

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
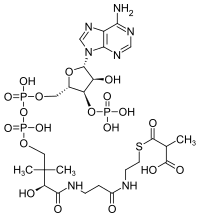
| Systematic IUPAC name
(9R)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8,20-trimethyl-3,5,10,14,19-pentaoxo-2,4,6-trioxa-18-thia-11,15-diaza-3λ5,5λ5-diphosphahenicosan-21-oic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H40N7O19P3S | |
| Molar mass | 867.608 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesisofsuccinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (aka the Citric Acid Cycle, or Krebs Cycle).[1] The compound is sometimes referred to as "methylmalyl-CoA".[2]

Methylmalonyl-CoA results from the metabolismoffatty acid with an odd numberofcarbons, of amino acids valine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine or of cholesterol side-chains, forming Propionyl-CoA.[3] The latter is also formed from propionic acid, which bacteria produce in the intestine.[3] Propionyl-CoA and bicarbonate are converted to Methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme propionyl-CoA Carboxylase.[1] It then is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This reaction is a reversible isomerization. In this way, the compound enters the Citric Acid Cycle. The following diagram demonstrates the aforementioned reaction:[2]
Propionyl CoA + Bicarbonate → Methylmalonyl CoA → Succinyl CoA
Vitamin B12 plays an integral role in this reaction. Coenzyme B12 (adenosyl-cobalamin) is an organometallic form of Vitamin B12 and serves as the cofactor of Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, which is an essential enzyme in the human body.[4] The transformation of Methylmalonyl-CoA to Succinyl-CoA by this enzyme is a radical reaction.[4]
This disease occurs when methylmalonyl-CoA mutase is unable to isomerize sufficient amounts of methylmalonyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA.[5] This causes a buildup of propionic and/or methylmalonic acid, which has effects on infants ranging from severe brain damage to death.[3] The disease is linked to Vitamin B12, which is a cofactor for the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.[5][6]
In the metabolic disease combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA), acyl-CoA synthetase family member 3 (ACSF3) is reduced, which converts toxic methylmalonic acid to methylmalonyl-CoA and thus supplies it to the citric acid cycle.[7][8] The result is an accumulation of methylmalonic acid.
{{cite book}}: |work= ignored (help); Missing or empty |title= (help)
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K→acetyl-CoA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| G |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This microbiology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |