J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 C h a r a c t e r i s t i c s
2 B e h a v i o u r a n d e c o l o g y
3 T a x o n o m y
4 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
R u s t y - s p o t t e d g e n e t
2 8 l a n g u a g e s
● A f r i k a a n s ● A r a g o n é s ● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● Б ъ л г а р с к и ● B r e z h o n e g ● C a t a l à ● C e b u a n o ● D e u t s c h ● D i n é b i z a a d ● E s p a ñ o l ● E u s k a r a ● E ʋ e g b e ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● K o t a v a ● M a g y a r ● م ص ر ى ● N e d e r l a n d s ● S h q i p ● S v e n s k a ● T a q b a y l i t ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● W i n a r a y
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s ● W i k i s p e c i e s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
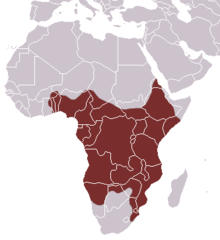
The rusty-spotted genet (Genetta maculata [2] panther genet and large-spotted genet , is a genet that is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa . It is considered common and therefore listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List .[1]
Characteristics [ edit ]
The rusty-spotted genet has short whitish grey to pale yellow coloured fur with dark spots and a continuous dark line across the back. The spots of the upper two dorsal rows are round or square, brown in the center and darker outside. In head-to-body length it ranges from 42 to 52 cm (17 to 20 in ). Its 40 to 53 cm (16 to 21 in ) long tail is ringed and has a dark tip. Its feet are of the same colour as the fur. It weighs from 1.3 to 3 kg (2.9 to 6.6 lb ).[3]
Behaviour and ecology [ edit ]
Research in southeastern Nigeria revealed that the rusty-spotted genet has an omnivorous diet. It feeds on rodents like giant pouched rats (Cricetomys ), Nigerian shrew (Crocidura nigeriae ), Temminck's mouse (Mus musculoides ), Tullberg's soft-furred mouse (Praomys tulbergi ), Peters's striped mouse (Hybomys univittatus ), typical striped grass mouse (Lemniscomys striatus ), red-eyed dove (Streptopelia semitorquata ), common agama (Agama agama ), Mabuya Myriapoda , spiders , Orthoptera and Coleoptera as well as eggs, fruits, berries and seeds.[4]
Taxonomy [ edit ]
In 1830, John Edward Gray first described a rusty-spotted genet using the name Viverra maculata based on a zoological specimen that lived in the menagerie at the Tower of London .[5] species and subspecies for specimens obtained by natural history museums :[2]
aequatorialis Heuglin , 1866[7]
erlangeri , gleimi , schraderi , stuhlmanni , suahelica , zambesiana Matschie , 1902[8]
matschiei Neumann , 1902[9]
pumila Hollister , 1916[10]
insularis Cabrera , 1921[11]
rubiginosa zuluensis Roberts , 1924[12]
soror Schwarz , 1929[13]
rubiginosa albiventris Roberts, 1932[14]
deorum Funaioli and Simonetta, 1960[15]
pardina schoutedeni Crawford-Cabral, 1970[16]
Genetta letabae Thomas and Schwann, 1906),[17] [18]
References [ edit ]
^ Gaubert, P.; Taylor, P. J. & Veron, G. (2005). "Integrative taxonomy and phylogenetic systematics of the genets (Carnivora, Viverridae, Genetta ): a new classification of the most speciose carnivoran genus in Africa" (PDF) . In Huber, B. A.; Sinclair, B. J. & Lampe, K.-H. (eds.). African Biodiversity: Molecules, Organisms, Ecosystems. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium of Tropical Biology . Bonn: Museum König. pp. 371–383.
^ Angelici, F. M. (2000). "Food habits and resource partitioning of carnivores (Herpestidae, Viverridae) in the rainforests of southeastern Nigeria: preliminary results" (PDF) . Revue d'Écologie (La Terre et la Vie) . 55
^ Gray, J. E. (1830). "Fam. Felidae. Gen. Viverra" . Spicilegia zoologica; or, original figures and short systematic descriptions of new and unfigured animals . London: Treüttel, Würtz. p. 9.
^ Du Chaillu, P. (1860). "Descriptions of five new species of mammals discovered in western equatorial Africa" . Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History . 7 29 ): 298−304.
^ Heuglin, T. (1866). "Genetta aequatorialis Heugl" . Systematische Übersicht der Säugethiere Nordost-Afrika's mit Einschluss der arabischen Küste, des rothen Meeres, der Somáli-und der Nilquellen-Länder, südwärts bis zum vierten Grade nördlicher Breite . Wien: Kaiserliche Akademie der Wissenschaften. p. 23.
^ Matschie, P. (1902). "Über die individuellen und geographischen Abänderungen der Ginsterkatzen" . In Matschie, P. (ed.). Verhandlungen des V. Internationalen Zoologen-Congresses . Jena: Gustav Fischer. pp. 1128–1144.
^ Neumann, O. R. (1902). "Über einige neue Arten der Ginsterkatzen" . Sitzungsberichte der Gesellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin . 8
^ Hollister, N. (1916). "Descriptions of a new genus and eight new species and subspecies of African mammals" (PDF) . Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections . 66
^ Cabrera, A. (1921). "Algunos carnívoros africanos nuevos" . Boletín de la Real Sociedad Española de Historia Natural . 21
^ Roberts, A. (1924). "Some additions to the list of South African mammals" (PDF) . Annals of the Transvaal Museum . 10 2 ): 59−76.
^ Schwarz, E. (1929). "On two new genets from the upper Congo". Annals and Magazine of Natural History . Series 10. 3 13 ): 47−48. doi :10.1080/00222932908672935 .
^ Roberts, A. P. (1932). "reliminary description of fifty-seven new forms of South African mammals" (PDF) . Annals of the Transvaal Museum . 15 1 ): 1−19.
^ Funaioli, U.; Simonetta, A.M. (1960). "Spedizione biologica in Somalia, 1959. Risultati zoologici. Carnivora". Monitore Zoologico Italiano . 68
^ Crawford-Cabral, J. (1970). "As genetas da Africa Central". Boletim do Instituto de Investigação Científica de Angola . 7
^ Thomas, O.; Schwann, H. (1906). "The Rudd exploration of South Africa. − V. List of mammals obtained by Mr. Grant in North East Transvaal" . Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London : 575−591.
^ Gaubert, P.; Taylor, P. J. & Veron, G. (2005). "Integrative taxonomy and phylogenetic systematics of the genets (Carnivora, Viverridae, Genetta ): a new classification of the most speciose carnivoran genus in Africa" (PDF) . In Huber, B. A.; Sinclair, B. J. & Lampe, K.-H. (eds.). African Biodiversity: Molecules, Organisms, Ecosystems. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium of Tropical Biology, Museum König, Bonn . Springer. pp. 371–383.
t
e
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Rusty-spotted_genet&oldid=1177645841 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● I U C N R e d L i s t l e a s t c o n c e r n s p e c i e s ● G e n e t s ( a n i m a l s ) ● M a m m a l s o f S u b - S a h a r a n A f r i c a ● M a m m a l s d e s c r i b e d i n 1 8 3 0 ● T a x a n a m e d b y J o h n E d w a r d G r a y ● C a r n i v o r a s t u b s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h ' s p e c i e s ' m i c r o f o r m a t s ● A l l s t u b a r t i c l e s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 2 8 S e p t e m b e r 2 0 2 3 , a t 1 7 : 4 4 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w