

|
→Medical uses: serperated
|
→Cross-protection: we already state this above
|
||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
| url = http://jama.jamanetwork.com/data/Journals/JAMA/4454/joc90010_945_953.pdf |
| url = http://jama.jamanetwork.com/data/Journals/JAMA/4454/joc90010_945_953.pdf |
||
}}</ref> |
}}</ref> |
||
=== Cross-protection === |
|||
Annual seasonal flu vaccination provides some protection against flu viruses that the vaccine was not designed for, including novel viruses.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Xie H, Jing X, Li X, et al. |title=Immunogenicity and cross-reactivity of 2009–2010 inactivated seasonal influenza vaccine in US adults and elderly |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=e16650 |year=2011 |pmid=21304946 |pmc=3031605 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0016650|bibcode = 2011PLoSO...616650X }}</ref> The CDC made the following statement in relation to the 2007–2008 vaccine: |
|||
: ...[A]ntibodies made in response to vaccination with one strain of influenza viruses can provide protection against different, but related strains. A less than ideal match may result in reduced vaccine effectiveness against the variant viruses, but it still can provide enough protection to prevent or lessen illness severity and prevent flu-related complications. In addition, it is important to remember that the influenza vaccine contains three virus strains so the vaccine can also protect against the other two viruses. For these reasons, even during seasons when there is a less than ideal match, CDC continues to recommend influenza vaccination. This is particularly important for people at high risk for serious flu complications and their close contacts.<ref name="cross-protection"/> |
|||
===Cost-effectiveness=== |
===Cost-effectiveness=== |
||
The influenza vaccination is an annual vaccination using a vaccine specific for a given year to protect against the highly variable influenza virus.[1] Each seasonal influenza vaccine contains antigens representing three (trivalent vaccine) or four (quadrivalent vaccine) influenza virus strains: one influenza type A subtype H1N1 virus strain, one influenza type A subtype H3N2 virus strain, and either one or two influenza type B virus strains.[2] Influenza vaccines may be administered as an injection, also known as a flu shot, or as a nasal spray.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that everyone over the ages of 6 months should receive the seasonal influenza vaccine.[3] Vaccination campaigns usually focus on people who are at high risk of serious complications if they catch the flu, such as the elderly and people living with chronic illness or those with weakened immune systems, as well as health care workers.[3][4]
Most flu vaccines provide modest protection against contracting influenza, with the effect seasonably variable depending on antigenic drift.[5] Some studies have concluded that there is little evidence for efficacy among the elderly, while others concluded that efficacy ranges from "acceptable" to "high" depending on the specific vaccine formulation.[6][7]
According to the CDC, getting the flu vaccine is the best way to protect people against the flu and prevent its spread. The flu vaccine can also reduce the severity of the flu if a person contracts a strain of the flu that the vaccine did not contain.[8]
It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled Effectiveness of influenza vaccines. (Discuss) (March 2015)
|
A vaccine is assessed by its efficacy; the extent to which it reduces risk of disease under controlled conditions, and its effectiveness, the observed reduction in risk after the vaccine is put into use.[9] In the case of influenza, effectiveness is expected to be lower than the efficacy because it is measured using the rates of influenza-like illness, which is not always caused by influenza.[10] Influenza vaccines generally show high efficacy, as measured by the antibody production in animal models or vaccinated people,[11] However, studies on the effectiveness of flu vaccines in the real world are difficult; vaccines may be imperfectly matched, virus prevalence varies widely between years, and influenza is often confused with other influenza-like illnesses.[12] However, in most years (16 of the 19 years before 2007), the flu vaccine strains have been a good match for the circulating strains,[13] and even a mis-matched vaccine can often provide cross-protection.[14]
Trials of both live and inactivated influenza vaccines against seasonal influenza have been summarized in several 2012 meta-analyses. Studies on live vaccines have very limited data, but these preparations may be more effective than inactivated vaccines.[15] The meta-analyses examined the efficacy and effectiveness of inactivated vaccines against seasonal influenza in adults,[10] children,[16] and the elderly.[17][18] In adults, vaccines show a 75% reduction in risk of contracting influenza (4% influenza rate among the unvaccinated versus 1% among vaccinated persons) when the vaccine is perfectly matched to the virus and a one-half reduction (2% get flu without vaccine versus 1% with vaccine) when it is not, but only four trials examined the rate of hospitalization. Although each showed a trend toward reduced hospitalizations, the effect was not statistically significant.[10] In children, vaccines again showed high efficacy, but low effectiveness in preventing "flu-like illness". In children under the age of two the data are extremely limited, but vaccination appeared to confer no measurable benefit.[16]
During an influenza pandemic, where a single strain of virus is responsible for illnesses, an effective vaccine could produce a large decrease in the number of cases and be highly effective in controlling an epidemic.[19] However, such a vaccine would have to be produced and distributed rapidly to have maximum effect.[20] Such distribution challenges may be met with good success. Overall, vaccines against the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic were found to be effective in a Scottish study.[21]
A 2011 meta analysis found that flu shots were efficacious 67 percent of the time; the populations that benefited the most were HIV-positive adults ages 18 to 55 (76 percent), healthy adults ages 18 to 46 (approximately 70 percent) and healthy children ages 6 to 24 months (66 percent).[22]
As mortality is also high among infants who contract influenza, the household contacts and caregivers of infants should be vaccinated to reduce the risk of passing an influenza infection to the infant.[4] Data from the years when Japan required annual flu vaccinations for school-aged children indicate that vaccinating children—the group most likely to catch and spread the disease—has a strikingly positive effect on reducing mortality among older people, due to herd immunity: one life saved for every 420 children who received the flu vaccine.[23] However, a 2010 Cochrane review found that the same benefit did not extend to vaccinating health care workers working with elderly patients in long-term care facilities.[24] In working adults, by contrast, Cochrane found that vaccination reduced both influenza symptoms and working days lost, without affecting transmission or influenza-related complications.[10]
An example of lack of protection from a mutated strain was reported in 2014–2015; vaccine effectiveness was estimated to be about 3%, rather than the 50% achieved most years.[25][26]
In the elderly, while many individual studies show effectiveness,[27][28][29] the overall evidence is still insufficient evidence to draw clear conclusions on the effectiveness of vaccination,[17][18][30][22] including a new high-dose flu vaccine specifically formulated to provide a larger immune response.[31] Available evidence indicates that the high-dose vaccine produces a stronger immune response.[32] The group most vulnerable to non-pandemic flu, the elderly, is also the least to benefit from the vaccine. There are multiple reasons behind this steep decline in vaccine efficacy, the most common of which are the declining immunological function and frailty associated with advanced age.[33] In a non-pandemic year, a person in the United States aged 50–64 is nearly ten times more likely to die an influenza-associated death than a younger person, and a person over age 65 is over ten times more likely to die an influenza-associated death than the 50–64 age group.[34]
Flu vaccines are available either as
TIV induces protection after injection (typically intramuscular, though subcutaneous and intradermal routes can also be protective)[35] based on an immune response to the antigens present on the inactivated virus, while cold-adapted LAIV works by establishing infection in the nasal passages.[36]
LAIV is not recommended for individuals under age 2 or over age 50,[37] but might be comparatively more effective among children over age 2.[38] Furthermore, health care personnel who care for severely immunocompromised persons should receive TIV or QIV rather than LAIV.[39]
A study of military personnel showed that flu shots yielded less illness than nasal spray. This study was based on one of the largest head-to-head studies comparing LAIV and TIV. It was conducted by the U.S. Armed Forces Surveillance Center, on military personnel stationed in the U.S. during three flu seasons from 2004 through 2007. Investigators concluded that: "It may be prudent to use TIV in patients who were vaccinated at least once in the past 2 years [...] but LAIV against pandemic strains may be more protective than inactivated vaccines, because the population will probably lack preexisting immunity."[40]
The cost-effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccination has been widely evaluated for different groups and in different settings.[41] In the elderly (aged over 65 years) the majority of published studies have found that vaccination is cost saving, with the cost savings associated with influenza vaccination (e.g. prevented health care visits) outweighing the cost of vaccination.[42] In older adults (aged 50–64 years), several published studies have found that influenza vaccination is likely to be cost-effective, however the results of these studies were often found to be dependent on key assumptions used in the economic evaluations.[43] The uncertainty in influenza cost-effectiveness models can partially be explained by the complexities involved in estimating the disease burden,[44] as well as the seasonal variability in the circulating strains and the match of the vaccine.[45][46] In healthy working adults (aged 18–49 years), a 2012 review found that vaccination was generally not cost-saving, with the suitability for funding being dependent on the willingness to pay to obtain the associated health benefits.[47] In children, the majority of studies have found that influenza vaccination was cost-effective, however many of the studies included (indirect) productivity gains, which may not be given the same weight in all settings.[48] Several studies have attempted to predict the cost-effectiveness of interventions (including prepandemic vaccination) to help protect against a future pandemic, however estimating the cost-effectiveness has been complicated by uncertainty as to the severity of a potential future pandemic and the efficacy of measures against it.[49]
Influenza vaccine has been demonstrated to significantly reduce disease, hospitalization, and death, both in numerous controlled studies and in scientific reviews of these studies. The CDC reports that studies demonstrate that vaccination is a cost-effective counter-measure to seasonal outbreaks of influenza.[50]
According to research published in July 2010, vaccination against influenza is especially important for members of high-risk groups who would be likely to suffer complications from influenza, for example pregnant women[51][52] and children and teenagers from six months to 18 years of age;[53]
The trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine is protective in pregnant women infected with HIV.[55]
For healthy, working adults, influenza vaccines can provide moderate protection[citation needed] against virologically confirmed influenza, but such protection is greatly reduced or absent in some seasons. Evidence for protection in adults aged 65 years or older is lacking. New vaccines with improved clinical efficacy and effectiveness are needed to further reduce influenza-related morbidity and mortality.[56]
Influenza vaccination has been shown highly effective in health care workers (HCW), with minimal adverse effects. In a study of forty matched nursing homes, staff influenza vaccination rates were 69.9% in the vaccination arm versus 31.8% in the control arm. The vaccinated staff experienced a 42% reduction in sick leave from work (P=.03).[57] A review of eighteen studies likewise found a strong net benefit to health care workers.[58] Of these eighteen HCW studies, only two also assessed the relationship of patient mortality relative to staff influenza vaccine uptake; both found that higher rates of health care worker vaccination correlated with reduced patient deaths.[58] An analysis of data and patient population health in New Mexico's 75 long-term care facilities nursing homes found that as vaccination rates of health care personnel with direct patient contact rose from 51 to 75 percent, the chances of a flu outbreak among patients in that facility went down by 87 percent. The New Mexico study showed that vaccinating health care personnel provided more protection to residents than vaccinating the residents themselves.[59] In a 2010 survey of United States healthcare workers, 63.5% reported that they received the flu vaccine during the 2010–11 season, an increase from 61.9% reported the previous season. Health professionals with direct patient contact had higher vaccination uptake, such as physicians and dentists (84.2%) and nurse practitioners (82.6%).[60][61][62]
It is important to note that the flu vaccine takes about two weeks to build up enough antibodies to protect against the flu (thus making the vaccinated person protected against the disease),[2] and that the vaccine does not protect against every strain of the flu.[2]
Children born to mothers who received flu vaccination while pregnant are strongly protected from having to be hospitalized with the flu. "The effectiveness of influenza vaccine given to mothers during pregnancy in preventing hospitalization among their infants, adjusted for potential confounders, was 91.5%."[63]
In 2006, the United States began recommending influenza vaccinations for preschoolers, but Canada did not follow suit until 2010, "thereby creating a natural experiment to evaluate the effect of the policy in the United States."[64]
In another six-year observational study, vaccination of children aged six months through five years was found to prevent illness in more than half.[65]
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that everyone except children under the age of six months should receive the seasonal influenza vaccine.[3] Vaccination campaigns usually focus special attention on people who are at high risk of serious complications if they catch the flu, such as pregnant women, children over six months, the elderly,[66] and people living with chronic illness or those with weakened immune systems, as well as those to whom they are exposed, such as health care workers.[3][4]
While side effects of the flu vaccine may occur, they will be minor and the safety of flu vaccines is high. Furthermore, the side effects and risks of inoculation are mild and temporary when compared to the risks and severe health effects of the annual influenza epidemic's well-documented toll of illness, hospitalization, and death.[67]
Flu vaccination may lead to side effects such as runny nose and sore throat, which can last for up to several days. Egg allergy may also be a concern, since flu vaccines are typically made using eggs,[68][69] however research into egg-allergy and influenza vaccination [70] has led some advisory groups to recommend vaccine delivery protocols for egg allergic persons.[71] On January 17, 2013, the U.S. FDA approved Flublok, a faster-turnaround influenza vaccine which is the first grown in insect cells instead of eggs. It will be available in the 2013–14 season for people age 18–49, and avoids the problem with egg allergies.[72]
Although Guillain-Barré syndrome had been feared as a complication of vaccination, the CDC states that most studies on modern influenza vaccines have seen no link with Guillain-Barré.[73][74] Getting infected by influenza itself increases both the risk of death (up to 1 in 10,000) and increases the risk of developing Guillain-Barré syndrome to a much higher level than the highest level of suspected vaccine involvement (approx. 10 times higher by 2009 estimates).[75][76]
Although one review gives an incidence of about one case of Guillain-Barré per million vaccinations,[77] a large study in China, reported in The New England Journal of Medicine covering close to 100 million doses of vaccine against the 2009 H1N1 "swine" flu found only eleven cases of Guillain-Barre syndrome, (0.1 per million doses) total incidence in persons vaccinated, actually lower than the normal rate of the disease in China, and no other notable side effects; "The risk-benefit ratio, which is what vaccines and everything in medicine is about, is overwhelmingly in favor of vaccination."[78][79] Several studies have identified an increased incidence of narcolepsy among recipients of the pandemic H1N1 influenza ASO3-adjuvanted vaccine,[80] efforts to identify a mechanism for this suggest that narcolepsy is autoimmune, and that the H1N1 vaccine may mimic hypocretin, serving as a trigger.[81]
Some injection-based flu vaccines intended for adults in the United States contain thiomersal (also known as thimerosal), a mercury-based preservative. Despite some controversy in the media,[82] the World Health Organization's Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety has concluded that there is no evidence of toxicity from thiomersal in vaccines and no reason on grounds of safety to change to more-expensive single-dose administration.[83]

Various public health organizations, including the World Health Organization, have recommended that yearly influenza vaccination be routinely offered to people at risk of complications of influenza and those individuals who live with or care for high-risk individuals, including:
Both types of flu vaccines are contraindicated for those with severe allergies to egg proteins and people with a history of Guillain-Barré syndrome.[90]
As of 2013, the UN World Health Organization recommends vaccination for, in order of priority:[91]
According to the CDC, the live attenuated virus (which comes in the forum of the nasal spray in the US) should be avoided by:
In 2008, the National Advisory Committee on Immunization, the group that advises the Public Health Agency of Canada, recommended that everyone aged 2 to 64 years be encouraged to receive annual influenza vaccination, and that children between the age of six and 24 months, and their household contacts, should be considered a high priority for the flu vaccine.[93] The NACI also recommends the flu vaccine for:[94]
In the United States,『Routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged ≥ 6 months』since 2010.[51][95][96]
Within its blanket recommendation for general vaccination in the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who began recommending the influenza vaccine to health care workers in 1981, emphasizes to clinicians the special urgency of vaccination for members of certain vulnerable groups, and their caregivers:
The U.S. government requires hospitals to report worker vaccination rates. Some U.S. states and hundreds of U.S. hospitals require health-care workers to either get vaccinations or wear masks during flu season. These requirements occasionally engender union lawsuits on narrow collective bargaining grounds, but proponents note that courts have generally endorsed forced vaccination laws affecting the general population during disease outbreaks.[99]
This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this sectionbyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
Vaccines have been formulated against several of the avian H5N1 influenza varieties. Vaccination of poultry against the ongoing H5N1 epizootic is widespread in certain countries. Some vaccines also exist for use in humans, and others are in testing, but none have been made available to civilian populations, nor produced in quantities sufficient to protect more than a tiny fraction of the Earth's population in the event of an H5N1 pandemic.
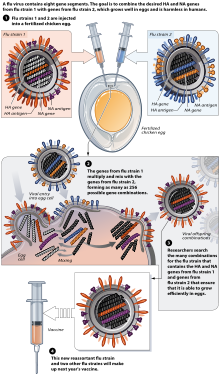
Flu vaccine is usually grown by vaccine manufacturers in fertilized chicken eggs.[100][101] In the Northern hemisphere, the manufacturing process begins following the announcement (typically in February) of the WHO recommended strains for the winter flu season.[100][102] Three strains (representing an H1N1, an H3N2, and a B strain) of flu are selected and chicken eggs inoculated separately, these monovalent harvests are then combined to make the trivalent vaccine.[103]
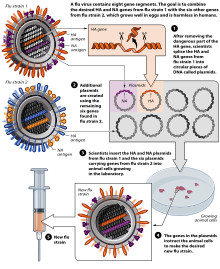
As of November 2007[update], both the conventional injection and the nasal spray are manufactured using chicken eggs.[101] The European Union has also approved Optaflu, a vaccine produced by Novartis using vats of animal cells.[101] This technique is expected to be more scalable and avoid problems with eggs, such as allergic reactions and incompatibility with strains that affect avians like chickens.[101] Research continues into the idea of a "universal" influenza vaccine that would not require tailoring to a particular strain, but would be effective against a broad variety of influenza viruses. However, no vaccine candidates had been announced by Nov 2007.[101]
A DNA-based vaccination, which is hoped to be even faster to manufacture, is as of 2011 in clinical trials, determining safety and efficacy.[104]
On November 20, 2012, Novartis received FDA approval for the first cell-culture vaccine.[105][106][107]
In a 2007 report, the global capacity of approximately 826 million seasonal influenza vaccine doses (inactivated and live) was double the production of 413 million doses. In an aggressive scenario of producing pandemic influenza vaccines by 2013, only 2.8 billion courses could be produced in a six-month time frame. If all high- and upper-middle-income countries sought vaccines for their entire populations in a pandemic, nearly 2 billion courses would be required. If China pursued this goal as well, more than 3 billion courses would be required to serve these populations.[108] Vaccine research and development is ongoing to identify novel vaccine approaches that could produce much greater quantities of vaccine at a price that is affordable to the global population.
Methods of vaccine generation that bypass the need for eggs include the construction of influenza virus-like particles (VLP). VLP resemble viruses, but there is no need for inactivation, as they do not include viral coding elements, but merely present antigens in a similar manner to a virion. Some methods of producing VLP include cultures of Spodoptera frugiperda Sf9 insect cells and plant-based vaccine production (e.g., production in Nicotiana benthamiana). There is evidence that some VLPs elicit antibodies that recognize a broader panel of antigenically distinct viral isolates compared to other vaccines in the hemagglutination-inhibition assay (HIA).[109]
Influenza vaccines are produced in pathogen-free eggs that are 11 to 12 days old.[110] The top of the egg is disinfected by wiping it with alcohol and then the egg is candled to identify a non-veinous area in the allantoic cavity where a small hole is poked to serve as a pressure release.[111] A second hole is made at the top of the egg, where the influenza virus is injected in the allantoic cavity, past the chorioallantoic membrane. The two holes are then sealed with melted paraffin and the inoculated eggs are incubated for 48 hours at 37 degrees Celsius.[110] During incubation time, the virus replicates and newly replicated viruses are released into the allantoic fluid [112]
After the 48 hour incubation period, the top of the egg is cracked and the 10 milliliters of allantoic fluid is removed, from which about 15 micrograms of the flu vaccine can be obtained. At this point, the viruses have been weakened or killed and the viral antigen is purified and placed inside vials, syringes, or nasal sprayers.[112] Done on a large scale, this method is used to produce the flu vaccine for the human population.
Each year, three strains are chosen for selection in that year's flu vaccination by the WHO Global Influenza Surveillance Network. The chosen strains are the H1N1, H3N2, and Type-B strains thought most likely to cause significant human suffering in the coming season. Starting with the 2012–2013 Northern Hemisphere influenza season (coincident with the approval of quadrivalent influenza vaccines), the WHO has also recommended a 2nd B-strain for use in quadrivalent vaccines. The World Health Organization coordinates the contents of the vaccine each year to contain the most likely strains of the virus to attack the next year.
The Global Influenza Surveillance Network's selection of viruses for the vaccine manufacturing process is based on its best estimate of which strains will predominate the next year, amounting in the end to well-informed but fallible guesswork.[114]
Formal WHO recommendations first issued in 1973; beginning 1999 there have been two recommendations per year, one for the northern hemisphere (N) and the other for the southern hemisphere (S).[115]
Historical annual reformulations of the influenza vaccine are listed in a separate article. Recent[update] WHO seasonal influenza vaccine composition recommendations:
The composition of trivalent virus vaccines for use in the 2015–2016 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization on February 26, 2015 was:
The WHO recommends that quadrivalent vaccines containing two influenza B viruses contain the above three viruses and a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus.[116]
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2015 Southern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization September 25, 2014 was:
WHO recommended that quadrivalent vaccines containing two influenza B viruses should contain the above three viruses and a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus.[117]
†Strain A(H1N1)pdm09 is a newer name for the strain used in the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine.[118]
Vaccines are used in both humans and nonhumans. Human vaccine is meant unless specifically identified as a veterinary, poultry or livestock vaccine.
