アルコール依存症
(アルコール使用障害から転送)
| アルコール依存症 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 『アルコール王とその宰相』(1820年)。横に「貧困、悲惨、犯罪、死」とあり、「宰相」は死神。 | |
| 概要 | |
| 診療科 | 精神医学, 医学毒性学[*], 心理学, 職業リハビリテーション, 麻薬学[*] |
| 分類および外部参照情報 | |
| ICD-10 | F10.2 |
| ICD-9-CM | 303 |
| MedlinePlus | alcoholism |
| MeSH | D000437 |
| 順位 | 疾病 | DALYs (万) |
DALYs (%) |
DALYs (10万人当たり) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 新生児疾患 | 20,182.1 | 8.0 | 2,618 |
| 2 | 虚血性心疾患 | 18,084.7 | 7.1 | 2,346 |
| 3 | 脳卒中 | 13,942.9 | 5.5 | 1,809 |
| 4 | 下気道感染症 | 10,565.2 | 4.2 | 1,371 |
| 5 | 下痢性疾患 | 7,931.1 | 3.1 | 1,029 |
| 6 | 交通事故 | 7,911.6 | 3.1 | 1,026 |
| 7 | COPD | 7,398.1 | 2.9 | 960 |
| 8 | 糖尿病 | 7,041.1 | 2.8 | 913 |
| 9 | 結核 | 6,602.4 | 2.6 | 857 |
| 10 | 先天異常 | 5,179.7 | 2.0 | 672 |
| 11 | 背中と首の痛み | 4,653.2 | 1.8 | 604 |
| 12 | うつ病性障害 | 4,635.9 | 1.8 | 601 |
| 13 | 肝硬変 | 4,279.8 | 1.7 | 555 |
| 14 | 気管、気管支、肺がん | 4,137.8 | 1.6 | 537 |
| 15 | 腎臓病 | 4,057.1 | 1.6 | 526 |
| 16 | HIV / AIDS | 4,014.7 | 1.6 | 521 |
| 17 | その他の難聴 | 3,947.7 | 1.6 | 512 |
| 18 | 墜死 | 3,821.6 | 1.5 | 496 |
| 19 | マラリア | 3,339.8 | 1.3 | 433 |
| 20 | 裸眼の屈折異常 | 3,198.1 | 1.3 | 415 |
アルコール依存症︵アルコールいそんしょう、アルコールいぞんしょう、英: Alcoholism︶、アルコール使用障害︵Alcohol use disorder、AUD︶とは、主に飲酒によるアルコール摂取で引き起こされる薬物依存症の一種。飲酒によって得られる精神的、肉体的な薬理作用に強く囚われ、自らの意思で飲酒行動をコントロールできなくなり、強迫的に飲酒行為を繰り返す精神障害である[2][3]。以前は慢性アルコール中毒︵アル中︶、慢性酒精中毒などと呼ばれていたこともある[4]が、振戦譫妄のような中毒症状が出てから診断が付いたのでは手遅れであり、かといって中毒症状が出ていない段階で﹁アルコール中毒﹂と診断が付いたのでは患者の反感を買う、という理由で﹁アルコール依存症﹂という名称に変更されたという歴史がある[5]。人体に対するアルコールの影響について最初に体系化されたのは1849年で、スウェーデンの医師マグヌス・フスによる。
症状は精神的依存と身体的依存から成り立っており、飲酒が自分の意志でコントロールできなくなる症状を精神的依存、振戦せん妄などの退薬症状︵アルコール離脱症候群、リバウンドともいう︶を身体的依存と言う[4]。患者は、アルコールによって自らの身体を壊してしまうのを始め、家族に迷惑をかけたり、様々な事件や事故・問題を引き起こしたりして社会的・人間的信用を失ったりすることがある︵アルコール乱用︶[3][6]。
かつては、このような状態になってしまうのは本人の意志が弱く、道徳観念や人間性が欠けているからだとの考え方で済まされて納得されてきていたが、最近では社会的な必要性からも医学のカバーする範囲がより拡大されていくことに伴って、医学的見地から精神障害の一つとして治療を促す対象と考えられている[4]。
世界保健機関︵WHO︶は、アルコール乱用・依存の未治療率は78.1%であると推定している︵2004年[7]︶。精神疾患の中でも罹患率が高く、各人の性格や意志にかかわらず誰でもかかる可能性がある病気であるとも言える。日本の飲酒人口は6,000万人程度と言われているが、このうちアルコール依存症の患者は230万人程度であると言われている。なお、この230万人という人数はWHOの算出方法により割り出されたものである。
治療法や支援法については﹁アルコール依存症#管理﹂を参照。
症状[編集]
「薬物依存症#診断基準」も参照
疾病及び関連保健問題の国際統計分類︵ICD︶の診断基準においては、渇望、セルフコントロール喪失、離脱症状、耐性、飲酒中心の生活が挙げられている[8]。
目が覚めている間、常にアルコールに対する強い渇望感が生じる。
強迫的飲酒が進んでくると、常にアルコールに酔った状態・体内にアルコールがある状態を求め、調子が出ないと思ったりして、目が覚めている間、飲んではいけない時︵勤務中や医者から止められている時など︶であろうとずっと飲酒を続けるという﹁連続飲酒発作﹂がしばしば起こることがある[8]。会社員など、昼間に人目のつく場所で飲酒ができない場合、トイレなどで隠れて飲酒をする例がある。さらに症状が進むと身体的限界が来るまで常に﹁連続飲酒﹂を続けるようになり、体がアルコールを受け付けなくなるとしばらく断酒し、回復するとまた連続飲酒を続けるというパターンを繰り返す﹁山型飲酒サイクル﹂に移行することがある。ここまで症状が進むとかなりの重度である。
飲酒を自分の意志でコントロールできない。
”人がアルコールを含む飲み物を切望し、その飲酒を制御することができない慢性疾患”︵ICD-9[9]︶
﹁強迫的飲酒﹂とは以下のような状態である。少量のアルコールの摂取によっても脳が麻痺してしまい、飲み始めたら、その後の飲酒の制御がほぼ不可能となるような状態である[8]。
