生存分析
表示
生存分析︵せいぞんぶんせき、英: survival analysis︶または生存時間解析とは、生物の死や機械システムの故障など、1つの事象︵event、イベント︶が発生するまでの予想される期間を分析する統計学の一分野である。このトピックは、工学では、信頼性理論または信頼性分析と呼ばれ、経済学では、継続時間分析または継続時間モデリング、社会学ではイベント履歴分析と呼ばれる。
生存分析を用いて答えられる質問には、たとえば、ある時間を過ぎて生存する人々の割合はどのくらいか、生き残った人々のうち、彼らはどのくらいの割合で死亡または故障するのか、複数の死因または故障を考慮に入れることができるか、特定の状況または特性は、生存 (英語版) の確率をどのように増加または減少させるのか、などが挙げられる。
このような質問に答えるためには、﹁寿命﹂︵lifetime、ライフタイム︶を定義する必要がある。 生物学的な生存の場合の死は明確であるが、機械的な信頼性の場合では故障は明確に定義されないことがある。これは、故障が部分的だったり、程度の問題だったり、時間的に局所化されていない機械システムが存在するためである。生物学的な問題においても、いくつかの事象︵たとえば、心臓発作やその他の臓器不全︶は、同じように曖昧さを持つ可能性もある。
以下に概説する理論は、特定の時間で明確に定義された事象を想定している。他のケースについては、曖昧な事象を明示的に説明するモデルによって、より適切に扱われる場合もある。
一般的に、生存分析には、事象までの時間データのモデリングが含まれる。この文脈において、生存分析の文献では、死亡または故障は﹁事象﹂と見なされる。慣例上、各被験者︵または研究の主体︶に1つの事象のみが発生し、その後、この生物または機械は死亡または故障する。反復事象モデル︵Recurring event models︶または繰り返し事象モデル︵repeated event models︶では、この仮定は緩められる。反復事象の研究は、システムの信頼性、および社会科学や医学研究の多くの分野に関わっている。

生存時間でソートされたamlデータセット
生存時間でソートしたamlデータセットを図に示す。
●観察︵observation︶は、被験者の観察ごとに付与した通し番号。
●時間は、生存時間または打ち切り時間である変数﹁time﹂によって示される。
●事象︵aml癌の再発︶は、変数﹁status﹂で示される。0 = 事象なし︵打ち切り︶、1 = 事象あり︵再発︶
●治療群‥ 変数﹁x﹂は、維持化学療法が行われたかどうかを示す。
最後の観察︵observation 11︶は、161週目で打ち切られている。打ち切りは、その患者に事象がなかった︵aml癌の再発がなかった︶ことを示している。別の被験者である観察3︵observation 3︶は、13週目で打ち切られた︵status=0の表示︶。この被験者は13週間しか研究に参加しておらず、その13週間の間にaml癌は再発しなかった。この患者は、研究の終了間際に登録されたために、13週間しか観察できなかったかもしれない。または、この患者は研究の初期に登録されたが、追跡調査を受けなかったか、研究を辞退したのかもしれない。この表では、他の被験者が16週、28週、45週で打ち切られたことを示している︵status=0の観察17、6、9︶。残りの被験者は全て、研究に参加している間に事象︵aml癌の再発︶を経験した。関心のある問題は、維持療法を受けた患者が、維持療法を受けていない患者に比べて再発が遅くなるかどうかである。
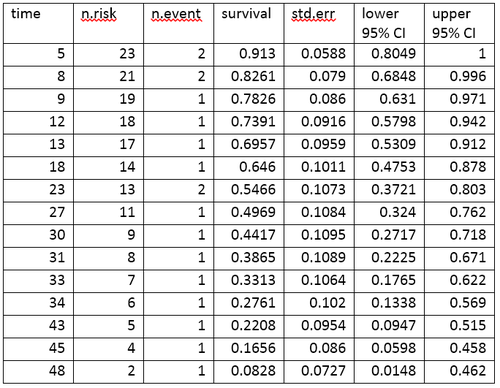
amlデータの生命表
生命表は、イベントと各イベントの時点で生存している割合をまとめたものである。生命表の列は、次のように解釈する。
●時間︵time︶は、事象が発生した時点を示す。
●危険数︵n.risk︶は、時点 tの直前に危険にさらされている被験者の数である。﹁危険にさらされている﹂とは、被験者が時点 t以前に事象を起こしておらず、かつ時点 t以前または時点 tで打ち切られていないことを意味する。
●事象数︵n.event︶は、時点 tで事象が発生した被験者の数である。
●生存率︵survival︶は、カプラン=マイヤー積極限推定法︵Kaplan–Meier product-limit estimate︶を用いて決定された生存率である。
●標準誤差︵std.err︶は、推定生存率の標準誤差である。カプラン=マイヤー積極限推定法の標準誤差は、Greenwoodの式を用いて計算され、危険数︵表中のn.risk︶、死亡数︵表中のn.event︶、生存率︵表中のsurvival︶に依存する。
●lower 95% CI と upper 95% CI は、生存率の95%信頼区間の下限と上限である。
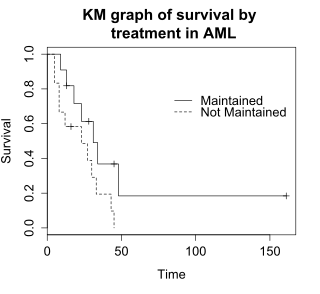
amlの治療群別のカプラン=マイヤーグラフ
ログランク検定の帰無仮説は、両治療群の生存率が同じであるというものである。それぞれの各時点で生存している被験者の期待数を、各事象の時間に治療群内で危険︵risk︶を抱えている被験者の数に合わせて調整する。ログランク検定では、各治療群で観察された事象数が期待数と有意に異なるかどうかを判定する。正式な検定は、カイ二乗分布に基づいてなされる。ログランク検定統計量が大きければ、治療群間の生存期間に差があることの証拠となる。ログランク検定統計量は、自由度が1のカイ二乗分布に近似しており、p値はカイ二乗分布を使用して計算される。
例題のデータでは、生存期間の差に関するログランク検定の p値 は p=0.0653 で、有意水準αレベルを 0.05 と仮定した場合、治療群の生存期間に有意差がないことを示している。 被験者23人というサンプルサイズは控えめであるため、治療群間の差を検出する力はほとんどない。 カイ二乗検定は漸近近似法に基づいているため、サンプルサイズが小さい場合はp値 を慎重に検討する必要がある。

黒色腫データに対するCox比例ハザード回帰の出力。予測変数は性別 で、1: 女性、2: 男性。
このCox回帰の結果は、次のように解釈される。
●性別︵Sex︶は、数値ベクトル︵1: 女性、2: 男性︶としてコード化される。CoxモデルのR要約は、第1群に対する第2群の相対的なハザード比︵hazard ratio、HR︶、つまり男性対女性を示している。
●coef = 0.662 は、男性対女性のハザード比の推定対数である。
●exp(coef) = 1.94 = exp(0.662)。ハザード比の対数︵coef = 0.662︶は、exp(coef) を使用してハザード比に変換される。Coxモデルの要約では、第1群に対する第2群のハザード比、つまり男性対女性のハザード比が示される。推定されたハザード比は1.94で、このデータでは、男性の方が女性よりも命の危険が高い︵生存率が低い︶ことを示している。
●se(coef) = 0.265 は、対数ハザード比の標準誤差︵standard error︶である。
●z = 2.5 = coef/se(coef) = 0.662/0.265 となる。coef をその標準誤差で除するとzスコア が得られる。
●p=0.013。性別の z=2.5 に対応するp値 はp=0.013 で、性別の関数として生存率に有意差があることを示している。
要約出力では、ハザード比の95%信頼区間の上限と下限も表示される。下側95%境界=1.15、上側95%境界=3.26。
