クラウディオス・プトレマイオス
表示

クラウディオス・プトレマイオス︵古代ギリシア語: Κλαύδιος Πτολεμαῖος, ラテン語: Claudius Ptolemæus, 83年頃 - 168年頃︶は、数学・天文学・占星学・音楽学・光学・地理学・地図製作学など幅広い分野にわたる業績を残した古代ローマの学者。英称はトレミー︵Ptolemy︶。エジプトのアレクサンドリアで活躍した。
﹃アルマゲスト﹄、﹃テトラビブロス﹄、﹃ゲオグラフィア﹄など、古代末期から中世を通して、ユーラシア大陸の西半分のいくつかの文明にて権威とみなされ、また、これらの文明の宇宙観や世界観に大きな影響を与えた学術書の著者である。

天文学のミューズに導かれ王冠をかぶった姿で描かれたプトレマイオス。 グレゴール・ライシュによるMargarita Philosophica(1508)の挿画。アブー・マアシャル・バルヒーのようにプトレマイオスがアレクサンダー大王のヘタイロイの一人でエジプトの王になったプトレマイオスと同族であると考えた例もあるが、本図の﹁プトレマイオス王﹂は自然科学の領域でプトレマイオスが上り詰めた地位を称賛しての呼称であると一般的に考えられている。
クラウディオス・プトレマイオスの生涯については、ほとんど何もわかっていない[1][2]。情報源はほぼ、プトレマイオス自身の著作と、古代末期やビザンツ期の文献に限られる[1]。プトレマイオスの著作﹃アルマゲスト﹄には、彼が西暦127年3月26日から141年2月2日の間にエジプトのアレクサンドリアで実施した天体観測の記録が載っており、これが彼の生涯を知るための最も確実な情報源になっている[1][2]。上記期間はハドリアヌス帝からアントニヌス・ピウス帝の統治期間内に収まる時期である[1]。この事実と、内容的に見て﹃アルマゲスト﹄より後に書かれたと推定される著作が何冊かあるという事実は、昔から言われている﹁クラウディオス・プトレマイオスはハドリアヌス帝からアウレリウス帝︵統治期間161年-180年︶の時期に活動していた人物である﹂という説と矛盾しない[1]。
﹁カノポス碑文 Canobic Inscription の写し﹂という、プトレマイオスの生涯の時期の特定に使えそうな資料もあるが、真正なものであるかどうかが疑わしい[1]。カノポス碑文の写しは、アントニヌス帝統治10年目の年︵147年︶に、当時ナイル川の河口にあったカノポスでプトレマイオスが天体観測記録を﹁救い主に﹂捧げるといったことが書かれている[1]。カノポス碑文中のデータは﹃アルマゲスト﹄中にあるデータと同一である[1]。
﹁クラウディオス・プトレマイオス﹂という名前の﹁プトレマイオス﹂の部分はヘレニズム時代のエジプト人の名前であることから、ギリシア系だと推測されている。﹁クラウディオス﹂の部分はローマ人の名前で[2]、彼がローマ帝国人で、ローマ皇帝が彼の先祖の誰かに恩恵として﹁クラウディオス﹂の氏族名を与えたことを示している[2]。なお、そのローマ皇帝はおそらくクラウディウスかネロである[1]。ただし、科学史家カッツが、一般論としてプトレマイオスなどのアレクサンドリア建設から数百年たった後の数学者たちの場合、ギリシア系であるか否かの断定は難しいと述べている[3]ように、この推測には若干の不確実性はある[4]。
10世紀イスラーム圏の地理学者マスウーディーは、﹁クラウディオス﹂をクラウディウス帝の子孫の意味であると信じる者がいると述べる[5]。マスウーディーはまた、この天文学者がプトレマイオス王朝の王統とつながりがあるという説に反論している[5]。9世紀イスラーム圏の天文学者アブー・マアシャル・バルヒーは﹃テトラビブロス﹄の著者﹁プトレマイオス﹂がプトレマイオス王朝の王のひとりであると書いたが[6]、この記述は混同によるものである[7]。
中世イスラーム圏ではマスウーディーのほか、10世紀のアブル・ファラジ・イスハーク・ワッラーク・ナディームや11世紀のサーイド・アンダルスィーがプトレマイオスの小伝を書いている[5]。サーイドによると、プトレマイオスは上エジプト出身であるという[8][9]。14世紀ビザンツの天文学者テオドロス・メリテニオテスは、プトレマイオスの出身地を上エジプトのナイル河畔の町プトレマイサ・エルミアと記載している[1]。テオドロス・メリテニオテスの説は正しい可能性がある[1]。なお、ルネサンス期のヨーロッパの文献では、プトレマイオスが下エジプトのペルシウムの出身であるとされる場合があるが、これは、中世のラテン語翻訳者が、﹁クラウディオス﹂からアラビア文字に音転写された "qalūdī" を "falūdī" と読み間違え、﹁ペルジウム出身の﹂を意味する "Phelud(i)ensis" にラテン語翻訳してしまった結果である[1]。
生涯[編集]

主な業績[編集]
天文学[編集]

