J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 M a n u f a c t u r i n g
2 A p p l i c a t i o n s
T o g g l e A p p l i c a t i o n s s u b s e c t i o n
2 . 1 P r e c u r s o r t o l i t h i u m h e x a f l u o r o p h o s p h a t e f o r b a t t e r i e s
2 . 2 I n m o l t e n s a l t s
2 . 3 O p t i c s
2 . 4 R a d i a t i o n d e t e c t o r s
2 . 5 N u c l e a r r e a c t o r s
2 . 6 C a t h o d e f o r P L E D a n d O L E D s
3 N a t u r a l o c c u r r e n c e
4 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
L i t h i u m f l u o r i d e
2 9 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● C a t a l à ● Č e š t i n a ● D e u t s c h ● Ε λ λ η ν ι κ ά ● E s p a ñ o l ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● М а к е д о н с к и ● മ ല യ ാ ള ം ● B a h a s a M e l a y u ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● Р у с с к и й ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● T ü r k ç e ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Lithium fluoride
__ Li + __ F −
__ Li + __ F −
Names
IUPAC name
Lithium fluoride
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol )
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.029.229
EC Number
PubChem CID
RTECS number
UNII
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI=1S/FH.Li/h1H;/q;+1/p-1 Y
Key: PQXKHYXIUOZZFA-UHFFFAOYSA-M Y
InChI=1/FH.Li/h1H;/q;+1/p-1
Key: PQXKHYXIUOZZFA-REWHXWOFAG
Properties
Chemical formula
LiF
Molar mass
25.939(2 ) g/mol
Appearance
White powder or colorless hygroscopic crystals
Density
2.635 g/cm3
Melting point
845 °C (1,553 °F; 1,118 K )
Boiling point
1,676 °C (3,049 °F; 1,949 K )
Solubility in water
0.127 g/(100 mL) (18 °C)
Solubility product (K sp
1.84× 10 −3 [1]
Solubility
soluble in HF alcohol
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
−10.1·10−6 cm 3
Refractive index (n D
1.3915
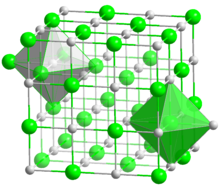
Structure
Crystal structure
Face-centered cubic
Lattice constant
a
Molecular shape
Linear
Thermochemistry
Heat capacity (C
1.507 J/(g·K)
Std molar (S ⦵ 298 )
35.73 J/(mol·K)
Std enthalpy of (Δf H ⦵ 298 )
-616 kJ/mol
Hazards
GHS labelling
Pictograms
Signal word
Danger
Hazard statements
H301 , H315 , H319 , H335 [2]
NFPA 704
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
LD 50 median dose )
143 mg/kg (oral, rat)[3]
Related compounds
Other anions
Lithium chloride Lithium bromide Lithium iodide Lithium astatide
Other cations
Sodium fluoride Potassium fluoride Rubidium fluoride Caesium fluoride
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Chemical compound
Lithium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiF. It is a colorless solid that transitions to white with decreasing crystal size.
Its structure is analogous to that of sodium chloride , but it is much less soluble in water. It is mainly used as a component of molten salts .[4] F 2 energies per mass of reactants , second only to that of BeO .
Manufacturing [ edit ]
LiF is prepared from lithium hydroxide or lithium carbonate with hydrogen fluoride .[5]
Applications [ edit ]
Precursor to lithium hexafluorophosphate for batteries [ edit ]
Lithium fluoride is reacted with hydrogen fluoride (HF ) and phosphorus pentachloride to make lithium hexafluorophosphate Li[PF 6 , an ingredient in lithium ion battery electrolyte .
The lithium fluoride alone does not absorb hydrogen fluoride to form a bifluoride salt.[6]
In molten salts [ edit ]
Fluorine is produced by the electrolysis of molten potassium bifluoride . This electrolysis proceeds more efficiently when the electrolyte contains a few percent of LiF, possibly because it facilitates formation of an Li-C-F interface on the carbon electrodes .[4] FLiNaK , consists of a mixture of LiF, together with sodium fluoride and potassium fluoride . The primary coolant for the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment was FLiBe ; 2LiF·BeF2 (66 mol% of LiF, 33 mol% of BeF2 ).
