味覚
表示
(味から転送)

味覚︵みかく︶は、動物の五感の一つであり、食する物質に応じて認識される感覚である。生理学的には、甘味、酸味、塩味、苦味、うま味の五味が基本味に位置づけられる。基本味の受容器はヒトの場合おもに舌にある。基本味が他の要素︵嗅覚、視覚、記憶など︶で拡張された知覚心理学的な感覚としての味は、風味︵ふうみ︶と呼ばれることが多い。また、認識の過程を味わう︵あじわう︶と言う。
概説[編集]
味覚は物質の受容に基づく化学感覚の一つである。味覚とは、口の中の物質が、口腔中の味蕾、主に舌の上にある味覚受容体細胞と化学的に反応するときに生成される知覚である。往々にしてそれは摂食時であり、対象は飲料を含む食料であり、匂いと共にそれが飲食可能であるかを判断する。味覚は感知するものが私たちの体に与える影響に応じて、嫌悪または食欲のいずれかに反応する[1]。甘味はエネルギーが豊富な食品を識別するのに役立ち、苦味は毒の警告サインとして機能する[2]。また、味覚は摂食時の楽しみの一つとして生活の質︵クオリティ・オブ・ライフ︶に関係する。 味覚は嗅覚と三叉神経の刺激︵食感、痛み、温度︶とともに、食品の味を決める。人間は味蕾や舌の上面や喉頭蓋などの他の領域にも味覚受容体を持っている。人間の場合味覚を受容する器官である味蕾は舌、咽頭部、軟口蓋にある[3][4]。 人間の舌は糸状乳頭という何千もの小さな隆起で覆われており、肉眼で見ることが可能である[4]。各糸状乳頭の中には、何百もの味蕾がある[5][6]。ただし例外的に味蕾を含まない糸状乳頭が舌の上下に2000から5000個程あるとされる[7]。各味蕾には50から100個の味覚受容体細胞が含まれている。人間の舌においては糸状舌乳頭の喪失と唾液生成量の減少のために、味覚は高齢になるにつれて衰える[8]。 他方、それ以外の動物では必ずしもこれに限らない。すべての哺乳類が同じ味覚様式を持っているわけではなく、一部の齧歯類はでんぷんを味わうことができる他、猫は甘さを味わうことができない[9]。人間の場合も味覚のゆがみ︵味覚障害︶も持つ可能性がある。また昆虫においてはチョウやハエなどで前肢の先端に物質受容器があり、食料に触れることで味見しているとされる。 以下、主としてヒトの味覚について記す。味覚の種類[編集]
「五味」も参照
かつて基本的な味の要素として挙げられていたものには、甘味、酸味、塩味、苦味、辛味、渋味、刺激味、無味、脂身味、アルカリ味、金属味、電気の味などがあった。1901年、ヘーニッヒ (D. P. Hänig) はアリストテレスの示した4つの味の舌の上での感覚領域[10]を示した。しかし今日ではこの説は否定されている。1916年、ドイツの心理学者ヘニング(Hans Henning)は、この4つの味とその複合で全ての味覚を説明する4基本味説を提唱した。ヘニングの説によると、甘味、酸味、塩味、苦味の4基本味を正四面体に配し︵味の四面体︶、それぞれの複合味はその基本味の配合比率に応じて四面体の稜上あるいは面上に位置づけることができると考えた。
日本では1908年に化学者の池田菊苗がうま味物質グルタミン酸モノナトリウム塩を発見した[注釈 1]。このうま味は4基本味では説明できないため、日本ではこれを基本味とする認識が定まった。しかし西洋では長らく4基本味説が支持され続け、うま味が認められたのは最近の1990年代からである[注釈 2]。現在では味蕾に受容体が存在するものとして定義されており、甘味、酸味、塩味、苦味、うま味の5つが該当し、五基本味と位置づけられる[11]。
五基本味以外の、辛味物質、アルコール、炭酸飲料などの化学的刺激や、温度︵熱さ・暖かさ・冷たさ︶、舌触り︵つぶつぶ感、柔らかさ、硬さ、滑らかさ︶などの物理的刺激は、基本味と合わせて総合的な味覚を形成する。ただし味覚刺激の全てについて神経に伝達されるまでの機構が解明されたわけではない。辛味の受容体は2種類明らかになっているが、これは体性感覚を伝える神経によって脳に伝わる。六番目の基本味の候補として、カルシウム味[12][13]、脂肪味、デンプンの味などが提案されている。[14]
知覚心理学的には、味覚は単独では存在しえず、大なり小なり嗅覚あるいは視覚や記憶など影響を受ける。たとえばレモンの酸味とライムの酸味は、酸味成分は同一であり基本味的には違いが無く、嗅覚、視覚あるいは記憶によって両者の違いが強調されて認識される。この様な知覚心理学的な意味での味のことを風味と呼ぶことがある。
