

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
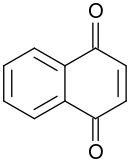
| Preferred IUPAC name
Naphthalene-1,4-dione | |
| Other names
1,4-Naphthoquinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.526 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 158.15 g/mol |
| Density | 1.422 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 126 °C (259 °F; 399 K) |
| Boiling point | Begins to sublime at 100 °C |
| 0.09 g/L | |
| -73.5·10−6cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
1,4-Naphthoquinoneorpara-naphthoquinone is a quinone derived from naphthalene. It forms volatile yellow triclinic crystals and has a sharp odor similar to benzoquinone. It is almost insoluble in cold water, slightly soluble in petroleum ether, and more soluble in polar organic solvents. In alkaline solutions it produces a reddish-brown color. Vitamin K is a derivative of 1,4-naphthoquinone. It is a planar molecule with one aromatic ring fused to a quinone subunit.[2] It is an isomerof1,2-naphthoquinone.
The industrial synthesis involves aerobic oxidation of naphthalene over a vanadium oxide catalyst:[3]
In the laboratory, naphthoquinone can be produced by the oxidation of a variety of naphthalene compounds. An inexpensive route involves oxidation of naphthalene with chromium trioxide.[4]
1,4-Naphthoquinone acts as strong dienophileinDiels-Alder reaction. Its adduct with 1,3-butadiene can be prepared by two methods: 1) long (45 days) exposure of naphthoquinone in neat liquid butadiene taken in huge excess at room temperature in a thick-wall glass tube or 2) fast catalyzed cycloaddition at low temperature in the presence of 1 equivalent of tin(IV) chloride:[5]

1,4-Naphthoquinone is mainly used as a precursor to anthraquinone by reaction with butadiene followed by oxidation. Nitration gives 5-nitro-1,4-naphthalenedione, precursor to an aminoanthroquinone that is used as a dye precursor.[3]
Naphthoquinone forms the central chemical structure of many natural compounds, most notably the K vitamins. 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, called menadione, is a more effective coagulant than vitamin K.
Other natural naphthoquinones include juglone, plumbagin, droserone.
Naphthoquinone derivatives have significant pharmacological properties. They are cytotoxic, they have significant antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, insecticidal, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. Plants with naphthoquinone content are widely used in China and the countries of South America, where they are used to treat malignant and parasitic diseases.[6]
Naphthoquinone functions as a ligand through its electrophilic carbon-carbon double bonds.[7]
Dichlone, a chlorinated derivative of 1,4-naphthoquinone, is used as a fungicide.
|
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat soluble |
| ||||||||
| Water soluble |
| ||||||||
| Combinations |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||