プトレマイオスは、天動説に基づく、円運動の組み合わせで天体の運動を説明する理論を作りあげ、古代ギリシアの天文学を集大成した。彼の理論は、当時の観測誤差の範囲内で主要な現象を説明した。そして、アリストテレスの自然学と結びついて、中世のアラビア語圏や13世紀以降の中世ラテン語圏で受け入れられた。
この方面のプトレマイオスの主要な著作は、﹃アルマゲスト﹄、﹃簡便表﹄(Πρόχειροι κανόνες)、﹃惑星仮説﹄(Ὑποθέσεις τῶν πλανωμένων)である。
主著﹃アルマゲスト﹄は、天体の軌道の幾何学的な理論が主な内容だが、天文学の方法論、観測、時間の決定、理論に現れるパラメータの決定、必要な数学の説明、簡単な宇宙論の概要など、天文学の様々な側面を秩序立てて説いている。
計算に便利なように﹃アルマゲスト﹄の各所に散らばる表をまとめ、さらに新たな表を加えて使用方法の説明を付したハンドブックが﹃簡便表﹄である。計算をするだけならば﹃簡便表﹄で足りるようになっており、また逆に﹃アルマゲスト﹄のみをもとに計算を進めるのは、少なくとも実用的とはいえなかった。
﹃惑星仮説﹄は、天体計算の理論の背景にある宇宙論を説いたものである。これを元に天体の運動を再現する模型を作ることができる程に、具体的に数値まであげながら、天体の軌道の物理的な構成と運動の機構を説いた[10]。
後世への影響では、最も中核にある内容を含み、かつ網羅的であった﹃アルマゲスト﹄が第一であった。古代から中世を通じて、多くの批判や修正はなされたが、天文学の最も重要な著作であり続けた。次いで﹃簡便表﹄も盛んに用いられ、中世の﹁天文表﹂(天文計算のためのハンドブック)の作成に役立てられた。一方、中世の宇宙論の書に採用された天体の配列順序や数値の出所をたどると、多くは﹃惑星仮説﹄に行きつく[11]。だが、﹃惑星仮説﹄はラテン語訳が16世紀から17世紀にかけてやっとなされる[12]ことからもわかるように、影響は間接的なルートを経たと思われる[13]。
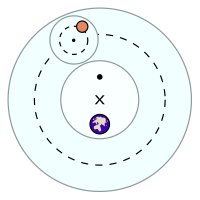
プトレマイオスによる惑星の運動惑星(黄色)は周転円(小さい円)に 沿って等速回転する。
周転円の中心は、従円(大きい円)に沿って動く。ただし、従円の中心Xは地球の中心とは異なる。周転円の中心の運動は、エカント点︵・︶から見る角速度が一定となるように動く。
プトレマイオスよりはるか以前から、古代ギリシアの思索家たちは、天体の動きを説明する仕組みについて、地動説から天動説まで、多様なアイデアを生み出していた。また、紀元前4世紀のエウドクソスは、地球を中心とする球体の回転の組み合わせで、天体の動きを説明しようとした(同心球体説)。アリストテレスは、エウドクソスの理論に基づいて、自らの宇宙論を組み上げた。
しかし、バビロニアの数理天文学の算術的な方法の方が、数値的な予測にははるかに優れていた[注釈 1]。そこでバビロニアの長所(算術やデータ、天文定数)を取り入れつつも、幾何学的な説明を主軸にした独自の天文学がヒッパルコス︵BC190年?-BC120年?)らによって生み出された。それをさらに発展させたのがプトレマイオスであった。円運動に基づき、地球中心で天を球体としている点はエウドクソスと同様だったが、より技巧的な仕組みを導入した。また、幾何的な説明を数値に結びつけるために﹁弦の表﹂を導入した。これは、円弧の長さと弦の長さ間の関係を表にしたもので、今の三角法の起源である。
惑星の天球上の軌道は、黄道から極端には外れない。そこで、黄道にそった回転︵黄経)と黄道からのずれ(黄緯)に分けて、まず前者を説明し、最後に後者を説明する機構を付け加えた。
黄経の理論においては従円と周転円に基づく説明を用いた。水星を除く惑星については、右図のように二つの円運動を組み合わせた。惑星の見かけの動きは、惑星の公転と地球の公転(の逆)の合成だが、その各々に一つづつ円運動を割り当てたことになっている。従来の手法に加えて、プトレマイオスは新たに﹁エカント﹂という機構を導入して、近似の精度を上げた。エカントを取り入れた円運動はケプラーの法則をよく近似した[注釈 2]。黄経の理論は、月や水星といった例外を除くと簡潔で、現象をよく説明した。
一方、惑星の黄緯の理論は複雑で、特に内惑星の黄緯の理論は理論計算すら難渋を極め、プトレマイオスは精度の悪い近似で済ませている。そして、のちの﹃簡便表﹄﹃惑星仮説﹄で順次モデルを簡潔にしてゆく。最後の﹃惑星仮説﹄のものが今日から見れば最も現象に合うが、後世に影響を及す事はなかった[14]。中世の理論家は、﹃アルマゲスト﹄の複雑な理論と格闘し、あるいはインド由来の理論や﹃簡便表﹄の不合理な理論を援用することになる[15]。コペルニクスも﹃アルマゲスト﹄を元に自身の理論を練り上げたため、その理論では、惑星の軌道は太陽を中心にしながらも、複雑に上下しながら回転することになった。
﹃アルマゲスト﹄は古代において既に天文学の基本的な書物とされ、また、﹃簡便表﹄共々、注釈書が書かれて天体の計算に広く用いられた。しかし、これらの内容を深めたり検証するといった科学的な進展は、古代に於いてはほとんどなかった[16]。これらの書物が天文学において活発に利用・検証され、かつ改良されるのはイスラム期の中東や中世後半の欧州においてであって、観測技術や数理的な手法の発達と変革を促し、科学革命を準備した。こうして改善されたプトレマイオスの理論は、中世までの観測誤差の範囲内では、中心的な問題については、ほぼ観測と整合的であった。ただし、月の理論は黄経は非常によく説明したが[注釈 3]、見かけの大きさ︵視半径︶については観測と全く合わなかった。そのほか、太陽の見かけの大きさの変動、惑星の明るさの変動など、周辺的な問題について観測に合わない点があった。
天文学は、観測の予測と説明の道具であると同時に、宇宙論にも示唆を与えるものであった。アリストテレスの宇宙論は、すでに見たようにエウドクソスその他の天文学者の見解を大いに利用しており、地球の大きさや恒星までの距離の見積もりから、地球の大きさは宇宙に比べれば無限小である、と述べている。だが、同時に天文学は天体の幾何学的な側面にのみ関わるもので、物理的な考察は自然学の役割であるとした。
プトレマイオスの宇宙論は、﹃アルマゲスト﹄第1巻や﹃惑星仮説﹄で明らかにされている[10]。また、﹃アルマゲスト﹄の序文で、自然学は論争が絶えず明瞭な結論が得られないが、天文学を含む数学的な学問は、確実な基礎を持ち、自然学の問題を考える上でも有用な結果を示すことが出来るとしている。続く宇宙論の中では、地球が球であることや自転していないことについて、自然学的な論議ではなく経験論的な証拠をあげることに努めている。
プトレマイオスの宇宙論は、アリストテレスのものに近く、周転円などの実態は透明な等速回転する球体であって、天体はそれに張り付いているとした。しかし、様々な点でアリストテレスと異なった考えも表明している。例えば、透明な球体の代わりに、上下の不要な部分を切り落とした形状のものでも問題ないとした。これは、﹃アルマゲスト﹄で球にほとんど言及せずに円で議論を済ませていたことを正当化する。また、天球の動く原因としてアリストテレスは不動の動者を設定し、内側の天球は外接する天球の運動に引きずられるとしていた。つまり、内側の天球の運動は、外接する天球の運動と自ら固有の運動の合成になる。これに対して、プトレマイオスは動物への喩えで惑星の動力因を説明し、アリストテレスが主張したような運動の合成を否定した。これはストア派の影響とされる[17]。
また、天文学の観点からより重要になるのは、従円と周転円を合理化するために等速の回転運動を全て許容した点で、地球の中心の回転しか認めなかったアリストテレスとはやや異なる立場であった。さらに、エカントに至っては、等速でない回転を許容する。惑星の黄緯の説明のために、周転円の傾きを振動させたが、この振動に至っては、回転運動で説明できるかどうかも不明だった。最後の2点は、自然学との齟齬を傍に於いたとしても、不自然であった。
﹃アルマゲスト﹄﹃惑星の仮説﹄の数理的な詳細を省いてその宇宙像を描写した書物も現れ[注釈 4]、百科全書的な書物の宇宙論の記述にも影響した。一方、自然学と齟齬を来している部分はさまざまな論議を呼び、プトレマイオスの理論が真の宇宙の体系とみなせるのか、あるいは単なる天体計算のための道具に過ぎないのか、時代や地域、論者によってさまざまな議論が展開された。こういった議論は、コペルニクスが新たな体系を志向するきっかけになる。
なお、﹃アルマゲスト﹄の本来の書名はギリシャ語で﹃Μαθηματικὴ Σύνταξις﹄︵Mathematike Syntaxis、Mathematical Treatise、数学全書︶である。通称として﹃Ἡ Μεγάλη Σύνταξις﹄︵He Megale Syntaxis、The Great Treatise、大全書︶が用いられており、アラビア語に翻訳された際に付いた定冠詞Alが、ラテン語に再翻訳されたときにもそのまま残り、Syntaxis(Treatise)が省略されて﹃Almagest﹄︵The-greatest、最大︶になった。当時、天文学は幾何学、算術、光学、音楽、機械学などとともに数学的な学問の中に含められていた。
﹃アルマゲスト﹄に現れるデータの由来や取り扱いについては様々な議論がある。特に﹁恒星表﹂については、自らの観測ではなく︵﹃アルマゲスト﹄での説明と異なって︶ヒッパルコスのデータから計算しなおしたものではないかという疑問がティコ・ブラーエ以来一度ならず取り上げられている[注釈 5]。

占星術分野[編集]
