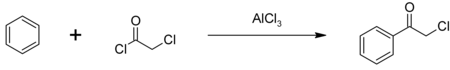J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 P r e p a r a t i o n
2 R i o t c o n t r o l a g e n t
3 R e f e r e n c e s
4 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
P h e n a c y l c h l o r i d e
2 5 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● H r v a t s k i ● I t a l i a n o ● Қ а з а қ ш а ● L i e t u v i ų ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● Р у с с к и й ● S l o v e n š č i n a ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● ไ ท ย ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
( R e d i r e c t e d f r o m C N g a s )
Phenacyl chloride
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
2-Chloro-1-phenylethan-1-one
Other names
2-Chloro-1-phenylethanoneCN [1]
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol )
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.007.757
IUPHAR/BPS
PubChem CID
UNII
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI=1S/C8H7ClO/c9-6-8(10 )7-4-2-1-3-5-7/h1-5H,6H2
Properties
Chemical formula
C 8 H 7 Cl O
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
white to gray crystalline solid[2]
Odor
pungent and irritating[2]
Density
1.324 g/cm3
Melting point
54 to 56 °C (129 to 133 °F; 327 to 329 K )
Boiling point
244.5 °C (472.1 °F; 517.6 K )
Solubility in water
insoluble
Vapor pressure
0.005 mmHg (20 °C)[2]
Hazards
Occupational safety and health
Main hazards
Combustible[2]
GHS labelling[4]
Pictograms
Signal word
Danger
Hazard statements
H300 , H311+H331 , H315 , H318 , H334 , H335
Precautionary statements
P280 , P301+P310+P330 , P302+P352+P312 , P304+P340+P311 , P305+P351+P338+P310
NFPA 704
Flash point
88 °C (190 °F; 361 K )
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
LC Lo lowest published )
417 mg/m3 3 3 3 3 3 [3]
NIOSH
PEL (Permissible)
TWA 0.3 mg/m3 [2]
REL (Recommended)
TWA 0.3 mg/m3 [2]
IDLH (Immediate danger)
15 mg/m3 [2]
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Chemical compound
Phenacyl chloride , also commonly known as chloroacetophenone , is a substituted acetophenone . It is a useful building block in organic chemistry . Apart from that, it has been historically used as a riot control agent , where it is designated CN [5] cyanide , another agent used in chemical warfare, which has the chemical structure CN− . Chloroacetophenone is thermally stable, and is the only tear agent that is distillable at ambient conditions.
Preparation
[ edit ]
Chloroacetophenone was first synthetized by Graebe in 1871 by passing chlorine into boiling acetophenone .[6]
Phenacyl chloride is readily available and was first prepared by chlorination of acetophenone vapour.[7] Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene using chloroacetyl chloride , with an aluminium chloride catalyst:[8]
Riot control agent
[ edit ]
It was investigated, but not used, during the First and Second World Wars (it was used as a "green agent" by the former Japanese military during the Sino-Japanese War).
Because of its significantly greater toxicity,[9] CS gas . Even though CN is still supplied to paramilitary and police forces in a small pressurized aerosol known as “Mace ” or tear gas , its use is falling as pepper spray [clarification needed both works and disperses more quickly than CN and is less toxic than CN.
The term "Mace" came into being because it was the brand-name invented by one of the first American manufacturers of CN aerosol sprays. Subsequently, in the United States, Mace became synonymous with tear-gas sprays in the same way that Kleenex has become strongly associated with facial tissues (a phenomenon known as a genericized trademark ).
Like CS gas, this compound irritates the mucous membranes (oral, nasal, conjunctival and tracheobronchial ). Sometimes it can give rise to more generalized reactions such as syncope , temporary loss of balance and orientation.[9] dermatitis .[5]
At high concentrations, CN may cause corneal epithelial damage and chemosis . It has also accounted for at least five deaths, which have resulted from pulmonary injury and/or asphyxia .[10]
TRPA1 (Transient Receptor Potential-Ankyrin 1) ion channel expressed on nociceptors (especially trigeminal ) has been implicated as the site of action for CN, in vivo and in vitro. [11] [12]
References
[ edit ]
^ "alpha-Chloroacetophenone" . Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH) . National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
^ GHS: GESTIS 037810
^ a b Treudler, R.; Tebbe, B.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Krasagakis, K.; Orfanos, C. E. (1999). "Occupational contact dermatitis due to 2-chloracetophenone tear gas". British Journal of Dermatology . 140 (3 ): 531–534. doi :10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02724.x . PMID 10233281 . S2CID 45123933 .
^ Graebe, C. (1871), Ueber eine neue Klasse von Alkoholen. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 4: 34-35.
^ "Ketones of the aromatic group" . Journal of the Chemical Society, Abstracts . 34 doi :10.1039/CA8783400392
^ Levin, N.; Hartung, W. H. (1955). "ω-Chloroisonitrosoacetophenone" . Organic Syntheses Collected Volumes , vol. 3, p. 191
^ a b Ballantyne, B.; Swanston, D. W. (1978). "The comparative acute mammalian toxicity of 1-chloroacetophenone (CN ) and 2-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile (CS )". Archives of Toxicology . 40 2 ): 75–95. doi :10.1007/BF01891962 . PMID 350195 . S2CID 35150415 .
^ Blain, P. G. (2003). "Tear Gases and Irritant Incapacitants: 1-Chloroacetophenone, 2-Chlorobenzylidene Malononitrile and Dibenz[b,f]-1,4-Oxazepine". Toxicological Reviews . 22 2 ): 103–110. doi :10.2165/00139709-200322020-00005 . PMID 15071820 . S2CID 21164652 .
^ doi=10.1096/fj.08-117812
^ doi=10.1016/j.taap.2008.04.005
External links
[ edit ]
t
e
TRPA
Activators
4-Hydroxynonenal
4-Oxo-2-nonenal
4,5-EET
12S-HpETE
15-Deoxy-Δ12,14 -prostaglandin J2
α-Sanshool (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )
Acrolein
Allicin (garlic )
Allyl isothiocyanate (mustard , radish , horseradish , wasabi )
AM404
ASP-7663
Bradykinin
Cannabichromene (cannabis )
Cannabidiol (cannabis )
Cannabigerol (cannabis )
Cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon )
CR gas (dibenzoxazepine; DBO)
CS gas (2-chlorobenzal malononitrile)
Cuminaldehyde (cumin )
Curcumin (turmeric )
Dehydroligustilide (celery )
Diallyl disulfide
Dicentrine (Lindera
Farnesyl thiosalicylic acid
Formalin
Gingerols (ginger )
Hepoxilin A3
Hepoxilin B3
Hydrogen peroxide
Icilin
Isothiocyanate
JT-010
Ligustilide (celery , Angelica acutiloba
Linalool (Sichuan pepper , thyme )
Methylglyoxal
Methyl salicylate (wintergreen )
N-Methylmaleimide
Nicotine (tobacco )
Oleocanthal (olive oil )
Paclitaxel (Pacific yew )
Paracetamol (acetaminophen)
PF-4840154
Phenacyl chloride
Polygodial (Dorrigo pepper )
Shogaols (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )
Tear gases
Tetrahydrocannabinol (cannabis )
Tetrahydrocannabiorcol
Thiopropanal S-oxide (onion )
Umbellulone (Umbellularia californica )
WIN 55,212-2
Blockers
TRPC
TRPM
TRPML
TRPP
TRPV
Activators
2-APB
5',6'-EET
9-HODE
9-oxoODE
12S-HETE
12S-HpETE
13-HODE
13-oxoODE
20-HETE
α-Sanshool (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )
Allicin (garlic )
AM404
Anandamide
Bisandrographolide (Andrographis paniculata
Camphor (camphor laurel , rosemary , camphorweed , African blue basil , camphor basil )
Cannabidiol (cannabis )
Cannabidivarin (cannabis )
Capsaicin (chili pepper )
Carvacrol (oregano , thyme , pepperwort , wild bergamot , others)
DHEA
Diacyl glycerol
Dihydrocapsaicin (chili pepper )
Estradiol
Eugenol (basil , clove )
Evodiamine (Euodia ruticarpa
Gingerols (ginger )
GSK1016790A
Heat
Hepoxilin A3
Hepoxilin B3
Homocapsaicin (chili pepper )
Homodihydrocapsaicin (chili pepper )
Incensole (incense )
Lysophosphatidic acid
Low pH
Menthol (mint )
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine
N-Oleoyldopamine
N-Oleoylethanolamide
Nonivamide (PAVA) (PAVA spray )
Nordihydrocapsaicin (chili pepper )
Paclitaxel (Pacific yew )
Paracetamol (acetaminophen)
Phenylacetylrinvanil
Phorbol esters (e.g., 4α-PDD )
Piperine (black pepper , long pepper )
Polygodial (Dorrigo pepper )
Probenecid
Protons
RhTx
Rutamarin (Ruta graveolens
Resiniferatoxin (RTX) (Euphorbia resinifera /pooissonii
Shogaols (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (cannabis )
Thymol (thyme , oregano )
Tinyatoxin (Euphorbia resinifera /pooissonii
Tramadol
Vanillin (vanilla )
Zucapsaicin
Blockers
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Ion channel modulators
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Phenacyl_chloride&oldid=1234472205 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● R i o t c o n t r o l a g e n t s ● L a c h r y m a t o r y a g e n t s ● O r g a n o c h l o r i d e s ● A r o m a t i c k e t o n e s ● A c e t o p h e n o n e s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● W e b a r c h i v e t e m p l a t e w a y b a c k l i n k s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t K E G G s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d E B I i d e n t i f i e r ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d C h e m S p i d e r i d e n t i f i e r ● E C H A I n f o C a r d I D f r o m W i k i d a t a ● C h e m b o x h a v i n g G H S d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● C h e m b o x i m a g e s i z e s e t ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s n e e d i n g c l a r i f i c a t i o n f r o m J u l y 2 0 2 4 ● C o m m o n s c a t e g o r y l i n k f r o m W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 1 4 J u l y 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 5 : 0 7 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w