無痛分娩
無痛分娩︵むつうぶんべん、英: epidural birth︶とは、麻酔を用いて痛みを緩和しながら分娩︵経膣分娩︶を行うことである[1]。麻酔法は一般的に硬膜外麻酔である[2]。分娩前後の痛みを緩和する手段は、硬膜外麻酔以外にも数多くある。これらは硬膜外麻酔の代替として行われるだけではなく、硬膜外麻酔と併用されることも多い。本稿では、これらの鎮痛手段についても概説する。
| 無痛分娩 | |
|---|---|
| 治療法 | |
 陣痛中の母親 | |
| 診療科 | 産科麻酔科学、産科学、麻酔科学 |
概要[編集]
無痛分娩では、主に硬膜外麻酔により、下半身の痛みを緩和しながら経膣分娩を行う[3][4][5][6]。この間、脊椎内の硬膜外腔に細いカテーテルを挿入して留置し、局所麻酔薬やオピオイドが投与される[7]。場合によっては、脊髄くも膜下麻酔︵脊椎麻酔︶が併用され[4]、専門的には脊髄くも膜下硬膜外併用麻酔︵略称は脊硬麻又はCSEA︶と呼ばれる。CSEAは効果発現が迅速である。麻酔を用いた分娩は、普通分娩時よりも麻酔薬の影響で下半身に力が入りにくくなるため、分娩時間が長くなって吸引分娩や鉗子分娩となったり[8]、最終的に帝王切開となることもある[4]。
﹁無痛﹂ではない分娩にも麻酔を用いないで済むタイプの様々な鎮痛方法がある。欧米では、亜酸化窒素吸入がよく行われている。オピオイドの一種であるペチジンの注射も無痛分娩に適応がある。これらの医学的鎮痛方法の代替、ないしは追加の鎮痛方法としては、非薬理学的鎮痛方法、すなわちラマーズ法などの呼吸法やマッサージ、水中出産や産後ドゥーラによるサポートなどが知られている。
欧米では硬膜外無痛分娩の普及率が高く7割を超えるが、日本では実施率は8.6%︵2020年︶である。欧米では大規模な医療施設での出産が多いのに対して、日本に多い小規模な産科での出産では麻酔科医が不足していることが、こうした格差の一因とされる[9]。
歴史上、分娩の痛みは手術と同様、有効な鎮痛手段を長らく持たなかったが、19世紀半ばに実用化されたクロロホルムやジエチルエーテルの吸入による全身麻酔で無痛分娩が可能となった。しかし、全身麻酔は手術に用いることは歓迎されたものの、出産に用いることは医学界や宗教界からは当初根強い反対があった。無痛分娩は、1853年にイギリスのヴィクトリア女王に対して行われたことで広く一般にも行われるようになった。20世紀初頭には薄暮睡眠安産法︵twilight sleep︶、すなわちモルヒネとスコポラミンの注射による鎮静が麻酔方法に加わった。しかし、母体に対する全身麻酔は、誤嚥による肺炎︵メンデルソン症候群︶が1946年に報告されて以降問題視されるようになり、1960年代以降は硬膜外麻酔が主流となっている。
-
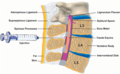
硬膜外麻酔の模式図
語義[編集]
一般的[注釈 1]にも専門的[10]にも無痛分娩、との呼称が普及しているが、陣痛が始まってから鎮痛を開始する[11]、すなわち、多かれ少なかれ痛みを感じてからの鎮痛であるために、﹁無痛﹂分娩とはいうものの、必ずしも無痛ではない[12][注釈 2]。この意を表すために、日本では和痛分娩や減痛分娩[12]、産痛緩和などとも表現される。産痛緩和は厚労省のガイドラインや日本産婦人科医会では硬膜外麻酔のみならず非薬理学的鎮痛方法をも含めた鎮痛手段全般とされている[13][14]。語義の上では無痛分娩も産痛緩和も鎮痛方法までは指定していないため、硬膜外麻酔を明示するためには、硬膜外無痛分娩[15]と呼ばれる。
英語圏でも、無痛分娩に相当する言葉は多様であり、一般的にはepidural birth, painless delivery, painless labor[10]、医学英語ではlabor analgesiaなどと表記される。analgesiaは"an:無"+"algesia:痛み"と語源の上では無痛[16]だが、専門家の間では主として鎮痛の意味で用いられている[17]。すなわち、英語圏においても、無痛に関して一般人と専門家との間で、語義において認識の相違が生じる余地がある。硬膜外麻酔に留まらない出産前後の鎮痛全般を表す言葉としてはPain management during childbirth[18][19]や"labor pain relief"[20]などがあるが、十分に定義されておらず[19]、対応する定訳も2023年現在確立されているとは言い難い[注釈 3]。
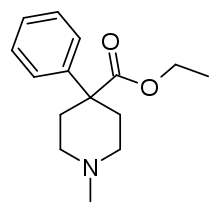
ペチジンの化学構造
分娩時の鎮痛には多くの方法がある。 オピオイドは、鎮痛を補助するために出産時に一般的に使用される鎮痛薬の一種である [22]。オピオイドの中ではペチジンが米国や英国などで使用されてきた[23]。オピオイドは、注射として筋肉に直接注入したり、静脈内に注入したりすることができる。これらの薬剤は、陣痛中の母親に眠気、かゆみ、吐き気、嘔吐などの望ましくない副作用を引き起こすことがある[22]。すべてのオピオイドは胎盤を通過する可能性があり、心拍数、呼吸、脳機能に問題を起こすなど、胎児に悪影響を及ぼす可能性がある。 このため、オピオイドは分娩直前には投与されない[22]。しかし、オピオイドは痛みを和らげる効果があるが、母体が動いたりいきんだりする能力を損なわないため、分娩初期には有益である。 また、オピオイドの使用は帝王切開の可能性が高くなることとは関連していないようである[22]。分娩時にオピオイドを使用するかどうかを決定する際には、考慮すべきことが多くあり、これらの選択肢やリスクと利益について、妊婦は訓練を受けた医療専門家と分娩第1期の早い段階以前に話し合う必要がある。 児に影響を及ぼす可能性のある処置や薬物について聞くことは、有効な質問である[21]。
準備[編集]
出産の準備は、出産時に経験する痛みの大きさに影響する。母親学級に参加したり、医療従事者や公的扶助サービスに相談したり、質問を書き留めたりすることで、痛みを管理するために必要な情報を得ることができる。友人や家族との簡単な交流が不安を和らげることもある[21]。医学的ないしは薬理学的鎮痛法[編集]
医師、看護師、助産師、ナース・プラクティショナー、医療助手︵physician assistant︶[注釈 4]は通常、陣痛中の女性に鎮痛の必要性を尋ねる。 訓練を受けた経験豊富な医療従事者が行えば、多くの鎮痛方法が有効である。また、分娩の段階によって鎮痛方法は使い分けられる。それでも、すべての病院や分娩センターですべての選択肢が利用できるわけではない。産婦の病歴やアレルギーの有無、その他の懸念事項によって、他の選択肢よりも有効なものもある[21]。オピオイド[編集]


硬膜外麻酔と脊髄くも膜下麻酔[編集]

硬膜外麻酔は、腰部の脊髄周囲の狭い空間︵硬膜外腔︶にチューブ︵硬膜外カテーテル︶を入れる処置である。陣痛中、必要に応じて少量の薬をチューブから投与することができる。硬膜外麻酔では、薬を投与してから10~20分後に痛みの緩和が始まる。しびれの程度は調節できる[21]。
分娩時に母親が感じる痛みは非常に強いとされ、さらに分娩の進行に伴い強くなっていくため母親にとって大きな負担となる。硬膜外麻酔による無痛分娩ではこの苦痛を相当強力に軽減できる[注釈 5]ほか、産後の育児や家事、仕事に必要な体力を温存することができる[9]。
特に母親が妊娠高血圧症候群である場合、分娩の痛みにより血圧が過度に上昇してしまうおそれや、ストレスホルモンによって血管が収縮して胎児への血流が非常に少なくなってしまう危険があるため、無痛分娩が有用とされる[25][26]。また、分娩中に緊急に帝王切開が必要になった場合、通常であれば脊髄くも膜下麻酔又は全身麻酔を行う必要があるが、硬膜外カテーテルを留置している無痛分娩であれば硬膜外麻酔で管理することができる[27]。
妊婦は硬膜外麻酔中、身体を動かすことは可能だが、薬が運動機能に影響を及ぼすと一時的に歩けなくなることがある。硬膜外麻酔は母体の血圧を下げ、胎児の心拍を遅くする可能性がある[28]。このリスクを下げるために点滴で水分を補給する。しかし、陣痛中の女性は、硬膜外麻酔の有無にかかわらず、しばしば発熱[29]や震え︵シバリング︶が起こる。硬膜外腔からオピオイド(主としてフェンタニル)を投与した場合には痒みや尿閉︵おしっこが出にくくなり膀胱に溜まること︶が起こることがある。脊髄の被膜︵硬膜︶が太い硬膜外針によって穿刺されると、ひどい頭痛が生じることもある︵硬膜穿刺後頭痛︶[28]。治療によって頭痛は改善可能である。硬膜外麻酔は、分娩数日間腰痛を起こすこともある。硬膜外麻酔により、分娩の第1期と第2期が長引くことがある[28]。陣痛が始まったのが遅かったり、薬の量が多すぎたりすると、いざというときにいきみにくくなることがある。硬膜外麻酔は器械分娩のリスクも高くなる[21]とされてきたが、コクランの2018年のシステマティック・レビューでは、近年の研究からはこのような傾向は見られないとされる[30]。
硬膜外麻酔で、まれに起こる重大な合併症としては、硬膜外麻酔の管がくも膜下腔に入り、脊髄くも膜下麻酔になってしまうことや局所麻酔薬中毒などがある[28]。無痛分娩を行う際には、これらの合併症に対応できるよう専門的な知識や技術が必要である。
CSEA[編集]
分娩がすでに進行している場合、素早く鎮痛を行うために硬膜外麻酔に脊髄くも膜下麻酔を併用する場合もある︵脊髄くも膜下硬膜外併用麻酔︵Combined spinal and epidural anaesthesia: 略称は脊硬麻又はCSEA︶︶[28]。脊髄くも膜下麻酔では、少量の薬を腰の髄液中に注射する[注釈 6]。脊髄くも膜下麻酔は通常、陣痛中に1回だけ行われる。脊髄くも膜下麻酔の場合、鎮痛効果はすぐに始まるが、持続するのは1~2時間である[21]。硬膜外麻酔では、カテーテルが留置されている限り、鎮痛時間に制限はない[注釈 7]。硬膜外麻酔と脊髄くも膜下麻酔により、ほとんどの女性は陣痛や出産時にほとんど痛みを感じることなく、目を覚まし、注意力を保っていることができる。CSEAでは胎児の徐脈が問題となることがある[28]。DPE[編集]
Dural puncture epidural︵DPE︶とは、近年、米国を中心に報告されている、硬膜外麻酔による無痛分娩の新しいテクニックである[28]。硬膜外麻酔においては頭痛が問題となるために、通常は硬膜穿刺を避けるが、本法では硬膜外麻酔に用いる太い針ではなく、脊髄くも膜下麻酔に用いる細い針で意図的に硬膜に穴を開け、その後で通常の硬膜外カテーテル留置を行うことにより、脊髄腔内への薬液の流入を増やして鎮痛効果を高める、というものである[28]。日本では1996年に鈴木らによって初めて発表された[28]。硬膜外麻酔単独やCSEAと遜色のない麻酔効果が得られ、合併症も少ないとする無作為化比較対象試験の結果が2017年に得られ[31]、産科麻酔科医に注目されている[28]。陰部神経ブロック[編集]
「陰部神経ブロック」を参照
この手技では、膣とその近くの陰部神経に局所麻酔薬を注射する。この神経は膣の下部と外陰部の感覚を司る。この鎮痛法は陣痛の後期、通常は胎児の頭が出てくる直前にのみ用いられる。陰部神経ブロックを行うと、痛みは多少和らぐとともに、産婦は意識を保ったまま、胎児を押し出すことができる。胎児は麻酔薬の影響を受けず、デメリットはほとんどない[21][32]。鉗子分娩となった場合の鎮痛効果も期待できるが、成功率は必ずしも高くない[28]。
笑気麻酔[編集]

ここまでに述べてきた薬理学的鎮痛方法は注射によるものであったが、これ以外に、陣痛中の母親が利用できる薬理学的鎮痛のもう1つの形態は、吸入亜酸化窒素である。 これは、典型的には、吸入鎮痛薬および麻酔薬である亜酸化窒素と空気との50/50混合物である。 亜酸化窒素は、1800年代後半から出産の疼痛管理に用いられてきた。吸入鎮痛は、英国、フィンランド、オーストラリア、シンガポール、ニュージーランドで一般的に使用されており、米国でも人気が高まっている[33]。
この鎮痛法は硬膜外麻酔ほどの鎮痛効果は得られないが、多くの利点がある。 亜酸化窒素は安価で、陣痛のどの段階でも安全に使用できる。 可動性を維持しながら軽い鎮痛効果を得たい女性に有用で、硬膜外麻酔ならば必要とされるであろうモニタリングも少なくて済む[33]。また、陣痛早期には鎮痛を補助するために有用であり、分娩ボール、体位変換、さらには水中出産など、他の非薬理学的鎮痛方法と併用される。 ガスは自己投与可能であるため、陣痛中の母親は、任意の時点でどれだけのガスを吸入したいかを完全に制御できる[33]。
亜酸化窒素には、副作用が少ないという利点もある。 一部の母親は、めまい、吐き気、嘔吐、眠気を経験するかもしれないが、投与量は患者によって決定されるため、これらの症状が始まれば、使用を制限することができる。 ガスはすぐに効果を発揮するが、持続時間も短いため、鎮痛効果を得るためには、マスクを顔に当て続けていなければならない[33]。亜酸化窒素ガスは、新生児が呼吸を始めるとすぐに排出されるため、新生児への影響はほとんどない[33]。 新生児の出生直後の評価項目である、アプガー指数や臍帯血液ガスにおいては、非薬理学的および薬理学的な疼痛管理の他の方法と比較して、亜酸化窒素ガスの使用に臨床的に重大な危険因子があることを示唆するエビデンスはない。 また、亜酸化窒素の使用に関連して医療従事者の職業上のリスクが増加するかどうかを判断するエビデンスも限られている[33]。
非薬理学的鎮痛方法[編集]
女性をリラックスさせ、鎮痛が容易になる多くの方法がある。 痛みを和らげるための非薬物的アプローチの有効性を検討した結果、水に浸かる、リラクゼーション法、鍼が痛みを和らげることがわかっている[34]。これらやその他の非薬物的疼痛管理法については、以下でさらに詳しく述べる。
●呼吸法とリラクゼーション法
●呼吸法︵ラマーズ法など︶ないしはリラクゼーション法は器械分娩のリスク軽減に役立つ可能性がある[21][34]。
●温かいシャワーや入浴[21]。
●マッサージ
●陣痛のさまざまな段階で、多くの種類のマッサージが行われる[21][35]。文献によれば、軽いタッチやなでるようなマッサージ法はオキシトシンの分泌を助け、子宮収縮を促し、子宮頸管の拡張を促進する可能性がある。 また、さまざまな種類のマッサージは、陣痛の痛みを和らげ、紛らわすのに役立つ可能性がある[36]。
●温湿布または冷湿布︵腰を温める、額に冷たい手ぬぐいなど︶
●子宮頸管が拡張している間に温湿布、特に腰部に温湿布を貼ることは、分娩第1期の痛みを軽減し、分娩自体の長さを短くするのに役立つかもしれないが、これを支持するエビデンスは限られている[21][36]。
●体位
●陣痛中に体位を変える[21]︵立つ、しゃがむ、座る、歩くなど︶
●バランスボール[21]の使用
産後ドゥーラが妊婦にバランスボールの使い方をアドバイスしている
●分娩中にバランスボールを使用するようになったのは1980年代からである。 陣痛の第1期に使用するのが最適である。バランスボールを使用することで、会陰部を支え、子宮頸管拡張中にその部分に優しい刺激を与えることで痛みを緩和しやすくするというエビデンスがあるとされる。 また、さまざまな体位変換運動や重力を利用して胎児の下降を助けることができる[37]。
●音楽を聴く
●痛みを軽減する効果的な方法として音楽[21]を支持するエビデンスはほとんどないが、気晴らしを提供したり、より肯定的な出産体験を作り出す手助けをしたりすることで、最終的に産後に否定的な転帰をたどる可能性を低下させる可能性がある[36]。
●鍼治療
●鍼は、器械分娩や帝王切開の減少に関連している可能性がある[34]。
陣痛に耐える妊婦に寄り添う産後ドゥーラ 最愛の人、病院スタッフ、または産後ドゥーラによる継続的なサポートケア[21]
●産後ドゥーラまたは何らかの支持者がいれば、薬理学的疼痛コントロールの必要性が減少し、帝王切開ではなく自然経腟分娩の可能性を高める可能性がある[38]。積極的な支援者は、より前向きな出産体験につながる環境づくりも支援してくれるだろう[39]。
