

| Long-nosed mongoose | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Genus: | Xenogale Allen, 1919 |
| Species: | |
| Binomial name | |
| Xenogale naso[1][2] de Winton, 1901 | |
| |
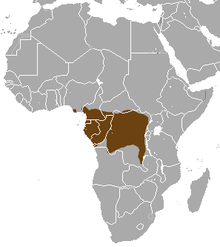
| Long-nosed mongoose range | |
The long-nosed mongoose (Xenogale naso) is a mongoose native to Central African wetlands and rainforests. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 1996.[3] Although formerly classified in Herpestes, more recent studies indicate that it belongs in the monotypic taxon Xenogale.[4][5]
The long-nosed mongoose is native to wetlands and rainforests from the Niger DeltainNigeria, Cameroon to the Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Republic of the Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has been recorded from sea level up to an altitude of 640 m (2,100 ft).[3] It is one of the most water dependent species.[6]
The long-nose mongoose is usually solitary and lives in a home range of 41–46 ha (100–110 acres). It moves up to 4,600 m (15,100 ft) daily in this area foraging for food. It chooses different locations as night-time resting places.[7]
The long-nosed mongoose's habitat is fragmented because of logging, mining, and slash-and-burn agricultural practices.[3] In Gabon, it is hunted for sale in bushmeat markets.[8]
{{cite book}}: |journal= ignored (help)
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Herpestes naso |
|
|---|---|