

|
→Popular Culture: Remove trivial Arrested Development reference
|
Undid revision 169569657 by 81.77.135.145 (talk)
|
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
It is also used to treat a very wide range of infections; see [[tetracycline antibiotics]] for details. |
It is also used to treat a very wide range of infections; see [[tetracycline antibiotics]] for details. |
||
==Popular Culture== |
|||
Tetracycline plays a pivotal role in the [[Arrested Development]] episode [[Fakin'_It|Fakin' It]], in which a physician's instruction ''not'' to administer tetracycline due to an [[allergy]] is ignored because of [[George_Oscar_%22G.O.B.%22_Bluth_II|Gob's]] theft of a [[microcassette]] [[recorder]]. As a result, the patient is placed in grave danger. |
|||
==Other uses== |
==Other uses== |
||
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral, topical (skin & eye), im, iv |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60-80% Oral, while fasting <40% Intramuscular |
| Metabolism | Not metabolised |
| Elimination half-life | 6-11 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal and Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.438 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
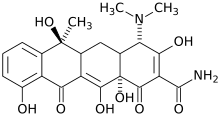
| Formula | C22H24N2O8 |
| Molar mass | 444.435 g/mol g·mol−1 |
Tetracycline (INN) (IPA: [ ˌtɛtrəˈsaɪklin ]) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic produced by the Streptomyces bacterium, indicated for use against many bacterial infections. It is commonly used to treat acne. It is sold under the brand names Sumycin, Terramycin, Tetracyn, and Panmycin, among others. Actisite is a thread-like fiber form, used in dental applications. It is also used to produce several semi-synthetic derivatives, which together are known as the Tetracycline antibiotic group.
It works by inhibiting action of the prokaryotic 30S ribosome, by binding aminoacyl-tRNA.
Toxicity may be result of inactivation of mitochondrial 30S ribosomes in host cells.
The tetracyclines are a large family of antibiotics that were discovered as natural products by Benjamin Minge Duggar and first described in 1948.[1] Tetracycline was then discovered by Lloyd Conover in the research departments of Pfizer. The patent for tetracycline, U.S. patent 2,624,354, was first issued in 1950. However, Nubian mummies have been studied in the 1990s and were found to contain significant levels of tetracycline; there is evidence that the beer brewed at the time could have been the source.[2] Tetracycline sparked the development of many chemically altered antibiotics and in doing so has proved to be one of the most important discoveries made in the field of antibiotics. It is used to treat many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and some protozoa.
Are as those of the tetracycline antibiotics group:
Tetracycline's primary use is for the treatment of acne vulgaris and rosacea.
It is also used to treat a very wide range of infections; see tetracycline antibiotics for details.
Tetracycline plays a pivotal role in the Arrested Development episode Fakin' It, in which a physician's instruction not to administer tetracycline due to an allergy is ignored because of Gob's theft of a microcassette recorder. As a result, the patient is placed in grave danger.
Since tetracycline is absorbed into bone, it is used as a marker of bone growth for biopsies in humans, and as a biomarker in wildlife to detect consumption of medicine- or vaccine-containing baits.[3] The presence of tetracycline in bone is detected by its fluorescence.[4]
In genetic engineering tetracycline is used in transcriptional activation. Tetracycline is also one of the antibiotics used to treat ulcers caused by bacterial infections.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in: |date= (help)
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics |
| ||||||
| Chemotherapeutics |
| ||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Antibacterial |
|
| Keratolytic |
|
| Anti-inflammatory |
|
| Antibiotics |
|
| Hormonal |
|
| Retinoids |
|
| Other |
|
| Combinations |
|
| |
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30S |
| ||||||||||||||
| 50S |
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||