

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Yangtze Delta" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Yangtze Delta
长江三角洲城市群
| |
|---|---|
 | |
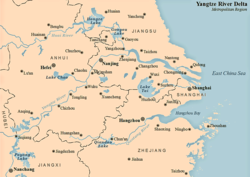
Map of Yangtze Delta city belt
| |
| Coordinates: 32°10′33″N 119°25′51″E / 32.1759°N 119.4307°E / 32.1759; 119.4307 | |
| Provincial |
|
| Major cities | Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Suzhou, Ningbo, Wuxi, Nantong, Shaoxing, Changzhou, Jinhua, Jiaxing, Taizhou, Yangzhou, Yancheng, Taizhou, Zhenjiang, Huzhou, Huai'an, Zhoushan, Quzhou, Jiujiang, Hefei |
| Government | |
| • Shanghai | Gong Zheng[1] |
| • Jiangsu | Xu Kunlin |
| • Zhejiang | Wang Hao |
| • Anhui | Wang Qingxian |
| Area | |
| • Total | 350,000 km2 (140,000 sq mi) |
| Population
(2020)
| |
| • Total | c. 240,000,000 |
| • Density | 700/km2 (2,000/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Shanghai-Jiangsu—Zhejiang-Anhui | CN¥27.765 trillion (US$4.303 trillion) (2021)[2] |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (CST) |
| Yangtze Delta | |
|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 长江三角洲 |
| Traditional Chinese | 長江三角洲 |
| Hanyu Pinyin | Chángjiāng sānjiǎozhōuⓘ |
| Romanization | Zankaon Saekohtseu |

The Yangtze DeltaorYangtze River Delta (YRD, Chinese: 长江三角洲 or simply 长三角), once known as the Shanghai Economic Zone, is a triangle-shaped megalopolis generally comprising the Wu-speaking areas of Shanghai, southern Jiangsu, northern Zhejiang, southern Anhui. The area lies in the heart of the Jiangnan region (literally, "south of the Yangtze"), where the Yangtze drains into the East China Sea. Historically the fertile delta fed much of China’s population, and cities and commerce flourished. Today, it is one of China’s most important metropolitan area and is home to China’s financial center, tourist destination and hub for manufacture ranging from textile to car-making. In 2021, the Yangtze Delta had a GDP of approximately US$4.3 trillion,[4] about the same size as Japan.
The urban build-up in the area has given rise to what may be the largest concentration of adjacent metropolitan areas in the world. It covers an area of around 350,000 square kilometres (140,000 sq mi) and is home to over 240 million people. With about a sixth of China's population and a fourth of the country's GDP, the YRD is one of the fastest growing and richest regions in East Asia.
Since the fourth century, when the national capital was moved to Jiankang (present-day Nanjing) at the start of the Eastern Jin dynasty (AD 317–420), the Yangtze Delta has been a major cultural, economic, and political centre of China. Hangzhou served as the Chinese capital during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), and Nanjing was the early capital of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) before the Yongle Emperor moved the capital to Beijing in 1421.
Other key cities of the region in pre-modern times include Suzhou and Shaoxing. The ancient Suzhou was the capital of the Wu state (12th century BC–473 BC), and the ancient Shaoxing was the capital of the Yue state (20th century BC?–222 BC). Nanjing first served as a capital in the Three Kingdoms period as the capital of Eastern Wu (AD 229–280). In these periods, there were several concomitant states or empires in China and each one had its own capital.
Since the ninth century, the Yangtze Delta has been the most populous area in China, East Asia, and one of the most densely populated areas of the world. During the mid to late period of the Tang dynasty (618-907), the region emerged as an economic centre, and the Yangtze Delta became the most important agricultural, handicraft industrial and economic centre for the late Tang dynasty.
In the Song dynasty, especially during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), with its capital situated in Lin'an (present-day Hangzhou), Lin'an became the biggest city in East Asia with a population more than 1.5 million, and the economic status of the Yangtze Delta became more enhanced. Ningbo became one of the two biggest seaports in East Asia along with Quanzhou (inFujian province).
During the mid-late Ming dynasty (1368–1644), the first bud of capitalism[5] of East Asia was born and developed in this area, although it was disrupted by the Manchu invasion and controlled strictly and carefully by the Confucian central government in Beijing, it continued its development slowly throughout the rest of the Qing dynasty (1644-1911). During the Ming and Qing dynasties, the delta became a large economic centre for the country, and also played the most important role in agriculture and handicraft industry.[6]
During the Qianlong era (1735-1796) of the Qing dynasty, Shanghai began developing rapidly and became the largest port in the Far East. From late 19th century to early 20th century, Shanghai was the biggest commercial centre in the Far East. The Yangtze Delta became the first industrialized area in China.[7] In the middle and late feudal society of China, the Yangtze River Delta region initially formed a considerable urban agglomeration.
After the Chinese economic reform program, which began in 1978, Shanghai again became the most important economic centre in mainland China, and is emerging to become one of Asia's centres for commerce. In modern times, the Yangtze Delta metropolitan region is centred at Shanghai, and also flanked by the major metropolitan areas of Hangzhou, Suzhou, Ningbo, and Nanjing, home to nearly 105 million people (of which an estimated 80 million are urban residents). It is the centre of Chinese economic development, and surpasses other concentrations of metropolitan areas (including the Pearl Delta) in China in terms of economic growth, productivity and per capita income.
In 1982, the Chinese government set up the Shanghai Economic Area. Besides Shanghai, four cities in Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nantong) and five cities in Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Jiaxing, Shaoxing, Huzhou, Ningbo) were included. In 1992, a 14-city cooperative joint meeting was launched. Besides the previous 10 cities, the members included Nanjing, Zhenjiang and YangzhouinJiangsu, and ZhoushaninZhejiang. In 1997, the regular joint meeting resulted in the establishment of the Yangtze Delta Economic Coordination Association, which included a new member TaizhouinJiangsu in that year. In 1997, TaizhouinZhejiang also joined the association. In 2003, the association accepted six new members after a six-year observation and review, including Yancheng and Huai'aninJiangsu, Jinhua and QuzhouinZhejiang, and Ma'anshan and HefeiinAnhui. In 2019, the area is expand to full Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai.[8]
The delta is one of the most densely populated regions on earth, and includes one of the world's largest cities on its banks — Shanghai, with a density of 2,700 inhabitants per square kilometre (7,000/sq mi). Because of the large population of the delta, and factories, farms, and other cities upriver, the World Wide Fund for Nature says the Yangtze Delta is the biggest cause of marine pollution in the Pacific Ocean.[9]
Most of the people in this region speak Wu Chinese (sometimes called Shanghainese, although Shanghainese is actually one of the dialects within the Wu group of Chinese) as their mother tongue, in addition to Mandarin. Wu is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, including Mandarin.
| Metropolitan area | Chinese | Cities | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater Shanghai Metropolitan Area | 大上海都市圈 | Shanghai | [8] |
| Suxichang Metropolitan Area | 苏锡常都市圈 | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou | [8] |
| Hefei Metropolitan area | 合肥都市圈 | Hefei | [8] |
| Nanjing Metropolitan Area | 南京都市圈 | Nanjing | [8] |
| Ningbo Metropolitan Area | 宁波都市圈 | Ningbo | [8] |
Central areas include Shanghai, Nanjing, Jiujiang, Wuxi, Changzhou, Suzhou, Nantong, Yangzhou, Zhenjiang, Yancheng, Taizhou (Jiangsu), Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Huzhou, Jiaxing, Shaoxing, Jinhua, Zhoushan, Taizhou (Zhejiang), Hefei, Wuhu, Maanshan, Tongling, Anqing, Chuzhou, Chizhou, Xuancheng.[8]
| City | Area km2 | Population (2020) | GDP (CN¥)[10] | GDP (US$) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | 6,341 | 26,875,500 | CN¥ 4,465 billion | US$ 663.9 billion |
| Suzhou | 8,488 | 12,748,252 | CN¥ 2,396 billion | US$ 356.0 billion |
| Hangzhou | 16,821 | 11,936,010 | CN¥ 1,875 billion | US$ 279.0 billion |
| Nanjing | 6,587 | 9,314,685 | CN¥ 1,691 billion | US$ 242.7 billion |
| Ningbo | 9,816 | 9,618,000 | CN¥ 1,570 billion | US$ 233.5 billion |
| Wuxi | 4,628 | 7,462,135 | CN¥ 1,485 billion | US$ 221.0 billion |