プトレマイオスの著書﹃テトラビブロス﹄︵Tetrabiblos、四つの書︶は、占星術の古典として知られている。古代において既に基本的な書物として認識され、イスラム期の中東においても同様であった。本書がもたらした権威故にプトレマイオスはルネサンス期ヨーロッパの占星術師・学者から﹁最も神聖なるプトレマイオス﹂と呼ばれることとなった。 ﹃テトラビブロス﹄の原題は﹁影響﹂である。プトレマイオスは、本書を通して、常に変化する星々の位置が世界にもたらす﹁影響﹂について説明︵ロゴス︶を与えることを意図した[18]。星々の位置は、地球、太陽、月、惑星、星辰の運動により常に変化する。この運動については前著﹃アルマゲスト﹄において、数学を道具として用いて論じた。これに対して、星々の位置の影響について論じる﹃テトラビブロス﹄においては、哲学を道具として用いて論じた[18]。このように﹃アルマゲスト﹄を第一部とした場合、﹃テトラビブロス﹄は第二部に相当する[18]。地理学[編集]
詳細は「地理学 (プトレマイオス)」を参照

プトレマイオスの著作﹃ゲオグラフィア﹄(Geographia、地理学)は、地球球体説に基づいた最古の体系的な数理地理学書で、古代の人々の地理に関する知識を集成したものである。本書には本書には、緯度の測定方法などの測量に関する理論、球面を平面に投影して図示する様々な方法が説明され、地球の周長︵子午線一度分の長さ︶や各地点の緯度や経度といったデータが収められている。また、地中海世界の各地域ごとの地図と左図のような世界地図を載せている。これは世界で初めて経緯線を用いたものである。
天体観測を用いて比較的容易に計測できた緯度と異なり、本書に記される各地の経度は誤差が大きく、地中海の東西の経度差を過大に見積もっている。これは、相互の距離の測定に大きく依拠していたためだと思われる。10世紀後半から11世紀になると、継続的な天体観測から地中海のサイズはほぼ正確に見積もられる。この知識は、イベリア半島内で作成された殆どの地理データ表に反映された[注釈 6]。しかし、この知識が一般化することはなかったようであり、このため後に中国についての地理的な情報が付け加えられたとき、その場所が実際よりも大幅に東に位置づけらてしまった。このため、約1,000年後の大航海時代、クリストファー・コロンブスは﹁東よりも西方に航海したほうがアジアへは近道である﹂と考えてアメリカ大陸を発見する事になる。
なお、本書は地球の周長の値を1800スタジオンとし、それを﹁︵一般に︶受け入れられている値﹂としている。距離の単位﹁スタジオン﹂が時代や地域によって長さがまちまちであるため、現代の計測結果との比較は難しい[注釈 7]が、大きく見積もっても誤差は数割程度で、また原理的には正しい計測方法を用いている。

ラファエロ画﹁アテナイの学堂﹂の一部。天球儀を手にするヒッパルコ スと王冠をかぶり地球儀を手にするプトレマイオス。
﹃ハルモニア論﹄第1巻冒頭では、ハルモニアの判別者について述べている[19]。判別者は質料としての聴覚と形相としての理性の二者であるとして、聴覚と理性によりハルモニアが調和であることが判別可能となる[19]。その上で調和音程をどのように定めるかというピュタゴラス以後、古代ギリシア世界で考えられてきた問題を論じる[20]。ピュタゴラス及びその教団は、万物の根源は数であると考え、特に総和が10となる1,2,3,4の4つの数︵テトラクテュス︶を神聖視し[21]、楽音の音律もこのテトラクテュスに基づく数比により設定した︵ピュタゴラス音律︶[22]。これに対し、古代ギリシア思想の古典期に登場したアリストクセノスは、最初はピュタゴラス派の教説に学んだものの飽き足らず、アリストテレスの学説を学んだ人物であるが[22]、完全四度の音程の間に設定する2つの楽音を定めるにあたって[注釈 8]、完全四度の音程が完全五度と完全四度の音程の差を単位音程︵トノス︶として、単位音程二個半であるとした[23]。つまり数比を徹底的に用いる方法によらず、聴覚に従った定性的な方法を示した。プトレマイオスの時代から見て500年前の説であるが、﹃ハルモニア論﹄によると徐々に紀元2世紀頃のアレクサンドリアの若い世代に広まっていたとされる[24]。これに対してプトレマイオスは、アルキュタスやディデュモスら、ピュタゴラス派の先人の説を批判的に継承しつつ数比を用いた音律を示し、これが聴覚にも調和として判別されることを説いてアリストクセノス派に反論した。
﹃ハルモニア論﹄第2巻では主に第1巻の論証で得られた音律に基づく旋法について述べられている[25]。続く第3巻後半で、プトレマイオスは、死すべきものども、その中でもとりわけ人間が判別するハルモニアを論じることから離れて、完全なる調和の世界である天上の世界で奏でられている調和の音楽︵宇宙の諧調︶を解き明かそうとする[26]。しかしながら、現伝する筆写本は中途半端なところで切れており、これについてはテキストが散佚したと見る説と、未完成であると見る説とがある[25]。また、そもそも第3巻後半部自体が偽作であるという説もある[27][28]。当該箇所は3、4世紀には早くも一度散佚しており、14世紀にビザンチンの学者ニケフォロス・グレゴラスが再発見して補填したとされる[27][28]。真作説をとる場合、この部分の筆致の確信に満ちた様子から、﹃ハルモニア論﹄が﹃アルマゲスト﹄や﹃テトラビブロス﹄を書き上げた後の最晩年の作であるという見方もある[25]。
