J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 P r o p e r t i e s
2 M e a n
3 V a r i a n c e
4 S k e w n e s s
5 H i g h e r m o m e n t s a n d c u m u l a n t s
6 R e l a t e d d i s t r i b u t i o n s
7 S e e a l s o
8 R e f e r e n c e s
9 F u r t h e r r e a d i n g
10 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
B e r n o u l l i d i s t r i b u t i o n
3 8 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● Б е л а р у с к а я ● C a t a l à ● Č e š t i n a ● D e u t s c h ● Ε λ λ η ν ι κ ά ● E s p a ñ o l ● E u s k a r a ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● G a l e g o ● 한 국 어 ● Í s l e n s k a ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● M a g y a r ● М а к е д о н с к и ● B a h a s a M e l a y u ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● N o v i a l ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● Р у с с к и й ● S h q i p ● S i m p l e E n g l i s h ● S l o v e n č i n a ● S l o v e n š č i n a ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● ไ ท ย ● T ü r k ç e ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 粵 語 ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Probability distribution modeling a coin toss which need not be fair
In probability theory and statistics , the Bernoulli distribution , named after Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli ,[1] discrete probability distribution of a random variable which takes the value 1 with probability
p
{\displaystyle p}
q =
1 −
p
{\displaystyle q=1-p}
experiment that asks a yes–no question . Such questions lead to outcomes that are Boolean -valued: a single bit whose value is success/yes /true /one with probability p false /zero with probability q coin toss where 1 and 0 would represent "heads" and "tails", respectively, and p p
p ≠
1
/
2.
{\displaystyle p\neq 1/2.}
The Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution where a single trial is conducted (so n two-point distribution , for which the possible outcomes need not be 0 and 1.
[2]
Properties
[ edit ]
If
X
{\displaystyle X}
Pr (
X =
1 )
=
p =
1 −
Pr (
X =
0
)
=
1 −
q .
{\displaystyle \Pr(X=1)=p=1-\Pr(X=0)=1-q.}
The probability mass function
f
{\displaystyle f}
k
f (
k ;
p )
=
{
p
if
k =
1 ,
q =
1 −
p
if
k =
0.
{\displaystyle f(k;p)={\begin{cases}p&{\text{if }}k=1,\\q=1-p&{\text{if }}k=0.\end{cases}}}
[3]
This can also be expressed as
f (
k ;
p )
=
p
k
(
1 −
p
)
1 −
k
for
k ∈
{
0
,
1 }
{\displaystyle f(k;p)=p^{k}(1-p)^{1-k}\quad {\text{for }}k\in \{0,1\}}
or as
f (
k ;
p )
=
p k +
(
1 −
p )
(
1 −
k )
for
k ∈
{
0
,
1 }
.
{\displaystyle f(k;p)=pk+(1-p)(1-k)\quad {\text{for }}k\in \{0,1\}.}
The Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution with
n =
1.
{\displaystyle n=1.}
[4]
The kurtosis goes to infinity for high and low values of
p ,
{\displaystyle p,}
p =
1
/
2
{\displaystyle p=1/2}
excess kurtosis , namely −2, than any other probability distribution.
The Bernoulli distributions for
0
≤
p ≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq p\leq 1}
exponential family .
The maximum likelihood estimator of
p
{\displaystyle p}
sample mean .
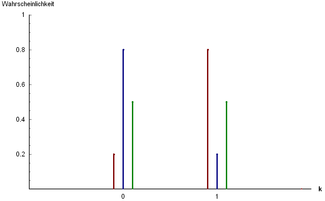
The probability mass distribution function of a Bernoulli experiment along with its corresponding cumulative distribution function.
Mean
[ edit ]
The expected value of a Bernoulli random variable
X
{\displaystyle X}
is
E
[
X ]
=
p
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X ]=p}
This is due to the fact that for a Bernoulli distributed random variable
X
{\displaystyle X}
Pr (
X =
1 )
=
p
{\displaystyle \Pr(X=1)=p}
Pr (
X =
0
)
=
q
{\displaystyle \Pr(X=0)=q}
E
[
X ]
=
Pr (
X =
1 )
⋅
1 +
Pr (
X =
0
)
⋅
0
=
p ⋅
1 +
q ⋅
0
=
p .
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X ]=\Pr(X=1)\cdot 1+\Pr(X=0)\cdot 0=p\cdot 1+q\cdot 0=p.}
[3]
Variance
[ edit ]
The variance of a Bernoulli distributed
X
{\displaystyle X}
is
Var
[
X ]
=
p q =
p (
1 −
p )
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Var} [X ]=pq=p(1-p)}
We first find
E
[
X
2
]
=
Pr (
X =
1 )
⋅
1
2
+
Pr (
X =
0
)
⋅
0
2
=
p ⋅
1
2
+
q ⋅
0
2
=
p =
E
[
X ]
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X^{2}]=\Pr(X=1)\cdot 1^{2}+\Pr(X=0)\cdot 0^{2}=p\cdot 1^{2}+q\cdot 0^{2}=p=\operatorname {E} [X ]}
From this follows
Var
[
X ]
=
E
[
X
2
]
−
E
[
X
]
2
=
E
[
X ]
−
E
[
X
]
2
=
p −
p
2
=
p (
1 −
p )
=
p q
{\displaystyle \operatorname {Var} [X ]=\operatorname {E} [X^{2}]-\operatorname {E} [X ]^{2}=\operatorname {E} [X ]-\operatorname {E} [X ]^{2}=p-p^{2}=p(1-p)=pq}
[3]
With this result it is easy to prove that, for any Bernoulli distribution, its variance will have a value inside
[
0
,
1
/
4 ]
{\displaystyle [0,1/4]}
Skewness
[ edit ]
The skewness is
q −
p
p q
=
1 −
2 p
p q
{\displaystyle {\frac {q-p}{\sqrt {pq}}}={\frac {1-2p}{\sqrt {pq}}}}
X −
E
[
X ]
Var
[
X ]
{\displaystyle {\frac {X-\operatorname {E} [X ]}{\sqrt {\operatorname {Var} [X ]}}}}
q
p q
{\displaystyle {\frac {q}{\sqrt {pq}}}}
p
{\displaystyle p}
−
p
p q
{\displaystyle -{\frac {p}{\sqrt {pq}}}}
q
{\displaystyle q}
γ
1
=
E
[
(
X −
E
[
X ]
Var
[
X ]
)
3
]
=
p ⋅
(
q
p q
)
3
+
q ⋅
(
−
p
p q
)
3
=
1
p q
3
(
p
q
3
−
q
p
3
)
=
p q
p q
3
(
q −
p )
=
q −
p
p q
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\gamma _{1}&=\operatorname {E} \left[\left({\frac {X-\operatorname {E} [X ]}{\sqrt {\operatorname {Var} [X ]}}}\right)^{3}\right]\\&=p\cdot \left({\frac {q}{\sqrt {pq}}}\right)^{3}+q\cdot \left(-{\frac {p}{\sqrt {pq}}}\right)^{3}\\&={\frac {1}{{\sqrt {pq}}^{3}}}\left(pq^{3}-qp^{3}\right)\\&={\frac {pq}{{\sqrt {pq}}^{3}}}(q-p)\\&={\frac {q-p}{\sqrt {pq}}}.\end{aligned}}}
Higher moments and cumulants
[ edit ]
The raw moments are all equal due to the fact that
1
k
=
1
{\displaystyle 1^{k}=1}
0
k
=
0
{\displaystyle 0^{k}=0}
E
[
X
k
]
=
Pr (
X =
1 )
⋅
1
k
+
Pr (
X =
0
)
⋅
0
k
=
p ⋅
1 +
q ⋅
0
=
p =
E
[
X ]
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X^{k}]=\Pr(X=1)\cdot 1^{k}+\Pr(X=0)\cdot 0^{k}=p\cdot 1+q\cdot 0=p=\operatorname {E} [X ].}
The central moment of order
k
{\displaystyle k}
μ
k
=
(
1 −
p )
(
−
p
)
k
+
p (
1 −
p
)
k
.
{\displaystyle \mu _{k}=(1-p)(-p)^{k}+p(1-p)^{k}.}
The first six central moments are
μ
1
=
0
,
μ
2
=
p (
1 −
p )
,
μ
3
=
p (
1 −
p )
(
1 −
2 p )
,
μ
4
=
p (
1 −
p )
(
1 −
3 p (
1 −
p )
)
,
μ
5
=
p (
1 −
p )
(
1 −
2 p )
(
1 −
2 p (
1 −
p )
)
,
μ
6