5つの基本味は以下の通りである。
●甘味
●酸味
●塩味
●苦味
●うま味
6番目の味覚[編集]
舌はまた、基本的な味には一般的に含まれていない他の感覚を感じることができる。これらは主に体性感覚によって引き起こされる。人間の場合、味覚は12の脳神経のうちの3つを介して伝えられる。顔面神経 (VII) は舌の前部3分の2から味覚を伝達し、舌咽神経 (IX) は舌の後部3分の1から味覚を伝達し、迷走神経 (X) は口腔の裏側から味覚を伝達する。三叉神経 (V) は、食品の一般的な食感と、コショウまたはスパイスからの辛味に関連する感覚に関する情報を伝達する。 6番目の味覚には、脂肪、炭水化物の味[14]、コク味[15]、カルシウム味、金属味といった多くの提案がなされている。2015年Runningらのヒトの官能評価によって脂肪酸の味が心理学的に他の基本味と重ならないことが報告されていた[16]が、うま味と一部重なっていた点は不十分だった。しかし、他の基本味と重ならない脂肪の味質を伝える神経の発見[17]で完全な独立性を示す神経科学的な証拠が示された。今後の研究によって基本味は変更される可能性がある。 感覚から来る味覚、及び研究中の味覚は以下の通りである。 ●辛味 …カプサイシン、ピペリンなどが、高温を痛みとして感じる受容体TRPV1を刺激することにより灼熱感を感じる辛味を感じさせる。わさびなどに含まれるアリルイソチオシアネートは冷刺激受容体TRPA1を刺激してツンとした辛味を与える[18]。 ●麻味 …四川料理などで使われる花椒の舌が痺れるような辛さ。日本では辛味と同意義となされることがほとんどであるが、基本的に一つの味覚とみなされる。 ●冷たい感覚 …メントールなどが冷刺激受容体TRPM8を刺激することで舌や口内が冷たい感覚に感じられる。辛味︵熱刺激︶のTRPV1、冷感刺激のTRPA1、TRPM8はヒトの全身に分布しており舌に限って存在する受容体ではなく、体︵特に粘膜︶にカプサイシンやメントールを塗りつけられても同じ感覚が発生する。これらは﹁味蕾で感じる味﹂ではなく﹁痛覚﹂や﹁刺激﹂であると説明されることがある。 ●渋み …タンニンなどで口内が収れん作用を起こすことが渋みとして感じられる。苦味に似るが別の味である。 ●蘞味…筍や山菜などは灰汁が強く、のどや舌がいがらっぽく感じる。舌では無く、触覚による物。 ●金属味 …金属味は、食べ物や飲み物、特定の薬、またはアマルガム修復などによって感じられる。金属味は、口の中の電気反応によって引き起こされる可能性がある[19]。一部の人工甘味料は、TRPV1を刺激する事による金属味を持っているとされている[20]。また、多くの人は、血液に金属味を感じるとされる[21][22]。口の中の金属味はさまざまな病状の症状によって引き起こされる事があり、その場合味覚障害または味覚障害の症状に分類される可能性がある[23]。 ●カルシウム味 …マウスを使った実験でカルシウム感知受容体がマウスの舌に発見されている。ヒトにこれが当てはまるかは不明としている[24]。 ●脂肪 …ラットとマウスの実験で脂肪酸の輸送に関わるCD36タンパク質がマウスの味蕾細胞に局所しておりCD36をノックアウトした所油脂への嗜好性が失われたこと、ラットの舌に油脂を与えた際に消化酵素の分泌が活性化されていること、ラットの舌へのリノール酸の摂取により舌咽神経に信号があったこと、またマウスが脂肪酸の含まれた水を特に好んで摂取したことから、ラット・マウスの舌には何らかの油脂受容体が存在すると考えられている[25][26]。マウス[27]やヒト[28]でGタンパク共役型受容体のGPR120が味蕾細胞に存在し、中、長鎖脂肪酸を受容し、舌前方も後方ももそれぞれ鼓索神経、舌咽神経によって脳に情報を送っている。またマウスの鼓索神経では脂肪酸に特化した情報を伝える神経が2018年に発見され、基本味の条件﹁他の味との独立性﹂の条件を満たした。GPR120ノックアウトマウスではこの神経が激減しており、脂肪味の神経はGPR120を発現するII型味細胞からの情報だと示された[17]。 ●コク味 …グルタチオンがカルシウム受容体に働きかけることで﹁コク味[注釈 3]﹂を感じると想定されている。グルタミルバリルグリシンは更に強いコク味を感じさせる。 ●デンプン味 …2016年の研究では、人間は甘味などの他の味とは無関係にデンプン (具体的にはグルコースやオリゴマーなど) 味わうことができることが示唆された。しかし、この味に反応する化学受容体はまだ見つかっていない[29][30][31]。味覚の生理学[編集]