アルコール依存症の人も、適量のアルコールで済ませておこうとか、今日は飲まずにいようかと考えていることは多い。しかし、飲み始めてしまうとアルコールの作用の方を選んでしまう[8]。また、アルコールを長期的に飲まないことの利益は多いが、アルコールの影響で誤った思考や判断となったり、目先の快感の方を選択してしまう。このように繰り返されることで、状況が悪化し症状も進行するとは思っていないため、必要性を見出せず、明確な禁酒の意志を持つことができず、アルコールによる快感を選択してしまう。そして、飲み始めたら酩酊するまで飲んでしまう[8]。
飲酒で様々なトラブルを起こし後で激しく後悔するも、それを忘れようとまた飲酒を続ける。
”社会的または職業的機能に深刻な障害を引き起こす、飲酒パターンを特徴とする障害”(ICD-9[9])
飲酒量が極端に増えると、やがて自分の体を壊したり︵内臓疾患など︶、社会的・経済的問題を引き起こしたり、ドメスティック・バイオレンスなど家族とのトラブルを起こしたりするようになる。それでさらにストレスを感じたり、激しく後悔したりするものの、その精神的苦痛を和らげようとさらに飲酒を繰り返す。このように自分にとっての損失が強くなっているにもかかわらず飲酒し続ける行動を﹁罰への抵抗﹂と呼ぶ。

振戦せん妄 (DT)
離脱症状︵退薬・禁断症状︶が出る。
アルコール摂取を中断した際、様々な症状が生じる。軽いものであれば、頭痛、不眠、イライラ感、発汗、手指や全身の震え︵振戦︶、眩暈、吐き気などがあるが、重度になってくると﹁誰かに狙われている﹂といった妄想や振戦せん妄、痙攣発作︵アルコール誘発性てんかん︶なども起こるようになる[8][10]。幻覚︵幻視・幻聴︶も頻繁に起こる症状で、小さな虫のようなものが見えたり、いるはずのない人が見えたり、耳鳴りや人の声が聞こえたりと症状は患者によって様々であるが、幻覚を全く経験しない人も多くいる。患者にとってこれらは苦痛であるため、それから逃れるために飲酒をすることになる。
また、急性期の離脱症状を過ぎた後でも、怒りっぽくなったり、抑うつ状態になったりするなどの情動性の不安定な遷延性離脱症候群とよばれる状態が数か月続く場合がある。
耐性の増大。
同じ酩酊を感じるのに要する飲酒量が増大する[8]。または、同じ飲酒量での酩酊感が減弱する[8]。

合併症[編集]
アルコール依存症の患者は、心身に多くの疾患を抱える危険性を持っている。逆に、他の精神障害がアルコール依存症を誘発することが分かっている。精神神経の疾患[編集]
うつ病[8] アルコール依存症によってうつ病が引き起こされる場合がある[3][6]。逆に、うつ病によってアルコール依存症に陥ることもある︵誤ったセルフメディケーション︶。有病者の30-40%が、一生のうちにうつ病の診断基準を満たす[2]。 不安障害[8] パニック障害、社交不安障害など。 双極性感情障害︵躁鬱病︶ 双極性感情障害の患者が自己治療的に飲酒を続けた結果、アルコール依存症に陥る場合がある。 統合失調症 統合失調症の患者が自己治療的に飲酒を続けた結果、アルコール依存症に陥る場合がある。 ウェルニッケ‐コルサコフ症候群[8] チアミン︵ビタミンB1︶の欠乏によって発症する疾患で、急性症状をウェルニッケ脳症︵アルコール性脳症︶、慢性状態をコルサコフ症候群という。ウェルニッケ脳症は可逆的で数週間以内に自然に消失することがあるが、コルサコフ症候群に進展すれば80パーセントが回復しないが、生命の危険は少ない。意識障害、外眼筋麻痺、記憶障害、小脳失調、失見当識の症状がでる。コルサコフ症候群では記憶障害の結果として、記憶の不確かな部分を作話で補おうとすることが知られる。チアミン投与が有効である。 アルコール幻覚症 被害的内容の幻聴︵英・auditory hallucination︶を主とする幻覚が、飲酒中止時や大量飲酒時に急性・亜急性に出現する。飲酒を中止することで、数週間以内に消失することが多い。幻覚により殺人に至るケースも起きている[11]。 アルコール性妄想状態 アルコール依存症でみられ、了解可能な嫉妬妄想が主。断酒によって次第に消失する。 ニコチン酸欠乏脳症︵ペラグラ︶ ニコチン酸︵ナイアシン︶の欠乏によって発症する。幻覚、妄想やせん妄の症状がでる。 小脳変性症 文字通り小脳がアルコールの影響で変性することで発症する。歩行障害など下肢の失調が起こる。 アルコール性認知症 アルコール自体が認知症の原因となりうるのかは不明であるが、臨床的にはアルコール摂取が背景になっていると見られる認知症が確かに存在する。画像検査では、脳室系の拡大と大脳皮質の萎縮が見られる。 アルコール性多発神経炎︵末梢神経炎︶ アルコールが原因の栄養障害︵ビタミンB群とニコチン酸の欠乏︶により発症する。四肢の異常感覚や痛み、感覚鈍麻や疼痛、手足の筋肉の脱力、転びやすい、走りにくいなどの症状。コルサコフ症候群に合併すれば﹁アルコール性多発神経炎性精神病﹂と呼ばれる。身体的疾患[編集]
身体的疾患はアルコールにより引き起こされているものなので、酒を断つことにより回復するケースもある。しかし数日単位での回復は無理で、数か月から長い場合では数年ほど回復に期間がかかることが多い。また、脳や身体に不可逆的にダメージを受けある程度以上は治癒しないケースもある。
高血圧[3][8]
不整脈[8]
悪性腫瘍
口腔癌、肝臓癌、腸癌、乳癌[3]
アルコール性肝疾患
アルコール性脂肪肝[8] - 肝臓に脂肪が蓄積され、放置すると肝硬変、肝臓癌へと進む危険を持つ。自覚症状はほとんどない。
アルコール性肝炎[8] - 肝臓が炎症を起こし、肝細胞が破壊される病気。全身の倦怠感、上腹部の痛み、黄疸、腹水等の症状が出る。
アルコール性肝硬変[3] - 肝細胞の破壊が広範に起こり細胞が繊維化される病気。肝炎と類似の症状がでる。日本国内の患者数は4.5万人いると言われる。
アルコール性胃炎
胃粘膜の炎症である。慢性化して、胃潰瘍に発展する場合もある。胃痛、胸やけ、吐血等の症状。
アルコール性膵炎[8]
膵臓の炎症で、慢性膵炎の約半数がアルコール性のものと言われている。腹部や背中の痛み、発熱等の症状。急性膵炎や慢性膵炎の急性増悪では、落命することもある。
食道静脈瘤
肝硬変の副次的な症状として現れる。本来肝臓に流れるべき血流が、食道の静脈に流れることにより、瘤状の膨らみができる。万一破裂すると大量出血で命に関わることがある。
アルコール性心筋症
アルコールの影響で心筋がびまん性に萎縮して線維化が進行、心収縮力が弱まり血液を送り出す機能が低下する。
マロリー・ワイス症候群
飲酒後に繰り返し嘔吐するため、出血を起こす。
アルコール離脱[編集]
詳細は「アルコール離脱症候群」を参照
アルコール依存からの離脱は、適切な管理を伴わなければ、バルビツール酸系やベンゾジアゼピン系といった催眠鎮静薬と同様、致命的となる可能性がある[12]。アルコールの主な作用は、GABAA受容体への刺激を増加させ、中枢神経の抑制を促すことである。アルコールの大量消費を繰り返すとこの受容体は感度が減少し、また数が減る。そのために薬物耐性と身体性依存が起こる。アルコールを急速に断酒すると、中枢神経系はシナプス発火のコントロールを失う。これによって不安、致命的な発作、振戦、せん妄、幻覚、心不全などを招く[13][14]。その他の中枢神経系では、主にドーパミン、NMDA、グルタミン酸が関係している[15]。
急性離脱症状は、1〜3週間ほど続くことが多い。重篤ではない症状︵不眠、不安、無快感症︶は、遷延性離脱症候群として1年、またそれ以上の断酒により、徐々に改善されていく[16][17][18]。離脱症状は、体と中枢神経系がアルコール耐性とGABA機能について正常に向かって復元されるまで続く[19][20]。
形成と特徴[編集]
通常は飲酒行動を、主にアルコールによって得られる肉体的・精神的変容に求めることが多いが、初期は毎日飲むわけではなく、何かの機会に時々飲むだけという機会飲酒から始まる。しかし、何らかの原因で毎日飲む習慣性飲酒に移行することも多く、習慣性飲酒となると同じ量の飲酒では同じように酔うことができなくなり、次第に飲酒量が増えていくことになる︵耐性の形成︶。つまり、アルコール依存症になることはこの﹁習慣性飲酒﹂と深い関係があるということになる。もちろん、習慣性飲酒をする者すべてがアルコール依存症患者であるとは言えないが、何らかのきっかけがあればさらに飲酒量が増え、いつの間にか依存症に陥ってしまうという危険性は充分はらんでいると言える。
一見すると本人が自分の判断で好んで飲酒しているようにみえ、患者自身も好きで飲酒していると錯誤している場合が多い。そのため、患者にアルコール依存症のことを告げると﹁自分は違う﹂などと激しく拒絶をされることも多々あり、否認の病気とも言われている[4]。しかし、依存が重度になると断酒によって肉体的・精神的に離脱症状︵禁断症状︶が出るため、楽しむためではなく離脱症状を避ける目的で飲酒を繰り返すことになる[4]。このような状態に陥ってしまうと、もはや自分の意志だけで酒を断つことが極めて困難となる︵セルフコントロールの喪失︶[4]。
また、アルコール依存症の形成を助長するものとして、本人の周囲には、酒代になりうる小遣いを提供したり、過度の飲酒で生じる社会的な数々の不始末︵他人に迷惑をかける、物品を壊す、等︶に対して本人になり代わり謝罪したり、飲酒している本人の尻ぬぐいをする家族など、イネーブラー︵enabler︶が存在することが多い[21]。イネーブラーは飲酒している当人の反省を必要とさせず、延々と過度に飲酒することを可能にしてしまうとされる。逆に、一切のイネーブラーがいなくなったり、医師から死を宣告されたりしたことをきっかけに、本人が﹁底つき体験﹂︵﹁どん底体験﹂ともターニング・ポイントとも呼んだりする[21]。“このままでは大変なことになる”という意識の発生︶をし、それをきっかけにアルコール依存症から立ち直ることがある[21]︵セルフコントロール不能のアクセプタンス︶[4]。
さらに、アルコール依存症者の配偶者などには、アルコール依存症者に必要とされることを必要とする共依存︵co-dependency︶ の状態に陥っている人もいる[4][21]。そのため、アルコール依存症者本人以外の家族も問題となっている可能性もあり、アルコール依存症者本人の治療だけでなく、その配偶者などに対しても正しいカウンセリングなどが必要となるケースもある[4][21]。
この他にも、アルコール依存症患者の症状およびその周囲を取り巻く社会への影響から、この病気は次のような特徴を持っている。

﹃飲酒者の辿る過程﹄︵1846年︶。アルコール依存は貧困、犯罪、 自殺を導くことを描いた。
進行性疾患
自分が依存的に飲酒していると気付かずにそれを続けるとさらに飲酒量が増えて症状が悪化し、悪循環に陥る。
慢性疾患
一度依存に陥ると回復が極めて困難である。いわゆる﹁上手に酒を飲む﹂ということができなくなる。
人格変化を引き起こす疾患[4]
依存に陥ったことを否認するため、周囲のせいにしたりして攻撃的・他罰的・自己中心的な性格になる[4]。他人への関心を失い、手段として使うようになる[4]。あるいは逆に自分のせいにして自虐的になり、後悔・不安・孤独に苛まれるようになる。また、アルコールの入っていない状態であっても酔っているとき同じような言動をする﹁ドライドランク﹂と呼ばれる状態になることもしばしばある。これらの結果として、周囲の人は本人と﹁付き合えなく﹂なってしまい、社会性を失う[4]。
不治の疾患
アルコール依存症になった者が元の機会飲酒者に戻ることはほとんど不可能であるとされている。たとえ身体的に回復し、数年にわたる断酒を続けていた者であっても、一口でも飲酒をすることによって再び元の強迫的飲酒状態に戻ってしまう可能性が非常に高い。そして、進行性の病気であるためにさらに症状は悪化していく。つまり、悪くなることはあっても、決して良くなることはない病気であり、寛解︵かんかい︶の状態で再発つまり再飲酒をどう防ぐかが治療の重要な点となる。
死に至る疾患
適切な対処をしなければ、内臓疾患あるいは精神ストレスなどによる自殺または事故死など、何らかの形で死に至る場合が多い。アルコール依存症者の予後10年の死亡率は30 - 40%と非常に高く、節酒を試みた患者と通常に飲酒した患者とでは死亡率に差が見られず、断酒することによってのみ生存率が高まる[22]。
機能不全家族の形成要因
飲酒による問題行動により、その家族は常にストレスに苛まれることになる。家族は常に飲酒をやめさせることばかり考えるようになり、家族まで精神疾患を罹患してしまうケースも少なくない。家族との信頼関係の亀裂に始まり、別居や離婚へと発展して家族が崩壊する原因となったりする[4]。
