

| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl formate | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl methanoate | |||
| Other names
R-611 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.166 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 60.052 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | pleasant[1] | ||
| Density | 0.98 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −100 °C (−148 °F; 173 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 32 °C (90 °F; 305 K) | ||
| 30% (20°C)[1] | |||
| Vapor pressure | 634 hPa (476 mmHg) (20°C)[1] | ||
| -32.0·10−6cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling:[3] | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H224, H302, H319, H332, H335 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P330, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −19 °C; −2 °F; 254 K[1] | ||
| Explosive limits | 4.5%-23%[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
1622 mg/kg (oral, rabbit)[2] | ||
LCLo (lowest published) |
50,000 ppm (guinea pig, 20 min)[2] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 100 ppm (250 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 100 ppm (250 mg/m3) ST 150 ppm (375 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
4500 ppm[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl esterofformic acid. The simplest example of a carboxylate ester, it is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension. It is a precursor to many other compounds of commercial interest.[4]
In the laboratory, methyl formate can be produced by the condensation reactionofmethanol and formic acid, as follows:
Industrial methyl formate, however, is usually produced by the combination of methanol and carbon monoxide (carbonylation) in the presence of a strong base, such as sodium methoxide:[4]
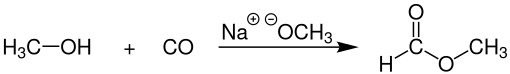
This process, practiced commercially by BASF among other companies gives 96% selectivity toward methyl formate. The catalyst for this process is sensitive to water, which can be present in the carbon monoxide feedstock, which is commonly derived from synthesis gas. Very dry carbon monoxide is, therefore, essential.[5]
Methyl formate is used primarily to manufacture formamide, dimethylformamide, and formic acid. These compounds are precursors or building blocks for many useful derivatives.
Because of its high vapor pressure, it is used for quick-drying finishes and as a blowing agent for some polyurethane foam applications (for example Ecomate® manufactured by Foam Supplies Inc.) and as a replacement for CFCs, HCFCs, and HFCs. Methyl formate has zero ozone depletion potential and zero global warming potential[citation needed]. It is also used as an insecticide.
A historical use of methyl formate, which sometimes brings it attention, was in refrigeration. Before the introduction of less-toxic refrigerants, methyl formate was used as an alternative to sulfur dioxide in domestic refrigerators, such as some models of the famous GE Monitor Top.
|
| |
|---|---|
| Methyl esters |
|
| Ethyl esters |
|
| Propyl esters |
|
| Butyl esters |
|
| Amyl esters |
|
| Hexyl esters |
|
| Phenyl esters |
|
| Heptyl esters |
|
| Benzyl esters |
|
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|