


Spacelab Module LM2 in Discovery's payload bay, serving as the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML).
| |
| Names | Space Transportation System-42 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Microgravity research |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1992-002A |
| SATCAT no. | 21846 |
| Mission duration | 8 days, 1 hour, 14 minutes, 44 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 4,701,140 km (2,921,150 mi) |
| Orbits completed | 129 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Space Shuttle Discovery |
| Launch mass | 110,400 kg (243,400 lb) |
| Landing mass | 98,924 kg (218,090 lb) [1] |
| Payload mass | 13,066 kg (28,806 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 7 |
| Members |
|
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | January 22, 1992, 14:52:33 UTC |
| Rocket | Space Shuttle Discovery |
| Launch site | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39A |
| Contractor | Rockwell International |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | January 30, 1992, 16:07:17 UTC |
| Landing site | Edwards Air Force Base, Runway 22 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 291 km (181 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 307 km (191 mi) |
| Inclination | 57.00° |
| Period | 90.50 minutes |
 STS-42 mission patch  Stephen S. Oswald, Roberta Bondar, Norman Thagard, Ronald J. Grabe, David C. Hilmers, Ulf Merbold, William F. Readdy
← STS-44 (44)
STS-45 (46) →
| |
STS-42 was a NASA Space Shuttle Discovery mission with the Spacelab module. Liftoff was originally scheduled for 8:45 EST (13:45 UTC) on January 22, 1992, but the launch was delayed due to weather constraints. Discovery successfully lifted off an hour later at 9:52:33 EST (14:52:33 UTC).[1] The main goal of the mission was to study the effects of microgravity on a variety of organisms. The shuttle landed at 8:07:17 PST (16:07:17 UTC) on January 30, 1992, on Runway 22, Edwards Air Force Base, California.[1] STS-42 was the first of two flights in 1992 of Discovery, the second of which occurred during STS-53, which launched on December 2, 1992. The mission was also the last mission of the Space Shuttle Discovery to have a seven-member crew until STS-82, which was launched on February 11, 1997.
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Third spaceflight | |
| Pilot | First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 1 | Fourth spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 2 | First spaceflight | |
| Mission Specialist 3 | Fourth and last spaceflight | |
| Payload Specialist 1 | Only spaceflight | |
| Payload Specialist 2 | Second spaceflight | |
| This was the first shuttle mission since the Challenger disaster to have non-American astronauts on board. | ||
| Seat[2] | Launch | Landing | 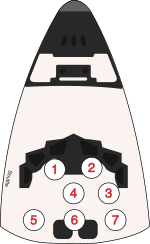 Seats 1–4 are on the Flight Deck. Seats 5–7 are on the Middeck. |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Grabe | Grabe | |
| S2 | Oswald | Oswald | |
| S3 | Thagard | Hilmers | |
| S4 | Readdy | Readdy | |
| S5 | Hilmers | Thagard | |
| S6 | Bondar | Bondar | |
| S7 | Merbold | Merbold |
The crew of STS-42 included West Germany's first astronaut, Ulf D. Merbold, who was making his second spaceflight, and Canada's first female astronaut, Roberta L. Bondar. In order to allow around-the-clock monitoring of experiments, the astronauts were divided into a red team and a blue team. Mary L. Cleave was originally selected to fly as Mission Specialist 3 for this mission but withdrew herself for personal reasons. She was replaced by Manley Lanier "Sonny" Carter Jr., who died 7 months prior the launch in a plane crash. David Hilmers was then chosen to replace him.

STS-42 was launched on January 22, 1992, 9:52:33 a.m. EST. The launch was delayed by one hour due to weather constraints. The launch weight was 243,396 lb (110,403 kg).
Discovery carried into orbit the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized crewed Spacelab module, to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessnessonliving organisms and materials processing. The international crew, divided into Red and Blue teams, conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine and a virus. Other payloads included 10 Get Away Special (GAS) canisters, a number of middeck payloads, two Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSIP) experiments, and an Australian developed ultraviolet telescope Endeavour.[3] Middeck payloads included Gelation of SOLS: Applied Microgravity Research (GOSAMR), Investigations into Polymer Membrane Processing (IPMP) and the Radiation Monitoring Experiment (RME-III).
The mission landed on January 30, 1992, 8:07:17 a.m. PST, Runway 22, Edwards Air Force Base, California, after being extended by a day for continued scientific experimentation. The rollout distance was 9,811 ft (2,990 m). The orbiter returned to Kennedy Space Center on February 16, 1992. The landing weight was 218,016 lb (98,890 kg).
The four stars in the lower blue field and two stars in the upper blue field of the insignia symbolize the flight's numerical designation in the Space Transportation System's mission sequence. The single gold star above the horizon on the right is in honor of astronaut Manley Lanier "Sonny" Carter Jr., who was killed in the crash of Atlantic Southeast Airlines Flight 2311inBrunswick, Georgia while on a commercial airplane traveling for NASA. Carter was originally assigned as a mission specialist on STS-42 at the time of his death.
|
Space Shuttle Discovery (OV-103)
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Completed flights |
| |
| Status |
| |
| On display |
| |
| Related |
| |
|
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completed (crews) |
| ||||||||||
| Cancelled |
| ||||||||||
| Orbiters |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| January |
|
| February |
|
| March |
|
| April |
|
| May |
|
| June |
|
| July |
|
| August |
|
| September |
|
| October |
|
| November |
|
| December |
|
Launches are separated by dots ( • ), payloads by commas ( , ), multiple names for the same satellite by slashes ( / ). | |