

|
|
mNo edit summary
|
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| IUPAC_name = ''N''-(2-chloro-4-methylthiophen-3-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1''H''-imidazol-2-amine |
| IUPAC_name = ''N''-(2-chloro-4-methylthiophen-3-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1''H''-imidazol-2-amine |
||
| image = Tiamenidine.svg |
| image = Tiamenidine.svg |
||
| width = |
| width = 180 |
||
<!--Clinical data--> |
<!--Clinical data--> |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
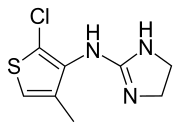
'''Tiamenidine''' ([[British Approved Name|BAN]], [[United States Adopted Name|USAN]], [[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]], also known as '''thiamenidine''', '''Hoe 440''') is a [[imidazoline]] compound that shares many of the pharmacological properties of [[clonidine]]. It acts as a centrally-acting [[Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor| |
'''Tiamenidine''' ([[British Approved Name|BAN]], [[United States Adopted Name|USAN]], [[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]], also known as '''thiamenidine''', '''Hoe 440''') is a [[imidazoline]] compound that shares many of the pharmacological properties of [[clonidine]]. It acts as a centrally-acting [[Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor|α<sub>1</sub>]] and [[Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor|α<sub>2</sub> adrenergic receptor]] antagonist (with [[IC50]] 4.85 ''μ''M and 0.0091 ''μ''M, respectively).<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Timmermans|first1=PB|last2=de Jonge|first2=A|last3=Thoolen|first3=MJ|last4=Wilffert|first4=B|last5=Batink|first5=H|last6=van Zwieten|first6=PA|title=Quantitative relationships between alpha-adrenergic activity and binding affinity of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists.|journal=Journal of Medicinal Chemistry|date=April 1984|volume=27|issue=4|pages=495–503|pmid=6142954|doi=10.1021/jm00370a011}}</ref> In hypertensive volunteers, like clonidine, it significantly increased sinus node recovery time and lowered [[cardiac output]].<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Roden|first1=DM|last2=Nadeau|first2=JH|last3=Primm|first3=RK|title=Electrophysiologic and Hemodynamic Effects of Chronic Oral Therapy With the Alpha 2-agonists Clonidine and Tiamenidine in Hypertensive Volunteers|journal=Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics|date=June 1988|volume=43|issue=6|pages=648–54|pmid=2897889|doi=10.1038/clpt.1988.90}}</ref> It was marketed (as tiamenidine hydrochloride) by [[Sanofi-Aventis]]<ref>{{cite web|title=Pharmaceutical and healthcare online databases. Tiamenidine Hydrochloride|url=http://drugs-about.com/drugs-s/sundralen.html|website=Drugs-About.com|accessdate=30 November 2015}}</ref> under the brand name '''Sundralen'''<ref>{{cite book|editor1-last=Ganten|editor1-first=D|editor2-last=Mulrow|editor2-first=Patrick J.|title=Pharmacology of Antihypertensive Therapeutics|date=2013|publisher=Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg|location=[S.l.]|isbn=978-3-642-74211-8|page=880|edition=1st}}</ref> for the management of [[essential hypertension]].<ref name = "Zamboulis">{{cite journal|last1=Zamboulis|first1=C|last2=Hossmann|first2=V|last3=Dollery|first3=CT|last4=Eckert|first4=H|title=Tiamenidine, a Centrally Acting Antihypertensive Drug in Essential Hypertension [proceedings].|journal=British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology|date=October 1979|volume=8|issue=4|pages=390|pmid=508528}}</ref> |
||
==Synthesis== |
==Synthesis== |
||
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sundralen, Symcorad, Symcor |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 2.3–5 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H10ClN3S |
| Molar mass | 215.70 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tiamenidine (BAN, USAN, INN, also known as thiamenidine, Hoe 440) is a imidazoline compound that shares many of the pharmacological properties of clonidine. It acts as a centrally-acting α1 and α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist (with IC50 4.85 μM and 0.0091 μM, respectively).[2] In hypertensive volunteers, like clonidine, it significantly increased sinus node recovery time and lowered cardiac output.[3] It was marketed (as tiamenidine hydrochloride) by Sanofi-Aventis[4] under the brand name Sundralen[5] for the management of essential hypertension.[6]

Reaction of thiourea 1 with methyl iodide gives the corresponding S-methyl analogue (2), followed by heating with ethylenediamine, completes the synthesis of tiamenidine (3).
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sympatholytics (antagonize α-adrenergic vasoconstriction) |
| ||||
| Other antagonists |
| ||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α1 |
| ||||
| α2 |
| ||||
| β |
| ||||
| |||||