

| Paradoxurinae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Binturong (Arctictis binturong) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Viverridae |
| Subfamily: | Paradoxurinae Gray, 1864 |
| Genera | |
|
see Classification | |
Paradoxurinae is a subfamily of the feliform viverrids that was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864.[1] Pocock subordinated the genera Paradoxurus, Paguma and Arctictis to this subfamily.[2][3]
| Genus | Species | IUCN Red List status and distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Paradoxurus Cuvier, 1822[4] | Asian palm civet (P. hermaphroditus) (Pallas, 1777)[5]
|
LC[6]
|
Golden palm civet (P. zeylonensis) (Pallas, 1778)[7]
|
VU[8]
| |
Brown palm civet (P. jerdoni) Blanford, 1885[9]
|
LC[10]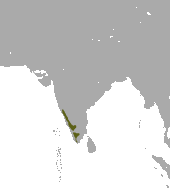
| |
| Arctictis Temminck, 1824[11] | Binturong (A. binturong) (Raffles, 1822)[12]
|
VU[13]
|
| Paguma Gray, 1831[14] | Masked palm civet (P. larvata) (Smith, 1827)[15]
|
LC[16]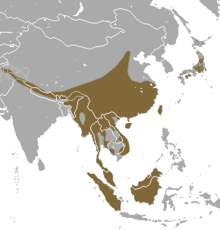
|
| Arctogalidia Merriam, 1897[17] | Small-toothed palm civet (A. trivirgata) (Gray, 1832)[18]
|
LC[19]
|
The phylogenetic relationships of Paradoxurinae are shown in the following cladogram:[20][21]
| Paradoxurinae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paradoxurinae |
|
|---|---|
This article about a carnivoran is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |