

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cadmium(II) cyanide | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.027 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cd(CN)2 | |
| Molar mass | 164.45 g/mol |
| Appearance | white cubic crystals |
| Density | 2.226 g/cm3 |
| 1.71 g/100 mL (15 °C) 2.2 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in alcohol dissolves in alkali, metal cyanides and hydroxides |
| -54.0·10−6cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
[1910.1027] TWA 0.005 mg/m3 (as Cd)[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
Ca[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [9 mg/m3 (as Cd)][1] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Cadmium chloride, Cadmium iodide |
Other cations |
Zinc cyanide, Calcium cyanide, Magnesium cyanide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Cadmium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(CN)2. It is a white crystalline compound that is used in electroplating.[2] It is very toxic, along with other cadmium and cyanide compounds.
Cadmium cyanide is prepared commercially by treating cadmium hydroxide with hydrogen cyanide:[3]
It can also be generated from tetracyanocadmate:

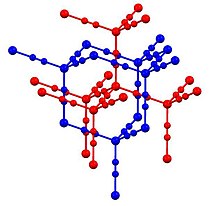
Cadmium cyanide and zinc cyanide adopt similar structures.[4] As such, each metal has tetrahedral coordination sphere. Cyanide ligands interconnect pairs of metal centers. Two of the resulting diamondoid structures are interpenetrated. The structure is related to that of cristobalite, a polymorphs of SiO2. This structural similarity of cadmium dicyanide and cristobalite was foundational in the development of mineralomimetic chemistry: "the build-up of mineral-like structures using materials that never give stable minerals."[5]
It is used as an electrolyte for electrodeposition of thin metallic cadmium coatings on metal to protect against corrosion.
Like zinc cyanide, cadmium cyanide is fairly soluble in water, which is unusual for transition metal cyanides. The solubility increases with the additional cyanide, this reaction proceeding via "[Cd(CN)3]−" and [Cd(CN)4]2−. With acids, its solutions evolve hydrogen cyanide. When it is crystallizes in the presence of certain small molecules, it forms clathrates.[4]
|
Salts and covalent derivatives of the cyanide ion
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|