アダルトチルドレン︵AC、Adult Children of Alcoholics アルコール依存症の親のもとで育ち、成人した人々︶の語源となっているように、アルコール依存症者のいる家庭での家族に与える影響は多大なものであり、特に親から子へアルコール依存などの嗜癖問題が世代間で伝播する現象がよく見られる。そのため、アルコール依存症は患者本人だけの問題ではなく、家族全体を巻き込み、特に機能不全家族の形成を助長する。

男女差[編集]
女性は、男性に比べ一般的に体が小さいこと、体内の水分率が男性より低いこと、女性ホルモンはアルコール代謝を阻害する要因となることなどから、同じ量のアルコールを摂取しても男性よりも少量の摂取で影響がでる[23]。アルコール依存症患者は、飲酒歴が長期に渡っているのが特徴であるが、女性の場合は短期の飲酒歴でかつ飲酒量が比較的少量でも急速にアルコール依存症となってしまう危険がある。ギリシャ語で“酒に酔わない”というところから、アルコール依存症になった女性をアメシストと呼ぶこともある。 一説によると、習慣飲酒からアルコール依存症への進行の期間は男性で約10年、女性では約6年であるとも言われている[誰によって?]。診断[編集]
診断スケールには以下のものがある[24]。 ●AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test) ●SADQ (Severity of Alcohol Dependence Questionnaire) ●LDQ ●Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment of Alcohol Scale, revised (CIWA-Ar) ●APQ ●新久里浜式アルコール症スクリーニングテスト (KAST) 軽度依存︵SADQスコア15以下︶の場合、たいてい離脱支援は必要としない[3]。中度依存︵SADQスコア15-30︶の場合は、離脱支援が必要であるが、他にリスクが無ければ外来で治療できる[3]。重度依存︵SADQスコア30以上︶の場合は、大抵は入院治療が必要となる。管理[編集]
飲酒をやめて、短時間で手が震えるなど振戦が起こる場合には、身体性依存が形成されており、その数日後にはアルコール離脱症候群は最大となり、この際に振戦せん妄に至ると死亡の危険性がある。こうした場合には、離脱症状の医学的な管理が必要であり、飲酒をやめないままアルコール外来などを受診することになる。 精神科において自助グループへの参加を奨励すると共に、抗酒剤の使用により、アルコール摂取を禁止して治療を進める病院が多い。都道府県の精神保健福祉センターや保健所ではアルコール依存症に関する無料相談を受けており、専門の病院を紹介することもある。 英国国立医療技術評価機構︵NICE︶は、軽度のアルコール依存の場合は心理療法を提供する[25]。その場合は、認知行動療法では週1回60分のセッションを12週、行動療法では週1回60分のセッションを12週行うとされる[25]。 またNICEは、中重度のアルコール依存の場合は、離脱後にアカンプロサートもしくはナルトレキソンの投薬と、個人精神療法︵認知行動療法、行動療法、社会ネットワーク・環境ベース療法︶を組み合わせるとしている[26]。ジスルフィラムはそれら薬物のセカンドラインとして提案している[26]。援助の方針[編集]
- 断酒の三本柱[27]
- 通院
- 抗酒剤
- 自助グループへの参加
- HALTの法則(飲酒欲求を生じる要因)
- H - ハングリー(hungry、お腹を減らさない)
- A - アングリー(angry、怒らない)
- L - ロンリー(lonely、独りにならない)
- T - タイアード(tired、疲れない)
アルコール依存症の治療でまず肝心なことは﹁本人の認識﹂である。多くのケースでは依存を認めてしまうと飲酒ができなくなるため、患者は自分がアルコール依存症であることを認めたがらない。何よりもまず、本人に疾患の自覚︵病識︶と治療の意志を持たせることが大切であり、回復への第一歩となる[21]。心身や生活への影響をなるべく抑えるためには、早期の治療開始が望ましい[28]。
アルコール依存症の人の過剰な飲酒は﹁意志が弱いから﹂﹁道徳感が低いから﹂と言われたり、不幸な心理的・社会的問題が原因であると考えられたりしがちだが実際はそうではなく、多くの場合この病気の結果であることが多い。つまり、アルコールによって病的な変化が身体や精神に生じ、そのために過剰な飲酒行動が起こるということである。このことをまず本人や周囲の者が理解し、認めることが、この病気から回復する上での欠かせない第一歩となる。しかし援助者は、治療という名目で処罰を与えてはならない[29]。
アルコール離脱症候群までに至っていなければ、飲酒量を減らす減酒もある程度有効であるが、一度アルコール依存症になってしまうと、基本的な対処は酒を一切飲まない断酒しかない[28]。しかし本人の意志だけでは解決することが難しいため、周囲の理解や協力が求められる。重度の場合は入院治療が必要な場合もある。しかし完治することはない不治の疾患とも呼ばれる事があり、断酒をして何年、十何年と長期間経過した後でも、たった一口酒を飲んだだけで、遅かれ早かれまた以前の状態に逆戻りしてしまうケースが多い[21]。そのため、治療によって回復した場合であっても、アルコール依存症者が一生涯断酒を続けることは大変な努力を要する。
急性期の管理[編集]
急性期のアルコール離脱症候群の管理には、ベンゾジアゼピン︵クロルジアゼポキシドやジアゼパム︶、カルバマゼピンが用いられる[29][30][31]。NICEはクロメチアゾールも選択肢の一つであるが、入院患者に限って注意深く使用すべきであり[30]、乱用リスクがあるため外来では処方してはならないとしている[32]。振戦せん妄の管理には、ロラゼパムが第一選択肢である[30]。抗精神病薬は、精神病症状が出ている期間に限って使用できる[29]。 また外来治療の場合、オーバードーズや転用リスクがあるため、常に2日分以上の薬を患者が保持しないよう処方すべきである[31]。心理社会的ケア[編集]
