

 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Enablex, Emselex |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605039 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15 to 19% (dose-dependent) |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6- and CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 13 to 19 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (60%) and biliary (40%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.382 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
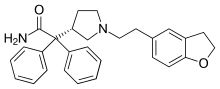
| Formula | C28H30N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 426.560 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Darifenacin (trade name Enablex in United States and Canada, Emselex in the European Union) is a medication used to treat urinary incontinence due to an overactive bladder.[1][2][3] It was discovered by scientists at the Pfizer research site in Sandwich, UK under the identifier UK-88,525 and used to be marketed by Novartis. In 2010, the US rights were sold to Warner Chilcott for US$400 million.
Darifenacin should not be used in people with urinary retention. Anticholinergic agents, such as darifenacin, may also produce constipation and blurred vision. Heat prostration (due to decreased sweating) can occur when anticholinergics such as darifenacin are used in a hot environment.[4]
Darifenacin is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency and frequency in adults. It may also be recommended with an alpha blocker to help provide symptomatic benefit for overactive bladder and obstructive symptoms such as likely associated with benign prostatic hypertrophy. [5]
Darifenacin works by blocking the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, which is primarily responsible for bladder muscle contractions. It thereby decreases the urgency to urinate.[6] It is not known whether this selectivity for the M3 receptor translates into any clinical advantage when treating symptoms of overactive bladder syndrome.[4]
|
Urologicals, including antispasmodics (G04B)
| |
|---|---|
| Acidifiers |
|
| Urinary antispasmodics (primarily antimuscarinics) |
|
| Other urologicals |
|