●その他の方法としては、催眠、バイオフィードバック、滅菌水注射、アロマセラピー、経皮的末梢神経電気刺激︵TENS︶などがあるが、これらの方法を用いて陣痛や分娩時の痛みを軽減することの有効性を示した研究は限られている[34]。


水中出産[編集]
詳細は「水中出産」を参照

米国女性保健局︵Office of Women's Health: OWH︶によると、水治療法︵hydrotherapy︶とも呼ばれる温浴槽での陣痛は、女性が身体的に支えられていると感じ、体を温めリラックスさせるのに役立つという。また、水中では、陣痛中の女性が動きやすくなり、楽な姿勢をとりやすくなることもある[21]。
分娩第1期の水浸は、鎮痛の必要性を減少させ、分娩期間を短縮させる可能性があるが、分娩第2期および第3期の水浸が薬理学的介入の使用を有意に減少させることを示唆するデータは限られている[40][41]。
水中出産では、女性は分娩のために水の中に残る。米国小児科学会は、水中出産の安全性を示す研究が不足していること、また、まれではあるが合併症の可能性が報告されていることから、水中出産に対する懸念を表明している[21]。

会陰切開の模式図
出産後の会陰部痛は、女性とその児に即時的かつ長期的な悪影響を及ぼす。これらの影響は、母乳育児や乳児の世話に支障をきたす可能性がある[42]。注射部位や会陰切開による痛みは、母親からの痛みの報告を頻繁に評価することで管理される。疼痛は、裂傷、切開、子宮収縮、乳首の痛みなどから生じる可能性がある。通常、適切な薬剤が投与される[43]。ルーチンの会陰切開は、出産後の疼痛レベルを低下させることは認められていない[44]。
産後の疼痛管理[編集]

歴史[編集]
無痛分娩が「無」の時代[編集]
20世紀以前は、出産は主に家庭で行われ、疼痛管理のための医療介入を受けることはできなかった[45]。出産は女性の主な死因であり、多くの女性がその過程を恐れていたため、疼痛管理に対する要望は大きかった[46]。しかし、女性達の要望にもかかわらず、19世紀半ば以前にはほとんど緩和措置がとられていなかったし、その手段も無かった。分娩時の鎮痛に対しては、かなりの一般的および宗教的反対があった[47]。1591年にはスコットランドで、2人の息子の出産のために痛み止めを求めたというだけで、ユーファム・マカレインという女性が生き埋めにされている[47]。

ジエームズ・シンプソン
手術における全身麻酔薬の投与は、1846年10月にボストンでウィリアム・トーマス・グリーン・モートン(1819–1868)によって、この種の最初の成功例として公に実証された[48]。この実践により、手術中のエーテル吸入による鎮痛作用が明らかになった。
モートンが麻酔薬としてエーテルを使用した後、スコットランドのジェームズ・ヤング・シンプソン(1811–1870)は1847年1月19日、エーテル投与に開放点滴法を用いて無痛分娩の臨床試験を行った[49][50][51]。彼が無痛分娩の先駆者である。その後、シンプソンは独自にクロロホルムの麻酔効果を発見し、1847年11月にクロロホルムの試用を公開することになった。シンプソンの発表を掲載した医学外科学会の出版物はあまり受け入れられず、その後、かなりの弁明を必要としたものの、エーテル麻酔後の吐き気や嘔吐も問題であったため、後にクロロホルムの使用も受け入れられた[50]。1847年4月7日、アメリカの産科で初めてエーテルが使用された[49][50]。ボストン医学外科学雑誌に記録されたN.C.キープによる最初の投与に続いて、米国のウォルター・チャニング(1786–1876)がエーテルを用いて成功したいくつかの産科症例について述べている[49][52]。最初の無痛分娩は吸入麻酔薬による全身麻酔で始まったのである[注釈 8]。

ジョン・スノウ
1853年4月7日、ロンドンのジョン・スノウ(1813–1858)[49][50][47]はクロロホルム吸入により、ビクトリア女王の分娩時の麻酔を担当した[59]。王妃の第8子であるレオポルド王子の誕生は一般には公表されなかったが、ロンドンの社交界の貴顕はこの出産にクロロホルムが使用されていることを知り、魅力的だと感じていた[49][50][47]。この処置は、﹁クロロホルム・ア・ラ・レーヌ︵chloroform à la reine: 女王風に︶﹂として女性たちに知られるようになった[54]。女王自身が無痛分娩を受け入れたことがきっかけとなり、反対派は減っていき、無痛分娩は普及していった[60][46][61]。シンプソンとスノウは無痛分娩の普及に大きな役割を果たしたが、鎮痛の積極性において異なる。スノウはシンプソンと大きく異なり、麻酔薬の適切な量の測定と、分娩第2期が始まるまで投与を遅らせることを強調した[62]。また、スノウは、陣痛を起こす患者には意識がなくなるまで麻酔をかけるべきだというシンプソンの主張にも反対していた。このような違いから、﹁産科麻酔の父﹂という称号はいずれにふさわしいか大きな論争を呼んだ[63]。

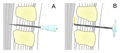
脊髄くも膜下麻酔では穿刺針が硬膜を貫いてくも膜下腔に到達する︵A ︶が、硬膜外麻酔では穿刺針は硬膜手前の硬膜外腔に留まり、カテーテルが留置される︵B︶。
おそらく産科麻酔における最も重要な発見は、区域麻酔の導入であり[50]、これは局所麻酔薬を使用して身体の広い領域からの痛みをブロック、すなわち無痛にするものである。最初の局所麻酔薬[51]であるコカインは、1884年にオーストリアの眼科医カール・コラーによって眼科で表面麻酔に使用された[50][51]。ドイツの外科医アウグスト・ビーアが最初の臨床脊髄くも膜下麻酔[50]、SicardとCathleinが1901年の硬膜外麻酔への仙骨アプローチ[50]、およびスペイン軍の外科医フィデル・パジェスが1921年の腰部硬膜外アプローチ[49][50]を完成させた。1921年、脊髄くも膜下麻酔下での最初の経膣分娩がドイツのKreissによって報告された[50]。ジョージ・ピトキンは、米国で分娩時の脊髄くも膜下麻酔を普及させたとされている[50]。チャールズ B. オドムは、1935年に腰部硬膜外麻酔を無痛分娩に応用した[49][50]。
全身麻酔の発明と出産への応用[編集]

宗教界からと医師からの反対[編集]
しかし、エーテルやクロロホルムを出産に対して使用することは、社会的、宗教的、および医学的な反対に直面した[53]。一部の医師や宗教的権威は、分娩時の痛みの緩和は、分娩に痛みを伴うようにした神の選択に反すると主張したが、この解釈に明確に異議を唱える者もいた。しかし、麻酔に対する反対のほとんどは、その健康への影響や陣痛への身体的影響に対する懸念という観点に立脚していた[54][55]。聖書の直訳解釈により、陣痛を罪に対する罰とみなす者が多く、無痛分娩は原始の呪いに関して不敬であるとされたのである[56]。反対派の産科医チャールズ・デルセナ・メイグスは、分娩痛に生理学的価値があるという信念を主張し[57]、19世紀中頃には一般の人々にも支持されるようになった。このような時代背景のため、無痛分娩は女性からは支持されたが、医師からの支持は消極的だった[46]。シンプソンは、麻酔薬の吸入は、分娩行為や子宮収縮の起こるメカニズムに影響を与えず、むしろ産婦を強い痛みに無感覚にさせると反駁した[58]。ビクトリア女王の無痛分娩による普及[編集]

モルヒネ[編集]
1800年代初頭にモルヒネが単離されたことは、産科麻酔におけるもう一つの画期的な出来事であった[49][50]。しかし、この薬が広く使われるようになったのは、1850年代に注射針が発明されてからである[49][50]。しかし、分娩時の疼痛コントロールにモルヒネを使用することは、新生児の呼吸抑制[注釈 9]の影響から人気がなくなり、1939年にドイツで初めて作られた、呼吸抑制の影響が少ない合成麻薬であるメペリジンに大きく取って代わられた[49][50]。メペリジンは、今日でも産科でよく使われている[50]。区域麻酔[編集]

