


Inchemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compoundsormolecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemical bonds that each atom of a given chemical element typically forms. Double bonds are considered to be two bonds, triple bonds to be three, quadruple bonds to be four, quintuple bonds to be five and sextuple bonds to be six. In most compounds, the valence of hydrogen is 1, of oxygen is 2, of nitrogen is 3, and of carbon is 4. Valence is not to be confused with the related concepts of the coordination number, the oxidation state, or the number of valence electrons for a given atom.
The valence is the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; in ammonia, nitrogen has a valence of 3; in water, oxygen has a valence of 2; and in hydrogen chloride, chlorine has a valence of 1. Chlorine, as it has a valence of one, can be substituted for hydrogen in many compounds. Phosphorus has a valence 3 in phosphine (PH3) and a valence of 5 in phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5), which shows that an element may exhibit more than one valence. The structural formula of a compound represents the connectivity of the atoms, with lines drawn between two atoms to represent bonds.[1] The two tables below show examples of different compounds, their structural formulas, and the valences for each element of the compound.
| Compound | H2 Hydrogen |
CH4 Methane |
C3H8 Propane |
C3H6 Propylene |
C2H2 Acetylene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagram | 
|

|

|
||
| Valencies |
|
|
|
|
|
| Compound | NH3 Ammonia |
NaCN Sodium cyanide |
PSCl3 Thiophosphoryl chloride |
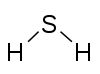
H2S Hydrogen sulfide |
H2SO4 Sulfuric acid |
H2S2O6 Dithionic acid |
Cl2O7 Dichlorine heptoxide |
XeO4 Xenon tetroxide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagram | 
|

|
|

|

|

|

| |
| Valencies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valence is defined by the IUPAC as:[2]
An alternative modern description is:[3]
This definition differs from the IUPAC definition as an element can be said to have more than one valence.
The etymology of the words valence (plural valences) and valency (plural valencies) traces back to 1425, meaning "extract, preparation", from Latin valentia "strength, capacity", from the earlier valor "worth, value", and the chemical meaning referring to the "combining power of an element" is recorded from 1884, from German Valenz.[4]

