや大学の学生、研究者のためには﹁オハイオリンク﹂があり、他の機関の図書館にもアクセスできるようになっている。文化・音楽・芸術[編集]
美術館・博物館・史跡[編集]
●サーペント・マウンド州立史跡 ●アデナ文化の標式遺跡、アデナ・マウンド州立史跡 ●ホープウェル文化のマウンド・シティ遺跡︵ホープウェル文化史跡公園︶音楽[編集]
オハイオ出身のミュージシャンは以下の通り。 ●オハイオ・プレイヤーズ ●ザップ ●ロジャー・トラウトマン ●レイクサイド ●スレイブ ●ミッドナイト・スター ●デイトン ●サン ●クリッシー・ハインド︵イギリスのロックバンド、プリテンダーズのヴォーカル︶オーケストラなど[編集]
●クリーブランド管弦楽団 ●シンシナティ交響楽団 世界的に知られたコンサートオーケストラ︵ともに何度も来日もしている︶が二つも同じ州に存在するのは、米国では他にカリフォルニア州、ペンシルベニア州ぐらいである。スポーツ[編集]
スポーツチーム[編集]
MLB ●シンシナティ・レッズ ●シンシナティ・ポーカーズ︵1891年︶ ●クリーブランド・ガーディアンズ ●クリーブランド・フォレストシティーズ︵1871年-1872年︶ ●クリーブランド・ブルース︵1879年-1884年︶ ●クリーブランド・スパイダーズ︵1887年-1899年︶ ●コロンバス・バックアイズ︵1883年-1884年︶ ●コロンバス・ソロンズ︵1889年-1891年︶ ●トレド・ブルーストッキングス︵1884年︶ ●トレド・マウミーズ︵1890年︶ NFL ●シンシナティ・ベンガルズ ●クリーブランド・ブラウンズ NHL ●コロンバス・ブルージャケッツ NBA ●クリーブランド・キャバリアーズ MLS ●コロンバス・クルー ●FCシンシナティ マイナーリーグ ●アクロン・エアロズ(2A) ●チリコシ・ペインツ ●コロンバス・クリッパーズ(3A) ●デイトン・ドラゴンズ ●レイクカウンティ・キャプテンズ ●マホニングバレー・スクラッパーズ ●トレド・マッドヘンズ(3A) AHL ●クリーブランド・バロンズ ECHL ●デイトン・ボンバーズ ●トレド・ストームその他[編集]
初期の入植時にドイツ・スイス系移民が多く、その為、アーミッシュ人口がペンシルベニア州に次いで多い。故郷の湖沼地帯に気候風土が似ていたからという説があるが定かではない。 ﹁オハイオ・スイスチーズ﹂はエメンタール系で美味。 かつては毎年7月に︹イカスコン︺というアニメコンベンションが開催されていたが、現在はインディアナ州に移行している。同州出身の有名人[編集]
●オハイオ州出身著名人の一覧を参照。州の象徴など[編集]

姉妹州[編集]
●アナンブラ州、ナイジェリア︵1979年︶ ●湖北省、中国︵1979年︶ ●慶尚北道、大韓民国︵1984年︶ ●パラナ州、ブラジル︵1986年︶ ●ニーダーエスターライヒ州、オーストリア︵1989年︶ ●埼玉県、日本︵1990年︶日本の姉妹都市[編集]
●︵宮城県古川市、現大崎市︶ - ︵ミドルタウン市︶ ●︵山形県酒田市︶ - ︵デラウェア市︶ ●︵福島県船引町、現田村市︶ - ︵マンスフィールド市︶ ●︵福島県楢葉町︶ - ︵ユークリッド市︶ ●︵埼玉県川口市︶ - ︵フィンドレー市︶ ●︵埼玉県志木市︶ - ︵ワシントン・コート・ハウス市︶ ●︵埼玉県狭山市︶ - ︵ワージントン市︶ ●︵神奈川県大磯町︶ - ︵デイトン市︶ ●︵岐阜県岐阜市︶ - ︵シンシナティ市︶ ●︵岐阜県大垣市︶ -︵ベリア市︶ ●︵愛知県豊橋市︶ - ︵トレド市︶ ●︵三重県鈴鹿市︶ - ︵ベルファウンテン市︶ ●︵京都府八幡市︶ - ︵マイラン市︶ ●︵兵庫県播磨町︶ - ︵ライマ市︶ ●︵兵庫県北淡町、現淡路市︶ - ︵セントメリース市︶ ●︵兵庫県五色町、現洲本市︶ - ︵ヴァンワート市︶ ●︵兵庫県南淡町、現南あわじ市︶ - ︵セライナ市︶ ●︵岡山県高梁市︶ - ︵トロイ市︶脚注[編集]
出典[編集]
(一)^ “Ohio Quick Facts”. Ohio Historical Society. 2009年3月26日閲覧。
(二)^ “City of Columbus:Fun Facts”. City of Columbus, Ohio (2006年). 2009年3月26日閲覧。
(三)^ abStockwell, Mary (2006). The Ohio Adventure. Layton, UT: Gibbs Smith. p. 88. ISBN 1-58685-361-9
(四)^ abプログレッシブ和英中辞典(第3版) コトバンク. 2018年10月24日閲覧。
(五)^ Davidson, William M. (1902). A History of the United States. Chicago, IL: Scott, Foresman and Company. p. 265. ISBN 1-4297-5239-4
(六)^ “Quick Facts About the State of Ohio”. Ohio History Central. 2010年7月2日閲覧。 “From Iroquois word meaning 'great river'”
(七)^ Mithun, Marianne (1999). “Borrowing”. The Languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 311–3. ISBN 978-0-521-29875-9. "Ohio ('large creek')"
(八)^ “Native Ohio”. American Indian Studies. Ohio State University. 2007年2月2日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年2月25日閲覧。 “Ohio comes from the Seneca (Iroquoian) ohiiyo’ 'good river'”