﹃ハルモニア論﹄は、執筆後1500年近く経ってヨハネス・ケプラーが読んだことによって、思いがけない形で科学史に影響を及ぼすこととなった[27][29]。ケプラーはプトレマイオスが宇宙の諧調を解き明かしていると考えられる第3巻の散佚した章の復元を試みるうちに、数々の重要な発見へと至る道を見つけた[27]。

﹁占星学者、アレクサンドリアのクラウディオス・プトレマイオス﹂と 題された16世紀の想像画
古代においては、現代の光学に相当する内容は、いくつかの分野に分かれて研究されていた。光と視覚の関係が明らかにされてそれらの研究が統合されるのは、中世の中程以降のことである。その時に土台を提供したのは、古代の幾何学的な視覚論、特にその最高峰たるプトレマイオスの大著﹃視学(光学)﹄であった。
プトレマイオス以前、アリストテレスの頃、すでに幾何学的な視覚の理論は、数学的な学問の一つの分野として成立しており、ユークリッドやヘロンによって発展させられていた。彼らの理論は、眼から放出される﹁視線﹂が対象に届いて視覚が成立するとする、ある種の外送理論であった。そして、視線を幾何学的に分析して、遠近法や測量、視覚にの明瞭さ、鏡による像の形成などを論じた。
当時は幾何学的な理論家のみでなく、プラトンや、当時有力な哲学の学派であったストア派の視覚論も、各々タイプの異なる外送理論であった。ただし、アリストテレスは外送理論を否定して、対象の﹁色﹂の眼への流入で視覚を説明して、魂論(霊魂論、心理学)の一部としての視覚の形成のプロセスを論じた[30]。これらの哲学者の視覚論に対し、幾何学者の視覚論は、扱う問題が限定される代わりに、厳密で強力だった。
プトレマイオスは、幾何学的な視覚論の伝統を受け継ぎつつも、アリストテレス的な感覚の理論を参考にし、錯視の原因をさまざまな階層に分類して論じるなど、より総合的な視覚論を展開した。視線の物理的な本性や眼のどこで像が形成されるかなど、数理的でない側面も積極的に論じ、ストア派の議論も一部取り込んだ。また、ユークリッドはもちろん、ヘロンに比べても経験論的な色彩が強い。ユークリッドやヘロンが視線の基本的な性質を仮定するか、あるいはより﹁基本的な﹂仮定から演繹するのに対して、プトレマイオスは経験や実験に訴えている。
プトレマイオス﹃視学(光学)﹄は屈折の本格的な理論が展開されている、現存する最古の書物である。簡単な実験器具を用いた入射角と屈折角の関係の計測について述べ、この二つの量の関係を空気ー水、水ーガラス、空気ーガラスについて表にまとめている。これらの表は数値がある規則を完全に満たしている[注釈 9]ので、理論的な計算だと思われる[31][注釈 10]。そして、表の数値はスネルの法則を用いた計算と比較しても極端な外れはない。イスラム圏では、この表はイブン・ハイサムやal-Farisinによって若干の値が用いられ、欧州ではウィテロの﹃光学﹄に若干修正したものが掲載されて流布した。さらに、大気層の上部の屈折で星の見かけの方向が真の方向からわずかにずれることにも触れている。
反射による像の形成については、ユークリッド﹃反射視学(反射光学)﹄が解釈の難しい仮定や誤りと思われる議論を含むのに対して、論理的に明晰で、一段と込み入った問題が論じられている。17世紀に盛んに論じられた、球面鏡に関する難問﹁アルハーゼン︵イブン・ハイサムのラテン名︶の問題﹂を最初に提起したのも本書である[注釈 11]。
これらの反射や屈折の研究は高度なものであるが、いずれも﹁視線﹂の反射・屈折であることに注意する必要である。基本法則を確認する実験でも標的を反対側から覗いたときに眼に入る角度を計測しており、意識されているの飽くまで﹁視線﹂である。その上、扱われる問題は全て、反射や屈折を通しての﹁像の形成﹂である。例えば、平面鏡での反射では、奥行きを含めて反転した物体がそこにあるように見える、といったことを導かねばならず、そのためには奥行きの認識についての仮定が当然必要になる。つまり、現在で言うところの光学のは収まらない問題を扱っている。その一方、光を一点に集めるための鏡︵Burning mirror)の研究が当時かなり進んでいたが、プトレマイオスはそれには一切ふれない[注釈 12]。
これら幾何学的な理論に加え、視覚論の書物にふさわしく、本書は様々な錯視を扱い、照度、色彩、大きさ、形、動き、両眼視に関する多くの現象に説明を加えている。また、錯視の原因については、﹁光学﹂的な要因によるものと、認識論的な要因によるものとに分けて考えた。太陽や月が地平線近くにあると見かけの大きさが大きく見える﹁月の錯視﹂については、後者に分類している[32][33]が、それは方向性としては正しい。錯視を扱った第二巻には、複数の色が塗られた物体を回転させると、それらが混ざった色が観測されることが記されているが、後年ジェームズ・クラーク・マクスウェルが混色の実験で用いるのは、正にこの方法であった。