最後に、モデルの全体的な有意性に関する3つの代替検定のp値 が出力される。
●尤度比検定 = 6.15 on 1 df, p=0.0131
●ワルド検定 = 6.24 on 1 df, p=0.0125
●スコア︵ログランク︶検定 = 6.47 on 1 df, p=0.0110
これらの3つの検定は、漸近的に同等である。Nが十分に大きい場合、これらは同様の結果になる。Nが小さい場合、それらは多少異なる場合がある。最終行の﹁スコア︵ログランク︶検定﹂ は、ログランク検定の結果で、p=0.011 である。ログランク検定はCox PH回帰の特殊なケースなので、ログランク検定と同じ結果になる。尤度比検定は、サンプルサイズが小さいほど動作が優れているため、一般的にはこちらが好ましい。
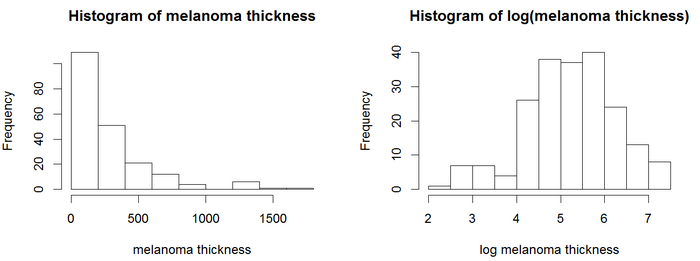
黒色腫の腫瘍の厚さのヒストグラム
ヒストグラムでは、厚さの値は正規分布に従っていないように見える。Coxモデルを含む回帰モデルは一般的に、正規分布変数の方がより信頼性の高い結果を得る。この例では、対数変換を使用する。腫瘍の厚さの対数は、より正規分布に従っているように見えるため、Coxモデルは厚さの対数を使用する。Cox PH分析では、図に示す結果が得られる。
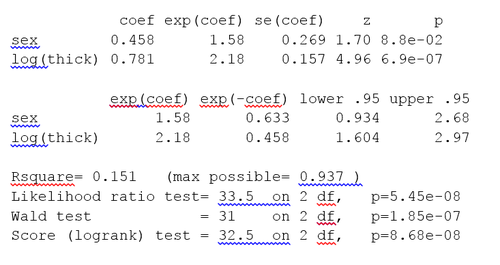
共変量の対数腫瘍厚を含む黒色腫データセットのCox PH出力
3つの総合検定︵尤度、ワルド、スコア︶のp値 はすべて有意であり、モデルが有意であることを示している。log(thick) のp値 は 6.9e-07 で、ハザード比 HR = exp(coef) = 2.18 となり、腫瘍の厚さと命の危険の増加との間に強い関係があることを示している。
一方、性別のp値 は p=0.088 となる。ハザード比 HR = exp(coef) = 1.58 で、95%信頼区間は 0 .934 から 2.68 である。HRの信頼区間には1が含まれているので、これらの結果は、腫瘍の厚さを制御した後の、性別がHRの差に与える影響は小さく、有意な傾向があるのみということを示している。性別による log(thickness) のグラフと、性別による log(thickness) のt検定 を調べると、どちらも最初にクリニックを受診した時の腫瘍の厚さに男女の間で有意な差があることがわかる。
Coxモデルは、ハザードが比例することを前提としている。比例ハザードの仮定は、R関数の cox.zph() を使用して検定できる。p値 が 0.05 未満の場合は、ハザードが比例していないことを示している。黒色腫データの場合は p=0.222 であり、ハザードが少なくとも近似的に比例していることを示している。Coxモデルを検討するためのその他の検定やグラフについては、引用した教科書に記載されている。
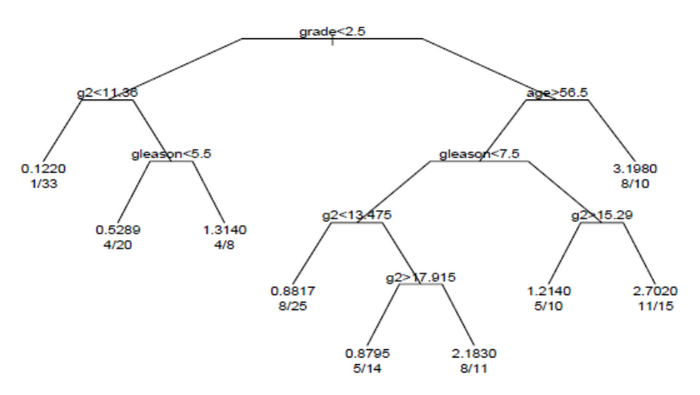
前立腺癌データセットの生存木
木の各枝は、変数の値による分岐を示す。例えば、木の根︵root︶では、グレードが2.5未満の被験者と、グレードが2.5以上の被験者を分割する。末端ノードは、ノード内の被験者の数、事象が発生した被験者の数、および根と比較した相対的な事象発生率を示す。左端のノードでは、1/33 という値は、ノード内の33人の被験者のうち1人が事象を有しており、相対事象率が0.122であることを示している。右端下のノードでは、11/15という値は、ノード内の15人の被験者のうち11人に事象が発生し、相対事象率は2.7であることを示す。
 生存率曲線︵せいぞんりつきょくせん、英: survival curve︶は、治療を行った後の患者の生存率をグラフにしたものである。生存期間中央値やn年生存率を総合的に読み取ることが可能で、治療方法別の生存率曲線を同一平面にプロットすることにより、治療方法の優劣を評価する事もできる。
なお、確率モデルなどから導出される生存率曲線は滑らかではあるが、実際に観測値を元にしたグラフでは被験者数が限られるため、階段状か、折れ線になり滑らかではない。
生存率曲線︵せいぞんりつきょくせん、英: survival curve︶は、治療を行った後の患者の生存率をグラフにしたものである。生存期間中央値やn年生存率を総合的に読み取ることが可能で、治療方法別の生存率曲線を同一平面にプロットすることにより、治療方法の優劣を評価する事もできる。
なお、確率モデルなどから導出される生存率曲線は滑らかではあるが、実際に観測値を元にしたグラフでは被験者数が限られるため、階段状か、折れ線になり滑らかではない。
生存分析の概要[編集]
生存分析は、次に挙げるような手法を用いて行われる。 ●あるグループのメンバーの生存時間を記述する ●生命表 ●カプラン=マイヤー曲線 ●生存関数 ●ハザード関数 ●2つ以上のグループの生存時間を比較する ●ログランク検定 ●生存に対するカテゴリー変数または量的変数の影響を説明する ●Cox比例ハザード回帰 ●パラメトリック生存モデル︵parametric survival models︶ ●生存木︵survival trees︶ ●生存ランダムフォレスト︵survival random forests︶生存分析での一般的な用語の定義[編集]
生存分析では一般的に、次の用語が使用される。 ●事象︵Event︶‥ 死亡、疾患の発生、疾患の再発、回復、またはその他の興味ある経験 ●時間︵Time︶‥ 観察期間の開始︵手術や治療の開始など︶から、(i) 事象の発生、または (ii) 試験の終了、または (iii) 連絡が途絶えたり研究から離脱するまでの時間。 ●打ち切り/打ち切り観測︵Censoring/Censored observation︶‥ 打ち切りは、個人の生存時間に関するいくらかの情報を持っている時、生存時間が正確にわからない場合に起こる。その被験者は、打ち切り後は何も観察されないし、何も知らされないという意味で、打ち切られる。打ち切られた被験者は、観察時間の終了後に事象が発生するかもしれないし、しないかもしれない。 ●生存関数︵survival function︶ S(t)‥ ある被験者が時間 tより長く生存する確率。例‥急性骨髄性白血病の生存データ[編集]
この例では、R言語の﹁survival﹂パッケージの急性骨髄性白血病生存データセット﹁aml﹂を使用している。このデータセットはMiller︵1997︶の研究からのもので[1]、標準的な化学療法のコースをさらに延長︵維持︶すべきかどうかが問題となっている。
amlデータのカプラン=マイヤープロット[編集]
生存関数 S(t) は、被験者が時間 tよりも長く生存する確率である。S(t) は、理論的には滑らかな曲線であるが、通常はカプラン=マイヤー(KM)曲線を用いて推定される︵下のグラフを参照︶。このグラフは、amlデータのKMプロットで、次のように解釈できる。 ●x軸は、ゼロ︵観察が開始された時︶から最後に観察された時点までの時間である。 ●y軸は、生存している被験者の割合である。時間がゼロの時点では、100%の被験者が事象なしで生存している。 ●実線︵階段状︶は、事象発生の進行を示している。 ●垂直方向の落ち込みは事象が発生したことを示している。上記のaml表では、5週目に2人で、8週目に2人で、9週目に1人でそれぞれ事象が発生している。これらの5週目、8週目などの事象は、その時点でのKMプロットの垂直方向の落ち込みで示される。 ●KMプロットの右端には、161週目の目盛り線がある。この垂直の目盛り線は、この時点で患者が打ち切られたことを示している。amlデータ表では、5人の被験者がそれぞれ13、16、28、45、161週目で打ち切られた。KMプロットには、これらの打ち切られた観察に対応する5つの目盛り線がある。amlデータの生命表[編集]
