

 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
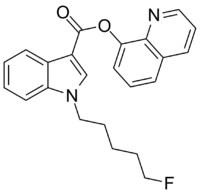
| Formula | C23H21FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 376.431 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
5F-PB-22 (5F-QUPICorquinolin-8-yl 1-pentyfluoro-1H-indole-3-8-carboxylate) is a designer drug which acts as a cannabinoid agonist.[2] The structure of 5F-PB-22 appears to have been designed with an understanding of structure–activity relationships within the indole class of cannabinoids.[3]
5F-PB-22 acts as a full agonist with a binding affinity of 0.468 nM at CB1 and 0.633 nM at CB2 cannabinoid receptors.[4]
As of October 2015 5F-PB-22 is a controlled substance in China.[5]
In January 2014, 5F-PB-22 was designated as a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States after several deaths were associated with its use.[6][7]
In the United Kingdom, 5F-PB-22 is now classified and controlled as a Class B drug, following the November 2016 amendment to the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. Several other synthetic cannabinoids structurally related to JWH-018, like 5F-PB-22, were also classified in this amendment.[8]