本書は古代の光学の最高峰であったが、﹃アルマゲスト﹄﹃テトラビブロス﹄﹃ハルモニア論﹄などが早々に教科書的な地位を獲得したのとは正反対に、古代においては引用も言及も非常に少ない[34]。古代末期において、天文学の教程に組み込まれて広く学ばれたのは、ユークリッド﹃光学﹄だった[35]。この傾向は、中世のイスラム圏にも引き継がれた。本書を利用した研究は10世紀にようやく現れる。まず、光のスネルの法則を先取りしたイブン・サフル(en:Ibn Sahl (mathematician))の屈折に関する研究は、プトレマイオスの影響を抜きには考え難い。また、光学を刷新したイブン・ハイサムの﹃光学の書(Kitab al-Manazir)﹄は、その構成が、(新たに眼球の構造を論じている他は)プトレマイオス﹃光学﹄をほぼなぞっていることからもわかるように、影響が顕著である。ただし、イブン・ハイサムが光を視覚の主要因と特定して光学を大きく書き換えたため、この後は直接の影響は限定的である[34]。
﹃視学(光学)﹄はラテン語訳のみで残るが、視覚論の基礎を含んだであろう第1巻を欠き、屈折の理論を展開する第5巻は、後半部が失われている。また、文意を尽くさない章句もある。ラテン語への翻訳は、今は失われたアラビア語版から、パレルモのエウゲニウスにより1154年頃になされた。イブン・ハイサムの言及と照らし合わせると、現存のラテン語版と、当時流布したアラビア語版は、基本的には同じ構造をしていたと思われる。
また、﹃視学(光学)﹄は﹃アルマゲスト﹄や﹃惑星仮説﹄よりも後に書かれたとされる。根拠の一つは、これらの書における、月の錯視や屈折の議論の比較の議論である。﹃アルマゲスト﹄第一巻では、この現象を大気による屈折とし、誤って﹁水の中にあるものは屈折で大きく見える﹂としている。﹃惑星仮説﹄では、さらに心理的な要因が加味され、﹃視学﹄では純粋に心理学的な効果だとしている。また、屈折の議論もずっと正確で洗練されている。古代末期から中世にかけて、﹃アルマゲスト﹄と同様の誤った屈折の理解は、広く見られる。
楽理分野[編集]
音楽については、音程を二つの音の数比で表すピュタゴラス派の方法論を批判的に継承した。定性的な方法を示した古典期のアリストクセノスの﹃ハルモニア原論﹄を新ピュタゴラス派︵ピュタゴラス派の伝統は紀元前4世紀の末に一度途切れている︶の立場から痛烈に批判し、独自の見解を提起したハルモニア論︵全三巻︶を著した。
光学分野[編集]

数学[編集]
天文学書﹃アルマゲスト﹄幾何学的な描像と、数値的な計算を結び付けるための強力な道具として用いられたのが、﹁弦の表﹂、すなわち円弧の長さと弦の長さの間の関係を表にしたものである。﹃アルマゲスト﹄では、これをヒッパルコスの発明としている[注釈 13]。また、﹃アルマゲスト﹄には、﹁弦の表﹂の様々な性質、例えば加法定理に相当するものなども示されている。ただし中世以降は、プトレマイオス以前に分岐して独自に発展を遂げた、インド流の三角法に置き換えられていく。 また、(球面幾何の︶メネラウス(英語版)の定理[注釈 14]に基づく球面三角法も展開されている。インドには球面三角法は生じず、中世に発展した球面三角法は﹃アルマゲスト﹄とメネラウス(英語版)の﹃球面幾何﹄が起源である。ただし、10 - 11世紀には、正弦定理などに基づくより洗練された形式が編み出され、﹃アルマゲスト﹄の手法を置き換えることになる。 このほかに、現存していないが平行線公準に関する著書もあったと推定されている。エウクレイデスの﹃原論﹄の第1巻にプロクロスが付けた注釈の中にプトレマイオスの著書に対する言及があることがその根拠である。[36]脚注[編集]

注釈[編集]
(一)^ 名高いアンティキラの機械も、一部バビロニアの理論に基づいているとされる。ヒッパルコス以降もバビロニア天文学は簡便な計算方法として生き残り、プトレマイオスの占星術書﹃テトラビブロス﹄に名残りを留める。また、バビロニア由来の天文定数は古代ギリシャ天文学にも引き継がれる。バビロニア天文日誌Asger Aaboe, Episodes from the Early History of Astronomy, New York: Springer, 2001, pp. 62–65. Alexander Jones, "The Adaptation of Babylonian Methods in Greek Numerical Astronomy," in The Scientific Enterprise in Antiquity and the Middle Ages, p. 99.