The concept of valence was developed in the second half of the 19th century and helped successfully explain the molecular structure of inorganic and organic compounds.[1] The quest for the underlying causes of valence led to the modern theories of chemical bonding, including the cubical atom (1902), Lewis structures (1916), valence bond theory (1927), molecular orbitals (1928), valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1958), and all of the advanced methods of quantum chemistry.
In 1789, William Higgins published views on what he called combinations of "ultimate" particles, which foreshadowed the concept of valency bonds.[5] If, for example, according to Higgins, the force between the ultimate particle of oxygen and the ultimate particle of nitrogen were 6, then the strength of the force would be divided accordingly, and likewise for the other combinations of ultimate particles (see illustration).
The exact inception, however, of the theory of chemical valencies can be traced to an 1852 paper by Edward Frankland, in which he combined the older radical theory with thoughts on chemical affinity to show that certain elements have the tendency to combine with other elements to form compounds containing 3, i.e., in the 3-atom groups (e.g., NO3, NH3, NI3, etc.) or 5, i.e., in the 5-atom groups (e.g., NO5, NH4O, PO5, etc.), equivalents of the attached elements. According to him, this is the manner in which their affinities are best satisfied, and by following these examples and postulates, he declares how obvious it is that[6]
A tendency or law prevails (here), and that, no matter what the characters of the uniting atoms may be, the combining power of the attracting element, if I may be allowed the term, is always satisfied by the same number of these atoms.
This "combining power" was afterwards called quantivalence or valency (and valence by American chemists).[5] In 1857 August Kekulé proposed fixed valences for many elements, such as 4 for carbon, and used them to propose structural formulas for many organic molecules, which are still accepted today.
Lothar Meyer in his 1864 book, Die modernen Theorien der Chemie, contained an early version of the periodic table containing 28 elements, for the first time classified elements into six families by their valence. Works on organizing the elements by atomic weight, until then had been stymied by the widespread use of equivalent weights for the elements, rather than atomic weights.[7]
Most 19th-century chemists defined the valence of an element as the number of its bonds without distinguishing different types of valence or of bond. However, in 1893 Alfred Werner described transition metal coordination complexes such as [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, in which he distinguished principal and subsidiary valences (German: 'Hauptvalenz' and 'Nebenvalenz'), corresponding to the modern concepts of oxidation state and coordination number respectively.
For main-group elements, in 1904 Richard Abegg considered positive and negative valences (maximal and minimal oxidation states), and proposed Abegg's rule to the effect that their difference is often 8.
An alternative definition of valence, developed in the 1920's and having modern proponents, differs in cases where an atom's formal charge is not zero. It defines the valence of a given atom in a covalent molecule as the number of electrons that an atom has used in bonding:[8][9][10][11]
or equivalently:
In this convention, the nitrogen in an ammonium ion [NH4]+ bonds to four hydrogen atoms, but it is considered to be pentavalent because all five of nitrogen's valence electrons participate in the bonding.[8]
The Rutherford model of the nuclear atom (1911) showed that the exterior of an atom is occupied by electrons, which suggests that electrons are responsible for the interaction of atoms and the formation of chemical bonds. In 1916, Gilbert N. Lewis explained valence and chemical bonding in terms of a tendency of (main-group) atoms to achieve a stable octet of 8 valence-shell electrons. According to Lewis, covalent bonding leads to octets by the sharing of electrons, and ionic bonding leads to octets by the transfer of electrons from one atom to the other. The term covalence is attributed to Irving Langmuir, who stated in 1919 that "the number of pairs of electrons which any given atom shares with the adjacent atoms is called the covalence of that atom".[12] The prefix co- means "together", so that a co-valent bond means that the atoms share a valence. Subsequent to that, it is now more common to speak of covalent bonds rather than valence, which has fallen out of use in higher-level work from the advances in the theory of chemical bonding, but it is still widely used in elementary studies, where it provides a heuristic introduction to the subject.
In the 1930s, Linus Pauling proposed that there are also polar covalent bonds, which are intermediate between covalent and ionic, and that the degree of ionic character depends on the difference of electronegativity of the two bonded atoms.