The first influenza pandemic was recorded in 1580.[119] However, the etiological cause of influenza, the orthomyxoviridae was discovered by the Medical Research Council (MRC) of the United Kingdom in 1933.[120]
| Name of pandemic | Date | Deaths | Case fatality rate | Subtype involved | Pandemic severity index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1889–1890 flu pandemic (Asiatic or Russian Flu)[123] |
1889–1890 | 1 million | 0.15% | possibly H3N8 orH2N2 |
NA |
| 1918 flu pandemic (Spanish flu)[124] |
1918–1920 | 20 to 100 million | 2% | H1N1 | 5 |
| Asian Flu | 1957–1958 | 1 to 1.5 million | 0.13% | H2N2 | 2 |
| Hong Kong Flu | 1968–1969 | 0.75 to 1 million | <0.1% | H3N2 | 2 |
| Russian flu | 1977–1978 | no accurate count | N/A | H1N1 | N/A |
| 2009 flu pandemic[125][126] | 2009–2010 | 18,000† | N/A | (H1N1)pdm09 |
† Because of lack of laboratory confirmation and underreporting among other factors, reported cases are "likely to be a gross underestimation of the true number of fatalities associated with the [2009] pandemic."[126] The 18,000 cases are those officially confirmed. Two statistical analyses, using different methods but producing similar results, estimated that the actual number was likely to be about ten times higher.[127][128]
In the world wide Spanish flu pandemic of 1918, "Physicians tried everything they knew, everything they had ever heard of, from the ancient art of bleeding patients, to administering oxygen, to developing new vaccines and sera (chiefly against what we now call Hemophilus influenzae—a name derived from the fact that it was originally considered the etiological agent—and several types of pneumococci). Only one therapeutic measure, transfusing blood from recovered patients to new victims, showed any hint of success."[129]
In 1931, viral growth in embryonated hens' eggs was reported by Ernest William Goodpasture and colleagues at Vanderbilt University. The work was extended to growth of influenza virus by several workers, including Thomas Francis, Jonas Salk, Wilson Smith and Macfarlane Burnet, leading to the first experimental influenza vaccines.[130] In the 1940s, the US military developed the first approved inactivated vaccines for influenza, which were used in the Second World War.[131] Hen's eggs continued to be used to produce virus used in influenza vaccines, but manufacturers made improvements in the purity of the virus by developing improved processes to remove egg proteins and to reduce systemic reactivity of the vaccine.[132] Recently, the US FDA has approved influenza vaccines made by growing virus in cell cultures[133] and influenza vaccines made from recombinant proteins[134] have been approved, with plant-based influenza vaccines being tested in clinical trials.[135]
According to the CDC: "Influenza vaccination is the primary method for preventing influenza and its severe complications. [...] Vaccination is associated with reductions in influenza-related respiratory illness and physician visits among all age groups, hospitalization and death among persons at high risk, otitis media among children, and work absenteeism among adults. Although influenza vaccination levels increased substantially during the 1990s, further improvements in vaccine coverage levels are needed".[136]
The egg-based technology (still in use as of 2005) for producing influenza vaccine was created in the 1950s.[137] In the U.S. swine flu scare of 1976, President Gerald Ford was confronted with a potential swine flu pandemic. The vaccination program was rushed, yet plagued by delays and public relations problems. Meanwhile, maximum military containment efforts succeeded unexpectedly in confining the new strain to the single army base where it had originated. On that base a number of soldiers fell severely ill, but only one died. The program was canceled, after about 24% of the population had received vaccinations. An excess in deaths of twenty-five over normal annual levels as well as 400 excess hospitalizations, both from Guillain-Barré syndrome, were estimated to have occurred from the vaccination program itself, illustrating that vaccine itself is not free of risks. The result has been cited to stoke lingering doubts about vaccination.[138] In the end, however, even the maligned 1976 vaccine may have saved lives. A 2010 study found a significantly enhanced immune response against the 2009 pandemic H1N1 in study participants who had received vaccination against the swine flu in 1976.[139]
Influenza research includes molecular virology, molecular evolution, pathogenesis, host immune responses, genomics, and epidemiology. These help in developing influenza countermeasures such as vaccines, therapies and diagnostic tools. Improved influenza countermeasures require basic research on how viruses enter cells, replicate, mutate, evolve into new strains and induce an immune response. The Influenza Genome Sequencing Project is creating a library of influenza sequences[140] that will help us understand what makes one strain more lethal than another, what genetic determinants most affect immunogenicity, and how the virus evolves over time. Solutions to limitations in current[when?] vaccine methods are being researched.
The rapid development, production, and distribution of pandemic influenza vaccines could potentially save millions of lives during an influenza pandemic. Due to the short time frame between identification of a pandemic strain and need for vaccination, researchers are looking at novel technologies for vaccine production that could provide better "real-time" access and be produced more affordably, thereby increasing access for people living in low- and moderate-income countries, where an influenza pandemic may likely originate, such as live attenuated (egg-based or cell-based) technology and recombinant technologies (proteins and virus-like particles).[141] As of July 2009, more than 70 known clinical trials have been completed or are ongoing for pandemic influenza vaccines.[142] In September 2009, the US Food and Drug Administration approved four vaccines against the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus (the 2009 pandemic strain), and expected the initial vaccine lots to be available within the following month.[143] A quadrivalent flu vaccine administered by nasal mist was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2012.[144][145] Fluarix Quadrivalent was approved by the FDA in December 2012.[146]
This section needs to be updated. The reason given is: some more recent additions, but lots of old stuff with no indication of outcome or progress. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (February 2015)
|
Many groups worldwide are pursuing development of a universal flu vaccine that does not require modification each year.[147] Companies pursuing the vaccine as of 2009 and 2010 include BiondVax,[148] Theraclone,[149] Dynavax Technologies Corporation,[150] VaxInnate,[151] Crucell NV,[152] Inovio Pharmaceuticals,[153] and Immune Targeting Systems (ITS)[154]
In 2008, Acambis announced work on a universal flu vaccine (ACAM-FLU-ATM) based on the less variable M2 protein component of the flu virus shell.[155] See also H5N1 vaccines.
