

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Drolban, Masteril, Masteron, others |
| Other names | Dromostanolone propionate; NSC-12198; Drostanolone 17β-propionate; 2α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 17β-propionate; 2α-Methyl-DHT propionate; 2α-Methyl-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one 17β-propionate |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection[1] |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 0–2% Intramuscular: 100% |
| Protein binding | High |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | Intramuscular: 2 days[1] |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.550 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H36O3 |
| Molar mass | 360.538 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Drostanolone propionate, or dromostanolone propionate, sold under the brand names Drolban, Masteril, and Masteron among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which was used to treat breast cancer in women but is now no longer marketed.[1][2] It is given by injection into muscle.[1]
Side effects of drostanolone propionate include symptomsofmasculinization like acne, increased hair growth, voice changes, and increased sexual desire.[1] It has no risk of liver damage.[1] The drug is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and hence is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[1][3] It has moderate anabolic effects and weak androgenic effects, which give it a mild side effect profile and make it especially suitable for use in women.[1] The drug has no estrogenic effects.[1] Drostanolone propionate is an androgen ester and a long-lasting prodrugofdrostanolone in the body.[1]
Drostanolone propionate was first described in 1959 and was introduced for medical use in 1961.[1][4][5] In addition to its medical use, drostanolone propionate is used to improve physique and performance.[1] The drug is a controlled substance in many countries and so non-medical use is generally illicit.[1][6]
The principal clinical indication of drostanolone propionate in the United States as well as international markets was the treatment of advanced inoperable breast cancer in women.[1]
Hormonal treatment is part of the complex therapy for some kind of tumors, particularly the ones associated with hormone-active tissues like breast or prostate cancer. Some types of breast cancer cells, expressing estrogen receptors (called ER+ cancers), use estrogen for their growth and dissemination. That is why drugs that block estrogen receptors or decrease their expression on the cell membrane, antiestrogens, could limit the tumor spread and size. Drostanolone propionate has been FDA approved[7] as an antiestrogenic drug for the treatment of breast cancer. By the time of its release, there were not many alternatives for patients with breast cancer and drostanolone propionate was a revolution for these patients. As it has lower androgenic rate compared to testosterone, the risk of virilization is much lighter. Due to this fact, women, who usually do not respond well to any AAS, were having much greater chance to survive cancer. Drostanolone propionate can also be used for breast tumors that do not respond well to other treatments or also as palliative care for advanced incurable tumors. The effects of the product depend of course on the dose and period of administration. The risk of virilization becomes greater with high doses and continuous administration period.
| Route | Medication | Form | Dosage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Methyltestosterone | Tablet | 30–200 mg/day | |
| Fluoxymesterone | Tablet | 10–40 mg 3x/day | ||
| Calusterone | Tablet | 40–80 mg 4x/day | ||
| Normethandrone | Tablet | 40 mg/day | ||
| Buccal | Methyltestosterone | Tablet | 25–100 mg/day | |
| Injection (IMTooltip intramuscular injectionorSCTooltip subcutaneous injection) | Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 3x/week | |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | 200–400 mg 1x/2–4 weeks | ||
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | 200–400 mg 1x/2–4 weeks | ||
| Mixed testosterone esters | Oil solution | 250 mg 1x/week | ||
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | 100 mg 3x/week | ||
| Androstanolone (DHT) | Aqueous suspension | 300 mg 3x/week | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | Oil solution | 100 mg 1–3x/week | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | 400 mg 3x/week | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 1x/1–3 weeks | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg/week | ||
| Note: Dosages are not necessarily equivalent. Sources: See template. | ||||
Drostanolone propionate is or has been used for physique- and performance-enhancing purposesbycompetitive athletes, bodybuilders, and powerlifters.[1]
Drostanolone propionate produces considerably less virilization in women compared to equal doses of testosterone propionate.[1] However, since the given dosage for breast cancer was relatively high (200 mg/twice a week),[8] mild virilization including oily skin, acne, voice deepening, hirsutism, and clitoral enlargement could still occur, and marked virilization could manifest with long-term therapy.[1] The drug has no estrogenic activity and hence has no propensity for causing gynecomastia (in males) or fluid retention.[1] Drostanolone propionate is not known to pose a risk of hepatotoxicity.[9][1]
| Medication | Ratioa |
|---|---|