(二)^ これは、これらの惑星の軌道離心率が小さい︵軌道が円に非常に近い︶からである。軌道離心率の大きな水星の場合は、月と同様の複雑な機構︵prosneusis)を用いることを強いられている。
(三)^ 出差とよばれる、主に太陽の重力の効果による円運動からのずれも説明できた。国立天文台の解説を参照。
(四)^ アルフラガヌスの﹃天の運動と天文知識の集成﹄やイブン・ハイサムの﹃世界の配置﹄などがあり、それらは西欧でも中東でもよく読まれた。
(五)^ 一連の議論については、例えば Claudius Ptolemy の後半や Evans, J. On the Origin of the Ptolemaic Star Catalogue - Part One, Journal for the History of Astronomy, Vol.18, NO. 3/AUG, P.155, 1987 や Gerd. G., The History of Ptolemy’s Star Catalogue,Springer, 1990 などを参照。これらの文献ではまた、プトレマイオスの他のデーターの取り扱いについても簡単なコメントがあり、体系的な誤差の処理の方法がなかったこと、全てのデータではなく取捨選択した結果のみがのせられていること、理論に合うデータを恣意的に選んでいる場合があること、またそれが必ずしも非合理的とも言えないことなどが指摘されている。
(六)^ https://islamsci.mcgill.ca/RASI/BEA/Majriti_BEA.htm の第5パラグラフの中程を参照。東方の天文表を現地の経度に合わせて書き直す際に、経度の評価がなされた。
(七)^ Diller, A., “The Ancient Measurements of the Earth”,Isis, 40, 1, No 119, 1949, 7–8. 本論文によると、エラトステネスの値とプトレマイオスの値の差は用いた﹁スタジオン﹂の違いに起因する可能性が高い。古代の地球の計測についてはウィキペディアのエラトステネスの項目なども参照。
(八)^ この問題は﹁テトラコルドの分割﹂と呼ばれ、キタラという四弦琴の内側の二弦を調律する際に重要な問題であった[21]。
(九)^ 例えば、二次関数に正確に乗っている。また、二階差分が空気ー水、水ーガラス、空気ーガラスの3つの表ですべて共通の値。そして値に端数がない。
(十)^ Smith(Smith 1996)は古代バビロニア天文学で用いられた手法だと推定している。また、Boyer(Boyer 1959)は入射角60度の場合を除いては理論計算だと述べている。
(11)^ ただし、解法を初めて与えたのはイブン・ハイサム。
(12)^ ただし、光線と視線が同じ屈折や反射の法則に従うことは自明とされた。
(13)^ ギリシア起源であることは確実とされるが、ヒッパルコス以前に遡る可能性は排除できない。
(14)^ 現在、平面幾何のメネラウスの定理とよばれるものは、この定理の平面幾何版でメネラウス以前から知られていたと思われる。ここで指しているのは、この平面幾何の定理の球面幾何への拡張版で、現存する文献の中ではメネラウス﹃球面幾何﹄が初出。
出典[編集]
(一)^ abcdefghijklJones, Alexander (16 October 2020). "Ptolemy (or Claudius Ptolemaeus)". Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography. 2020年11月23日閲覧。
(二)^ abcdO'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., “Claudius Ptolemy”, MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews.
(三)^ Katz, Victor J. (2009). A history of mathematics : an introduction (3rd ed ed.). Boston: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-321-38700-7. OCLC 71006826の"SIDEBAR6.2 Who Were the Alexandrian Mathematicians?”を参照。
(四)^ 同様に、Netzも民族についての情報が得られるのは、例外的な場合に限られることを注意し、何人かの著名な﹁古代ギリシア﹂数学者が非ギリシア系である可能性を示す。 Netz, R., Greek Mathematicians: A Group Picture, in: Christopher Tuplin, T. E. Rihll., Science and mathematics in ancient Greek culture, Oxford: Oxford University Press. (2002). 本論文のp.199を参照。
(五)^ abcPlessner, M. (1960). "BAṬLAYMŪS". In Gibb, H. A. R.; Kramers, J. H. [in英語]; Lévi-Provençal, E. [in英語]; Schacht, J. [in英語]; Lewis, B.; Pellat, Ch. [in英語] (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume I: A–B. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 1100–1102.
(六)^ Abu Ma’shar, De magnis coniunctionibus, ed.-transl. K. Yamamoto, Ch. Burnett, Leiden, 2000, 2 vols. (Arabic & Latin text); 4.1.4.
(七)^ Jones 2010, p. 68‘Ptolemy’s Doctrine of the Terms and Its Reception’ by Stephan Heilen
(八)^ Bernal, Martin (1992). “Animadversions on the Origins of Western Science”. Isis 83 (4): 596–607 [602, 606] 2020年11月23日閲覧。.
(九)^ J. F. Weidler (1741). Historia astronomiae, p. 177. Wittenberg: Gottlieb. (cf. Martin Bernal (1992). "Animadversions on the Origins of Western Science", Isis 83(4), p. 596–607 [606].)
(十)^ abMurschel, 1995
(11)^ Albert Van Heiden, 1985, pp.15-27.
(12)^ ラテン語訳成立年代については、下記リンク参照。 https://ptolemaeus.badw.de/work/141
(13)^ Langermann, Y. Tzvi. “Arabic Cosmology.” Early Science and Medicine, vol. 2, no. 2, 1997, pp. 185–213. のpp.185-186を参照。
(14)^ Swerdlow, N.M. 2005. Ptolemy’s theories of the latitude of the planets in the Almagest, handy tables, and planetary hypotheses. In Wrong for the right reasons, ed. J.Z. Buchwald, and A. Franklin, 41–71 (Springer)を参照。﹃惑星仮説﹄では﹁軌道の物理的な説明をする﹂とのみあり、モデルを観測に合うように改善したとは書いていない。しかし、Swerdlowは﹃惑星仮説﹄のモデルは、観測を重ねて改良を続けた結果だと推測している。その根拠として、従円の傾斜と現代知られている軌道面と黄道面の間の角度がよく一致していることを挙げている。
(15)^ Mozaffari, S.M. Planetary latitudes in medieval Islamic astronomy: an analysis of the non-Ptolemaic latitude parameter values in the Maragha and Samarqand astronomical traditions. Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 70, 513–541 (2016).
(16)^ 古代の﹃アルマゲスト﹄の受容については、Pedersen, Olaf, ed,2011 pp.13-14に簡潔な説明があり、また、Pingree, David. "The Teaching of the Almagest in Late Antiquity" Apeiron, vol. 27, no. 4, 1994, pp. 75-98 に詳しく論じられている。古代の天文学の進展については、Saliba, G., “Greek Astronomy and the Medieval Arabic Tradition: The Medieval Islamic Astronomers Were Not Merely Translators. They May Also Have Played a Key Role in the Copernican Revolution.” American Scientist, vol. 90, no. 4, pp. 360–367, 2002の p.360 に以下のように評されている‥"Seven centuries passed before Ptolemy's writings reached the Islamic world, and there appears to have been relatively little development of the science during the intervening period.”