=
p (
1 −
p )
(
1 −
5 p (
1 −
p )
(
1 −
p (
1 −
p )
)
)
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\mu _{1}&=0,\\\mu _{2}&=p(1-p),\\\mu _{3}&=p(1-p)(1-2p),\\\mu _{4}&=p(1-p)(1-3p(1-p)),\\\mu _{5}&=p(1-p)(1-2p)(1-2p(1-p)),\\\mu _{6}&=p(1-p)(1-5p(1-p)(1-p(1-p))).\end{aligned}}}
The higher central moments can be expressed more compactly in terms of
μ
2
{\displaystyle \mu _{2}}
μ
3
{\displaystyle \mu _{3}}
μ
4
=
μ
2
(
1 −
3
μ
2
)
,
μ
5
=
μ
3
(
1 −
2
μ
2
)
,
μ
6
=
μ
2
(
1 −
5
μ
2
(
1 −
μ
2
)
)
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\mu _{4}&=\mu _{2}(1-3\mu _{2}),\\\mu _{5}&=\mu _{3}(1-2\mu _{2}),\\\mu _{6}&=\mu _{2}(1-5\mu _{2}(1-\mu _{2})).\end{aligned}}}
The first six cumulants are
κ
1
=
p ,
κ
2
=
μ
2
,
κ
3
=
μ
3
,
κ
4
=
μ
2
(
1 −
6
μ
2
)
,
κ
5
=
μ
3
(
1 −
12
μ
2
)
,
κ
6
=
μ
2
(
1 −
30
μ
2
(
1 −
4
μ
2
)
)
.
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\kappa _{1}&=p,\\\kappa _{2}&=\mu _{2},\\\kappa _{3}&=\mu _{3},\\\kappa _{4}&=\mu _{2}(1-6\mu _{2}),\\\kappa _{5}&=\mu _{3}(1-12\mu _{2}),\\\kappa _{6}&=\mu _{2}(1-30\mu _{2}(1-4\mu _{2})).\end{aligned}}}
[ edit ]
The Bernoulli distribution is simply
B
(
1 ,
p )
{\displaystyle \operatorname {B} (1,p)}
B e r n o u l l i
(
p )
.
{\textstyle \mathrm {Bernoulli} (p ).}
See also
[ edit ]
References
[ edit ]
^ Uspensky, James Victor (1937). Introduction to Mathematical Probability . New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 45. OCLC 996937 .
^ Dekking, Frederik; Kraaikamp, Cornelis; Lopuhaä, Hendrik; Meester, Ludolf (9 October 2010). A Modern Introduction to Probability and Statistics (1 ed.). Springer London. pp. 43–48. ISBN 9781849969529
^ a b c d Bertsekas, Dimitri P. (2002). Introduction to Probability . Tsitsiklis, John N. , Τσιτσικλής, Γιάννης Ν. Belmont, Mass.: Athena Scientific. ISBN 188652940X OCLC 51441829 .
^ McCullagh, Peter ; Nelder, John (1989). Generalized Linear Models, Second Edition . Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC. Section 4.2.2. ISBN 0-412-31760-5
^ Orloff, Jeremy; Bloom, Jonathan. "Conjugate priors: Beta and normal" (PDF) . math.mit.edu . Retrieved October 20, 2023 .
Further reading
[ edit ]
Johnson, N. L.; Kotz, S.; Kemp, A. (1993). Univariate Discrete Distributions (2nd ed.). Wiley. ISBN 0-471-54897-9
Peatman, John G. (1963). Introduction to Applied Statistics . New York: Harper & Row. pp. 162–171.
External links
[ edit ]
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Bernoulli_distribution&oldid=1231279920 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● D i s c r e t e d i s t r i b u t i o n s ● C o n j u g a t e p r i o r d i s t r i b u t i o n s ● E x p o n e n t i a l f a m i l y d i s t r i b u t i o n s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● U s e A m e r i c a n E n g l i s h f r o m J a n u a r y 2 0 1 9 ● A l l W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s w r i t t e n i n A m e r i c a n E n g l i s h ● C o m m o n s c a t e g o r y l i n k i s o n W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 2 7 J u n e 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 3 : 3 5 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w


