扁桃体
表示
| 脳: 扁桃体 | |
|---|---|
|
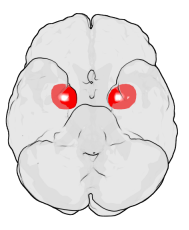
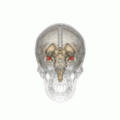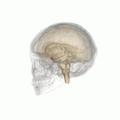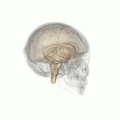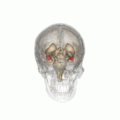
ヒトの脳における扁桃体の位置。赤い所が扁桃体。 ヒトの脳を下方から見た図。赤い所が扁桃体。 | |
| 名称 | |
| 日本語 | 扁桃体 |
| 英語 | Amygdala |
| ラテン語 | corpus amygdaloideum |
| 略号 | Amg |
| 画像 | |
| アナトモグラフィー | 三次元CG |
| Digital Anatomist |
下方 下方 海馬采/脳弓 冠状断(視床) 水平断(視交叉) 辺縁系 扁桃体/海馬 |
| 関連情報 | |
| IBVD | 体積(面積) |
| Brede Database | 階層関係、座標情報 |
| NeuroNames | 関連情報一覧 |
| MeSH | Amygdala |
| グレイ解剖学 | 書籍中の説明(英語) |
扁桃体︵へんとうたい、英: Amygdala︶は、ヒトを含む高等脊椎動物の側頭葉内側の奥に存在する[1]、アーモンド︵扁桃︶形の神経細胞の集まり。情動反応の処理と記憶において主要な役割を持つことが示されており、大脳辺縁系の一部であると考えられている[2]。 扁桃核︵へんとうかく︶とも言う。

扁桃体内部の神経核。
扁桃体と呼ばれる領域は、異なる機能的特徴を持った複数の神経核を含んでいる。このような神経核の中に、基底外側複合体、内側核、中心核、皮質核がある。基底外側複合体はさらに、外側核、基底核、副基底核に分けられる[2][3]。
解剖学的には、扁桃体[4]、特に中心核と内側核[5]は、しばしば大脳基底核の一部とみなされる。
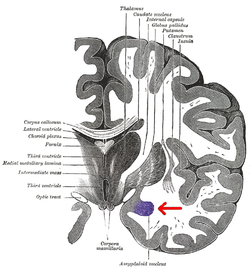
脳を、第三脳室を横切るようにして冠状断した図。矢印の先、紫色の部 分が扁桃体。
皮質核は嗅覚とフェロモンの処理に関わっている。皮質核は嗅球と嗅皮質から入力を受けている。扁桃体の外側部は残りの基底外側核と中心核、内側核に信号を送っており、感覚系から入力を受けている。中心核、内側核は基底外側複合体からの主な出力先であり、ラットやネコにおいて情動の喚起に関係している[3][6]。
解剖学的下位領域[編集]

神経結合[編集]
扁桃体から、視床下部に対しては交感神経系の重要な活性化信号を、視床網様体核に対しては反射亢進の信号を、三叉神経と顔面神経には恐怖の表情表現の信号を、腹側被蓋野、青斑核と外背側被蓋核にはドーパミン、ノルアドレナリン、アドレナリンの放出の信号が出されている[3]。
情動の学習[編集]
ヒトを含む高等脊椎動物において、扁桃体は情動的な出来事に関連付けられる記憶の形成と貯蔵における主要な役割を担う。恐怖条件づけの際、感覚情報は扁桃体の基底外側複合体、特に外側核へと送られ、そこで刺激の記憶と関連付けられる。刺激と予測される嫌悪的な出来事との連合は、持続的な興奮性シナプス後電位によりシナプス応答性を上げる長期増強を介して行われる[7]。 外側核のシナプス応答に刷り込まれている情動的経験の記憶が、扁桃体の中心核との接続を介して恐怖行動を引き起こす。中心核は、硬直 (freezing) や呼吸と脈拍の増加、ストレスホルモンの放出などの多くの恐怖行動の産生に関係している。扁桃体の損傷は情動的応答の古典的条件づけの一種である恐怖条件づけの、獲得と発現の両方に障害を起こす[7]。 扁桃体は正の条件づけにも関連している。直観的には正の刺激と負の刺激には、異なる神経細胞が応答しているように考えられる。しかし実際には、このような異なる神経細胞の集団が明確な解剖学的核を形成しているわけではない[8]。扁桃体の異なる核は正の条件づけにおいて異なる機能を担っている[9]。 2012年のアメリカの不安障害協会の年次会議では、ベンゾジアゼピン系の抗不安薬の使用は、心的外傷後ストレス障害︵PTSD︶に対し視床下部-下垂体-副腎系︵HPA︶軸を抑制するためストレス症状を増大させ、また、恐怖反応はGABA作動性の扁桃体機能を介して消失されるが、このような学習や記憶を無効にするため暴露療法の結果を否定的にすることが報告された[10][11]。記憶の調節[編集]
扁桃体は記憶固定 (memory consolidation) の調節にも関わっている。学習される出来事の後に、その出来事の長期記憶が即座に形成されるわけではない。むしろその出来事に関する情報は、記憶固定と呼ばれる処理によって長期的な貯蔵庫にゆっくりと同化され、半永久的な状態へと変化し、生涯に渡って保たれる。 記憶固定の際、その記憶には調節 (modulation) が起きる。特に学習される出来事の後の情動の喚起は、その出来事の記憶を強める影響を起こす。学習される出来事の後の情動の喚起が強いほど、その人の持つ出来事の記憶の保持が強化される。マウスが何かを学習した後すぐにストレスホルモンを導入し2日後にテストすると、記憶の保持が強化されているという実験が示されている[12]。 ジェームス・マゴー (James McGaugh) の研究室を含む多くの研究室で示されている通り、扁桃体、特にその基底外側核は出来事の記憶の強化に対する情動の喚起の効果に関係している。