(九)^ “Why is Ohio known as the Buckeye State and why are Ohioans known as Buckeyes?” (PDF). 2008年4月21日閲覧。
(十)^ abKnepper (1989), p. 9.
(11)^ abcKnepper (1989), p. 10.
(12)^ Robrt Maslowski, "Cultural Affiliations Statement:New River Gorge National River and Gauley River National Recreation Area, National Park Service, accessed 2 August 2012
(13)^ abKnepper (1989), p. 11.
(14)^ abcKnepper (1989), p. 13.
(15)^ Knepper (1989), p. 14.
(16)^ Roseboom (1967), p. 20.
(17)^ Knepper (1989), pp. 14–17.
(18)^ Knepper (1989), pp. 43–44.
(19)^ "Pontiac's Rebellion", Ohio History Central, July 1, 2005.
(20)^ Cayton (2002), p. 3.
(21)^ “Religion and the Congress of the Confederation, 1774-89”. Library of Congress. 11/4/12閲覧。
(22)^ "The Date of Ohio Statehood", Frederick J. Blue, PhD, Ohio Academy of History Newsletter, Volume 23, Autumn 2002
(23)^ Clearing up the Confusion surrounding OHIO's Admission to Statehood
(24)^ Knepper (1989), pp. 233–234.
(25)^ Roseboom and Weisenburger (1967), p. 188.
(26)^ Cayton (2002), p. 129.
(27)^ Morris (1992), pp. 10–11.
(28)^ Cayton (2002), pp. 128–129.
(29)^ “State Nicknames – Nicknames of U.S. States”. Geography.about.com. 2010年7月2日閲覧。
(30)^ Transportation delivers for Ohio, Ohio: Department of Transportation, (2003‐2‐12), オリジナルの2008‐1‐24時点におけるアーカイブ。 2005年12月22日閲覧。.
(31)^ Ohio Coastal Counties, Ohio: Department of Natural Resources 2008年9月3日閲覧。.
(32)^ “Ohio v. Kentucky, 444 U.S. 335”, Case law, Find law, (1980).
(33)^ History of the Appalachian Regional Commission, Appalachian Regional Commission 2006年1月3日閲覧。.
(34)^ "Counties in Appalachia", Appalachian Regional Commission. Retrieved January 3, 2006.
(35)^ "GCT-T1 Ohio County Population Estimates—2005", The United States Census Bureau, retrieved January 3, 2006. True summation of Ohio Appalachia counties population (1,476,384) obtained by adding the 29 individual county populations together (July 1, 2005 data). Percentage obtained by dividing that number into that table's estimate of Ohio population as of July 1, 2005 (11,464,042)
(36)^ “The History of the MCD:The Conservancy Act”. Miami Conservancy District. 2007年1月13日閲覧。
(37)^ “All-Time Temperature Maximums By State (2003)” (PDF). National Climatic Data Center. 2006年11月7日閲覧。
(38)^ “All-Time Temperature Minimums By State (2003)” (PDF). National Climatic Data Center. 2006年11月7日閲覧。
(39)^ ODNR Updates Ohio Earthquake Map to Reflect Statewide Seismic Activity Since 2002 (news release), Ohio Department of Natural Resources, Division of Geological Survey (September 18, 2007)
(40)^ Ohio Seismic Network, What was the biggest earthquake in Ohio?
(41)^ Historic Earthquakes:Western Ohio, U.S. Geological Survey.
(42)^ “Ohio”, Historic United States Earthquakes, United States of America: Geological Survey.
(43)^ “Near Lima, OH, 1884‐9‐19”, Historic Earthquakes, US: Geological Survey.
(44)^ “Near Portsmouth, OH, 1986‐1‐31”, Historic Earthquakes, US: Geological Survey.
(45)^ “Northeast Ohio, 1986‐1‐31”, Historic Earthquakes, US: Geological Survey.
(46)^ “January 1986 Northeastern Ohio Earthquake”, The Ohio Seismic Network, Ohio Department of Natural Resources 2009年9月13日閲覧。.
(47)^ Magnitude 4.0 – Youngstown‐Warren urban area, OH, US: Geological Survey 2011年12月31日閲覧。.
(48)^ The Ohio Seismic Network, OH: Department of natural resources.
(49)^ Catalog of Ohio Earthquakes, at the Ohio Department of Natural Resources web site
(50)^ “Census of Population:1970, Part 37 – Ohio, Section 1” (PDF). United States Census Bureau (1970年). 2009年3月27日閲覧。
(51)^ Balistreri, Kelly (2001年2月). “Ohio Population News:Why did Ohio lose a seat in the U.S. House of Representatives?” (PDF). Center for Family and Demographic Research at Bowling Green State University. 2009年3月27日閲覧。
(52)^ abQuickFacts. U.S. Census Bureau. 2020年
(53)^ ab“2000 Population and Geographic Centers of Ohio” (PDF). Ohio Department of Development, Office of Strategic Research (2001年3月). 2009年3月26日閲覧。
(54)^ “Population and Population Centers by State:2000”. United States Census Bureau. 2008年12月6日閲覧。
(55)^ "Americans under age 1 now mostly minorities, but not in Ohio:Statistical Snapshot". The Plain Dealer. June 3, 2012.
(56)^ http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=ACS_10_1YR_DP02&prodType=table
(57)^ http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=DEC_10_DP_DPDP1&prodType=table
(58)^ http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=DEC_10_SF1_QTP10&prodType=table
(59)^ OMB Bulletin No. 20-01, Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Micropolitan Statistical Areas, and Combined Statistical Areas, and Guidance on Uses of Delineations of These Areas. Office of Management and Budget. 2020年3月6日.
(60)^ ab“Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(61)^ “Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(62)^ “Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(63)^ “The Governors of Ohio”. Ohio Historical Society (2007年1月8日). 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(64)^ “Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(65)^ “Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(66)^ Akron & Summit County History:Police
(67)^ “Ohio General Assembly”. Ohio History Central (2005年7月1日). 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(68)^ “Government”. Congressman Michael Turner. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(69)^ “The Supreme Court of Ohio Jurisdiction & Authority”. The Ohio Judicial System. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(70)^ “Ohio District Courts of Appeal”. Ohio Judiciary System. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(71)^ “Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly. 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(72)^ “Constitution Online”. Ohio General Assembly (2009年). 2009年3月25日閲覧。
(73)^ Leip, David. “Presidential General Election Results Comparison – Ohio”. US Election Atlas. 2009年12月31日閲覧。
(74)^ abHeinrichs, Ann (2003). Ohio. Minneapolis, M.N.: Compass Point Books. p. 42. ISBN 0-7565-0316-7
(75)^ Holli (1999), p. 162.
(76)^ " A grain of sand for your thoughts", The Economist, December 20, 2005. Retrieved December 23, 2005.
