

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
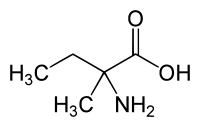
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-2-methylbutanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Amino-2-methylbutyric acid; 2-Ethylalanine; α-Ethylalanine | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 117.148 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Isovaline is a rare amino acid transported to Earth by the Murchison meteorite[citation needed], which landed in Australia in 1969. The discovery of isovaline in the biosphere demonstrates an extraterrestrial origin of amino acids and has been linked to the homochirality of life on Earth,[1] suggesting a role in the origin of life.[2]
Isovaline is an isomer of the common amino acid valine, with the position of one methyl group shifted slightly (from position 3 to position 2). The structure of isovaline is also somewhat similar to the amino acids GABA and glycine, the chief inhibitory neurotransmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Isovaline acts as an analgesic in mice[3][4] by activating peripheral GABAB receptors.[4][5] In a mouse model of osteoarthritis isovaline restored mobility, suggesting inhibition of nociception by isovaline in the synovial membrane of the mouse knee.[4]
Isovaline does not cross the blood–brain barrier[4] and does not enter into the brain or spinal cord. Drugs such as opioids cross the blood–brain barrier to produce analgesia but often produce in addition confusion, sedation, and addiction.
Isovaline acts downstream to the cyclooxygenase system that NSAIDs inhibit, suggesting a means to avoid adverse effects such as irritation of the gastrointestinal system.