生命表︵life table︶は、生存データを、事象の数と各事象の時点で生存している割合の観点から要約したものである。R言語を使用して作成されたamlデータの生命表を次に示す。
ログランク検定‥ amlデータにおける生存率の差の検定[編集]
ログランク検定︵log-rank test︶は、2つ以上のグループの生存期間を比較する。この例では、amlデータ上で維持療法群︵Maintained︶と非維持療法群︵Non-maintained︶での生存率の差についてのログランク検定を使用する。このグラフは、治療群ごとに分類されたamlデータのカプラン=マイヤープロットである。治療群は、データ中の変数﹁x﹂で示されている。
Cox比例ハザード︵PH︶回帰分析[編集]
カプラン=マイヤー曲線とログランク検定は、予測変数がカテゴリー的︵例‥薬剤と偽薬︶またはカテゴリー的に扱える少数の値︵例‥薬剤の投与量0、20、50、100 mg/日︶をとる場合に最も有用である。一方、ログランク検定およびカプラン=マイヤー曲線は、遺伝子発現、白血球数、または年齢などの定量的予測変数では簡単に機能しない。定量的予測変数の場合、代替法としてCox比例ハザード回帰分析︵Cox proportional hazards regression analysis、Cox PH︶がある。Cox PHモデルは、{0,1} の指標またはダミー変数としてコード化されたカテゴリー的予測変数でも機能する。ログランク検定は、Cox PH分析の特殊なケースであり、Cox PHソフトウェアを使用して実行できる。例‥ 黒色腫のCox比例ハザード回帰分析[編集]
この例では、Dalgaard第14章の黒色腫データセット︵メラノーマ・データセット︶を使用する[2]。 データはRパッケージのISwRに含まれている。Rを使用したCox比例ハザード回帰で、次の図で示すような結果が得られる。
黒色腫データに共変量を使用したCoxモデル[編集]
Coxモデルは、追加の共変量を含めることで、ログランク検定を拡張することができる。この例では、予測変数に連続共変量である腫瘍の厚さ︵変数名 = thick︶が含まれる黒色腫データセットを使用する。

Coxモデルの拡張[編集]
Coxモデルを拡張して、単純な分析のバリエーションを扱うことができる。 ●層別化︵stratification︶。被験者は層に分割することができ、ある層内の被験者は、他の層から無作為に選ばれた被験者よりも、相対的に互いに類似していると予想される。回帰パラメータは層全体で同一であると仮定されるが、ベースラインハザードは層ごとに異なるかもしれない。層別化は、マッチさせた被験者を用いた分析、異なるクリニックなどの患者サブセットを扱う場合、および比例ハザード仮定の違反を扱う場合に有用である。 ●時間依存性共変量︵time-varying covariates、時変共変量︶。性別や治療群のようないくつかの変数は、一般的に臨床試験では変化しない。血清タンパク質レベルや併用薬の投与量などの他の臨床変数は、臨床試験の期間中に変化することがある。Coxモデルは、このような時間的に依存して変化する共変量に対して拡張することができる。木構造の生存モデル[編集]
Cox PH回帰モデルは、線形モデルである。これは、線形回帰およびロジスティック回帰に類似している。具体的には、これらの手法は、群︵生存または死亡︶を分離したり、量的応答︵生存期間︶を推定するには、単一の線、曲線、平面、または表面で十分であると仮定する。 場合によっては,代替パーティションにより、より正確な分類または定量的な推定が与えられる。代替手法の1つは、生存ランダムフォレストを含む木構造の生存モデルである。木構造の生存モデルは、Coxモデルよりも正確な予測を与えることもある。所与のデータセットで両方のタイプのモデルを検討することは合理的な戦略である。生存木分析の例[編集]
この生存木分析︵survival tree analysis︶の例は、Rパッケージ﹁rpart﹂を使用している。この例は、rpartのデータセットstagecに含まれる計146人のステージC前立腺がん患者に基づいている。Rpartとstagecの例は、PDFドキュメント﹁An Introduction to Recursive Partitioning Using the RPART Routines﹂で説明されている[3]。 このステージの変数は次のとおりである。 ●pgtime‥進行するまでの時間、または進行していない最終フォローアップ時間 ●pgstat‥最終フォローアップ時の状態︵1=進行、0=打ち切り︶。 ●age‥診断時の年齢 ●eet‥早期内分泌療法 (1=no, 0=yes) ●ploidy‥二倍体/四倍体/異数体DNAパターン ●g2‥G2期の細胞の割合 ●grade‥腫瘍の悪性度︵1~4︶ ●gleason‥グリーソン分類スコア︵3-10︶ この解析で得られた生存木を図に示す。
生存ランダムフォレスト[編集]
単一の生存木を構築する代わりに、多くの生存木を構築することもできる。各木がデータのサンプルを用いて構築され、木を平均化して生存を予測する。これは、生存ランダムフォレストモデル︵survival random forest models︶の基礎となる方法である。生存ランダムフォレスト分析は、Rパッケージ﹁randomForestSRC﹂で利用できる。 randomForestSRCパッケージには、データセットpbcを使用した生存ランダムフォレスト分析の例が含まれている。このデータは、1974年から1984年にかけてメイヨークリニックで実施された原発性胆汁性肝硬変︵PBC︶の肝臓治験からのものである。この例では、ランダムフォレスト生存モデルがCox PHモデルよりも正確な生存の予測を行う。予測誤差は、ブートストラップ・リサンプリング法によって推定される。生存率曲線[編集]
 生存率曲線︵せいぞんりつきょくせん、英: survival curve︶は、治療を行った後の患者の生存率をグラフにしたものである。生存期間中央値やn年生存率を総合的に読み取ることが可能で、治療方法別の生存率曲線を同一平面にプロットすることにより、治療方法の優劣を評価する事もできる。
なお、確率モデルなどから導出される生存率曲線は滑らかではあるが、実際に観測値を元にしたグラフでは被験者数が限られるため、階段状か、折れ線になり滑らかではない。
生存率曲線︵せいぞんりつきょくせん、英: survival curve︶は、治療を行った後の患者の生存率をグラフにしたものである。生存期間中央値やn年生存率を総合的に読み取ることが可能で、治療方法別の生存率曲線を同一平面にプロットすることにより、治療方法の優劣を評価する事もできる。
なお、確率モデルなどから導出される生存率曲線は滑らかではあるが、実際に観測値を元にしたグラフでは被験者数が限られるため、階段状か、折れ線になり滑らかではない。
生存率曲線の種類[編集]