注射による鎮静法の開発と衰退[編集]
20世紀初頭、ドイツのフライブルクに住む二人の医師、カール・ガウスとベルンハルト・クローニッヒによって、"薄暮睡眠安産法︵twilight sleep︶"として知られる薬物誘発状態が開発された。この方法は、モルヒネとスコポラミンの筋肉内注射による一種の鎮静法であり、特に訓練を受けていない医師が行った場合、多くのリスクと副作用があった︵妊婦の徐脈、呼吸抑制、せん妄など︶[64]。その盛衰は、第一波フェミニズムと第一次世界大戦中に生じた反ドイツ感情の両方と重なった。日本では、1915年に一般向け冊子で紹介されたが、﹁無害有効である﹂など、その情報は正確さを欠いていた[65]。 1946年にはアメリカの産科医であるカーティス・メンデルソンにより、妊婦に全身麻酔を行った際の誤嚥による肺炎︵メンデルソン症候群︶が報告され[66]、妊婦に全身麻酔を行うことの危険性と全身麻酔前の絶食の重要性が広く認識され、無痛分娩に全身麻酔を回避する機運のきっかけとなった[66][注釈 10]。一世紀ぶりのカトリックによる承認、硬膜外麻酔の普及[編集]
ヨーロッパにおいて、宗教界は長年無痛分娩を承認していなかったが、1956年には、ようやくローマ教皇ピウス12世は無痛分娩の使用を承認した[61]。1960年代には、疼痛管理のための硬膜外麻酔が台頭し[67][68]、2023年現在まで無痛分娩の主流となっている。日本[編集]
日本における無痛分娩という言葉の歴史は少なくとも1903年にまで遡ることが出来るが、鎮痛法は催眠術であった[69]。会陰部への局所浸潤麻酔による無痛分娩が日本で初めて報告されたのは、1919年であるが、 カクシテ尚痲酔不充分ナルトキハ注射ヲ新タニスルモ何等妨ゲアルナシ—安藤畫一 (岡山醫專産婦人科教室)、所謂無痛分娩法ニ對スル私見併セテ局所麻醉法ノ應用ヲ推奬ス、[70]
と報告されていることから、無痛分娩という名称ではあっても、必ずしも無痛ではなかったことが窺える。1960年の段階では、呼吸法や鎮静剤、吸入麻酔による方法が主流で﹁まだ無痛分娩とは縁遠い状態﹂[71]にもかかわらず無痛分娩という言葉だけは普及していた。1961年には、産科医らにより、第1回無痛分娩研究会が開催された[72]。この研究会は1994年の﹁分娩と麻酔研究会﹂を経て、2009年には麻酔科医も加わり、日本産科麻酔学会に改名した[72]。硬膜外麻酔による無痛分娩の日本での報告は1962年が最初であり[73]、以後は麻酔方法としては硬膜外麻酔が欧米同様、他の麻酔法に取って代わっていったものの、その一般への認知は遅々としており、1978年の段階でも呼吸法であるラマーズ法が﹁無痛分娩法﹂として助産師や看護師向けの雑誌で紹介されていた[74]。
麻酔科医分散による低普及率問題・解決案[編集]
欧米では硬膜外無痛分娩の普及率が高い︵フィンランドは89%[75]、フランスは82%[75]、アメリカ合衆国は73.1%[76]︶なのに対して、日本では硬膜外無痛分娩そのものの施行率が8.6%︵2020年9月の厚労省調査︶[77]である。 背景として、欧米では大規模な医療施設での出産が多い。逆に日本では、小規模な病院の産科やクリニックでの出産が多く、麻酔科医を事実上分散させる状態にさせてしまっていることで﹁麻酔科医がいないので出来ない﹂ことが、無痛分娩の大きな普及差の一因とされる[9][78][79]。また﹁自然を好む﹂風潮も無痛分娩普及を妨げている一因との主張もあるが[77]、無痛分娩賛成率は8割である[78]。 それでも日本において、総分娩数に占める無痛分娩数の割合は、4.6%︵2014年度︶、5.5%︵2015年度︶、6.1%︵2016年度︶と上昇傾向である[80]。 将来的には、検診は地域の産科クリニックなどで受けつつ、出産場所を総合病院などに集める﹃出産施設の集約化﹄が必要だと指摘されている[78]。脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
(一)^ 2023年8月現在、Google検索では237万件の検索結果
(二)^ 陣痛はいつ起こるか予測が困難で、痛みがないのに鎮痛剤を投与し続けることは母児への害が大きい。陣痛促進剤を用い、子宮口の開大の程度を評価して硬膜外麻酔をはじめる、すなわち計画分娩であれば、最初から無痛とすることも可能ではあるが、陣痛促進剤によって陣痛が誘発されるかどうか、硬膜外麻酔がどの程度痛みを軽減できるか、不確定要素が大きい。
(三)^ 2023年現在の﹁麻酔科学用語集第5版﹂には無痛分娩という言葉そのものが採録されていない。
(四)^ ナースプラクティショナーと医療助手は2023年時点の日本には公的には存在しない職種である。
(五)^ 硬膜外麻酔の鎮痛は強力で、分娩だけでなく手術にも利用可能であり、胃の全摘手術も硬膜外麻酔単独で行える[24]ほどである。
(六)^ 2023年現在の日本では、無痛分娩に対して、あまり一般的な方法では無い。
(七)^ 鎮痛時間に制限は無いが、分娩時間が長引くと妊婦や胎児は疲労するので、経腟分娩から帝王切開に変更となることはある。
(八)^ 厳密には、この時代の全身麻酔の何割かは﹁浅い﹂全身麻酔、すなわち﹁鎮静﹂であったものと思われる。鎮静と全身麻酔の違いについては鎮静レベルを参照。
(九)^ 通常、新生児は出生直後に産声を上げる、すなわち呼吸をはじめるが、母体に投与されたモルヒネは胎盤を経由して胎児に移行すると、その影響で新生児が息をしない可能性があった。
(十)^ この時代は気管挿管などの確実な気道確保によって、気道と消化管を分離して気道を誤嚥から保護する技術が未発達だった。メンデルソンが報告した全身麻酔に伴う誤嚥は主として吸入麻酔薬によるものであったが、薄暮睡眠安産法も、薬剤の投与経路が異なるだけで妊婦の意識を混濁させて誤嚥のリスクを上昇させるものであった。
出典[編集]
(一)^ “Q3. 無痛分娩で用いられる鎮痛法にはどんな方法があるのですか? | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年8月28日閲覧。
(二)^ “︻第3回︼7.産痛緩和”. 日本産婦人科医会 (2022年7月26日). 2023年8月29日閲覧。
(三)^ “無痛分娩を受けられる方へ|丸石製薬株式会社|ベーシックドラッグ、周術期医療・感染対策領域のメーカー”. www.maruishi-pharm.co.jp (2019年10月21日). 2024年5月21日閲覧。
(四)^ abc痛くないお産 麻酔分娩がよ〜くわかる本 痛くないお産 麻酔分娩がよ〜くわかる本p18 ,メディカ出版 ,島田信宏
(五)^ “Q3. 無痛分娩で用いられる鎮痛法にはどんな方法があるのですか? | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年8月28日閲覧。
(六)^ “︻第3回︼7.産痛緩和”. 日本産婦人科医会 (2022年7月26日). 2023年8月29日閲覧。
(七)^ “医療関係者の皆様へ | JMS 医療関係者向けサイト”. medical.jms.cc. 2024年5月21日閲覧。
(八)^ Hasegawa, Junichi; Farina, Antonio; Turchi, Giovanni; Hasegawa, Yuko; Zanello, Margherita; Baroncini, Simonetta (2013-02-01). “Effects of epidural analgesia on labor length, instrumental delivery, and neonatal short-term outcome” (英語). Journal of Anesthesia 27 (1): 43–47. doi:10.1007/s00540-012-1480-9. ISSN 1438-8359.
(九)^ abchttps://www.facebook.com/mainichishimbun.+“広がらない無痛分娩 実施率9割のフィンランドにヒントはあるか”. 毎日新聞. 2023年7月15日閲覧。
