

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Fluoroimidogen | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
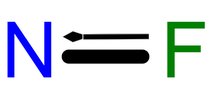
| FN | |
| Molar mass | 33.005 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related isoelectronic |
Dioxygen, nitroxyl anion |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nitrogen monofluoride (fluoroimidogen) is a metastable species that has been observed in laser studies. It is isoelectronic with O2. Like boron monofluoride, it is an instance of the rare multiply-bonded fluorine atom.[1][2] It is unstable with respect to its formal dimer, dinitrogen difluoride, as well as to its elements, nitrogen and fluorine.
Nitrogen monofluoride is produced when radical species (H, O, N, CH3) abstracts a fluorine atom from nitrogen difluoride (NF2). Stoichiometrically, the reaction is extremely efficient, regenerating a radical for long-lasting chain propagation. However, radical impurities in the end product also catalyze that product's decomposition. Azide decomposition offers a less-efficient but more pure technique: fluorine azide (which can be formed in situ via reaction of atomic fluorine with hydrazoic acid) decomposes upon shock into NF and N2.[3][4]
Many NF-producing reactions give the product in an excited state with characteristic chemiluminescence. They have thus been investigated for development as a chemical laser.[4][5]
|
Nitrogen species
| |
|---|---|
| Hydrides |
|
| Organic |
|
| Oxides |
|
| Halides |
|
| Oxidation states | |