

| gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | GABBR1 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 2550 | ||||||
| HGNC | 4070 | ||||||
| OMIM | 603540 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_021905 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q9UBS5 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 6 p21.3 | ||||||
| |||||||
| gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | GABBR2 | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | GPR51 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 9568 | ||||||
| HGNC | 4507 | ||||||
| OMIM | 607340 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_005458 | ||||||
| UniProt | O75899 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 9 q22.1-22.3 | ||||||
| |||||||
GABAB receptors (GABABR) are G-protein coupled receptors for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), therefore making them metabotropic receptors, that are linked via G-proteinstopotassium channels.[1] The changing potassium concentrations hyperpolarize the cell at the end of an action potential. The reversal potential of the GABAB-mediated IPSP (inhibitory postsynaptic potential) is −100 mV, which is much more hyperpolarized than the GABAA IPSP. GABAB receptors are found in the central nervous system and the autonomic division of the peripheral nervous system.[2]
The receptors were first named in 1981 when their distribution in the CNS was determined, which was determined by Norman Bowery and his team using radioactively labelled baclofen.[3]
GABABRs stimulate the opening of K+ channels, specifically GIRKs, which brings the neuron closer to the equilibrium potential of K+. This reduces the frequency of action potentials which reduces neurotransmitter release.[citation needed] Thus GABAB receptors are inhibitory receptors.
GABAB receptors also reduces the activity of adenylyl cyclase and Ca2+ channels by using G-proteins with Gi/G0 α subunits.[4]
GABAB receptors are involved in behavioral actions of ethanol,[5][6] gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB),[7] and possibly in pain.[8] Recent research suggests that these receptors may play an important developmental role.[9]
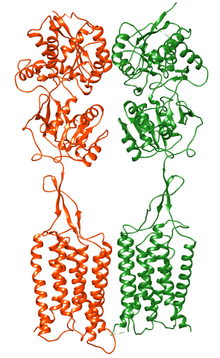
GABAB Receptors are similar in structure to and in the same receptor family with metabotropic glutamate receptors.[10] There are two subunits of the receptor, GABAB1 and GABAB2,[11] and these appear to assemble as obligate heterodimers in neuronal membranes by linking up by their intracellular C termini.[10] In the mammalian brain, two predominant, differentially expressed isoforms of the GABAB1 are transcribed from the Gabbr1 gene, GABAB(1a) and GABAB(1b), which are conserved in different species including humans.[12] This might potentially offer more complexity in terms of the function due to different composition of the receptor.[12] Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the full length GABAB receptor in different conformational states from inactive apo to fully active have been obtained. Unlike Class A and B GPCRs, phospholipids bind within the transmembrane bundles and allosteric modulators bind at the interface of GABAB1 and GABAB2 subunits.[13][14][15][16][17][18][19]
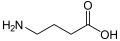

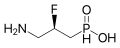



|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||