(十)^ ab“日本医学会医学用語辞典”. jams.med.or.jp. 2023年8月29日閲覧。
(11)^ “Q9. 硬膜外鎮痛は、いつ、どのように始めるのですか? | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年8月28日閲覧。
(12)^ ab“リスクは? 痛みは? 無痛分娩にまつわる誤解︻専門医監修︼ | ミキハウス 妊娠・出産・子育てマガジン”. baby.mikihouse.co.jp. 2023年8月30日閲覧。
(13)^ “Front/PublicGuideline”. minds.jcqhc.or.jp. 2023年8月30日閲覧。
(14)^ “︻第3回︼7.産痛緩和”. 日本産婦人科医会 (2022年7月26日). 2023年8月30日閲覧。
(15)^ “Q11. 硬膜外無痛分娩をしたとき、お産のあとはどうなりますか? | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年8月30日閲覧。
(16)^ 高久史麿﹃ステッドマン医学大辞典﹄︵改訂第5版︶メジカルビュー社、2002年2月20日、69頁。ISBN 4-7583-0000-3。
(17)^ “Definition of ANALGESIA” (英語). www.merriam-webster.com. 2023年8月30日閲覧。
(18)^ Wolf, Michael (2021-12-31). “Pain Management during Childbirth” (英語). Journal of Labor and Childbirth 4 (1): 01.
(19)^ abLindholm, Annika; Hildingsson, Ingegerd (2015-06). “Women's preferences and received pain relief in childbirth - A prospective longitudinal study in a northern region of Sweden”. Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare: Official Journal of the Swedish Association of Midwives 6 (2): 74–81. doi:10.1016/j.srhc.2014.10.001. ISSN 1877-5764. PMID 25998874.
(20)^ “Labor Pain Relief: Options & Side Effects” (英語). Cleveland Clinic. 2023年8月30日閲覧。
(21)^ abcdefghijklmnopq“Pregnancy Labor and Birth”. Office on Women's Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2017年2月1日). 2017年7月15日閲覧。 この記事には現在パブリックドメインとなった次の出版物からの記述が含まれています。
(22)^ abcd“ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 177: Obstetric Analgesia and Anesthesia”. Obstetrics & Gynecology 100 (1): 177–191. (April 2017). doi:10.1097/00006250-200207000-00032. ISSN 0029-7844.
(23)^ “Parenteral opioids for labor pain relief: A systematic review - American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology”. www.ajog.org. 2015年7月11日閲覧。
(24)^ 原野清、平川奈緒美、福井雅士、十時忠秀﹁私の推奨する麻酔法‥ 開腹手術の麻酔 硬膜外麻酔法のみによる胃切除術﹂﹃日本臨床麻酔学会誌﹄第16巻第3号、日本臨床麻酔学会、1996年、225-229頁、CRID 1390001204759031168、doi:10.2199/jjsca.16.225、ISSN 0285-4945。
(25)^ ﹃妊娠高血圧症候群の診療指針 2015 - Best Practice Guide -﹄
(26)^ “Q13. 硬膜外無痛分娩のメリットはなんですか? | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年7月15日閲覧。
(27)^ 公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会 2012, p. 344.
(28)^ abcdefghijk岡原祥子、角倉弘行﹁正常分娩の鎮痛・鎮静﹂﹃日本臨床麻酔学会誌﹄第38巻第4号、日本臨床麻酔学会、2018年7月、556-561頁、CRID 1390845712995668352、doi:10.2199/jjsca.38.556、ISSN 0285-4945。
(29)^ Sharpe, Emily E.; Arendt, Katherine W. (2017-06). “Epidural Labor Analgesia and Maternal Fever”. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 60 (2): 365–374. doi:10.1097/GRF.0000000000000270. ISSN 1532-5520. PMID 28079555.
(30)^ Anim-Somuah, Millicent; Smyth, Rebecca MD; Cyna, Allan M; Cuthbert, Anna (2018-05-21). Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group. ed. “Epidural versus non-epidural or no analgesia for pain management in labour” (英語). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018 (5). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000331.pub4. PMC PMC6494646. PMID 29781504.
(31)^ Chau, Anthony; Bibbo, Carolina; Huang, Chuan-Chin; Elterman, Kelly G.; Cappiello, Eric C.; Robinson, Julian N.; Tsen, Lawrence C. (2017-02). “Dural Puncture Epidural Technique Improves Labor Analgesia Quality With Fewer Side Effects Compared With Epidural and Combined Spinal Epidural Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Trial”. Anesthesia and Analgesia 124 (2): 560–569. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000001798. ISSN 1526-7598. PMID 28067707.
(32)^ Maclean A, Reid W (2011). "40". In Shaw RM (ed.). Gynaecology. Edinburgh New York: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 599–612. ISBN 978-0-7020-3120-5。
(33)^ abcdef“Nitrous oxide for the management of labor pain: a systematic review”. Anesthesia and Analgesia 118 (1): 153–167. (January 2014). doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182a7f73c. PMID 24356165.
(34)^ abcdJones L, Othman M, Dowswell T, Alfirevic Z, Gates S, Newburn M, et al. (March 2012). "Pain management for women in labour: an overview of systematic reviews". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3(3): CD009234. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009234.pub2. PMC 7132546. PMID 22419342. S2CID 7358365。
(35)^ Smith CA, Levett KM, Collins CT, Jones L (February 2012). "Massage, reflexology and other manual methods for pain management in labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009290. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009290.pub2. PMID 22336862。
(36)^ abcSmith CA, Levett KM, Collins CT, Armour M, Dahlen HG, Suganuma M (March 2018). "Relaxation techniques for pain management in labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (3): CD009514. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd009514.pub2. PMC 6494625. PMID 29589650。
(37)^ Makvandi S, Latifnejad Roudsari R, Sadeghi R, Karimi L (November 2015). "Effect of birth ball on labor pain relief: A systematic review and meta-analysis". The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. 41(11): 1679–1686. doi:10.1111/jog.12802. PMID 26419499. S2CID 476947。
(38)^ Bohren MA, Hofmeyr GJ, Sakala C, Fukuzawa RK, Cuthbert A (July 2017). "Continuous support for women during childbirth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (8): CD003766. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003766.pub6. PMC 6483123. PMID 28681500。
(39)^ “Creating a positive perception of childbirth experience: systematic review and meta-analysis of prenatal and intrapartum interventions”. Reproductive Health 15 (1): 73. (May 2018). doi:10.1186/s12978-018-0511-x. PMC 5932889. PMID 29720201.
(40)^ Cluett ER, Burns E, Cuthbert A (May 2018). "Immersion in water during labour and birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 5(6): CD000111. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd000111.pub4. PMC 6494420. PMID 29768662。
(41)^ “Immersion in Water During Labor and Delivery - ACOG”. www.acog.org. 2019年1月25日閲覧。
(42)^ Shepherd E, Grivell RM (July 2020). "Aspirin (single dose) for perineal pain in the early postpartum period". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (7): CD012129. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012129.pub3. PMC 7388929. PMID 32702783。
(43)^ Henry, p. 122.
(44)^ Jiang H, Qian X, Carroli G, Garner P (February 2017). "Selective versus routine use of episiotomy for vaginal birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (2): CD000081. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000081.pub3. PMC 5449575. PMID 28176333。
(45)^ Pollesche J (2018). "Twilight Sleep". ASU Embryo Project Encyclopedia. ISSN 1940-5030. 2023年7月10日閲覧。
(46)^ abcSandelowski M (1984). Pain, pleasure, and American childbirth: from the twilight sleep to the read method. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press. pp. 3–26.
(47)^ abcdTolmie, John D.; Birch, Alexander (1986). Anesthesia for the uninterested (2nd ed.). Rockville, Md: Aspen Publishers. pp. 163. ISBN 978-0871892966
(48)^ Gordon, Henry L. Sir James Young Simpson and Chloroform (1811-1870). Ed. Ernest Hart. Pasternoster Square, London: Urwin, 1897. Masters of Medicine. Web. 2017.
(49)^ abcdefghijMarx, Gertie F.; Bassell, Gerard M. (1980). Obstetric Analgesia and Anaesthesia. The Netherlands: Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press. pp. 1, 5–8, 10, 12–13. ISBN 978-0-444-80137-1
(50)^ abcdefghijklmnopqRamanathan, Sivam (1988). Obstetric anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-0-8121-1118-7
(51)^ abcMiller, Ronald D.; Pardo, Manuel C. Jr. (2012). Basics of anesthesia (6th ed.). Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-81-312-2898-2. OCLC 742301032
(52)^ Johann Hermann Baas、trans. Henry Ebenezer Handerson﹃Outlines of the History of Medicine and the Medical Profession﹄J.H. Vail & Co.、1889年、1096頁。
(53)^ “A short history of Obstetric Anaesthesia”. Res Medica 3 (1). (2014). doi:10.2218/resmedica.v3i1.972. ISSN 2051-7580.
(54)^ abBarry, Ellen (2019年5月6日). “Chloroform in Childbirth? Yes, Please, the Queen Said”. The New York Times 2022年10月15日閲覧。
(55)^ Corretti, Carolyn; Desai, Sukumar P. (1 July 2018). “The Legacy of Eve's Curse: Religion, Childbirth Pain, and the Rise of Anesthesia in Europe: c. 1200-1800s”. Journal of Anesthesia History 4 (3): 182–190. doi:10.1016/j.janh.2018.03.009. PMID 30217391.
(56)^ Simpson, J. Y. (1853). “The Propriety and Morality of Using Anæsthetics in Instrumental and Natural Parturition”. Association Medical Journal 1 (27): 582–589. JSTOR 25494769.
(57)^ “Charles Delucena Meigs ( 1792 - 1869 )”. www.general-anaesthesia.com. 2023年7月17日閲覧。
(58)^ Simpson, J. Y. (1848). “Letter in Reply to Dr. Collins, on the Duration of Labour as a Cause of Danger and Mortality to the Mother and Infant”. Provincial Medical and Surgical Journal 12 (22): 601–606. JSTOR 25500540.
(59)^ “Queen Victoria uses chloroform in childbirth, 1853”. Financial Times. (2017年11月28日). オリジナルの2022年12月10日時点におけるアーカイブ。
(60)^ Waserman, Manfred (1980). “Sir James Y Simpson And London's "Conservative And So Curiously Prejudiced" Dr Ramsbotham”. The British Medical Journal (BMJ) 280 (6208): 161. JSTOR 25438475.
(61)^ abCamann W (2014). "A History of Pain Relief During Childbirth". The Wondrous Story of Anesthesia. pp. 847–858. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8441-7_62. ISBN 978-1-4614-8440-0。
(62)^ Snow, John (1853). “On the Administration of Chloroform during Parturition”. Association Medical Journal 1 (23): 500–502. doi:10.1136/bmj.s3-1.23.500. JSTOR 25494691. PMC 2449612. PMID 20740854.
(63)^ Gordon, Henry L. Sir James Young Simpson and Chloroform (1811-1870). Ed. Ernest Hart.
(64)^ “Twilight Sleep | The Embryo Project Encyclopedia”. embryo.asu.edu. 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(65)^ 家庭問題研究会 編﹃ご存知でせうか﹄平凡社、1915年、85-86頁。doi:10.11501/954861。
(66)^ abSalik, Irim; Doherty, Tara M. (2023), Mendelson Syndrome, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30969586 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(67)^ Noble, A. D.; de Vere, R. D. (1970-05-02). “Epidural Analgesia in Labour”. British Medical Journal 2 (5704): 296. ISSN 0007-1447. PMC 1700456. PMID 5420187.
(68)^ Kandel, P. F.; Spoerel, W. E.; Kinch, R. A. (1966-11-05). “Continuous epidural analgesia for labour and delivery: review of 1000 cases”. Canadian Medical Association Journal 95 (19): 947–953. ISSN 0008-4409. PMC 1935745. PMID 5922909.
(69)^ 塚原傳﹁催眠術ニ由ル無痛分娩ニ就テ﹂﹃産婆學雜誌﹄第四六、1903年、ページ記載なし。
(70)^ 安藤畫一 (1919). “所謂無痛分娩法ニ對スル私見併セテ局所麻醉法ノ應用ヲ推奬ス”. 實驗醫報 第五年第五三: ページ記載なし.