In 2009, the Wistar Institute received a patent for using "a variety of peptides" in a flu vaccine, and announced it was seeking a corporate partner.[156]
In 2010, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) of the U.S. NIH announced a breakthrough; the effort targets the stem, which mutates less often than the head of the virus.[157]
DNA vaccines, such as VGX-3400X (aimed at multiple H5N1 strains), contain DNA fragments (plasmids).[153][158] Inovio's SynCon DNA vaccines include H5N1 and H1N1 subtypes.[159]
In July 2011, researchers created an antibody, which targets a protein found on the surface of all influenza A viruses called haemagglutinin.[160][161][162] F16 is the only known antibody that binds (its neutralizing activity is controversial) to all 16 subtypes of the influenza A virus hemagglutinin and might be the lynchpin for a universal influenza vaccine.[160][161][162] The subdomain of the hemagglutinin that is targeted by FI6, namely the stalk domain, was actually successfully used earlier as universal influenza virus vaccine by Peter Palese's research group at Mount Sinai School of Medicine.[163]
Other vaccines are polypeptide based.[164]
By 2010 some universal flu vaccines had started early stage clinical trials.
Based on the results of animal studies, a universal flu vaccine may use a two-step vaccination strategy — priming with a DNA-based HA vaccine followed by a second dose with an inactivated, attenuated, or adenovirus-vector–based vaccine.[171]
Some people given a 2009 H1N1 flu vaccine have developed broadly protective antibodies, raises hopes for a universal flu vaccine.[172][173][174]
On February 13, 2013, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Chief Scientist Jesse Goodman predicted that a universal flu vaccine was still 5 to 10 years away. When asked about the prospects of a universal flu vaccine in a hearing before House Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations, Goodman replied "Nature is very tricky and as this is a very crafty virus, so I'd be very hesitant to predict... I think the earliest we'd begin to see something with clinical benefit might be 5 to 10 years."[175]
"Vaccination in the veterinary world pursues four goals: (i) protection from clinical disease, (ii) protection from infection with virulent virus, (iii) protection from virus excretion, and (iv) serological differentiation of infected from vaccinated animals (so-called DIVA principle). In the field of influenza vaccination, neither commercially available nor experimentally tested vaccines have been shown so far to fulfill all of these requirements."[176]
Horses with horse flu can run a fever, have a dry hacking cough, have a runny nose, and become depressed and reluctant to eat or drink for several days but usually recover in two to three weeks. "Vaccination schedules generally require a primary course of 2 doses, 3–6 weeks apart, followed by boosters at 6–12 month intervals. It is generally recognized that in many cases such schedules may not maintain protective levels of antibody and more frequent administration is advised in high-risk situations."[177]
It is a common requirement at shows in the United Kingdom that horses be vaccinated against equine flu and a vaccination card must be produced; the International Federation for Equestrian Sports (FEI) requires vaccination every six months.[178][179]
Poultry vaccines for bird flu are made on the cheap and are not filtered and purified like human vaccines to remove bits of bacteria or other viruses. They usually contain whole virus, not just hemagglutinin as in most human flu vaccines. Purification to standards needed for humans is far more expensive than the original creation of the unpurified vaccine from eggs. There is no market for veterinary vaccines that are that expensive. Another difference between human and poultry vaccines is that poultry vaccines are adjuvated with mineral oil, which induces a strong immune reaction but can cause inflammation and abscesses. "Chicken vaccinators who have accidentally jabbed themselves have developed painful swollen fingers or even lost thumbs, doctors said. Effectiveness may also be limited. Chicken vaccines are often only vaguely similar to circulating flu strains — some contain an H5N2 strain isolated in Mexico years ago. 'With a chicken, if you use a vaccine that's only 85 percent related, you'll get protection,' Dr. Cardona said. 'In humans, you can get a single point mutation, and a vaccine that's 99.99 percent related won't protect you.' And they are weaker [than human vaccines]. 'Chickens are smaller and you only need to protect them for six weeks, because that's how long they live till you eat them,' said Dr. John J. Treanor, a vaccine expert at the University of Rochester. Human seasonal flu vaccines contain about 45 micrograms of antigen, while an experimental A(H5N1) vaccine contains 180. Chicken vaccines may contain less than 1 microgram. 'You have to be careful about extrapolating data from poultry to humans,' warned Dr. David E. Swayne, director of the agriculture department's Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory. 'Birds are more closely related to dinosaurs.'"[180]
Researchers, led by Nicholas Savill of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, used mathematical models to simulate the spread of H5N1 and concluded that "at least 95 percent of birds need to be protected to prevent the virus spreading silently. In practice, it is difficult to protect more than 90 percent of a flock; protection levels achieved by a vaccine are usually much lower than this."[181] The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations has issued recommendations on the prevention and control of avian influenza in poultry, including the use of vaccination.[182]
A filtered and purified Influenza A vaccine for humans is being developed[when?] and many countries have recommended it be stockpiled so if an Avian influenza pandemic starts jumping to humans, the vaccine can quickly be administered to avoid loss of life. Avian influenza is sometimes called avian flu, and commonly bird flu.[183]
Swine origin influenza virus (SoIV) vaccines are extensively used in the swine industry in Europe and North America. Most swine flu vaccine manufacturers include an H1N1 and an H3N2 SoIV strains.