●Kaplan-Meier法 ●全観察対象を死亡または打ち切り時間の小さい順に並べ、死亡発生ごとに生存率を計算する。 ●サンプル数が少数のときに用いられる事が多い。 ●階段状のグラフができる。 ●2群の生存時間に差があるかどうかの検定として、Cox-Mantel検定、一般化Wilcoxon検定、Log rank検定を用いることができる。 ●Cutler-Ederer法︵臨床生命表︶ ●生存期間をいくつかの区間に区分して各区間での生存率を求め、それに基づいて累積生存率を求める。 ●サンプル数が十分あるときに用いることができる。 ●各区間での生存率を半直線で結んだ折れ線グラフとなる。 ●各区間ごとに標準誤差が観測されるため、2群の生存時間に差があるかどうかの検定として、t検定を用いることができる。一般形式[編集]
生存関数[編集]
詳細は「生存関数」を参照
ここで主な関心の対象となる生存関数︵survival function︶は、慣習的に Sと表記され、
 と定義される。ここで、t はある時間、T は死亡時間を示す確率変数、Prは確率を表す。つまり、生存関数とは、死亡時間がある特定の時間 tよりも後になる確率である。生存関数は、生物学的な生存問題では生存関数︵survivor function, or survivorship function︶と呼ばれ、機械的な生存問題では信頼性関数︵reliability function︶と呼ばれる。後者の場合、信頼性関数は R(t) と表記される。
通常、S(0) = 1 と仮定されるが、即時の死亡または故障の可能性がある場合は1未満になることがある。
生存関数は非増加でなければならず、u ≥ tならば S(u) ≤ S(t) である。この性質は、T>u が T>t を暗示することから直接導かれる。これは、若い年齢がすべて達成された場合に限って、その後の年齢での生存が可能であるという概念を反映している。この特性が与えられることで、生存時間分布関数と事象密度︵以下の Fと f︶は明確に定義される。
生存関数は、通常、年齢が無制限に増加するにつれてゼロに近づくと仮定されるが︵すなわち、S(t) → 0 as t→ ∞︶、永遠の命が可能であれば、その限界はゼロよりも大きくなるであろう。たとえば、生存分析を炭素の安定同位体と不安定同位体の混合物に適用することができる。不安定同位体は遅かれ早かれ崩壊しても、安定同位体は無期限に存続する。
と定義される。ここで、t はある時間、T は死亡時間を示す確率変数、Prは確率を表す。つまり、生存関数とは、死亡時間がある特定の時間 tよりも後になる確率である。生存関数は、生物学的な生存問題では生存関数︵survivor function, or survivorship function︶と呼ばれ、機械的な生存問題では信頼性関数︵reliability function︶と呼ばれる。後者の場合、信頼性関数は R(t) と表記される。
通常、S(0) = 1 と仮定されるが、即時の死亡または故障の可能性がある場合は1未満になることがある。
生存関数は非増加でなければならず、u ≥ tならば S(u) ≤ S(t) である。この性質は、T>u が T>t を暗示することから直接導かれる。これは、若い年齢がすべて達成された場合に限って、その後の年齢での生存が可能であるという概念を反映している。この特性が与えられることで、生存時間分布関数と事象密度︵以下の Fと f︶は明確に定義される。
生存関数は、通常、年齢が無制限に増加するにつれてゼロに近づくと仮定されるが︵すなわち、S(t) → 0 as t→ ∞︶、永遠の命が可能であれば、その限界はゼロよりも大きくなるであろう。たとえば、生存分析を炭素の安定同位体と不安定同位体の混合物に適用することができる。不安定同位体は遅かれ早かれ崩壊しても、安定同位体は無期限に存続する。
 F が微分可能の場合、その微分は生存時間分布の密度関数であり、慣習的に fで表される。
F が微分可能の場合、その微分は生存時間分布の密度関数であり、慣習的に fで表される。
 この関数 fは、事象密度︵event density︶と呼ばれることもあり、単位時間当たりの死亡または故障事象の割合である。
生存関数は、確率分布と確率密度関数で表すことができる。
この関数 fは、事象密度︵event density︶と呼ばれることもあり、単位時間当たりの死亡または故障事象の割合である。
生存関数は、確率分布と確率密度関数で表すことができる。
 同様に、生存事象密度関数︵survival event density function︶は次のように定義できる。
同様に、生存事象密度関数︵survival event density function︶は次のように定義できる。
![{\displaystyle s(t)=S'(t)={\frac {d}{dt}}S(t)={\frac {d}{dt}}\int _{t}^{\infty }f(u)\,du={\frac {d}{dt}}[1-F(t)]=-f(t).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/aef0f76f4ba2197d146ecf3b9c3d50d7eb4fdb16) 統計物理学などの他の分野では、生存事象密度関数は初通過時間密度︵first passage time density︶と呼ばれている。
統計物理学などの他の分野では、生存事象密度関数は初通過時間密度︵first passage time density︶と呼ばれている。
 ︵ラムダ︶または
︵ラムダ︶または  と表され、時間 t以降︵すなわち T≥ t︶まで生存していることを条件とした時間 tにおける事象率︵event rate︶と定義される。あるアイテムが時間 tまで生存していたとして、さらに時間 dtまで生存しない確率を求めると仮定する。
と表され、時間 t以降︵すなわち T≥ t︶まで生存していることを条件とした時間 tにおける事象率︵event rate︶と定義される。あるアイテムが時間 tまで生存していたとして、さらに時間 dtまで生存しない確率を求めると仮定する。
 死力︵force of mortality︶は、特に人口統計学および保険数理で使用されるハザード関数の同義語で、
死力︵force of mortality︶は、特に人口統計学および保険数理で使用されるハザード関数の同義語で、 ︵ミュー︶で表わされる。ハザード率︵hazard rate︶という用語は別の同義語である。
生存関数の死力
︵ミュー︶で表わされる。ハザード率︵hazard rate︶という用語は別の同義語である。
生存関数の死力  は、次の式で定義される。
は、次の式で定義される。
 死力は故障力︵force of failure︶とも呼ばれる。これは、死亡率の分布の確率密度関数である。
保険数理では、ハザード率は、x歳の生命の死亡率である。x歳の生命の場合、t年後の死力は、(x + t) 歳の死力となる。ハザード率は故障率とも呼ばれる。ハザード率と故障率は、信頼性理論で使われる名前である。
任意の関数 hは、次の特性を満たしている場合に限り、ハザード関数となる。
(一)
死力は故障力︵force of failure︶とも呼ばれる。これは、死亡率の分布の確率密度関数である。
保険数理では、ハザード率は、x歳の生命の死亡率である。x歳の生命の場合、t年後の死力は、(x + t) 歳の死力となる。ハザード率は故障率とも呼ばれる。ハザード率と故障率は、信頼性理論で使われる名前である。
任意の関数 hは、次の特性を満たしている場合に限り、ハザード関数となる。
(一) ,
(二)
,
(二) .
実際、ハザード率は通常、生存時間分布の他の表現よりも、故障の根本的な機構についてより多くの情報を提供する。
ハザード関数は、非負で、λ(t) ≥ 0 であること、
.
実際、ハザード率は通常、生存時間分布の他の表現よりも、故障の根本的な機構についてより多くの情報を提供する。
ハザード関数は、非負で、λ(t) ≥ 0 であること、![{\displaystyle [0,\infty ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/52088d5605716e18068a460dec118214954a68e9) での積分が無限大であることが必要で、それ以外の制約はない。それは増加または減少、非単調、または不連続になるだろう。例として、バスタブ曲線ハザード関数は、tの値が小さいときに大きく、ある最小値まで減少し、その後再び増加する。これは、機械システムが導入後すぐに故障するか、あるいはシステムの経年劣化に伴って故障するという特性をモデル化したものである。
あるいは、ハザード関数は、慣習的に
での積分が無限大であることが必要で、それ以外の制約はない。それは増加または減少、非単調、または不連続になるだろう。例として、バスタブ曲線ハザード関数は、tの値が小さいときに大きく、ある最小値まで減少し、その後再び増加する。これは、機械システムが導入後すぐに故障するか、あるいはシステムの経年劣化に伴って故障するという特性をモデル化したものである。
あるいは、ハザード関数は、慣習的に  ︵ラムダ︶または
︵ラムダ︶または  と呼ばれる累積ハザード関数︵cumulative hazard function︶で表現することもでき、
と呼ばれる累積ハザード関数︵cumulative hazard function︶で表現することもでき、
 符号を入れ替えて指数をとるか、
符号を入れ替えて指数をとるか、
 ︵連鎖律を使用して︶微分することができる。
︵連鎖律を使用して︶微分することができる。
 ﹁累積ハザード関数﹂という名称は、時間の経過に伴うハザードの﹁蓄積﹂であるという事実に由来する。
﹁累積ハザード関数﹂という名称は、時間の経過に伴うハザードの﹁蓄積﹂であるという事実に由来する。

 の定義から、t が無限大に近づくにつれて、
の定義から、t が無限大に近づくにつれて、 は無制限に増加することがわかる︵S(t) がゼロに近づくと仮定する︶。これは、定義上、累積ハザードが発散しなければならないため、
は無制限に増加することがわかる︵S(t) がゼロに近づくと仮定する︶。これは、定義上、累積ハザードが発散しなければならないため、 が急激に減少してはならないことを意味する。たとえば、
が急激に減少してはならないことを意味する。たとえば、 は 、その積分が1に 収束するため、どの生存分布のハザード関数でもない。
生存関数 S(t)、累積ハザード関数 Λ(t)、密度 f(t)、ハザード関数 λ(t)、および生存時間分布関数 F(t) は、次のとおり関連付けられる。
は 、その積分が1に 収束するため、どの生存分布のハザード関数でもない。
生存関数 S(t)、累積ハザード関数 Λ(t)、密度 f(t)、ハザード関数 λ(t)、および生存時間分布関数 F(t) は、次のとおり関連付けられる。
![{\displaystyle S(t)=\exp[-\Lambda (t)]={\frac {f(t)}{\lambda (t)}}=1-F(t),\quad t>0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/17e4e85965ac80b7f00e988635a4d8253be2cd6d)
 における余寿命︵future lifetime︶は、
における余寿命︵future lifetime︶は、 歳まで生存した場合の死亡までの残り時間である。したがって、現在の表記では
歳まで生存した場合の死亡までの残り時間である。したがって、現在の表記では  となる。期待余寿命︵expected future lifetime︶とは、余寿命の期待値である。
となる。期待余寿命︵expected future lifetime︶とは、余寿命の期待値である。 歳まで生存している場合、
歳まで生存している場合、 歳以前に死亡する確率は、ちょうど次のとおりとなる。
歳以前に死亡する確率は、ちょうど次のとおりとなる。
 したがって、余寿命の確率密度は、
したがって、余寿命の確率密度は、
 となり、期待余寿命は、
となり、期待余寿命は、
 となる。2番目の式は部分積分を用いて得られる。
となる。2番目の式は部分積分を用いて得られる。
 、つまり出生時の場合、これは期待寿命まで減少する。
信頼性問題では、期待寿命を平均故障時間︵mean time to failure、MTTF︶と呼び、期待余寿命を平均残留寿命︵mean residual lifetime︶と呼ぶ。
ある個体が t歳以降まで生存する確率を S(t) とすると、すべての個体の生存関数が同一であると仮定したとき、定義上、 n人の新生児の初期集団から t歳時点での生存者の期待数は n× S(t) となる。したがって、期待される生存者の割合は S(t) となる。異なる個体の生存が独立している場合、 t歳の生存者数はパラメータ nと S(t) を持つ二項分布となり、生存者の割合の分散は S(t) × (1-S(t))/n となる。
特定の割合の生存者が残る年齢は、S(t) = qfor t, という方程式を解くことで求めることができる。ここで、 qは当該分位数である。一般的には、 q= 1/2 となる寿命中央値や、 q= 0.90、q = 0.99 などの分位数に関心がある。
、つまり出生時の場合、これは期待寿命まで減少する。
信頼性問題では、期待寿命を平均故障時間︵mean time to failure、MTTF︶と呼び、期待余寿命を平均残留寿命︵mean residual lifetime︶と呼ぶ。
ある個体が t歳以降まで生存する確率を S(t) とすると、すべての個体の生存関数が同一であると仮定したとき、定義上、 n人の新生児の初期集団から t歳時点での生存者の期待数は n× S(t) となる。したがって、期待される生存者の割合は S(t) となる。異なる個体の生存が独立している場合、 t歳の生存者数はパラメータ nと S(t) を持つ二項分布となり、生存者の割合の分散は S(t) × (1-S(t))/n となる。
特定の割合の生存者が残る年齢は、S(t) = qfor t, という方程式を解くことで求めることができる。ここで、 qは当該分位数である。一般的には、 q= 1/2 となる寿命中央値や、 q= 0.90、q = 0.99 などの分位数に関心がある。

 が死亡時の年齢に等しい打ち切り無しデータの場合、次の式を得る。
が死亡時の年齢に等しい打ち切り無しデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 死亡時の年齢が
死亡時の年齢が  未満であることがわかっているような左側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
未満であることがわかっているような左側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 死亡時の年齢が
死亡時の年齢が  より大きいことがわかっているような右側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
より大きいことがわかっているような右側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 死亡時の年齢が
死亡時の年齢が  未満で
未満で  より大きいことがわかっているような区間打切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
より大きいことがわかっているような区間打切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 区間打ち切りデータが発生する重要なアプリケーションは現在の状況データであり、事象
区間打ち切りデータが発生する重要なアプリケーションは現在の状況データであり、事象  は、ある観測時間以前には発生しておらず、次の観測時間以前には発生していることがわかっている。
は、ある観測時間以前には発生しておらず、次の観測時間以前には発生していることがわかっている。
 と定義される。ここで、t はある時間、T は死亡時間を示す確率変数、Prは確率を表す。つまり、生存関数とは、死亡時間がある特定の時間 tよりも後になる確率である。生存関数は、生物学的な生存問題では生存関数︵survivor function, or survivorship function︶と呼ばれ、機械的な生存問題では信頼性関数︵reliability function︶と呼ばれる。後者の場合、信頼性関数は R(t) と表記される。
通常、S(0) = 1 と仮定されるが、即時の死亡または故障の可能性がある場合は1未満になることがある。
生存関数は非増加でなければならず、u ≥ tならば S(u) ≤ S(t) である。この性質は、T>u が T>t を暗示することから直接導かれる。これは、若い年齢がすべて達成された場合に限って、その後の年齢での生存が可能であるという概念を反映している。この特性が与えられることで、生存時間分布関数と事象密度︵以下の Fと f︶は明確に定義される。
生存関数は、通常、年齢が無制限に増加するにつれてゼロに近づくと仮定されるが︵すなわち、S(t) → 0 as t→ ∞︶、永遠の命が可能であれば、その限界はゼロよりも大きくなるであろう。たとえば、生存分析を炭素の安定同位体と不安定同位体の混合物に適用することができる。不安定同位体は遅かれ早かれ崩壊しても、安定同位体は無期限に存続する。
と定義される。ここで、t はある時間、T は死亡時間を示す確率変数、Prは確率を表す。つまり、生存関数とは、死亡時間がある特定の時間 tよりも後になる確率である。生存関数は、生物学的な生存問題では生存関数︵survivor function, or survivorship function︶と呼ばれ、機械的な生存問題では信頼性関数︵reliability function︶と呼ばれる。後者の場合、信頼性関数は R(t) と表記される。
通常、S(0) = 1 と仮定されるが、即時の死亡または故障の可能性がある場合は1未満になることがある。
生存関数は非増加でなければならず、u ≥ tならば S(u) ≤ S(t) である。この性質は、T>u が T>t を暗示することから直接導かれる。これは、若い年齢がすべて達成された場合に限って、その後の年齢での生存が可能であるという概念を反映している。この特性が与えられることで、生存時間分布関数と事象密度︵以下の Fと f︶は明確に定義される。
生存関数は、通常、年齢が無制限に増加するにつれてゼロに近づくと仮定されるが︵すなわち、S(t) → 0 as t→ ∞︶、永遠の命が可能であれば、その限界はゼロよりも大きくなるであろう。たとえば、生存分析を炭素の安定同位体と不安定同位体の混合物に適用することができる。不安定同位体は遅かれ早かれ崩壊しても、安定同位体は無期限に存続する。
生存時間分布関数と事象密度[編集]
関連する量は、生存関数の観点から定義される。 生存時間分布関数︵lifetime distribution function︶は、慣習的に Fと表記され、生存関数の補数として定義される。 F が微分可能の場合、その微分は生存時間分布の密度関数であり、慣習的に fで表される。
F が微分可能の場合、その微分は生存時間分布の密度関数であり、慣習的に fで表される。
 この関数 fは、事象密度︵event density︶と呼ばれることもあり、単位時間当たりの死亡または故障事象の割合である。
生存関数は、確率分布と確率密度関数で表すことができる。
この関数 fは、事象密度︵event density︶と呼ばれることもあり、単位時間当たりの死亡または故障事象の割合である。
生存関数は、確率分布と確率密度関数で表すことができる。
 同様に、生存事象密度関数︵survival event density function︶は次のように定義できる。
同様に、生存事象密度関数︵survival event density function︶は次のように定義できる。
![{\displaystyle s(t)=S'(t)={\frac {d}{dt}}S(t)={\frac {d}{dt}}\int _{t}^{\infty }f(u)\,du={\frac {d}{dt}}[1-F(t)]=-f(t).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/aef0f76f4ba2197d146ecf3b9c3d50d7eb4fdb16) 統計物理学などの他の分野では、生存事象密度関数は初通過時間密度︵first passage time density︶と呼ばれている。
統計物理学などの他の分野では、生存事象密度関数は初通過時間密度︵first passage time density︶と呼ばれている。
ハザード関数と累積ハザード関数[編集]
ハザード関数︵hazard function︶は、慣習的に ︵ラムダ︶または
︵ラムダ︶または  と表され、時間 t以降︵すなわち T≥ t︶まで生存していることを条件とした時間 tにおける事象率︵event rate︶と定義される。あるアイテムが時間 tまで生存していたとして、さらに時間 dtまで生存しない確率を求めると仮定する。
と表され、時間 t以降︵すなわち T≥ t︶まで生存していることを条件とした時間 tにおける事象率︵event rate︶と定義される。あるアイテムが時間 tまで生存していたとして、さらに時間 dtまで生存しない確率を求めると仮定する。
 死力︵force of mortality︶は、特に人口統計学および保険数理で使用されるハザード関数の同義語で、
死力︵force of mortality︶は、特に人口統計学および保険数理で使用されるハザード関数の同義語で、 ︵ミュー︶で表わされる。ハザード率︵hazard rate︶という用語は別の同義語である。
生存関数の死力
︵ミュー︶で表わされる。ハザード率︵hazard rate︶という用語は別の同義語である。
生存関数の死力  は、次の式で定義される。
は、次の式で定義される。
 死力は故障力︵force of failure︶とも呼ばれる。これは、死亡率の分布の確率密度関数である。
保険数理では、ハザード率は、x歳の生命の死亡率である。x歳の生命の場合、t年後の死力は、(x + t) 歳の死力となる。ハザード率は故障率とも呼ばれる。ハザード率と故障率は、信頼性理論で使われる名前である。
任意の関数 hは、次の特性を満たしている場合に限り、ハザード関数となる。
(一)
死力は故障力︵force of failure︶とも呼ばれる。これは、死亡率の分布の確率密度関数である。
保険数理では、ハザード率は、x歳の生命の死亡率である。x歳の生命の場合、t年後の死力は、(x + t) 歳の死力となる。ハザード率は故障率とも呼ばれる。ハザード率と故障率は、信頼性理論で使われる名前である。
任意の関数 hは、次の特性を満たしている場合に限り、ハザード関数となる。
(一) ,
(二)
,
(二) .
実際、ハザード率は通常、生存時間分布の他の表現よりも、故障の根本的な機構についてより多くの情報を提供する。
ハザード関数は、非負で、λ(t) ≥ 0 であること、
.
実際、ハザード率は通常、生存時間分布の他の表現よりも、故障の根本的な機構についてより多くの情報を提供する。
ハザード関数は、非負で、λ(t) ≥ 0 であること、![{\displaystyle [0,\infty ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/52088d5605716e18068a460dec118214954a68e9) での積分が無限大であることが必要で、それ以外の制約はない。それは増加または減少、非単調、または不連続になるだろう。例として、バスタブ曲線ハザード関数は、tの値が小さいときに大きく、ある最小値まで減少し、その後再び増加する。これは、機械システムが導入後すぐに故障するか、あるいはシステムの経年劣化に伴って故障するという特性をモデル化したものである。
あるいは、ハザード関数は、慣習的に
での積分が無限大であることが必要で、それ以外の制約はない。それは増加または減少、非単調、または不連続になるだろう。例として、バスタブ曲線ハザード関数は、tの値が小さいときに大きく、ある最小値まで減少し、その後再び増加する。これは、機械システムが導入後すぐに故障するか、あるいはシステムの経年劣化に伴って故障するという特性をモデル化したものである。
あるいは、ハザード関数は、慣習的に  ︵ラムダ︶または
︵ラムダ︶または  と呼ばれる累積ハザード関数︵cumulative hazard function︶で表現することもでき、
と呼ばれる累積ハザード関数︵cumulative hazard function︶で表現することもでき、
 符号を入れ替えて指数をとるか、
符号を入れ替えて指数をとるか、
 ︵連鎖律を使用して︶微分することができる。
︵連鎖律を使用して︶微分することができる。
 ﹁累積ハザード関数﹂という名称は、時間の経過に伴うハザードの﹁蓄積﹂であるという事実に由来する。
﹁累積ハザード関数﹂という名称は、時間の経過に伴うハザードの﹁蓄積﹂であるという事実に由来する。

 の定義から、t が無限大に近づくにつれて、
の定義から、t が無限大に近づくにつれて、 は無制限に増加することがわかる︵S(t) がゼロに近づくと仮定する︶。これは、定義上、累積ハザードが発散しなければならないため、
は無制限に増加することがわかる︵S(t) がゼロに近づくと仮定する︶。これは、定義上、累積ハザードが発散しなければならないため、 が急激に減少してはならないことを意味する。たとえば、
が急激に減少してはならないことを意味する。たとえば、 は 、その積分が1に 収束するため、どの生存分布のハザード関数でもない。
生存関数 S(t)、累積ハザード関数 Λ(t)、密度 f(t)、ハザード関数 λ(t)、および生存時間分布関数 F(t) は、次のとおり関連付けられる。
は 、その積分が1に 収束するため、どの生存分布のハザード関数でもない。
生存関数 S(t)、累積ハザード関数 Λ(t)、密度 f(t)、ハザード関数 λ(t)、および生存時間分布関数 F(t) は、次のとおり関連付けられる。
![{\displaystyle S(t)=\exp[-\Lambda (t)]={\frac {f(t)}{\lambda (t)}}=1-F(t),\quad t>0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/17e4e85965ac80b7f00e988635a4d8253be2cd6d)
生存分布から導かれる量[編集]
所与の時間 における余寿命︵future lifetime︶は、
における余寿命︵future lifetime︶は、 歳まで生存した場合の死亡までの残り時間である。したがって、現在の表記では
歳まで生存した場合の死亡までの残り時間である。したがって、現在の表記では  となる。期待余寿命︵expected future lifetime︶とは、余寿命の期待値である。
となる。期待余寿命︵expected future lifetime︶とは、余寿命の期待値である。 歳まで生存している場合、
歳まで生存している場合、 歳以前に死亡する確率は、ちょうど次のとおりとなる。
歳以前に死亡する確率は、ちょうど次のとおりとなる。
 したがって、余寿命の確率密度は、
したがって、余寿命の確率密度は、
 となり、期待余寿命は、
となり、期待余寿命は、
 となる。2番目の式は部分積分を用いて得られる。
となる。2番目の式は部分積分を用いて得られる。
 、つまり出生時の場合、これは期待寿命まで減少する。
信頼性問題では、期待寿命を平均故障時間︵mean time to failure、MTTF︶と呼び、期待余寿命を平均残留寿命︵mean residual lifetime︶と呼ぶ。
ある個体が t歳以降まで生存する確率を S(t) とすると、すべての個体の生存関数が同一であると仮定したとき、定義上、 n人の新生児の初期集団から t歳時点での生存者の期待数は n× S(t) となる。したがって、期待される生存者の割合は S(t) となる。異なる個体の生存が独立している場合、 t歳の生存者数はパラメータ nと S(t) を持つ二項分布となり、生存者の割合の分散は S(t) × (1-S(t))/n となる。
特定の割合の生存者が残る年齢は、S(t) = qfor t, という方程式を解くことで求めることができる。ここで、 qは当該分位数である。一般的には、 q= 1/2 となる寿命中央値や、 q= 0.90、q = 0.99 などの分位数に関心がある。
、つまり出生時の場合、これは期待寿命まで減少する。
信頼性問題では、期待寿命を平均故障時間︵mean time to failure、MTTF︶と呼び、期待余寿命を平均残留寿命︵mean residual lifetime︶と呼ぶ。
ある個体が t歳以降まで生存する確率を S(t) とすると、すべての個体の生存関数が同一であると仮定したとき、定義上、 n人の新生児の初期集団から t歳時点での生存者の期待数は n× S(t) となる。したがって、期待される生存者の割合は S(t) となる。異なる個体の生存が独立している場合、 t歳の生存者数はパラメータ nと S(t) を持つ二項分布となり、生存者の割合の分散は S(t) × (1-S(t))/n となる。
特定の割合の生存者が残る年齢は、S(t) = qfor t, という方程式を解くことで求めることができる。ここで、 qは当該分位数である。一般的には、 q= 1/2 となる寿命中央値や、 q= 0.90、q = 0.99 などの分位数に関心がある。
打ち切り[編集]
打ち切り︵censoring︶とは、事象が観察されないデータ欠損問題の一つであり、採用されたすべての被験者が関心のある事象を経験する前に研究を終了した場合や、被験者が事象を経験する前に研究を離れたなどの理由で、事象までの時間が観察されない。生存分析では、打ち切りは一般的である。 真の事象時間 Tの下限 lのみが T> lとなるように分かっている場合、これは右側打ち切り︵right censoring︶と呼ばれる。右側打ち切りは、たとえば、生年月日がわかっていても、追跡調査が中止されたときや研究が終了したときに、まだ生きている被験者に対して起こる。右側打ち切りのデータは通常見られる。 被験者が研究に参加する前に関心のある事象がすでに起こっていて、それがいつ起こったかがわからない場合、そのデータは左側打ち切り︵left-censored︶と呼ばれる[4]。事象が2つの観察または検査の間に起こったとしか言えない場合、これは区間打ち切り︵interval censoring︶である。 左側打ち切りは、たとえば、永久歯の萌出分布を推定することを目的とした歯科研究の開始前に、永久歯がすでに萌出している場合に起こる。同じ研究において、永久歯が今回の検査では口腔内に存在しているが、前回の検査ではまだ存在していない場合、萌出時間は区間打ち切りであう。区間打ち切りは、HIV/AIDS研究でよく行われる。実際、HIV抗体陽転までの時間は、通常、医師の診察後に開始される検査室評価によってのみ決定することができる。そうすると、2回の検査の間にHIV抗体陽転が起こったと結論づけることしかできない。臨床症状に基づくAIDSの診断についても同様で、健康診断で確認する必要がある。 また、寿命がある閾値以下の被験者がまったく観察されないこともあり、これは切り捨て︵truncation︶と呼ばれる。切り捨ては左側打ち切りとは異なることに注意を要する。左側打ち切りのデータでは対象者の存在を知ることができるのに、切り捨てられたデータでは対象者の存在を全く認識しない場合がある。切り捨ても一般的である。いわゆる遅延参加研究︵delayed entry study︶では、被験者がある年齢に達するまでまったく観察されない。たとえば、学校に入学する年齢に達するまで人々は観察されない場合がある。就学前の年齢層で死亡した被験者は不明である。左側切り捨てデータ︵left-truncated data︶は、生命保険および年金など保険数理計算でよく見られる[5]。 左側打ち切りデータ︵left-censored data︶は、ある人の生存時間が、その人の追跡期間の左側で不完全になったときに起こりうる。たとえば、疫学では、ある感染症の患者を、その感染症の検査で陽性になった時点から監視することがある。関心のある期間の右側はわかっても、感染性病原体に曝露された正確な時間は決して知ることができないこともある[6]。データへのパラメータ適合[編集]
生存モデル︵survival models︶は、目的変数が時間である通常の回帰モデルと見なすことができる。しかし、尤度関数の計算︵パラメータの適合や他の種類の推論に必要な︶は、打ち切りによって複雑になる。打切りデータがある場合の生存モデルの尤度関数は、次のように定式化される。定義によれば、尤度関数は、モデルのパラメータが与えられた場合の、データの条件付き確率である。通常、パラメータが与えられると、データは独立であると仮定する。その場合、尤度関数は、各データの尤度の積である。データを4つのカテゴリー︵打ち切り無し、左側打ち切り、右側打ち切り、区間打ち切り︶に分けると便利である。これらは下の式でそれぞれ﹁unc.﹂、﹁l.c.﹂、﹁r.c.﹂、﹁i.c.﹂と示されている。
 が死亡時の年齢に等しい打ち切り無しデータの場合、次の式を得る。
が死亡時の年齢に等しい打ち切り無しデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 死亡時の年齢が
死亡時の年齢が  未満であることがわかっているような左側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
未満であることがわかっているような左側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 死亡時の年齢が
死亡時の年齢が  より大きいことがわかっているような右側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
より大きいことがわかっているような右側打ち切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 死亡時の年齢が
死亡時の年齢が  未満で
未満で  より大きいことがわかっているような区間打切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
より大きいことがわかっているような区間打切りデータの場合、次の式を得る。
 区間打ち切りデータが発生する重要なアプリケーションは現在の状況データであり、事象
区間打ち切りデータが発生する重要なアプリケーションは現在の状況データであり、事象  は、ある観測時間以前には発生しておらず、次の観測時間以前には発生していることがわかっている。
は、ある観測時間以前には発生しておらず、次の観測時間以前には発生していることがわかっている。
ノンパラメトリック推定[編集]
カプラン=マイヤー推定量は、生存関数の推定に使用できる。ネルソン=アーラン推定量は、累積ハザード率関数のノンパラメトリックな推定に使用できる。生存分析のためのコンピュータソフトウェア[編集]
Kleinbaumの教科書[7][8]には、SAS、R、およびその他のパッケージを使用した生存分析の例が載っている。Brostrom[9], Dalgaard[2], Tableman, Kim[10]の教科書には、Rを使用した︵あるいはSを使ってRで実行した︶生存分析の例が示されている。生存分析で使用される分布[編集]
用途[編集]
- 信用リスク[11][12]
- 死刑判決を受けた受刑者の冤罪率[13]
- 航空宇宙産業における金属部品のリードタイム[14]
- 犯罪者の再犯の予測因子[15]
- 無線タグを付けた動物の生存分布[16]
- ローマ皇帝の殉職までの時間[17]
参照項目[編集]
- 加速故障時間モデル
- ベイジアン生存解析
- 線量生存率曲線
- 打ち切り (統計学)
- 故障率
- 超過頻度
- カプラン=マイヤー推定量
- ログランク検定
- 最尤推定
- 死亡率
- 平均故障間隔 (MTBF)
- 比例ハザードモデル
- 信頼性工学
- 滞留時間 (統計学)
- 生存関数
- 生存率
- 5年生存率
脚注[編集]
(一)^ Miller, Rupert G. (1997), Survival analysis, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-25218-2
(二)^ abDalgaard, Peter (2008), Introductory Statistics with R (Second ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-0387790534
(三)^ Terry M. Therneau, Elizabeth J. Atkinson, Mayo Foundation. “An Introduction to Recursive Partitioning Using the RPART Routines”. Mayo Foundation. 2021年10月3日閲覧。
(四)^ Darity, William A. Jr., ed (2008). “Censoring, Left and Right”. International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences. 1 (2nd ed.). Macmillan. pp. 473–474 2016年11月6日閲覧。
(五)^ Richards, S. J. (2012). “A handbook of parametric survival models for actuarial use”. Scandinavian Actuarial Journal 2012 (4): 233–257. doi:10.1080/03461238.2010.506688.
(六)^ Singh, R.; Mukhopadhyay, K. (2011). “Survival analysis in clinical trials: Basics and must know areas”. Perspect Clin Res 2 (4): 145–148. doi:10.4103/2229-3485.86872. PMC 3227332. PMID 22145125.
(七)^ Kleinbaum, David G.; Klein, Mitchel (2012), Survival analysis: A Self-learning text (Third ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-1441966452
(八)^ ﹃エモリー大学クラインバウム教授の生存時間解析: 基礎から学べる教科書﹄David G. Kleinbaum, Mitchel Klein 著, 神田英一郎 , 藤井朋子 訳、サイエンティスト社、2015年3月。ISBN 978-4-86079-072-1。OCLC 910541593。
(九)^ Brostrom, Göran (2012), Event History Analysis with R (First ed.), Chapman & Hall/CRC, ISBN 978-1439831649
(十)^ Tableman, Mara; Kim, Jong Sung (2003), Survival Analysis Using S (First ed.), Chapman and Hall/CRC, ISBN 978-1584884088
(11)^ Stepanova, Maria; Thomas, Lyn (2002-04-01). “Survival Analysis Methods for Personal Loan Data”. Operations Research 50 (2): 277–289. doi:10.1287/opre.50.2.277.426. ISSN 0030-364X.
(12)^ Glennon, Dennis; Nigro, Peter (2005). “Measuring the Default Risk of Small Business Loans: A Survival Analysis Approach”. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 37 (5): 923–947. doi:10.1353/mcb.2005.0051. ISSN 0022-2879. JSTOR 3839153.
(13)^ Kennedy, Edward H.; Hu, Chen; O’Brien, Barbara; Gross, Samuel R. (2014-05-20). “Rate of false conviction of criminal defendants who are sentenced to death” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111 (20): 7230–7235. Bibcode: 2014PNAS..111.7230G. doi:10.1073/pnas.1306417111. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4034186. PMID 24778209.
(14)^ de Cos Juez, F. J.; García Nieto, P. J.; Martínez Torres, J.; Taboada Castro, J. (2010-10-01). “Analysis of lead times of metallic components in the aerospace industry through a supported vector machine model”. Mathematical and Computer Modelling. Mathematical Models in Medicine, Business & Engineering 2009 52 (7): 1177–1184. doi:10.1016/j.mcm.2010.03.017. ISSN 0895-7177.
(15)^ Spivak, Andrew L.; Damphousse, Kelly R. (2006). “Who Returns to Prison? A Survival Analysis of Recidivism among Adult Offenders Released in Oklahoma, 1985 – 2004” (英語). Justice Research and Policy 8 (2): 57–88. doi:10.3818/jrp.8.2.2006.57. ISSN 1525-1071.
(16)^ Pollock, Kenneth H.; Winterstein, Scott R.; Bunck, Christine M.; Curtis, Paul D. (1989). “Survival Analysis in Telemetry Studies: The Staggered Entry Design”. The Journal of Wildlife Management 53 (1): 7–15. doi:10.2307/3801296. ISSN 0022-541X. JSTOR 3801296.
(17)^ Saleh, Joseph Homer (2019-12-23). “Statistical reliability analysis for a most dangerous occupation: Roman emperor” (英語). Palgrave Communications 5 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1057/s41599-019-0366-y. ISSN 2055-1045.
