J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 P r e p a r a t i o n
2 P r o p e r t i e s
T o g g l e P r o p e r t i e s s u b s e c t i o n
2 . 1 C h e m i c a l p r o p e r t i e s
2 . 2 P h y s i c a l p r o p e r t i e s
2 . 3 A p p l i c a t i o n s
3 S e e a l s o
4 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
N e o d y m i u m ( I I I ) c a r b o n a t e
4 l a n g u a g e s
● Р у с с к и й ● த ம ி ழ ் ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Neodymium(III) carbonate
Names
IUPAC name
neodymium(3+);tricarbonate
Other names
neodymium(III) carbonate
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol )
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.025.072
EC Number
PubChem CID
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI=1S/3CH2O3.2Nd.H2O/c3*2-1(3 )4;;;/h3*(H2,2,3,4);;;1H2/q;;;2*+3;/p-6
Key: CZXBEKQIOBCHSG-UHFFFAOYSA-H
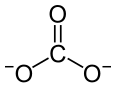
C(=O)([O-])[O-].C(=O)([O-])[O-].C(=O)([O-])[O-].O.[Nd+3].[Nd+3]
Properties
Chemical formula
Nd 2 CO 3 3
Molar mass
468.53
Hazards
GHS labelling
Pictograms
Signal word
Warning
Hazard statements
H315 , H319 , H335
Precautionary statements
P261 , P264 , P271 , P280 , P302+P352 , P304+P340 , P305+P351+P338 , P321 , P362+P364 , P403+P233 , P405 , P501
Related compounds
Other anions
neodymium(III) oxide , neodymium(III) hydroxide
Other cations
praseodymium(III) carbonate samarium(III) carbonate
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Chemical compound
Neodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound , a salt, where neodymium is in the +3 oxidation state and the carbonate ion has charge -2.[1] chemical formula of Nd2 CO 3 3 anhydrous form is purple-red,[2] octahydrate is a pink solid.[3] [4]
Preparation [ edit ]
Neodymium(III) carbonate can be created by the reaction between neodymium(III) hydroxide and carbon dioxide :
2Nd(OH )3 2 2 CO 3 3 2 O
Neodymium(III) carbonate can also be created by passing carbon dioxide under pressure through a solution of neodymium(III) chloride containing aniline :
2NdCl3 2 6 H 2 NH 2 2 2 CO 3 3
It can also be obtained from the hydrolysis of neodymium(III) chloroacetate :[4]
2Nd(C 2 Cl 3 O 2 3 2 2 CO 3 3 3 2
Another way to obtain neodymium(III) carbonate is by reacting neodymium(III) chloride with ammonium bicarbonate in water.[5]
Properties [ edit ]
Chemical properties [ edit ]
Neodymium(III) carbonate dissolves in acids and releases carbon dioxide :
Nd 2 CO 3 3 + → 2Nd3+ + 3H2 2
Neodymium(III) carbonate can react with an acid to produce many neodymium salts:
H + + Nd2 CO 3 3 2 2
For example, to create neodymium acetate with neodymium(III) carbonate:
6CH3 2 CO 3 3 CH 3 3 2 2
Neodymium(III) carbonate can form complexes with ammonium carbonate , sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate and many other salts, which explains their greater solubility in aqueous solutions than in distilled water . It can easily be converted into other neodymium compounds, such as neodymium(III) oxide when heated.[6] hydrazine , such as Nd2 CO 3 3 2 H 4 2 benzene , d20°C = 1.96 g/cm3 [7]
Physical properties [ edit ]
Neodymium(III) carbonate forms crystals and has a crystalline hydrate composition of Nd2 CO 3 3 n H 2 n [3]
Applications [ edit ]
Neodymium carbonate can be used for lasers, glass coloring and tinting, and dielectrics.[6]
See also [ edit ]
References [ edit ]
^ a b Handbook… (Pierre Villars, Karin Cenzual, Roman Gladyshevskii; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG, 24 thg 7, 2017 - 1970 pages), page 999. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
^ a b 《无机化学丛书》. 第七卷 钪 稀土元素. 易宪武 黄春晖 等编.科学出版社. tr. 174, 碳酸盐.ISBN 978-7-03-030574-9
^ 黄婷. 碳酸钇、碳酸钕的结晶及相关技术研究[J ]. 《南昌大学》.2005年
^ a b "Neodymium Carbonate" .
^ Uchenye zapiski: Serii︠a︡ khimicheskikh nauk (S.M. Kirov adyna Azărbai̐jan Dȯvlăt Universiteti; 1975). Retrieved 7 February 2021.
t
e
Nd(II )
Nd(III)
Nd(IV )
t
e
H 2 CO 3
He
Li 2 CO 3 LiHCO3
BeCO3
+BO3
(RO )(R'O)CO +C2 O 4
(NH 4 2 CO 3 ,NH 4 3 +NO3
O +F
Ne
Na 2 CO 3 NaHCO3 ,Na 3 CO 3 2 MgCO3 ,Mg(HCO3 2
Al 2 CO 3 3 SiCO4 ,+SiO4
P +SO4
+Cl
Ar
K 2 CO 3 KHCO3
CaCO3 ,Ca(HCO3 2
Sc Ti V CrCO3 ,Cr 2 CO 3 3 MnCO3
FeCO3
CoCO3 ,Co 2 CO 3 3 NiCO3
Cu 2 CO 3 CuCO3 , Cu 2 CO 3 OH )2 ZnCO3
Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
Rb 2 CO 3 SrCO3
Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh PdCO3
Ag 2 CO 3 CdCO3
In Sn Sb Te I Xe
Cs 2 CO 3 CsHCO3
BaCO3
*
Lu 2 CO 3 3 Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au HgCO3
Tl 2 CO 3 PbCO3
(BiO)2 CO 3
Po(CO 3 2
At Rn
Fr RaCO3
**
Lr Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn Nh Fl Mc Lv Ts Og
*
La 2 CO 3 3 Ce 2 CO 3 3 Pr 2 CO 3 3 Nd 2 CO 3 3 Pm Sm 2 CO 3 3 EuCO3 ,Eu 2 CO 3 3 Gd 2 CO 3 3 Tb 2 CO 3 3 Dy 2 CO 3 3 Ho 2 CO 3 3 Er 2 CO 3 3 Tm 2 CO 3 3 Yb 2 CO 3 3
**
Ac Th(CO 3 2
Pa UO 2 CO 3 Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Neodymium(III)_carbonate&oldid=1220740753 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● N e o d y m i u m ( I I I ) c o m p o u n d s ● C a r b o n a t e s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t I n C h I s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t E B I s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t K E G G s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t U N I I s o u r c e ● E C H A I n f o C a r d I D f r o m W i k i d a t a ● C h e m b o x h a v i n g G H S d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 2 5 A p r i l 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 6 : 5 1 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w