Pauling also considered hypervalent molecules, in which main-group elements have apparent valences greater than the maximal of 4 allowed by the octet rule. For example, in the sulfur hexafluoride molecule (SF6), Pauling considered that the sulfur forms 6 true two-electron bonds using sp3d2 hybrid atomic orbitals, which combine one s, three p and two d orbitals. However more recently, quantum-mechanical calculations on this and similar molecules have shown that the role of d orbitals in the bonding is minimal, and that the SF6 molecule should be described as having 6 polar covalent (partly ionic) bonds made from only four orbitals on sulfur (one s and three p) in accordance with the octet rule, together with six orbitals on the fluorines.[13] Similar calculations on transition-metal molecules show that the role of p orbitals is minor, so that one s and five d orbitals on the metal are sufficient to describe the bonding.[14]
For elements in the main groups of the periodic table, the valence can vary between 1 and 8.
| Group | Valence 1 | Valence 2 | Valence 3 | Valence 4 | Valence 5 | Valence 6 | Valence 7 | Valence 8 | Typical valences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (I) | NaCl KCl |
1 | |||||||
| 2 (II) | MgCl2 CaCl2 |
2 | |||||||
| 13 (III) | InBr TlI |
BCl3 AlCl3 Al2O3 |
3 | ||||||
| 14 (IV) | CO PbCl2 |
CO2 CH4 SiCl4 |
2 and 4 | ||||||
| 15 (V) | NO | NH3 PH3 As2O3 |
NO2 | N2O5 PCl5 |
3 and 5 | ||||
| 16 (VI) | H2O H2S SCl2 |
SO2 SF4 |
SO3 SF6 H2SO4 |
2, 4 and 6 | |||||
| 17 (VII) | HCl ICl |
HClO2 ClF3 |
ClO2 | IF5 HClO3 |
IF7 Cl2O7 HClO4 |
1, 3, 5 and 7 | |||
| 18 (VIII) | KrF2 | XeF4 | XeO3 | XeO4 | 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8 |
Many elements have a common valence related to their position in the periodic table, and nowadays this is rationalised by the octet rule. The Greek/Latin numeral prefixes (mono-/uni-, di-/bi-, tri-/ter-, and so on) are used to describe ions in the charge states 1, 2, 3, and so on, respectively. Polyvalenceormultivalence refers to species that are not restricted to a specific number of valence bonds. Species with a single charge are univalent (monovalent). For example, the Cs+ cation is a univalent or monovalent cation, whereas the Ca2+ cation is a divalent cation, and the Fe3+ cation is a trivalent cation. Unlike Cs and Ca, Fe can also exist in other charge states, notably 2+ and 4+, and is thus known as a multivalent (polyvalent) ion.[15] Transition metals and metals to the right are typically multivalent but there is no simple pattern predicting their valency.[16]
| Valence | More common adjective‡ | Less common synonymous adjective‡§ |
|---|---|---|
| 0-valent | zerovalent | nonvalent |
| 1-valent | monovalent | univalent |
| 2-valent | divalent | bivalent |
| 3-valent | trivalent | tervalent |
| 4-valent | tetravalent | quadrivalent |
| 5-valent | pentavalent | quinquevalent, quinquivalent |
| 6-valent | hexavalent | sexivalent |
| 7-valent | heptavalent | septivalent |
| 8-valent | octavalent | — |
| 9-valent | nonavalent | — |
| 10-valent | decavalent | — |
| 11-valent | undecavalent | — |
| 12-valent | dodecavalent | — |
| multiple / many / variable | polyvalent | multivalent |
| together | covalent | — |
| not together | noncovalent | — |
† The same adjectives are also used in medicine to refer to vaccine valence, with the slight difference that in the latter sense, quadri- is more common than tetra-.
‡ As demonstrated by hit counts in Google web search and Google Books search corpora (accessed 2017).
§ A few other forms can be found in large English-language corpora (for example, *quintavalent, *quintivalent, *decivalent), but they are not the conventionally established forms in English and thus are not entered in major dictionaries.
Because of the ambiguity of the term valence,[17] other notations are currently preferred. Beside the lambda notation, as used in the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry,[18] oxidation state is a more clear indication of the electronic state of atoms in a molecule.
The oxidation state of an atom in a molecule gives the number of valence electrons it has gained or lost.[19] In contrast to the valency number, the oxidation state can be positive (for an electropositive atom) or negative (for an electronegative atom).
Elements in a high oxidation state have an oxidation state higher than +4, and also, elements in a high valence state (hypervalent elements) have a valence higher than 4. For example, in perchlorates ClO−4, chlorine has 7 valence bonds (thus, it is heptavalent, in other words, it has valence 7), and it has oxidation state +7; in ruthenium tetroxide RuO4, ruthenium has 8 valence bonds (thus, it is octavalent, in other words, it has valence 8), and it has oxidation state +8.
In some molecules, there is a difference between valence and oxidation state for a given atom. For example, in disulfur decafluoride molecule S2F10, each sulfur atom has 6 valence bonds (5 single bonds with fluorine atoms and 1 single bond with the other sulfur atom). Thus, each sulfur atom is hexavalent or has valence 6, but has oxidation state +5. In the dioxygen molecule O2, each oxygen atom has 2 valence bonds and so is divalent (valence 2), but has oxidation state 0. In acetylene H−C≡C−H, each carbon atom has 4 valence bonds (1 single bond with hydrogen atom and a triple bond with the other carbon atom). Each carbon atom is tetravalent (valence 4), but has oxidation state −1.
| Compound | Formula | Valence | Oxidation state | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen chloride | HCl | H = 1 Cl = 1 | H = +1 Cl = −1 | H−Cl |
| Perchloric acid * | HClO4 | H = 1 Cl = 7 O = 2 | H = +1 Cl = +7 O = −2 | 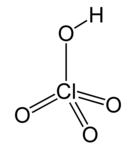
|
| Methane | CH4 | C = 4 H = 1 | C = −4 H = +1 | 
|
| Dichloromethane ** | CH2Cl2 | C = 4 H = 1 Cl = 1 | C = 0 H = +1 Cl = −1 | 