(71)^ 菅井正朝, 松葉弘﹃無痛分娩 : 産痛の精神予防法を主として (創元医学新書)﹄創元社、1960年。
(72)^ ab“学会概要 | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(73)^ 安井修平, 楠本雅彦, 下平和夫, 島中俊次, 大沢辰治, 伊藤宜孝, 清水昭造, 高橋哲也, 植松修﹁189. 持続硬膜外麻酔による無痛分娩﹂﹃日本産科婦人科學會雜誌﹄第14巻第8号、日本産科婦人科学会、1962年6月、715頁、CRID 1541698620245984128、NDLJP:10662345。
(74)^ 山本亮 (1978). “婦人の健康づくり対策”. 愛育 (恩賜財団母子愛育会) 43: 18-21. doi:10.11501/2268087.
(75)^ ab“Women feel Italy's north-south divide with lack of access to epidurals” (英語). euronews (2018年3月22日). 2023年8月27日閲覧。
(76)^ Butwick, Alexander J.; Bentley, Jason; Wong, Cynthia A.; Snowden, Jonathan M.; Sun, Eric; Guo, Nan (2018-12-07). “United States State-Level Variation in the Use of Neuraxial Analgesia During Labor for Pregnant Women”. JAMA network open 1 (8): e186567. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.6567. ISSN 2574-3805. PMC 6324365. PMID 30646335.
(77)^ ab“無痛分娩に﹁ずるい﹂﹁おなかを痛めてこそ母親﹂の声 日本では1割未満 広がらない背景は #令和の親”. www.chibanippo.co.jp. 千葉日報. 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(78)^ abc“︻後編︼麻酔科医が足りない…無痛分娩の賛成8割超えなのに実施率1割以下のワケ︻独自アンケート︼︵日テレNEWS︶”. Yahoo!ニュース. 2023年9月24日閲覧。
(79)^ 痛くないお産 麻酔分娩がよ〜くわかる本 痛くないお産 麻酔分娩がよ〜くわかる本p31 ,メディカ出版 ,島田信宏
(80)^ 海野信也; 板倉敦夫. “無痛分娩の安全性に関する検討”. 厚生労働省. 2023年8月27日閲覧。
この記事には現在パブリックドメインとなった次の出版物からの記述が含まれています。
(22)^ abcd“ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 177: Obstetric Analgesia and Anesthesia”. Obstetrics & Gynecology 100 (1): 177–191. (April 2017). doi:10.1097/00006250-200207000-00032. ISSN 0029-7844.
(23)^ “Parenteral opioids for labor pain relief: A systematic review - American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology”. www.ajog.org. 2015年7月11日閲覧。
(24)^ 原野清、平川奈緒美、福井雅士、十時忠秀﹁私の推奨する麻酔法‥ 開腹手術の麻酔 硬膜外麻酔法のみによる胃切除術﹂﹃日本臨床麻酔学会誌﹄第16巻第3号、日本臨床麻酔学会、1996年、225-229頁、CRID 1390001204759031168、doi:10.2199/jjsca.16.225、ISSN 0285-4945。
(25)^ ﹃妊娠高血圧症候群の診療指針 2015 - Best Practice Guide -﹄
(26)^ “Q13. 硬膜外無痛分娩のメリットはなんですか? | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年7月15日閲覧。
(27)^ 公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会 2012, p. 344.
(28)^ abcdefghijk岡原祥子、角倉弘行﹁正常分娩の鎮痛・鎮静﹂﹃日本臨床麻酔学会誌﹄第38巻第4号、日本臨床麻酔学会、2018年7月、556-561頁、CRID 1390845712995668352、doi:10.2199/jjsca.38.556、ISSN 0285-4945。
(29)^ Sharpe, Emily E.; Arendt, Katherine W. (2017-06). “Epidural Labor Analgesia and Maternal Fever”. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 60 (2): 365–374. doi:10.1097/GRF.0000000000000270. ISSN 1532-5520. PMID 28079555.
(30)^ Anim-Somuah, Millicent; Smyth, Rebecca MD; Cyna, Allan M; Cuthbert, Anna (2018-05-21). Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group. ed. “Epidural versus non-epidural or no analgesia for pain management in labour” (英語). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018 (5). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000331.pub4. PMC PMC6494646. PMID 29781504.
(31)^ Chau, Anthony; Bibbo, Carolina; Huang, Chuan-Chin; Elterman, Kelly G.; Cappiello, Eric C.; Robinson, Julian N.; Tsen, Lawrence C. (2017-02). “Dural Puncture Epidural Technique Improves Labor Analgesia Quality With Fewer Side Effects Compared With Epidural and Combined Spinal Epidural Techniques: A Randomized Clinical Trial”. Anesthesia and Analgesia 124 (2): 560–569. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000001798. ISSN 1526-7598. PMID 28067707.
(32)^ Maclean A, Reid W (2011). "40". In Shaw RM (ed.). Gynaecology. Edinburgh New York: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 599–612. ISBN 978-0-7020-3120-5。
(33)^ abcdef“Nitrous oxide for the management of labor pain: a systematic review”. Anesthesia and Analgesia 118 (1): 153–167. (January 2014). doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182a7f73c. PMID 24356165.
(34)^ abcdJones L, Othman M, Dowswell T, Alfirevic Z, Gates S, Newburn M, et al. (March 2012). "Pain management for women in labour: an overview of systematic reviews". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3(3): CD009234. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009234.pub2. PMC 7132546. PMID 22419342. S2CID 7358365。
(35)^ Smith CA, Levett KM, Collins CT, Jones L (February 2012). "Massage, reflexology and other manual methods for pain management in labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009290. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009290.pub2. PMID 22336862。
(36)^ abcSmith CA, Levett KM, Collins CT, Armour M, Dahlen HG, Suganuma M (March 2018). "Relaxation techniques for pain management in labour". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (3): CD009514. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd009514.pub2. PMC 6494625. PMID 29589650。
(37)^ Makvandi S, Latifnejad Roudsari R, Sadeghi R, Karimi L (November 2015). "Effect of birth ball on labor pain relief: A systematic review and meta-analysis". The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. 41(11): 1679–1686. doi:10.1111/jog.12802. PMID 26419499. S2CID 476947。
(38)^ Bohren MA, Hofmeyr GJ, Sakala C, Fukuzawa RK, Cuthbert A (July 2017). "Continuous support for women during childbirth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (8): CD003766. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003766.pub6. PMC 6483123. PMID 28681500。
(39)^ “Creating a positive perception of childbirth experience: systematic review and meta-analysis of prenatal and intrapartum interventions”. Reproductive Health 15 (1): 73. (May 2018). doi:10.1186/s12978-018-0511-x. PMC 5932889. PMID 29720201.
(40)^ Cluett ER, Burns E, Cuthbert A (May 2018). "Immersion in water during labour and birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 5(6): CD000111. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd000111.pub4. PMC 6494420. PMID 29768662。
(41)^ “Immersion in Water During Labor and Delivery - ACOG”. www.acog.org. 2019年1月25日閲覧。
(42)^ Shepherd E, Grivell RM (July 2020). "Aspirin (single dose) for perineal pain in the early postpartum period". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (7): CD012129. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012129.pub3. PMC 7388929. PMID 32702783。
(43)^ Henry, p. 122.
(44)^ Jiang H, Qian X, Carroli G, Garner P (February 2017). "Selective versus routine use of episiotomy for vaginal birth". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (2): CD000081. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000081.pub3. PMC 5449575. PMID 28176333。
(45)^ Pollesche J (2018). "Twilight Sleep". ASU Embryo Project Encyclopedia. ISSN 1940-5030. 2023年7月10日閲覧。
(46)^ abcSandelowski M (1984). Pain, pleasure, and American childbirth: from the twilight sleep to the read method. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press. pp. 3–26.