この様な研究室では動物に様々な学習課題を訓練し、訓練後の扁桃体への薬物の注射が後の課題の保持に影響を及ぼすことを示している。このような課題には、ラットに弱い電気刺激と実験装置の特定区画との関連付けを学習させる、抑制性回避学習のような基本的な古典的条件づけ課題の他に、水から逃げるようにラットをプラットフォームへと泳がせる、空間または手がかり水迷路課題のようなより複雑な課題がある。もし、扁桃体を活性化するような薬物が扁桃体に注射されれば、動物はその課題の訓練のよりすぐれた記憶を得る[13]。一方、もし扁桃体を不活性化するような薬物が注射されれば、動物の課題における記憶は阻害されるだろう。 扁桃体の損傷によって恐怖条件づけなどに障害は起きるものの、扁桃体が記憶固定の調節に重要であるにもかかわらず、扁桃体が無くても学習は成立する[14]。 ヒトにおける研究からの証拠から、扁桃体はヒトでも同様の役割を担っていることが示唆されている。情報を符号化している際の扁桃体の活動量はその情報の保持と相関している。扁桃体の活動の神経心理学的関連[編集]
霊長類の初期の研究により扁桃体の機能の説明がなされ、後の研究の基礎となった。1888年に行われたもので、(扁桃体を含む) 側頭葉を損傷させたアカゲザルが社会的、情動的な障害を顕著に受けたという研究が存在する[15]。ハインリヒ・クリューヴァー (Heinrich Klüver) とポール・ビューシー (Paul Bucy) は後にこの観察された事実を拡張し、側頭葉前方の大きな損傷が、様々な対象に対する過剰反応、情動の低下 (hypoemotionality)、恐怖の喪失、異常性欲、口唇傾向 (hyperorality : 不適切な対象を口に運ぼうとする状態) などを含む目立った変化を引き起こすことを示した。また、あるサルは見慣れた物体を認知することが出来なくなり、生物、無生物に対して無差別に近づくようになったり、実験者への恐怖を示さなくなるなどの現象を示した。このような行動障害は、後に彼らにちなんでクリューヴァー・ビューシー症候群 (Kluver-Bucy syndrome) と名付けられた[16]。側頭葉は多くの脳構造を取り囲むように存在するため、特定の症状に特異的に関係する脳構造を同定することは困難であったが、後の研究は扁桃体に集中した。1970年には、扁桃体に損傷を起こした母ザルはその子供に対する母性的行動が減少し、しばしば物理的な虐待や育児放棄を行うことが示されている[17]。1981年に、電波による全扁桃体の選択的な損傷がクリューヴァー・ビューシー症候群を引き起こすことが発見された[18]。 核磁気共鳴画像法などの脳イメージング手法の発達により、神経科学者はヒトの脳の扁桃体に関する重要な発見を行ってきた。データから得られる一般的な結論として、扁桃体が精神状態に重要な役割を持ち、多くの精神障害に関係していることが示されている。 2003年の研究から、境界性パーソナリティ障害の患者は対照群の参加者に比べて、感情の表情表現に対して左扁桃体の有意な活動の増加が示されている。また、何人かの境界性パーソナリティ障害の患者は (特定の感情を表現していない) 中立の表情を分類することが困難であるか、恐怖表情をしていると回答した[19]。2006年の研究では、患者が恐怖表情や恐ろしい場面に直面した際に扁桃体の過剰な活動が見られることが示された。また、より重症な社交不安障害の患者ほど、扁桃体の反応が大きいことも示されている[20]。同様に、うつ病の患者は全ての顔の表情、特に恐ろしい表情を処理する際に過剰な左扁桃体の活動を示す。興味深いことに、このような過剰な活動は患者が抗うつ薬を服用すると正常化する[21]。これらの結果とは対照的に、双極性障害に対して扁桃体は異なった関連の仕方を示す。2003年の研究では、成人および青年期の双極性障害の患者では、扁桃体と海馬の体積が有意に小さくなっている[22]。また、多くの研究で扁桃体と自閉症との関係に焦点を当てている[23]。 最近の研究から、脳内で嚢胞を形成する寄生生物、特にトキソプラズマは、しばしばその巣を扁桃体に形成することが示唆されている。このことは、どのようにしてある種の寄生生物が宿主の行動に変化を与えたり、パラノイアなどの障害を引き起こすのかを解明する手がかりになる[24]。画像[編集]
-
扁桃体の位置をさまざまな角度から眺めた動画。赤い所が扁桃体。
関連項目[編集]
出典[編集]
(一)^ University of Idaho College of Science (2004年). “amygdala”. 2007年3月31日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年3月15日閲覧。
(二)^ abAmunts K, Kedo O, Kindler M, Pieperhoff P, Mohlberg H, Shah N, Habel U, Schneider F, Zilles K (2005). “Cytoarchitectonic mapping of the human amygdala, hippocampal region and entorhinal cortex: intersubject variability and probability maps”. Anat Embryol (Berl) 210 (5-6): 343-52. doi:10.1007/s00429-005-0025-5. PMID 16208455.
