

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sellaite | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.086 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MgF2 | |
| Molar mass | 62.3018 g/mol |
| Appearance | White tetragonal crystals |
| Density | 3.148 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,263 °C (2,305 °F; 1,536 K) |
| Boiling point | 2,260 °C (4,100 °F; 2,530 K) |
| 0.013 g/(100 mL) | |
Solubility product (Ksp) |
5.16⋅10−11 |
| Solubility |
|
| −22.7⋅10−6cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.37397 |
| Structure | |
| Rutile (tetragonal), tP6 | |
| P42/mnm, No. 136 | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
61.6 J⋅mol−1⋅K−1 |
Std molar |
57.2 J⋅mol−1⋅K−1 |
Std enthalpy of |
−1124.2 kJ⋅mol−1 |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵) |
−1071 kJ/mol |
| Hazards[2][3] | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H303, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P405 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
2330[clarification needed] (rat, oral) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ChemicalBook |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
|
Other cations |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Magnesium fluoride is an ionically bonded inorganic compound with the formula MgF2. The compound is a white crystalline salt and is transparent over a wide range of wavelengths, with commercial uses in optics that are also used in space telescopes. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral sellaite.
Magnesium fluoride is prepared from magnesium oxide with sources of hydrogen fluoride such as can be obtained from the breakdown of ammonium bifluoride:
Related metathesis reactions are also feasible:
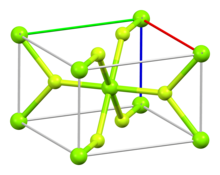
The compound crystallizes as tetragonal birefringent crystals. The structure of the magnesium fluoride is similar to that of rutile,[4][5] featuring octahedral Mg2+ cations and 3-coordinate F− anions.[6]
| Magnesium coordination | Fluorine coordination |
|---|---|

|

|
In the gas phase, monomeric MgF2 molecules adopt a linear molecular geometry.[4][5]
Magnesium fluoride is transparent over an extremely wide range of wavelengths. Windows, lenses, and prisms made of this material can be used over the entire range of wavelengths from 0.120 μm (vacuum ultraviolet) to 8.0 μm (infrared). High-quality, synthetic magnesium fluoride is one of two materials (the other being lithium fluoride) that will transmit in the vacuum ultraviolet range at 121 nm (Lyman alpha). Lower-grade magnesium fluoride is inferior to calcium fluoride in the infrared range.[citation needed]
Magnesium fluoride is tough and polishes well but is slightly birefringent and should therefore be cut with the optic axis perpendicular to the plane of the window or lens.[6] Due to its suitable refractive index of 1.37, magnesium fluoride is commonly applied in thin layers to the surfaces of optical elements as an inexpensive anti-reflective coating.[citation needed] Its Verdet constant is 0.00810 arcmin⋅G−1⋅cm−1 at 632.8 nm.[8]
Chronic exposure to magnesium fluoride may affect the skeleton, kidneys, central nervous system, respiratory system, eyes and skin, and may cause or aggravate attacks of asthma.[9]