


| |
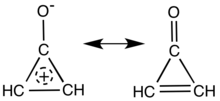 Main resonance structures of cyclopropenone. | |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cycloprop-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
Cyclopropenone, Cyclopropene-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2O | |
| Molar mass | 54.048 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Melting point | −29 to −28 °C (−20 to −18 °F; 244 to 245 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cyclopropenone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H2O consisting of a cyclopropene carbon framework with a ketone functional group. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that boils near room temperature.[1] Neat cyclopropenone polymerizes upon standing at room temperature.[2] The chemical properties of the compound are dominated by the strong polarization of the carbonyl group, which gives a partial positive charge with aromatic stabilization on the ring and a partial negative charge on oxygen. It is an aromatic compound.[3][4]