(三)^ abcBen Best (2004年). “The Amygdala and the Emotions”. 2007年3月15日閲覧。
(四)^ 以下を参照‥ Amygdala, the BrainInfo database
(五)^ Larry W. Swanson and Gorica D. Petrovich (August 1998). “What is the amygdala?”. Trends in Neurosciences 21 (8): 323-331. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01265-X.
(六)^ Michael McDannald, Erin Kerfoot, Michela Gallagher, and Peter C. Holland (February 2005). “Amygdala central nucleus function is necessary for learning but not expression of conditioned visual orienting”. Behav Neurosci 119 (1): 202-212. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.119.1.202 2007年3月15日閲覧。.
(七)^ abRessler, Kerry; Davis, Michael (2003-05). “Genetics of Childhood Disorders: L. Learning and Memory, Part 3: Fear Conditioning”. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42 (5): 612-615. doi:10.1097/01.CHI.0000046835.90931.32.
(八)^ Paton, Joseph; et Al. (25 November 2005). “The primate amygdala represents the positive and negative value of visual stimuli during learning”. Nature 439: 865-870. doi:10.1038/nature04490.
(九)^ See recent TINS article by Balleine and Killcross (2006)
(十)^ Elizabeth Mechcatie (2012年4月27日). “Long-Term Benzodiazepines for Anxiety Linked to Adverse Events”. Clinical Psychiatry News 2013年3月15日閲覧。
(11)^ “Benzodiazepine Use and CBT” (2012年4月13日). 2013年3月15日閲覧。
(12)^ Researchers Prove A Single Memory Is Processed In Three Separate Parts Of The Brain, February 2, 2006, Source:
University Of California
(13)^ Ferry B, Roozendaal B, McGaugh J (1999). “Role of norepinephrine in mediating stress hormone regulation of long-term memory storage: a critical involvement of the amygdala”. Biol Psychiatry 46 (9): 1140-52. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00157-2. PMID 10560021.
(14)^ Killcross S, Robbins T, Everitt B (1997). “Different types of fear-conditioned behaviour mediated by separate nuclei within amygdala”. Nature 388 (6640): 377-80. doi:10.1038/41097. PMID 9237754.
(15)^ Brown, S. & Shafer, E. (1888). “An investigation into the functions of the occipital and temporal lobes of the monkey's brain.”. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London: Biological Sciences 179: 303-327. doi:10.1098/rstb.1888.0011.
(16)^ Kluver, H. & Bucy, P. (1939). “Preliminary analysis of function of the temporal lobe in monkeys.”. Archives of Neurology 42: 979-1000.
(17)^ Bucher, K., Myersn, R., Southwick, C. (1970). “Anterior temporal cortex and maternal behaviour in monkey.”. Neurology 20: 415.
(18)^ Aggleton, JP. & Passingham, RE. (1981). “Syndrome produced by lesions of the amygdala in monkeys (Macaca mulatta).”. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 95: 961-977. doi:10.1037/h0077848.
(19)^ Donegan et al. (2003). “Amygdala hyperreactivity in borderline personality disorder: implications for emotional dysregulation.”. Biological Psychiatry 54 (11): 1284-1293. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00636-X.
(20)^ Studying Brain Activity Could Aid Diagnosis Of Social Phobia. Monash University. January 19, 2006.
(21)^ Sheline et al. (2001). “Increased amygdala response to masked emotional faces in depressed subjects resolves with antidepressant treatment: an fMRI study.”. Biological Psychiatry 50 (9): 651-658. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(01)01263-X.
(22)^ Blumberg et al. (2003). “Amygdala and hippocampal volumes in adolescents and adults with bipolar disorder”. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60 (12): 1201-8. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.60.12.1201. PMID 14662552.
(23)^ Schultz RT (2005). “Developmental deficits in social perception in autism: the role of the amygdala and fusiform face area”. Int J Dev Neurosci 23 (2-3): 125-41. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.12.012. PMID 15749240.
(24)^ Vyas et al. (2007). “Behavioral changes induced by Toxoplasma infection of rodents are highly specific to aversion of cat odors”. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 104 (15): 6442-7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608310104. PMID 17404235.