Because of the large band gap for LiF, its crystals are transparent to short wavelength ultraviolet radiation , more so than any other material . LiF is therefore used in specialized optics for the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum.[7] magnesium fluoride .) Lithium fluoride is used also as a diffracting crystal in X-ray spectrometry.
Radiation detectors [ edit ]
It is also used as a means to record ionizing radiation exposure from gamma rays , beta particles , and neutrons (indirectly, using the 6 3 Li nuclear reaction ) in thermoluminescent dosimeters . 6 [8]
Nuclear reactors [ edit ]
Lithium fluoride (highly enriched in the common isotope lithium-7) forms the basic constituent of the preferred fluoride salt mixture used in liquid-fluoride nuclear reactors . Typically lithium fluoride is mixed with beryllium fluoride to form a base solvent (FLiBe ), into which fluorides of uranium and thorium are introduced. Lithium fluoride is exceptionally chemically stable and LiF/BeF2 mixtures (FLiBe ) have low melting points (360 to 459 °C or 680 to 858 °F) and the best neutronic properties of fluoride salt combinations appropriate for reactor use. MSRE used two different mixtures in the two cooling circuits.
Cathode for PLED and OLEDs [ edit ]
Lithium fluoride is widely used in PLED and OLED as a coupling layer to enhance electron injection . The thickness of the LiF layer is usually around 1 nm dielectric constant (or relative permittivity, ε) of LiF is 9.0.[9]
Natural occurrence [ edit ]
Naturally occurring lithium fluoride is known as the extremely rare mineral griceite .[10]
References [ edit ]
^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–188. ISBN 978-1138561632
^ "Lithium fluoride - Product Specification Sheet" . Sigma-Aldrich . Merck KGaA. Retrieved 1 Sep 2019 .
^ "Lithium fluoride" . Toxnet . NLM . Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 10 Aug 2014 .
^ a b Aigueperse J, Mollard P, Devilliers D, et al. (2005). "Fluorine Compounds, Inorganic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi :10.1002/14356007.a11_307 . ISBN 9783527303854
^ Bellinger SL, Fronk RG, McNeil WJ, et al. (2012). "Improved High Efficiency Stacked Microstructured Neutron Detectors Backfilled With Nanoparticle 6 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 59 1 ): 167–173. Bibcode :2012ITNS...59..167B . doi :10.1109/TNS.2011.2175749 . S2CID 19657691 .
^ Aigueperse, Jean; Mollard, Paul; Devilliers, Didier; Chemla, Marius; Faron, Robert; Romano, René; Cuer, Jean Pierre (2000). "Fluorine Compounds, Inorganic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry doi :10.1002/14356007.a11_307 . ISBN 3527306730
^ "Lithium Fluoride (LiF) Optical Material" . Crystran 19 . 2012.
^ McGregor DS, Bellinger SL, Shultis JK (2013). "Present status of microstructured semiconductor neutron detectors". Journal of Crystal Growth . 379 : 99–110. Bibcode :2013JCrGr.379...99M . doi :10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2012.10.061 . hdl :2097/16983
^ Andeen C, Fontanella J, Schuele D (1970). "Low-Frequency Dielectric Constant of LiF, NaF, NaCl, NaBr, KCl, and KBr by the Method of Substitution". Phys. Rev. B 2 12 ): 5068–73. Bibcode :1970PhRvB...2.5068A . doi :10.1103/PhysRevB.2.5068 .
^ "Griceite mineral information and data" . Mindat.org . Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 22 Jan 2014 .
t
e
Salts and covalent derivatives of the
fluoride ion
t
e
PF 6 − , AsF6 − , SbF6 − compounds
AlF6 − compounds
chlorides, bromides, iodides
SiF6 2- , GeF6 2- compounds
Oxyfluorides
Organofluorides
with transition metal,
nitric acids
bifluorides
thionyl, phosphoryl,
Chemical formulas
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lithium_fluoride&oldid=1228153304 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● L i t h i u m c o m p o u n d s ● F l u o r i d e s ● A l k a l i m e t a l f l u o r i d e s ● O p t i c a l m a t e r i a l s ● C r y s t a l s ● M e t a l h a l i d e s ● R o c k s a l t c r y s t a l s t r u c t u r e H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t E B I s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t K E G G s o u r c e ● E C H A I n f o C a r d I D f r o m W i k i d a t a ● C h e m b o x h a v i n g G H S d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h G N D i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h L N B i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 9 J u n e 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 8 : 5 3 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w