Swine influenza has been recognized as a greater problem since the outbreak in 1976. Evolution of the virus has resulted in inconsistent responses to traditional vaccines. Standard commercial swine origin flu vaccines are effective in controlling the problem when the virus strains match enough to have significant cross-protection and custom (autogenous) vaccines made from the specific viruses isolated are created and used in the more difficult cases.[184] SoIV vaccine manufacture Novartis paints this picture: "A strain of swine origin influenza virus (SoIV) called H3N2, first identified in the US in 1998, has brought exasperating production losses to swine producers. Abortion storms are a common sign. Sows go off feed for two or three days and run a fever up to 106°F. Mortality in a naïve herd can run as high as 15%."[185]
In 2004, Influenza A virus subtype H3N8 was discovered to cause canine influenza. Because of the lack of previous exposure to this virus, dogs have no natural immunity to this virus. However, a vaccine is now available.[186]
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |author-separator= ignored (help)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Treanor was invoked but never defined (see the help page).{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |displayauthors= ignored (|display-authors= suggested) (help)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |displayauthors= ignored (|display-authors= suggested) (help)
Because pregnant women are at increased risk for severe disease associated with influenza infection, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices have recommended seasonal influenza vaccination for women while pregnant, regardless of trimester (1,2). In 2009, a novel strain of influenza A (H1N1) virus was identified (3), and pregnant women also were found at greater risk for influenza-related complications from this new virus (4). As a result, during the 2009–10 influenza season, two separate influenza vaccines were recommended to pregnant women: inactivated trivalent 2009–10 seasonal vaccine and influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccine (2,5)
Annual vaccination of all children aged 6 months – 18 years should begin as soon as the 2009–10 influenza vaccine is available. Annual vaccination of all children aged 6 months – 4 years (59 months) and older children with conditions that place them at increased risk for complications from influenza should continue to be a primary focus of vaccination efforts as providers and programs transition to routinely vaccinating all children.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
|pmid=19682118 instead.
|pmid=16546308 instead.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |coauthors= ignored (|author= suggested) (help)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in: |author= (help); Unknown parameter |author-separator= ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: |format= requires |url= (help)
Students or other persons in institutional settings (e.g., those who reside in dormitories or correctional facilities) should be encouraged to receive vaccine to minimize morbidity and the disruption of routine activities during influenza epidemics
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
In Canada, the National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI), the group that advises the Public Health Agency of Canada, currently says that children between the age of six and 24 months should be considered a high priority for the flu vaccine.
{{cite journal}}: |access-date= requires |url= (help); Unknown parameter |coauthors= ignored (|author= suggested) (help)
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |displayauthors= ignored (|display-authors= suggested) (help)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |author-separator= ignored (help)
|doi=10.1371/journal.pmed.1001558 instead. (>40 citations. By the WHO-supported Global Pandemic Mortality (GLaMOR) project)
|doi=10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70835-7 instead.]
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |coauthors= ignored (|author= suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter |author-separator= ignored (help)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General topics |
| ||||
| Viruses |
| ||||
Influenza A virus |
| ||||
| H1N1 |
| ||||
| H5N1 |
| ||||
| H5N8 |
| ||||
| Treatments |
| ||||
Pandemics and |
| ||||
| Non-human |
| ||||
| Complications |
| ||||
| Related topics |
| ||||
|
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development |
| ||||||||||
| Classes |
| ||||||||||
| Administration |
| ||||||||||
| Vaccines |
| ||||||||||
| Inventors/ researchers |
| ||||||||||
| Controversy |
| ||||||||||
| Related |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||