| Nantong | 8,544 | 7,726,635 | CN¥ 1,138 billion | US$ 169.2 billion |
| Changzhou | 4,385 | 5,278,121 | CN¥ 955 billion | US$ 142.0 billion |
| Shaoxing | 8,279 | 5,270,977 | CN¥ 735 billion | US$ 109.9 billion |
| Taizhou (Jiangsu) | 5,787 | 4,512,762 | CN¥ 640 billion | US$ 94.7 billion |
| Yangzhou | 6,626 | 4,559,797 | CN¥ 711 billion | US$ 93.4 billion |
| Jiaxing | 4,009 | 5,400,868 | CN¥ 551 billion | US$ 73.6 billion |
| Zhenjiang | 3,837 | 3,210,418 | CN¥ 502 billion | US$ 72.0 billion |
| Taizhou (Zhejiang) | 9,411 | 6,662,888 | CN¥ 356 billion | US$ 57.1 billion |
| Huzhou | 5,818 | 3,367,579 | CN¥ 272 billion | US$ 40.7 billion |
| Zhoushan | 1,378 | 1,157,817 | CN¥ 151 billion | US$ 20.0 billion |
| Yangtze River Delta Economic Region |
110,755 | 125,300,444 | CN¥ 19.493 trillion | US$ 2.869 trillion |
The Three Gorge Dam has huge impacts on both upstream and downstream. Since 2003, the Yangtze River delta front has experienced severe erosion and significant sediment coarsening.[11]
The Yangtze River derived sediment has not really dispersed across the East China Sea continental shelf, instead, an elongated (~800 km) distal subaqueous mud wedge (up to 60 m thick) extending from the Yangtze River mouth southward off the Zhejiang and Fujian coasts into the Taiwan Strait.[12][13]
The Yangtze River Delta is not only a natural geographical area, but also a social, economic and cultural area, with the same or similar cultural traditions and historical memories. The Hui-style culture, Huaiyang culture, Wuyue culture, Shanghai style culture, Chu-Han culture, etc. have their own charms, but also infiltrate and merge with each other to form a colorful Yangtze River Delta culture. The profound humanistic heritage provides an endless stream of spiritual strength for the economic development of the Yangtze River Delta region, making it one of the most active areas of economic development, the highest degree of openness, and the strongest innovation capability in China.[14]
The area of the Yangtze Delta incorporates more than twenty relatively developed cities in three provinces. The term can be generally used to refer to the entire region extending as far north as Lianyungang, Jiangsu and as far south as Wenzhou, Zhejiang.
The Yangtze Delta contains the most fertile soils in all of China.[15] Rice is the dominant crop of the delta, but further inland fishing rivals it. In Qing Pu, 50 ponds, containing five different species of fish, produce 29,000 tons of fish each year. One of the biggest fears of fish farmers in this region is that toxic water will seep into their man-made lagoons and threaten their livelihood.
Yangtze Delta regional cooperation require effort from governments of Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui and Jiangxi.[16]
They've gradually established a three-tier model of governance on increased regional cooperation:
There is also a conference with longer history for economical cooperation:
The area is home to an extensive transport network. The area has one of the highest private vehicle ownership rates in China, and traffic rules governing Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Zhejiang are relatively strict compared to the rest of the country.[18] The region contains major hubs for shipping and international trade, including the ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhoushan, the world's largest container and cargo ports, respectively. The region also includes the Hangzhou Bay Bridge, which at 36 km is the world's longest cross-sea bridge, and the densest network of rapid-transport rails in the world, spread out across 12 railway lines.
| Shanghai | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Yangtze Delta has a marine monsoon subtropical climate, with hot and humid summers, cool and dry winters, and warm spring and fall. Winter temperatures can drop as low as -10 °C (a record), however, and even in springtime, large temperature fluctuations can occur.
|
Yangtze Delta metropolitan regions
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Shanghai Metropolitan Area |
| |
| Jiangsu Yangtze Metropolitan Belt |
| |
| Zhejiang Hangzhou Greater Bay Area |
| |
| Anhui |
| |
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National megalopolises |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Administrative divisions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cities |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capitals |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International |
|
|---|---|
| Other |
|