治療法は現在のところ断酒以外にない[21]。しかし、依存性薬物であるアルコールを断つことは並大抵の努力ではなく、一生涯これを続けることは想像以上の困難または精神的苦痛を伴う。このため、断酒をサポートする様々な試みがなされている。
全てのアルコール乱用者には、須らく自助グループ︵例えばアルコホーリクス・アノニマスやSMART Recoveryなど︶の情報提供を行うべきであり、かつそれらに参加を支援・奨励されるべきである[33][29]。
アルコホーリクス・アノニマス︵AA︶
アルコール依存症患者の自助グループ。断酒会の原型である。1930年代にアメリカ合衆国で始まり、世界180か国以上に拡がっている。基本テキストである通称ビッグブックは、70か国以上に翻訳されている。アルコール依存からの回復のために﹁ミーティング﹂と呼ばれるグループワークや、﹁12ステップ﹂という回復のプログラムを用いる。プライバシーを守るため、また、個人よりも原理を優先させるために、フルネームは名乗らない。よって断酒会とは異なり、名簿や会費もなく組織化もされない。アルコール依存症者のみが参加できるクローズド・ミーティングと、家族や医療関係者など外部の人も参加できるオープン・ミーティングがある。さらには女性だけのミーティングや若者だけのミーティングもある。マーティ・マンはこの会で女性として初めて断酒に成功したと言われている[34]。
断酒会
アルコール依存症患者とその家族によって作られた自助グループ。会費制で、組織化されており、外部に対してもオープンな姿勢を取っている日本独自の団体。断酒を続けることを互いにサポートし合い、酒害をはじめ、アルコール依存に対する正しい理解・知識を広く啓蒙する活動を行っている。
また、ストレス解消のために飲酒がなされることもあることから、飲酒に代わるストレス対処方法︵﹁ストレス管理﹂﹁リラクゼーション﹂も参照︶を身につけるための支援・サポートの必要性も示唆される[35]。
「セルフケア不足看護理論」も参照
薬物療法[編集]
ウェルニッケ脳症防止のため、チアミン100mgを毎日摂取する[29]。
抗酒剤[編集]
詳細は「抗酒薬」を参照
アセトアルデヒドデヒドロゲナーゼ︵アセトアルデヒド脱水素酵素︶の働きを阻害する薬品で、服用すると飲酒時に血中のアセトアルデヒド濃度が高まるため、不快感で多量の飲酒ができなくなる。つまり﹁少量の飲酒で悪酔いさせる薬﹂であり、﹁飲酒欲求そのものを抑える薬ではない﹂[21]。抗酒剤を飲んで大量飲酒をすると命にかかわる危険があるため、医師の指導の下、本人への充分な説明と断酒の決意を行った上での服用が必須である[21]。アルコール依存者に知られぬよう密かに投与するようなことは厳禁である[21]。
●シアナミドとジスルフィラム︵商品名は﹁シアナマイド﹂と﹁ノックビン﹂︶の2種が日本では認可されている。
治療薬[編集]
抗酒剤とは別に、飲酒欲求そのものを抑制する薬剤物質としてのアカンプロサート︵商品名﹁レグテクト﹂︶が2013年から日本でも使用され始めた。服用に際しては自助グループや精神療法との併用が効果的で望ましい。 ●アカンプロサート - 脳内の伝達物質︵飲酒欲求にスイッチを入れる物質︶であるグルタミン酸によって引き起こされる脳内の過剰な欲求を緩和する。即ち、アカンプロサートが、神経細胞の受容体︵スイッチによる命令を受け入れる部署︶を封鎖して、伝達物質グルタミン酸分子の受容体への付着を防止することで欲求命令の伝達を防ぐ。アルコール依存症者の脳にはこのグルタミン酸が特に多量に見られる︵原因は不明︶。全ての患者に効能が認められるわけではないが、アルコール依存症者の治療にアカンプロサートが投薬され、一定の成果を挙げている[26][29]。 ●ナルメフェン‥飲酒の前に服用することで、飲酒量を減らす効果がある。減酒を目的とした治療に有効であり、日本では2019年に承認された︵商品名‥セリンクロ︶[36]。 ●ナルトレキソン[26][29] ●バクロフェン - 海外で有効性が報告されている。日本ではアルコール依存症を適応として持たない。 ●ゾニサミド - 抗てんかん薬、パーキンソン病治療薬。海外で有効性が報告されている。日本ではアルコール依存症を適応として持たない。 ●ベンゾジアゼピンは、急性アルコール離脱の管理に有用な一方、長期的に使用した場合はアルコール依存症を悪化させる[8]。ガイドラインでは、原則7日以内とし、遷延性離脱症候群のケースであっても4週間を超えてはならない[8]。アルコール依存症に対して慢性的にベンゾジアゼピン系を処方した場合、服用していないケースよりもアルコール断絶を達成できる確率は低い。しかし、この種類の薬は、一般的に不眠や不安の管理のために、アルコール依存症者に処方されている[37]。ベンゾジアゼピンまたは鎮静催眠薬が回復過程で投与された患者は、鎮静催眠薬を処方された後に再発する確率が高く、4倍以上であった。ベンゾジアゼピンの長期的服用者は急激な断薬をすべきではない。それは重度の不安とパニックが生じる可能性があり、アルコール乱用の再発の危険因子であると知られている。6〜12か月の減薬が、離脱の強度を減少させ、最も成功しやすいことが判明している[38][39]。 ●1960年代と1970年代の6件の研究の遡及的分析によれば、LSD補助心理療法はアルコール依存症の治療としての可能性がある[40]。心理療法[編集]
治療者は初診ではまず、受診したことを大きな一歩としてしっかりとねぎらい、患者の困りごとを丁寧に傾聴し、その解決を優先してサポートするという姿勢で、信頼関係を構築することが重要である[41]。その上で、以下のような心理療法を行っていく。動機づけ面接法[編集]
アルコール依存症をはじめ、依存症全般で動機づけ面接法の有効性が確認されている[42]。動機づけ面接法を進めていく中で、患者と治療者の間に共通理解が増え、治療同盟の構築が可能になる[42]。動機づけ面接法による非対決的な関わりと治療同盟、治療者が患者を共感的に理解しようとする温かいまなざしは、高い治療効果を持つ[42]。加えて、人生の目標を実現したり好きなことに取り組んだりできるという断酒のメリットを実感できるよう支援するとともに、短期間の断酒やささいな変化も賞賛して成功体験として認識できるようサポートし、患者に寄り添いながら断酒への動機の形成を援助していく[43]。認知行動療法[編集]