| Testosterone | ~1:1 |
| Androstanolone (DHT) | ~1:1 |
| Methyltestosterone | ~1:1 |
| Methandriol | ~1:1 |
| Fluoxymesterone | 1:1–1:15 |
| Metandienone | 1:1–1:8 |
| Drostanolone | 1:3–1:4 |
| Metenolone | 1:2–1:30 |
| Oxymetholone | 1:2–1:9 |
| Oxandrolone | 1:3–1:13 |
| Stanozolol | 1:1–1:30 |
| Nandrolone | 1:3–1:16 |
| Ethylestrenol | 1:2–1:19 |
| Norethandrolone | 1:1–1:20 |
| Notes: In rodents. Footnotes: a = Ratio of androgenic to anabolic activity. Sources: See template. | |
Drostanolone propionate is a prodrugofdrostanolone.[1] Like other AAS, drostanolone is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR).[1] It is not a substrate for 5α-reductase and is a poor substrate for 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD), and therefore shows a high ratio of anabolictoandrogenic activity.[1] As a DHT derivative, drostanolone is not a substrate for aromatase and hence cannot be aromatized into estrogenic metabolites.[1] While no data are available on the progestogenic activity of drostanolone, it is thought to have low or no such activity similarly to other DHT derivatives.[1] Since the drug is not 17α-alkylated, it is not known to cause hepatotoxicity.[1]
Drostanolone propionate, via its active form drostanolone, interacts with the AR and activates a cascade of genetic changes, including increased protein synthesis (anabolism) and decreased amino acid degradation (catabolism). It also induces a reduction or inhibition of prolactinorestrogen receptors in the breasts, which is linked to its antitumor effects.[10]
Drostanolone propionate is not active via the oral route and must be administered via intramuscular injection.[1] The elimination half-life of the drug via this route is approximately 2 days.[1] It has a much longer elimination half-life via intramuscular injection than drostanolone.[1] Drostanolone propionate is metabolized into drostanolone, which is the active form.[1]
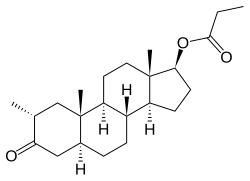
Drostanolone propionate, or drostanolone 17β-propionate, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a derivative of DHT.[11][12][1] It is the C17β propionate (propanoate) esterofdrostanolone, which itself is 2α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone (2α-methyl-DHT) or 2α-methyl-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one.[11][12][1]
| Anabolic steroid | Structure | Ester | Relative mol. weight |
Relative AAS contentb |
Durationc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Moiety | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Boldenone undecylenate | C17β | Undecylenic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.58 | 0.63 | Long | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | C17β | Propanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 | 1.18 | 0.84 | Short | ||
| Metenolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.14 | 0.88 | Short | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.37 | 0.73 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | C17β | Decanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 10 | 1.56 | 0.64 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | C17β | Phenylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6–7) | 1.48 | 0.67 | Long | ||
| Trenbolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.16 | 0.87 | Short | ||
| Trenbolone enanthated | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | Long | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of esterincarbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic fatty acids. b = Relative androgen/anabolic steroid content by weight (i.e., relative androgenic/anabolic potency). c = Durationbyintramuscularorsubcutaneous injectioninoil solution. d = Never marketed. Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
Drostanolone and drostanolone propionate were first described in 1959.[1][4] The related AAS oxymetholone and methasterone (methyldrostanolone) were first described in the same paper as well.[1] Drostanolone propionate was introduced for medical use in the United States in 1961 and in Europe shortly thereafter.[5]
Drostanolone propionate is the generic name of the drug and its BANMTooltip British Approved Name, while dromostanolone propionate is the USANTooltip United States Adopted Name and USPTooltip United States Pharmacopeia; there is no INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name for this form.[11][12][13] The generic name of the unesterified form of the drug is drostanoloneordromostanolone and the former is its INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name, BANTooltip British Approved Name, and DCFTooltip Dénomination Commune Française while there is no USANTooltip United States Adopted Name.[11][12][13][2]
Drostanolone propionate was marketed under a variety of brand names including Drolban, Masterid, Masteril, Masteron, Masterone, Mastisol, Metormon, Permastril, and Prometholone.[11][12][1]
Drostanolone propionate appears to no longer be marketed.[1][2] It was previously available in the United States, Europe, and Japan.[12][1] In Europe, it was specifically marketed in the United Kingdom, Germany, Belgium, France, Spain, Portugal, Italy, and Bulgaria.[12][1]
Drostanolone propionate, along with other AAS, is a schedule III controlled substance in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act.[6]
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARTooltip Androgen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||
| |||||||