(47)^ abcdTolmie, John D.; Birch, Alexander (1986). Anesthesia for the uninterested (2nd ed.). Rockville, Md: Aspen Publishers. pp. 163. ISBN 978-0871892966
(48)^ Gordon, Henry L. Sir James Young Simpson and Chloroform (1811-1870). Ed. Ernest Hart. Pasternoster Square, London: Urwin, 1897. Masters of Medicine. Web. 2017.
(49)^ abcdefghijMarx, Gertie F.; Bassell, Gerard M. (1980). Obstetric Analgesia and Anaesthesia. The Netherlands: Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press. pp. 1, 5–8, 10, 12–13. ISBN 978-0-444-80137-1
(50)^ abcdefghijklmnopqRamanathan, Sivam (1988). Obstetric anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-0-8121-1118-7
(51)^ abcMiller, Ronald D.; Pardo, Manuel C. Jr. (2012). Basics of anesthesia (6th ed.). Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-81-312-2898-2. OCLC 742301032
(52)^ Johann Hermann Baas、trans. Henry Ebenezer Handerson﹃Outlines of the History of Medicine and the Medical Profession﹄J.H. Vail & Co.、1889年、1096頁。
(53)^ “A short history of Obstetric Anaesthesia”. Res Medica 3 (1). (2014). doi:10.2218/resmedica.v3i1.972. ISSN 2051-7580.
(54)^ abBarry, Ellen (2019年5月6日). “Chloroform in Childbirth? Yes, Please, the Queen Said”. The New York Times 2022年10月15日閲覧。
(55)^ Corretti, Carolyn; Desai, Sukumar P. (1 July 2018). “The Legacy of Eve's Curse: Religion, Childbirth Pain, and the Rise of Anesthesia in Europe: c. 1200-1800s”. Journal of Anesthesia History 4 (3): 182–190. doi:10.1016/j.janh.2018.03.009. PMID 30217391.
(56)^ Simpson, J. Y. (1853). “The Propriety and Morality of Using Anæsthetics in Instrumental and Natural Parturition”. Association Medical Journal 1 (27): 582–589. JSTOR 25494769.
(57)^ “Charles Delucena Meigs ( 1792 - 1869 )”. www.general-anaesthesia.com. 2023年7月17日閲覧。
(58)^ Simpson, J. Y. (1848). “Letter in Reply to Dr. Collins, on the Duration of Labour as a Cause of Danger and Mortality to the Mother and Infant”. Provincial Medical and Surgical Journal 12 (22): 601–606. JSTOR 25500540.
(59)^ “Queen Victoria uses chloroform in childbirth, 1853”. Financial Times. (2017年11月28日). オリジナルの2022年12月10日時点におけるアーカイブ。
(60)^ Waserman, Manfred (1980). “Sir James Y Simpson And London's "Conservative And So Curiously Prejudiced" Dr Ramsbotham”. The British Medical Journal (BMJ) 280 (6208): 161. JSTOR 25438475.
(61)^ abCamann W (2014). "A History of Pain Relief During Childbirth". The Wondrous Story of Anesthesia. pp. 847–858. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8441-7_62. ISBN 978-1-4614-8440-0。
(62)^ Snow, John (1853). “On the Administration of Chloroform during Parturition”. Association Medical Journal 1 (23): 500–502. doi:10.1136/bmj.s3-1.23.500. JSTOR 25494691. PMC 2449612. PMID 20740854.
(63)^ Gordon, Henry L. Sir James Young Simpson and Chloroform (1811-1870). Ed. Ernest Hart.
(64)^ “Twilight Sleep | The Embryo Project Encyclopedia”. embryo.asu.edu. 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(65)^ 家庭問題研究会 編﹃ご存知でせうか﹄平凡社、1915年、85-86頁。doi:10.11501/954861。
(66)^ abSalik, Irim; Doherty, Tara M. (2023), Mendelson Syndrome, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30969586 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(67)^ Noble, A. D.; de Vere, R. D. (1970-05-02). “Epidural Analgesia in Labour”. British Medical Journal 2 (5704): 296. ISSN 0007-1447. PMC 1700456. PMID 5420187.
(68)^ Kandel, P. F.; Spoerel, W. E.; Kinch, R. A. (1966-11-05). “Continuous epidural analgesia for labour and delivery: review of 1000 cases”. Canadian Medical Association Journal 95 (19): 947–953. ISSN 0008-4409. PMC 1935745. PMID 5922909.
(69)^ 塚原傳﹁催眠術ニ由ル無痛分娩ニ就テ﹂﹃産婆學雜誌﹄第四六、1903年、ページ記載なし。
(70)^ 安藤畫一 (1919). “所謂無痛分娩法ニ對スル私見併セテ局所麻醉法ノ應用ヲ推奬ス”. 實驗醫報 第五年第五三: ページ記載なし.
(71)^ 菅井正朝, 松葉弘﹃無痛分娩 : 産痛の精神予防法を主として (創元医学新書)﹄創元社、1960年。
(72)^ ab“学会概要 | 一般社団法人 日本産科麻酔学会”. www.jsoap.com. 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(73)^ 安井修平, 楠本雅彦, 下平和夫, 島中俊次, 大沢辰治, 伊藤宜孝, 清水昭造, 高橋哲也, 植松修﹁189. 持続硬膜外麻酔による無痛分娩﹂﹃日本産科婦人科學會雜誌﹄第14巻第8号、日本産科婦人科学会、1962年6月、715頁、CRID 1541698620245984128、NDLJP:10662345。
(74)^ 山本亮 (1978). “婦人の健康づくり対策”. 愛育 (恩賜財団母子愛育会) 43: 18-21. doi:10.11501/2268087.
(75)^ ab“Women feel Italy's north-south divide with lack of access to epidurals” (英語). euronews (2018年3月22日). 2023年8月27日閲覧。
(76)^ Butwick, Alexander J.; Bentley, Jason; Wong, Cynthia A.; Snowden, Jonathan M.; Sun, Eric; Guo, Nan (2018-12-07). “United States State-Level Variation in the Use of Neuraxial Analgesia During Labor for Pregnant Women”. JAMA network open 1 (8): e186567. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.6567. ISSN 2574-3805. PMC 6324365. PMID 30646335.
(77)^ ab“無痛分娩に﹁ずるい﹂﹁おなかを痛めてこそ母親﹂の声 日本では1割未満 広がらない背景は #令和の親”. www.chibanippo.co.jp. 千葉日報. 2023年8月26日閲覧。
(78)^ abc“︻後編︼麻酔科医が足りない…無痛分娩の賛成8割超えなのに実施率1割以下のワケ︻独自アンケート︼︵日テレNEWS︶”. Yahoo!ニュース. 2023年9月24日閲覧。
(79)^ 痛くないお産 麻酔分娩がよ〜くわかる本 痛くないお産 麻酔分娩がよ〜くわかる本p31 ,メディカ出版 ,島田信宏
(80)^ 海野信也; 板倉敦夫. “無痛分娩の安全性に関する検討”. 厚生労働省. 2023年8月27日閲覧。
参考文献[編集]
●日本麻酔科学会﹁Ⅸ 産科麻酔薬﹂﹃麻酔薬および麻酔関連薬使用ガイドライン﹄︵第3版第4訂︶公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会、2018年4月27日。関連項目[編集]
●産科麻酔科学 ●腰椎穿刺 ●髄腔内投与外部リンク[編集]
●日本産科麻酔科学会 無痛分娩Q&A ●“日本周産期麻酔科学会”. 日本周産期麻酔科学会. 2023年11月28日閲覧。