認知行動療法の有効性は古くから確認されてきた[42]。認知行動療法では、自らの飲酒衝動や飲酒行動のメカニズムを知り、衝動の回避方法やストレスへの対処方法等を身につけることなどをサポートする[42]。なお、治療にあたっては、認知行動療法単独で実施するのではなく、認知行動療法を他の治療法︵薬物療法や動機づけ面接法、自助グループへの参加など︶と組み合わせて実施することが推奨される[42]。多重の中毒[編集]
アルコール依存では、その他の向精神薬依存治療をも必要なことがある[2][44]。患者に最も多く共通した依存はベンゾジアゼピン依存症であり、研究では10-20%のアルコール依存患者がベンゾジアゼピン乱用を併発していた。ベンゾジアゼピン系はアルコールへの欲求を増加させ、また飲酒量を増やす[45]。ベンゾジアゼピン依存はベンゾジアゼピン離脱症候群やその他の健康問題を避けるために注意深く減薬を行う必要がある。 その他の鎮静催眠薬への依存、ゾルピデムやゾピクロン、オピエートや違法薬物などもアルコール依存症では一般的である。 アルコールは鎮静催眠薬であり、バルビツール酸、ベンゾジアゼピン、非ベンゾジアゼピン系など他の鎮静催眠剤と交差耐性がある。催眠鎮静薬からの離脱は医学的に重症であり、慎重な管理なしでは精神病または発作の危険性がある。疫学[編集]

| データなし <50 50-170 170-290 290-410 410-530 530-650 | 650-770 770-890 890-1,010 1,010-1,130 1,130–1,250 >1,250 |
「アルコール乱用」も参照
WHOは2010年に、世界のアルコール依存患者は2億800万人︵15歳以上人口の4.1%︶との推定を発表している[46][47]。
米国の患者数は200万人と推定され、毎年8.8万人の死者を出している[2]。
英国では、成人人口の24%以上が危険な飲酒パターンにあるとされ、成人の4%はアルコール依存︵男性6%、女性2%︶であるが、しかし年間約6%しか治療につながっていない[3]。労働者のアルコール依存による労働時間逸失は、英国では年間およそ110万日︵12億ポンド︶に上ると推定されている[48]。
日本では、2003年の精神科病院における﹁アルコール使用による精神及び行動の障害﹂による入院患者数は2,751人であった[49]。アルコール依存による生活保護受給者は1万人ほど、平均年齢は57歳であった︵2015年︶[50]。
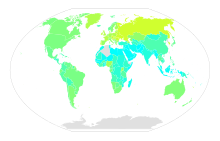
15歳以上成人の人口あたり年間飲酒量︵リットル︶[52]
フランスやスウェーデンなど複数の先進国においては、企業がアルコール飲料をテレビCMによって販売促進することを法律によって禁止している。北欧諸国では、アルコールは国営企業による専売制である。なお酒類の自動販売機は日本にしか存在しない[4]。
ベラルーシではアルコール依存症が社会問題になっており[53]、2010年のWHOの統計によるとアルコール依存症患者の割合は全国民中11%と統計の対象となる190ヶ国中1位、偏差値にして102.1という深刻な状況にあった。アルコール依存症による無業者が問題となっていたため、2015年には少なくとも半年間職に就かず、納税していない国民に罰金を科す新たな法令が成立した。罰金は少なくとも252米ドル︵約3万円︶で、支払わない場合は拘束され、地域社会での奉仕活動が命じられる[54]
日本では2014年1月にアルコール健康障害対策基本法が成立し、国および都道府県は、アルコール問題への対策計画を策定することが求められることとなった︵12、14条︶。また国民は、アルコール関連問題︵アルコール健康障害およびこれに関連して生ずる飲酒運転、暴力、虐待、自殺等の問題︶に関する関心と理解を深め、アルコール健康障害の予防に必要な注意を払うよう努めなければならないとされた︵7条︶。11月10日から16日までが、アルコール関連問題啓発週間と定められている︵10条︶。
予後[編集]
2002年に米国国立アルコール乱用・依存症研究所は、アルコール依存症の会合に参加する4,422人のグループに対して調査を行った。結果、1年後には一部の人々は低リスクの飲酒を行っていると著者は判断したが、いまだ25.5%のグループは治療を受けていた。詳細は、25%は未だ依存のまま、27.3%はいくつか症状が残っており部分寛解、11.8%は症状が現れることなく飲酒を続けている︵飲酒は再発可能性を増加させる︶、35.9%完全回復、17.7%は低リスク飲酒者、18.2%は断酒[51]。社会的状況[編集]

アルコール依存症をテーマにした作品[編集]
●ビリー・ワイルダー監督作品﹃失われた週末﹄︵1945年︶
●ブレイク・エドワーズ監督作品﹃酒とバラの日々﹄︵1962年︶
●東海テレビ制作昼ドラマ﹃華の別れ﹄︵1989年︶ - 手塚理美・速水亮主演。
●中島らも﹃今夜、すべてのバーで﹄︵1991年︶- 飲酒や薬物をインスピレーションにしていた著者がアルコール依存症に陥り、その経験をもとに書いた小説。
●﹃リービング・ラスベガス﹄︵1995年︶ - アルコール依存症で職を失った脚本家が、死ぬまで酒を飲み続けるべくラスベガスに行き、そこで知り合った娼婦との奇妙な交流を描く。ニコラス・ケイジ主演。マイク・フィギス監督。
●吾妻ひでお﹃失踪日記﹄︵2005年︶、﹃失踪日記2アル中病棟﹄︵2013年︶- 1997年頃からアルコール依存症に陥り、治療のため精神病院に入院した経験を描いたエッセイ漫画。
●﹃ウーマンズ・ビート ドラマスペシャル〜溺れる人〜﹄ - 2005年3月1日に日本テレビ系列にて放送されたテレビドラマ。主演は篠原涼子。アルコール依存症を克服すべく病と闘う女性、そしてその家族の姿を描いたシリアスな作品となっている。第31回放送文化基金賞テレビドラマ部門優秀賞受賞作品。
●鴨志田穣﹃酔いがさめたら、うちに帰ろう。﹄- 漫画家西原理恵子の元夫でジャーナリストの著者が、自らのアルコール依存症の経験をつづった私小説。2010年に監督東陽一、浅野忠信・永作博美主演で映画化された。
●まんしゅうきつこ﹃アル中ワンダーランド﹄︵2015年︶ - 家事や育児のストレスから重度のアルコール依存症となった経験を描いたエッセイ漫画。