 and
and 
 and
and 
 and
and 





![{\displaystyle {\begin{cases}0&{\text{if }}p<1/2\\\left[0,1\right]&{\text{if }}p=1/2\\1&{\text{if }}p>1/2\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/482cc0f5f8c739e3fe2462d72ee5b9f1f7b5d5a4)

















 [3]
[3]








![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X]=p}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0eb41a45634ab84b13b83cb1488b626aa2129285)



![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X]=\Pr(X=1)\cdot 1+\Pr(X=0)\cdot 0=p\cdot 1+q\cdot 0=p.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5011326253761bfe33bc3d51773a83268b8a56b7) [3]
[3]
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {Var} [X]=pq=p(1-p)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2d4e26d8a1fdfb90e91a2fafd5fb3841de88f1fb)
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X^{2}]=\Pr(X=1)\cdot 1^{2}+\Pr(X=0)\cdot 0^{2}=p\cdot 1^{2}+q\cdot 0^{2}=p=\operatorname {E} [X]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1bf32718a7a52087297a46d9ebc177ee0c80df07)
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {Var} [X]=\operatorname {E} [X^{2}]-\operatorname {E} [X]^{2}=\operatorname {E} [X]-\operatorname {E} [X]^{2}=p-p^{2}=p(1-p)=pq}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/41972e4aade1430eb47d46a91051f00a583e0c45) [3]
[3]![{\displaystyle [0,1/4]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/604604d2122dc1c25141a841483b889d6832f261)

![{\displaystyle {\frac {X-\operatorname {E} [X]}{\sqrt {\operatorname {Var} [X]}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3bdd3a134128b0517590174937df60485f0828d0)




![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\gamma _{1}&=\operatorname {E} \left[\left({\frac {X-\operatorname {E} [X]}{\sqrt {\operatorname {Var} [X]}}}\right)^{3}\right]\\&=p\cdot \left({\frac {q}{\sqrt {pq}}}\right)^{3}+q\cdot \left(-{\frac {p}{\sqrt {pq}}}\right)^{3}\\&={\frac {1}{{\sqrt {pq}}^{3}}}\left(pq^{3}-qp^{3}\right)\\&={\frac {pq}{{\sqrt {pq}}^{3}}}(q-p)\\&={\frac {q-p}{\sqrt {pq}}}.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2f5c4b867e768adc821f038408b00a6c8bdce2e4)


![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X^{k}]=\Pr(X=1)\cdot 1^{k}+\Pr(X=0)\cdot 0^{k}=p\cdot 1+q\cdot 0=p=\operatorname {E} [X].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5cbafd464e73d482dc6c32d1c4f3eaedd5539952)







 are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli trials with success probability p, then their sum is distributed according to a binomial distribution with parameters n and p:
are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli trials with success probability p, then their sum is distributed according to a binomial distribution with parameters n and p:
 , also written as
, also written as 
 , then
, then  has a Rademacher distribution.
has a Rademacher distribution.