(17)^ Langermann, 前掲, p.200
(18)^ abcテスター 1997, pp. 77–78.
(19)^ abハルモニア論 2008, I.I.
(20)^ 山本 2008, pp. 308–326.
(21)^ abファーガソン 2011, p. 149.
(22)^ ab山本 2008, pp. 300–302.
(23)^ 山本 2008, pp. 302–303.
(24)^ ハルモニア論 2008, I.X.
(25)^ abc山本 2008, pp. 344–345.
(26)^ ハルモニア論 2008, III.XI-XVI.
(27)^ abcdファーガソン 2011, pp. 262–267.
(28)^ ab山本 2008, pp. 287–289.
(29)^ テスター 1997, p. 314.
(30)^ Ross & Plug 1998.
(31)^ Boyer 1959.
(32)^ Ross & Ross 1976, pp. 377–395.
(33)^ Sabra 1987, pp. 217–247.
(34)^ abSmith 1996
(35)^ Alexander Jones. Peripatetic and Euclidean Theories of the Visual Ray. Physis 31 (1994) 47-76 (Pdf)
(36)^ ﹃ギリシア数学史﹄ 1998, p. 337.
参考文献[編集]
著作の日本語訳[編集]
●アルマゲスト 藪内清訳.恒星社厚生閣,1958 ●プトレマイオス世界図 大航海時代への序章.岩波書店,1978.3. ●宇宙誌 日本語版監修 下村寅太郎ほか 岩波書店,1984.2. ●プトレマイオス地理学 中務哲郎訳.東海大学出版会,1986.5. ●ハルモニア論 ●山本建郎 訳﹃古代音楽論集﹄京都大学学術出版会︿西洋古典叢書﹀、2008年5月15日。ISBN 978-4-87698-175-5。二次資料[編集]
●Boyer, Carl Benjamin (1959). The Rainbow: From Myth to Mathematics ●Albert Van Heiden, Measuring the universe: Cosmic dimensions from Aristarchus to Halley (Chicago, 1985) ●Jones, Alexander, ed (2010). Ptolemy in Perspective: Use and Criticism of his Work from Antiquity to the Nineteenth Century. 23. New York: Series: Archimedes. ISBN 978-90-481-2787-0 ●Murschel A. The Structure and Function of Ptolemy’s Physical Hypotheses of Planetary Motion. Journal for the History of Astronomy. 1995;26(1):33-61. doi:10.1177/002182869502600102 ●Neugebauer, O., The Exact Sciences in Antiquity, 2nd. Ed., Brown University Press, 1957. ●Neugebauer, O., A History of Ancient Mathematical Astronomy, Springer, 1975 ●Neugebauer, O., Astronomy and History - Selected Essays, Springer 1983 ●Pedersen, Olaf, ed (2011). A Survey of the Almagest. Springer-Verlag New York. ISBN 978-0-387-84825-9 ●Pingree, David (1994). “The Teaching of the Almagest in Late Antiquity.” In The Sciences in Greco–Roman Society, edited by Timothy D. Barnes. Edmonton: Academic Printing and Publishing, pp. 73–98. (For the survival of Theon's commentary on the Almagest.) ●Smith, A. Mark (1996). Ptolemy's Theory of Visual Perception– An English translation of the Optics. The American Philosophical Society. ISBN 0-87169-862-5 2009年6月27日閲覧。 ●Ross, H. W.; Plug, C. (1998). V. Walsh. ed. “The History of Size Constancy and Size Illusions”. Perceptual Constancy: Why Things Look as They Do (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press): 499–528. ●Ross, H. E.; Ross, G. M. (1976). “Did Ptolemy Understand the Moon Illusion?”. Perception 5: 377–395. ●Sabra, A. I. (1987). E. Grant. ed. “Psychology Versus Mathematics: Ptolemy and Alhazen on the Moon Illusion”. Mathematics and Its Application to Science and Natural Philosophy in the Middle Ages (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press): 217–247. ●S. J. テスター 著、山本啓二 訳﹃西洋占星術の歴史﹄恒星社厚生閣、1997年2月15日。ISBN 4-7699-0836-9。 ●T. L. ヒース 著、平田寛他 訳﹃ギリシア数学史﹄共立出版、1998年5月12日。ISBN 4-320-01588-6。 ●キティ・ファーガソン 著、柴田裕之 訳﹃ピュタゴラスの音楽﹄白水社、2011年9月20日。ISBN 978-4-560-08163-1。外部リンク[編集]
●アルマゲスト︵国立天文台・暦Wiki) ●アルマゲストの英訳(Toomer,1984) ●Claudius Ptolemy, McTutorHistory of Mathematics Archive ●Ptolemy,Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography COPYRIGHT 2008 Charles Scribner's Sons ●﹃プトレマイオス﹄ - コトバンク関連項目[編集]
- 地図学
- 地理学の歴史
- 天球儀
- トレミーの48星座
- トレミーの定理(彼の名前にちなんで命名された幾何学の定理)
- プトレマイオス (小惑星)
- 1世紀生まれの天文学者