●﹃フライト_(映画)﹄ - 制御不能となった航空機の不時着を成功させ英雄となったパイロットが、実はアルコール依存症で不時着時のフライトでもアルコールを摂取しており過失致死罪に問われる法廷映画作品。ロバート・ゼメキス監督。
●菊池真理子﹃酔うと化け物になる父がつらい﹄︵2017年︶ - アルコール依存症の父を持つ作者の実体験を基に描かれたエッセイ漫画。2020年に松本穂香と渋川清彦と主演で映画版が公開された。
●小田嶋隆﹃上を向いてアルコール ﹁元アル中﹂コラムニストの告白﹄︵2018年︶ - アルコール依存症となった著者のエピソードを纏めたエッセイ集。
脚注[編集]
(一)^ Global health estimates: Leading causes of DALYs (Excel) (Report). 世界保健機関. 2020年12月. Download the data > GLOBAL AND BY REGION > DALY estimates, 2000–2019 > WHO regions. 2021年3月27日閲覧。
(二)^ abcdB.J.Kaplan; V.A.Sadock﹃カプラン臨床精神医学テキスト DSM-5診断基準の臨床への展開﹄︵3版︶メディカルサイエンスインターナショナル、2016年5月31日、Chapt.20.2。ISBN 978-4895928526。
(三)^ abcdefghi英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Introduction.
(四)^ abcdefghijklmno信田さよ子﹃依存症﹄文芸春秋、2000年6月。ISBN 978-4166601080。
(五)^ なだいなだ﹃アルコール問答﹄pp.17-20.(岩波新書、1998年) ISBN 978-4004305484
(六)^ ab世界保健機関 2010, ALC.
(七)^ Kohn R, Saxena S, Levav I, Saraceno B (2004). “The treatment gap in mental health care”. Bull. World Health Organ. (世界保健機関) 82 (11): 858–66. PMC 2623050. PMID 15640922.
(八)^ abcdefghijklmnopqr日本アルコール関連問題学会 2018.
(九)^ ab“ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes 303.* : Alcohol dependence syndrome”. www.icd9data.com. 2019年5月閲覧。
(十)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 2010.
(11)^ ﹁病棟へ凶器持ち込み…アルコール幻覚症で隣室患者惨殺﹂﹃サンケイスポーツ﹄2005年6月4日
(12)^ Galanter, Marc; Kleber, Herbert D. (2008-07-01). The American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of Substance Abuse Treatment (4th ed.). United States of America: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc. p. 58. ISBN 978-1-58562-276-4
(13)^ Dart, Richard C. (2003-12-01). Medical Toxicology (3rd ed.). USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 139?140. ISBN 978-0-7817-2845-4
(14)^ Idemudia SO, Bhadra S, Lal H (June 1989). “The pentylenetetrazol-like interoceptive stimulus produced by ethanol withdrawal is potentiated by bicuculline and picrotoxinin”. Neuropsychopharmacology 2 (2): 115?22. doi:10.1016/0893-133X(89)90014-6. ISSN 0893-133X. PMID 2742726.
(15)^ Chastain, G (October 2006). “Alcohol, neurotransmitter systems, and behavior.”. The Journal of general psychology 133 (4): 329?35. doi:10.3200/GENP.133.4.329-335. ISSN 0022-1309. PMID 17128954.
(16)^ Martinotti G; Nicola, MD; Reina, D; Andreoli, S; Foca, F; Cunniff, A; Tonioni, F; Bria, P et al. (2008). “Alcohol protracted withdrawal syndrome: the role of anhedonia”. Subst Use Misuse 43 (3?4): 271?84. doi:10.1080/10826080701202429. ISSN 1082-6084. PMID 18365930.
(17)^ Stojek A; Madejski, J; Dedelis, E; Janicki, K (1990). “[Correction of the symptoms of late substance withdrawal syndrome by intra-conjunctival administration of 5% homatropine solution (preliminary report)]”. Psychiatr Pol 24 (3): 195-201. ISSN 0033-2674. PMID 2084727.
(18)^ Le Bon O; Murphy, JR; Staner, L; Hoffmann, G; Kormoss, N; Kentos, M; Dupont, P; Lion, K et al. (August 2003). “Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy of trazodone in alcohol post-withdrawal syndrome: polysomnographic and clinical evaluations”. J Clin Psychopharmacol 23 (4): 377?83. doi:10.1097/01.jcp.0000085411.08426.d3. ISSN 0271-0749. PMID 12920414.
(19)^ Sanna, E; Mostallino, Mc; Busonero, F; Talani, G; Tranquilli, S; Mameli, M; Spiga, S; Follesa, P et al. (2003-12-17). “Changes in GABA(A) receptor gene expression associated with selective alterations in receptor function and pharmacology after ethanol withdrawal”. Journal of Neuroscience 23 (37): 11711?24. ISSN 0270-6474. PMID 14684873.
(20)^ Idemudia SO, Bhadra S, Lal H (June 1989). “The pentylenetetrazol-like interoceptive stimulus produced by ethanol withdrawal is potentiated by bicuculline and picrotoxinin”. Neuropsychopharmacology 2 (2): 115?22. doi:10.1016/0893-133X(89)90014-6. PMID 2742726.
(21)^ abcdefghijk春日武彦﹃援助者必携 はじめての精神科﹄︵2版︶医学書院、2011年12月、126-131頁。ISBN 9784260014908。
(22)^ 世良守行, 米沢宏, 新貝憲利﹃アルコール依存症の治療と回復-慈友クリニックの実践﹄東峰書房 2002年 ISBN 978-4885920561
(23)^ 村正信, 野内俊彦, 小山恒 ほか﹁女性大酒家肝障害の臨床病理学的研究﹂﹃肝臓﹄1984年25巻10号 pp. 1246-1252, doi:10.2957/kanzo.25.1246
(24)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.2.1.4.
(25)^ ab英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.3.3.
(26)^ abcd英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.3.6.
(27)^ 山本由紀; 長坂和則﹃対人援助職のためのアディクションアプローチ‥依存する心の理解と生きづらさの支援﹄中央法規出版、2015年10月2日。ISBN 978-4805852538。
(28)^ ab︻医療ルネサンス 7746︼アルコール依存症(5)断酒が基本 減酒療法も/成増厚生病院・東京アルコール医療総合センター長 垣渕洋一さん﹃読売新聞﹄朝刊2022年4月15日くらし面
(29)^ abcdefg世界保健機関 2010, ALC1.
(30)^ abc英国国立医療技術評価機構 2010, Chapt.1.1.3.
(31)^ ab英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.3.5.
(32)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.3.5.7.
(33)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.3.1.
(34)^ カール・エリック・フィッシャー [著]‥松本俊彦 監訳‥小田嶋由美子 訳﹃依存症と人類 : われわれはアルコール・薬物と共存できるのか﹄みすず書房、2023年4月、156-189頁。ISBN 978-4-622-09602-3。
(35)^ 白倉 克之﹁ストレス・コーピングと飲酒行動(1997年/第38回日本心身医学会総会/東京)﹂﹃身医学﹄第38巻第5号、1998年、301-30頁、doi:10.15064/jjpm.38.5_301。
(36)^ 樋口 進﹃今すぐ始めるアルコール依存症治療﹄法研、2019年、123,126-128頁。
(37)^ Lindsay, S.J.E.; Powell, Graham E., eds (1998-07-28). The Handbook of Clinical Adult Psychology (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 402. ISBN 978-0-415-07215-1
(38)^ Gitlow, Stuart (2006-10-01). Substance Use Disorders: A Practical Guide (2nd ed.). USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. pp. 52 and 103?121. ISBN 978-0-7817-6998-3
(39)^ Kushner MG, Abrams K, Borchardt C (March 2000). “The relationship between anxiety disorders and alcohol use disorders: a review of major perspectives and findings”. Clin Psychol Rev 20 (2): 149?71. doi:10.1016/S0272-7358(99)00027-6. PMID 10721495.
(40)^ Frood, Arran. “LSD helps to treat alcoholism” (英語). Nature News. doi:10.1038/nature.2012.10200.
(41)^ 武藤 岳夫 (2022). “﹁俺はアルコール依存症なんかじゃない﹂―否認の強いアルコール使用障害患者―”. 精神科治療学 37 (増刊号): 178-181.
(42)^ abcdef佐久間 寛之 (2021). “アルコール使用症群”. 精神科治療学 36 (増刊号): 158-161.
(43)^ ﹃物質使用障害の治療‥多様なニーズに応える治療・回復支援﹄金剛出版、2020年、55-72頁。
(44)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 2011, Chapt.1.2.2.6.
(45)^ Poulos CX, Zack M (November 2004). “Low-dose diazepam primes motivation for alcohol and alcohol-related semantic networks in problem drinkers”. Behav Pharmacol 15 (7): 503?12. doi:10.1097/00008877-200411000-00006. ISSN 0955-8810. PMID 15472572.
(46)^ Global status report on alcohol and health 2014. World Health Organization. (2014). p. s8,51. ISBN 9789240692763
(47)^ “Global Population Estimates by Age, 1950–2050”. 2015年5月10日閲覧。
(48)^ OECD 2014, p. 75.
(49)^ 精神科病院入院患者の状況 (PDF) NCNP 国立精神・神経センター
(50)^ ﹃被保護者調査 - 平成25年﹄︵レポート︶厚生労働省、2015年、Table.5-1。GL08020101。
(51)^ The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, NIH News (2005年1月18日). “2001-2002 Survey Finds That Many Recover From Alcoholism”. National Institutes of Health. 2011年8月18日閲覧。
(52)^ Catherine Le Galès-Camus (2004) (PDF). Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004. World Health Organization. ISBN 92-4-156272-2
(53)^ ﹃読売新聞﹄2016年6月11日 ※記事名不明※
(54)^ 半年間﹁無職﹂の国民に罰金、奉仕活動の強制 ベラルーシ CNN 2015.04.18 Sat posted at 16:11 JST︵2017年10月7日閲覧︶