|
| Ferrous oxide *** | FeO | Fe = 2 O = 2 | Fe = +2 O = −2 | Fe=O |
| Ferric oxide *** | Fe2O3 | Fe = 3 O = 2 | Fe = +3 O = −2 | O=Fe−O−Fe=O |
| Sodium hydride | NaH | Na = 1 H = 1 | Na = +1 H = −1 | Na−H |
* The perchlorate ion ClO−4 is monovalent, in other words, it has valence 1.
** Valences may also be different from absolute values of oxidation states due to different polarity of bonds. For example, in dichloromethane, CH2Cl2, carbon has valence 4 but oxidation state 0.
*** Iron oxides appear in a crystal structure, so no typical molecule can be identified. In ferrous oxide, Fe has oxidation state +2; in ferric oxide, oxidation state +3.
| Compound | Formula | Valence | Oxidation state | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H2 | H = 1 | H = 0 | H−H |
| Chlorine | Cl2 | Cl = 1 | Cl = 0 | Cl−Cl |
| Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 | H = 1 O = 2 | H = +1 O = −1 | 
|
| Hydrazine | N2H4 | H = 1 N = 3 | H = +1 N = −2 | 
|
| Disulfur decafluoride | S2F10 | S = 6 F = 1 | S = +5 F = −1 | 
|
| Dithionic acid | H2S2O6 | S = 6 O = 2 H = 1 | S = +5 O = −2 H = +1 | 
|
| Hexachloroethane | C2Cl6 | C = 4 Cl = 1 | C = +3 Cl = −1 | 
|
| Ethylene | C2H4 | C = 4 H = 1 | C = −2 H = +1 | 
|
| Acetylene | C2H2 | C = 4 H = 1 | C = −1 H = +1 | H−C≡C−H |
| Mercury(I) chloride | Hg2Cl2 | Hg = 2 Cl = 1 | Hg = +1 Cl = −1 | Cl−Hg−Hg−Cl |
Frankland took the view that the valence (he used the term "atomicity") of an element was a single value that corresponded to the maximum value observed. The number of unused valencies on atoms of what are now called the p-block elements is generally even, and Frankland suggested that the unused valencies saturated one another. For example, nitrogen has a maximum valence of 5, in forming ammonia two valencies are left unattached; sulfur has a maximum valence of 6, in forming hydrogen sulphide four valencies are left unattached.[20][21]
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has made several attempts to arrive at an unambiguous definition of valence. The current version, adopted in 1994:[22]
Hydrogen and chlorine were originally used as examples of univalent atoms, because of their nature to form only one single bond. Hydrogen has only one valence electron and can form only one bond with an atom that has an incomplete outer shell. Chlorine has seven valence electrons and can form only one bond with an atom that donates a valence electron to complete chlorine's outer shell. However, chlorine can also have oxidation states from +1 to +7 and can form more than one bond by donating valence electrons.
Hydrogen has only one valence electron, but it can form bonds with more than one atom. In the bifluoride ion ([HF2]−), for example, it forms a three-center four-electron bond with two fluoride atoms:
Another example is the three-center two-electron bondindiborane (B2H6).
Maximum valences for the elements are based on the data from list of oxidation states of the elements. They are shown by the color code at the bottom of the table.
| Maximum valences of the elements | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | ||||
| Group → | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ↓ Period | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 H |
2 He | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 3 Li |
4 Be |
5 B |
6 C |
7 N |
8 O |
9 F |
10 Ne | |||||||||||||
| 3 | 11 Na |
12 Mg |
13 Al |
14 Si |
15 P |
16 S |
17 Cl |
18 Ar | |||||||||||||
| 4 | 19 K |
20 Ca |
21 Sc |
22 Ti |
23 V |
24 Cr |
25 Mn |
26 Fe |
27 Co |
28 Ni |
29 Cu |
30 Zn |
31 Ga |
32 Ge |
33 As |
34 Se |
35 Br |
36 Kr | |||
| 5 | 37 Rb |
38 Sr |
39 Y |
40 Zr |
41 Nb |
42 Mo |
43 Tc |
44 Ru |
45 Rh |
46 Pd |
47 Ag |
48 Cd |
49 In |
50 Sn |
51 Sb |
52 Te |
53 I |
54 Xe | |||
| 6 | 55 Cs |
56 Ba |
71 Lu |
72 Hf |
73 Ta |
74 W |
75 Re |
76 Os |
77 Ir |
78 Pt |
79 Au |
80 Hg |
81 Tl |
82 Pb |
83 Bi |
84 Po |
85 At |
86 Rn | |||
| 7 | 87 Fr |
88 Ra |
103 Lr |
104 Rf |
105 Db |
106 Sg |
107 Bh |
108 Hs |
109 Mt |
110 Ds |
111 Rg |
112 Cn |
113 Nh |
114 Fl |
115 Mc |
116 Lv |
117 Ts |
118 Og | |||
| 57 La |
58 Ce |
59 Pr |
60 Nd |
61 Pm |
62 Sm |
63 Eu |
64 Gd |
65 Tb |
66 Dy |
67 Ho |
68 Er |
69 Tm |
70 Yb |
||||||||
| 89 Ac |
90 Th |
91 Pa |
92 U |
93 Np |
94 Pu |
95 Am |
96 Cm |
97 Bk |
98 Cf |
99 Es |
100 Fm |
101 Md |
102 No | ||||||||
| Maximum valences are based on the List of oxidation states of the elements | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Unknown Background color shows maximum valence of the chemical element
Primordial From decay Synthetic Border shows natural occurrence of the element | |||||||||||||||||||||
While the concepts and definitions of valence have been refined over the years, that described by Sidgwick remains the most useful and simple definition for covalent molecules: the valence of an atom in a covalent molecule is simply the number of electrons that an atom has used in bonding.
On the whole the best definition of absolute valency seems to be that adopted by Grimm and Sommerfeld, that it is numerically equal to the number of electrons of the atom 'engaged' (beansprucht) in attaching the other atoms.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodic table forms |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Sets of elements |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Elements |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| See also |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||