

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ethynodiol; 3β-Hydroxynorethisterone; 17α-Ethynylestr-4-ene-3β,17β-diol |
| Drug class | Progestin; Progestogen |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.610 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 300.442 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Etynodiol, or ethynodiol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was never marketed.[1][2][3]Adiacylated derivative, etynodiol diacetate, is used as a hormonal contraceptive.[1][2] Etynodiol is sometimes used as a synonym for etynodiol diacetate.
It was patented in 1955.[4]
Etynodiol is a prodrugofnorethisterone, and is converted immediately and completely into norethisterone.[5][6][7] Etynodiol is an intermediate in the conversion of the prodrug lynestrenol into norethisterone.[8]
| Compound | Typea | PRTooltip Progesterone receptor | ARTooltip Androgen receptor | ERTooltip Estrogen receptor | GRTooltip Glucocorticoid receptor | MRTooltip Mineralocorticoid receptor | SHBGTooltip Sex hormone-binding globulin | CBGTooltip Corticosteroid binding globulin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norethisterone | – | 67–75 | 15 | 0 | 0–1 | 0–3 | 16 | 0 |
| 5α-Dihydronorethisterone | Metabolite | 25 | 27 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| 3α,5α-Tetrahydronorethisterone | Metabolite | 1 | 0 | 0–1 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| 3α,5β-Tetrahydronorethisterone | Metabolite | ? | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 3β,5α-Tetrahydronorethisterone | Metabolite | 1 | 0 | 0–8 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| Ethinylestradiol | Metabolite | 15–25 | 1–3 | 112 | 1–3 | 0 | 0.18 | 0 |
| Norethisterone acetate | Prodrug | 20 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? |
| Norethisterone enanthate | Prodrug | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Noretynodrel | Prodrug | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Etynodiol | Prodrug | 1 | 0 | 11–18 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| Etynodiol diacetate | Prodrug | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? |
| Lynestrenol | Prodrug | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? |
| Notes: Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were promegestone for the PRTooltip progesterone receptor, metribolone for the ARTooltip androgen receptor, estradiol for the ERTooltip estrogen receptor, dexamethasone for the GRTooltip glucocorticoid receptor, aldosterone for the MRTooltip mineralocorticoid receptor, dihydrotestosterone for SHBGTooltip sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol for CBGTooltip Corticosteroid-binding globulin. Footnotes: a = Active or inactive metabolite, prodrug, or neither of norethisterone. Sources: See template. | ||||||||
Etynodiol is a 19-nortestosterone derivative. Structurally, it is almost identical to norethisterone and lynestrenol, differing only in its C3 substituent. Whereas norethisterone has a ketone at C3 and lynestrenol has no substituent at C3, etynodiol has a hydroxyl group at the position.
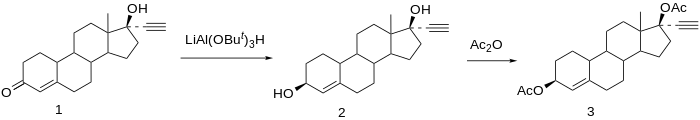
Etynodiol is the generic name of the drug and its INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name, while ethynodiol is its BANTooltip British Approved Name.[1][2]
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| |||||||
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARTooltip Androgen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |