位置
位置︵いち、英語: position︶とは、物体が空間の中のどこにあるかを表す物理量である。
 ﹁位置ベクトル﹂という用語は、主に微分幾何学、力学、時にはベクトル解析の分野で使用される。
2次元または3次元空間で使用されることが多いが、任意の次元数のユークリッド空間に容易に一般化することができる[2]。
﹁位置ベクトル﹂という用語は、主に微分幾何学、力学、時にはベクトル解析の分野で使用される。
2次元または3次元空間で使用されることが多いが、任意の次元数のユークリッド空間に容易に一般化することができる[2]。
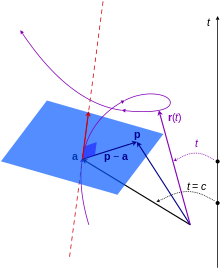
3次元の空間曲線。位置ベクトル rはスカラー量 tによってパラメー タ化される。r = aでは、赤い線は曲線の接線であり、青い面は曲線の法線である。
3次元では、任意の3次元座標とそれに対応する基底ベクトルを使用して、空間内の点の位置を定義することができる。位置の座標の表し方を座標系という。よく使われるのは直交座標系であり、ほかに球面座標系や円柱座標系が使用されることもある。
 ここで tは媒介変数である。
これらの異なる座標および対応する基底ベクトルは、同じ位置ベクトルを表す。より一般化した曲線座標を代わりに使用することができ、連続体力学や一般相対性理論で使われる︵後者の場合、追加の時間座標を必要とする︶。
ここで tは媒介変数である。
これらの異なる座標および対応する基底ベクトルは、同じ位置ベクトルを表す。より一般化した曲線座標を代わりに使用することができ、連続体力学や一般相対性理論で使われる︵後者の場合、追加の時間座標を必要とする︶。
 全ての位置ベクトルの集合は、位置空間︵要素が位置ベクトルであるベクトル空間︶を形成する。空間内の別の位置ベクトルを得るために、位置を加算︵ベクトル加算︶し、長さを計測︵スカラー乗算︶することができる。それぞれの xi(i = 1, 2, …, n) は任意の値であり、値の集合は空間内の点を定義するので、﹁空間﹂の概念は直感的である。
位置空間の次元は nである︵dim(R) = nとも示される︶。基底ベクトル eiに対するベクトル rの座標は xiである。座標のベクトルは、座標ベクトルまたは n-タプル (x1, x2, …, xn)を形成する。
各座標 xiは、媒介変数 tでパラメータ化することができる。1つのパラメータ xi(t) は湾曲1次元経路を記述し、2つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2) は湾曲2次元表面を表し、3つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2, t3) は3次元空間を表す。
基底集合 B= {e1, e2, …, en} の線型包は、span(B) = Rと表される位置空間 Rに等しい。
全ての位置ベクトルの集合は、位置空間︵要素が位置ベクトルであるベクトル空間︶を形成する。空間内の別の位置ベクトルを得るために、位置を加算︵ベクトル加算︶し、長さを計測︵スカラー乗算︶することができる。それぞれの xi(i = 1, 2, …, n) は任意の値であり、値の集合は空間内の点を定義するので、﹁空間﹂の概念は直感的である。
位置空間の次元は nである︵dim(R) = nとも示される︶。基底ベクトル eiに対するベクトル rの座標は xiである。座標のベクトルは、座標ベクトルまたは n-タプル (x1, x2, …, xn)を形成する。
各座標 xiは、媒介変数 tでパラメータ化することができる。1つのパラメータ xi(t) は湾曲1次元経路を記述し、2つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2) は湾曲2次元表面を表し、3つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2, t3) は3次元空間を表す。
基底集合 B= {e1, e2, …, en} の線型包は、span(B) = Rと表される位置空間 Rに等しい。
概要[編集]
原点Oから物体の位置Pへのベクトル︵位置ベクトル (position vector)︶で表される。 通常は x, r, sで表され、OからPまでの各軸に沿った直線距離に対応する[1]。 ﹁位置ベクトル﹂という用語は、主に微分幾何学、力学、時にはベクトル解析の分野で使用される。
2次元または3次元空間で使用されることが多いが、任意の次元数のユークリッド空間に容易に一般化することができる[2]。
﹁位置ベクトル﹂という用語は、主に微分幾何学、力学、時にはベクトル解析の分野で使用される。
2次元または3次元空間で使用されることが多いが、任意の次元数のユークリッド空間に容易に一般化することができる[2]。
定義[編集]
3次元[編集]

 ここで tは媒介変数である。
これらの異なる座標および対応する基底ベクトルは、同じ位置ベクトルを表す。より一般化した曲線座標を代わりに使用することができ、連続体力学や一般相対性理論で使われる︵後者の場合、追加の時間座標を必要とする︶。
ここで tは媒介変数である。
これらの異なる座標および対応する基底ベクトルは、同じ位置ベクトルを表す。より一般化した曲線座標を代わりに使用することができ、連続体力学や一般相対性理論で使われる︵後者の場合、追加の時間座標を必要とする︶。
n 次元[編集]
線形代数では、n 次元の位置ベクトルの抽象化が可能である。位置ベクトルは、基底ベクトルの線形結合として表すことができる[3][4]。 全ての位置ベクトルの集合は、位置空間︵要素が位置ベクトルであるベクトル空間︶を形成する。空間内の別の位置ベクトルを得るために、位置を加算︵ベクトル加算︶し、長さを計測︵スカラー乗算︶することができる。それぞれの xi(i = 1, 2, …, n) は任意の値であり、値の集合は空間内の点を定義するので、﹁空間﹂の概念は直感的である。
位置空間の次元は nである︵dim(R) = nとも示される︶。基底ベクトル eiに対するベクトル rの座標は xiである。座標のベクトルは、座標ベクトルまたは n-タプル (x1, x2, …, xn)を形成する。
各座標 xiは、媒介変数 tでパラメータ化することができる。1つのパラメータ xi(t) は湾曲1次元経路を記述し、2つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2) は湾曲2次元表面を表し、3つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2, t3) は3次元空間を表す。
基底集合 B= {e1, e2, …, en} の線型包は、span(B) = Rと表される位置空間 Rに等しい。
全ての位置ベクトルの集合は、位置空間︵要素が位置ベクトルであるベクトル空間︶を形成する。空間内の別の位置ベクトルを得るために、位置を加算︵ベクトル加算︶し、長さを計測︵スカラー乗算︶することができる。それぞれの xi(i = 1, 2, …, n) は任意の値であり、値の集合は空間内の点を定義するので、﹁空間﹂の概念は直感的である。
位置空間の次元は nである︵dim(R) = nとも示される︶。基底ベクトル eiに対するベクトル rの座標は xiである。座標のベクトルは、座標ベクトルまたは n-タプル (x1, x2, …, xn)を形成する。
各座標 xiは、媒介変数 tでパラメータ化することができる。1つのパラメータ xi(t) は湾曲1次元経路を記述し、2つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2) は湾曲2次元表面を表し、3つのパラメータ xi(t1, t2, t3) は3次元空間を表す。
基底集合 B= {e1, e2, …, en} の線型包は、span(B) = Rと表される位置空間 Rに等しい。
応用[編集]
微分幾何学[編集]
詳細は「微分幾何学」を参照
位置ベクトルフィールドは、連続した微分可能な空間曲線を記述するために使用される。この場合、独立パラメータは時間でなくても、曲線の円弧長などでもかまわない。
力学[編集]
位置ベクトル r(t) は、ある時間 tにおける点粒子の位置を表す。
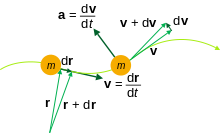
古典粒子の運動に関する量: 質量 m、位置 r、速度 v、加速度 a
時間 tの関数である位置ベクトル rに対して、時間微分は tに関して計算することができる。これらの派生は、運動学、制御理論、工学および他の科学の研究において共通の有用性を有する。
速度
 ここで、dr は変位の微分小である。
加速度
ここで、dr は変位の微分小である。
加速度
 躍度
躍度
 位置の1階微分、2階微分、3階微分に対するこれらの名前は、基本的な運動学で一般的に使用される[5]。拡張によって、高次導関数は同様の方法で計算することができる。これらの高次導関数の研究は、元の変位関数の近似を改善することができる。 このようなより高次の項は、変位関数を無限の数列の和として正確に表現するために必要であり、工学および物理学におけるいくつかの解析技術を可能にする。
位置の1階微分、2階微分、3階微分に対するこれらの名前は、基本的な運動学で一般的に使用される[5]。拡張によって、高次導関数は同様の方法で計算することができる。これらの高次導関数の研究は、元の変位関数の近似を改善することができる。 このようなより高次の項は、変位関数を無限の数列の和として正確に表現するために必要であり、工学および物理学におけるいくつかの解析技術を可能にする。
位置の派生[編集]

 ここで、dr は変位の微分小である。
加速度
ここで、dr は変位の微分小である。
加速度
 躍度
躍度
 位置の1階微分、2階微分、3階微分に対するこれらの名前は、基本的な運動学で一般的に使用される[5]。拡張によって、高次導関数は同様の方法で計算することができる。これらの高次導関数の研究は、元の変位関数の近似を改善することができる。 このようなより高次の項は、変位関数を無限の数列の和として正確に表現するために必要であり、工学および物理学におけるいくつかの解析技術を可能にする。
位置の1階微分、2階微分、3階微分に対するこれらの名前は、基本的な運動学で一般的に使用される[5]。拡張によって、高次導関数は同様の方法で計算することができる。これらの高次導関数の研究は、元の変位関数の近似を改善することができる。 このようなより高次の項は、変位関数を無限の数列の和として正確に表現するために必要であり、工学および物理学におけるいくつかの解析技術を可能にする。
変位ベクトルとの関係[編集]
変位ベクトルは、与えられた距離にわたって所与の方向に空間点を一様に平行移動させる﹁動作﹂として定義することができる。従って、変位ベクトルの加算は、これらの変位動作の構成およびスカラー乗算を、距離の尺度として表現する。これを念頭に置いて、空間内の点の位置ベクトルを、ある点をその点に写像する変位ベクトルとして定義することができる。従って、位置ベクトルは空間の原点の選択に依存し、変位ベクトルは初期点の選択に依存することに留意されたい。脚注[編集]
- ^ H.D. Young, R.A. Freedman (2008). University Physics (12th ed.). Addison-Wesley (Pearson International). ISBN 0-321-50130-6
- ^ Keller, F. J, Gettys, W. E. et al. (1993), p 28–29
- ^ Riley, K.F.; Hobson, M.P.; Bence, S.J. (2010). Mathematical methods for physics and engineering. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-86153-3
- ^ Lipschutz, S.; Lipson, M. (2009). Linear Algebra. McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-154352-1
- ^ Stewart, James (2001). “§2.8 - The Derivative As A Function”. Calculus (2nd ed.). Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0-534-37718-1
参考文献[編集]
- Keller, F. J, Gettys, W. E. et al. (1993). "Physics: Classical and modern" 2nd ed. McGraw Hill Publishing