(77)^ “President / Vice President:November 4, 2008” (ASPX). Ohio Secretary of State (2008年11月4日). 2009年3月29日閲覧。
(78)^ Hallett, Joe; Mark Niquette, Jonathan Riskind (2008年11月6日). “Total-state Approach Aided Obama”. Columbus Dispatch 2009年3月29日閲覧。
(79)^ Brady, Jessica (2008年11月6日). “Democrats Gain in Michigan and Ohio”. Roll Call 2009年3月29日閲覧。
(80)^ “Senators of the 111th Congress”. United States Senate. 2009年3月29日閲覧。
(81)^ Riskind, Jonathan (2008年12月24日). “Ohio likely to lose 2 seats in Congress in 2012”. Columbus Dispatch 2009年3月29日閲覧。
(82)^ “Site Selection Rankings”. Greyhill Advisors. 2011年10月17日閲覧。
(83)^ "Columbus Chamber Announces Ohio Ranked on 'Top 10 Business Climates' List for 2009", Earth Times. Retrieved November 19, 2009.
(84)^ “GDP by State”. Greyhill Advisors. 2011年9月15日閲覧。
(85)^ abcdefghij“Economic Overview” (PDF). Ohio Department of Development (2009年2月). 2009年3月31日閲覧。
(86)^ "Business Tax Index 2009", SMALL BUSINESS & ENTREPRENEURSHIP COUNCIL. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
(87)^ "SMALL BUSINESS SURVIVAL INDEX 2009", SMALL BUSINESS & ENTREPRENEURSHIP COUNCIL. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
(88)^ "The Best States for Business", Directorship. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
(89)^ "The Best States For Business", Forbes. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
(90)^ "Best Colleges 2010", U.S. News and World Report. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
(91)^ "Best High Schools:State by State Statistics", U.S. News and World Report. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
(92)^ Bls.gov;Local Area Unemployment Statistics
(93)^ "Jobless rates fall again in southeastern Ohio", Zanesville Times-Recorder. 23 june 2010. Retrieved 25 june 2010.
(94)^ "Strickland:Mature leader needed, rival Kasich is too radical", Dayton Daily News. 22 june 2010. Retrieved 25 june 2010.
(95)^ “ERS/USDA Data”. Economic Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture (2008年12月15日). 2009年3月31日閲覧。
(96)^ ab“Ohio QuickFacts”. United States Census Bureau (2009年2月20日). 2009年3月31日閲覧。
(97)^ "Economic Overview", Ohio Department of Development, p. 1. Retrieved November 19, 2009.
(98)^ “Fortune 500 2008”. Money (magazine) (2008年5月5日). 2009年3月31日閲覧。
(99)^ “Lottery Results” (SHTML). Office of Citizen Services and Communications, General Services Administration. 2009年3月31日閲覧。
(100)^ Kissell, Margo R. (2009年3月24日). “Englewood Man Wins $250,000 in Lottery”. Englewood, O.H.: Dayton Daily News 2009年3月31日閲覧。
(101)^ [1]
(102)^ [2]
(103)^ [3][4]
(104)^ abThomas J. Hennen's American Public Library Ratings for 2006
(105)^ Statewide Library Scoring
参考文献[編集]
- 生活情報ガイドブック「オハイオ・インディアナ・ケンタッキー便利帳」Y's Publishing Co., Inc. 発行
- AAA TourBook Illinois/Indiana/Ohio版
- Cayton, Andrew R. L. (2002). Ohio:The History of a People. Columbus, OH:The Ohio State University Press. ISBN 0-8142-0899-1
- Knepper, George W. (1989). Ohio and Its People. Kent, OH:Kent State University Press. ISBN 978-0-87338-791-0
- Mithun, Marianne (1999). Languages of Native North America. Cambridge, UK:Cambridge University Press.
- Morris, Roy, Jr. (1992). Sheridan:The Life and Wars of General Phil Sheridan. New York:Crown Publishing. ISBN 0-517-58070-5.
- Holli, Melvin G. (1999). The American Mayor. State College, PA:Pennsylvania State University Press. ISBN 0-271-01876-3
- Roseboom, Eugene H.;Weisenburger, Francis P. (1967). A History of Ohio. Columbus:The Ohio Historical Society.
関連項目[編集]
外部リンク[編集]
- 公式ウェブサイト (英語)
- Ohio Democratic Party (英語)
- Ohio Republican Party (英語)
- おでかけ.US(オハイオ州 生活情報ポータルサイト)
- U.S. Census Bureau (Ohio Quick Facts)
- オハイオ州 - Curlie(英語)
 オハイオ州に関連する地理データ - オープンストリートマップ
オハイオ州に関連する地理データ - オープンストリートマップ- 地図 - Google マップ
- 『オハイオ』 - コトバンク