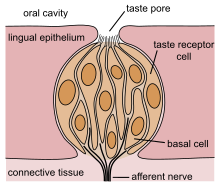
味覚は、嗅覚と同様に、主に化学的受容体に物質が結合することで検出される。嗅覚との差は、離れて感じるか、触れて感じるかの差である。舌に多く存在する味蕾は味覚受容体細胞と支持細胞から形成されており、化学的受容体は味覚受容体細胞の先端︵味蕾の味孔と呼ばれる開口部から突出している部分︶に分布する。 味覚受容体細胞の分布は動物の種によって異なり、ヒトの場合は主に舌で、他には軟口蓋︵口の奥の上面︶、喉頭蓋、および食道上部内面、すなわち口と喉に広く分布する。他にも、例えばナマズは体表全域に味覚受容体細胞が分布している。ヒトの舌では味蕾は舌乳頭上に存在し、舌乳頭には茸状乳頭︵舌の前2/3に多い、成人では退化︶、葉状乳頭︵舌の後ろ両側部に多い、人では存在するが未発達︶、有郭乳頭︵分界溝の前に分布︶などの形状分類がある[注釈 4]。無脊椎動物では口から離れた場所にある例もある。チョウでは、前足に接触性の物質受容器があり、強いて言えば足で味わうわけである。味覚の受容体[編集]
味覚受容体細胞は複数の物質の化学的刺激に対して膜電位が活性化され、その強度は物質によって異なる。1つの味覚受容体細胞に対して複数の神経がシナプス接合している。受容体細胞側では膜電位が伝達されると、Ca2+チャネルの働きにより、セロトニン(5-HT)がシナプス間隙に放出され、神経に刺激が伝達される。 味覚の刺激量と感覚の強度との関係は、他の感覚と同様で、刺激量のべきに比例して感覚の強度が大きくなる。一方、味覚の種類によって最小感度︵閾値︶と強度応答は異なる。一般に苦味が最も感度が高く、塩味、酸味、甘味と続く。また、苦味と塩味は応答範囲が広いが、酸味、甘味は狭く、特にショ糖による甘味は高濃度で応答が飽和する。また同種の味を持つ物質であってもキニーネとカフェイン、ショ糖とサッカリンとでは閾値は異なる。あるいは濃度により味が変わる場合もあり、サッカリンは低濃度では甘味を感じるが、閾値が低く、低濃度から感じて良い筈の苦味は高濃度で初めて感じる。味覚の間の交差も良く知られた現象で、塩味は甘味を増強する。 味覚を変化させる物質も知られており、ギムネマ酸とミラクリンがあげられる。ギムネマ酸はインドで自生するギムネマ・シルベスタの葉に含まれており、これを食べた後ではショ糖の甘味を感じなくなる。これは、甘味受容体に対するショ糖の結合をギムネマ酸が競合阻害していると考えられている[注釈 5]。ミラクリンはアフリカで自生するミラクルフルーツの実に含まれており、これを食べると酸味は消失し甘味として感じられるようになる。これはミラクリンが酸味受容体を抑制すると同時に甘味受容体の特異性を変化させるためと考えられている。 フェニルチオカルバミド (PTC) の苦味を感じる受容体の有無は遺伝によって決定され、受容体がない人は PTC の苦味を感じることができない。この現象は味盲と呼ばれる[32]。味覚の神経系[編集]
味覚神経は一次感覚ニューロンが直接中枢神経に伝達する(嗅覚神経は、二次感覚ニューロンも介す)。具体的には舌の前2/3に分布する茸状乳頭の味覚受容体細胞は顔面神経︵鼓索神経︶を介し、舌の後ろ3分の1に分布する葉状乳頭・有郭乳頭上の味覚は舌咽神経を介して、喉頭あるいは食道部の味覚は迷走神経を介して延髄に連絡する。また舌触りなど化学的受容体を介さない味覚刺激は三叉神経も介する。 一次感覚ニューロンは延髄の弧束核を経て、視床の後内側腹側核︵VPM核︶を経由して広義の大脳皮質味覚野に伝達される。具体的にはVPM核からは、大脳皮質43・11・3野への連絡が知られている。なお、11野はにおいの識別センターでもある。味覚障害[編集]
味覚障害は味覚の障害。薬物性のものの他、末梢・中枢の神経障害、亜鉛不足、身体化障害やうつ病などによる心因性のもの、口腔乾燥症などの口腔疾患や全身疾患、放射線治療後などにより引き起こされる[33]が、味覚障害の原因として一番多いものは薬剤性である[33]。分類[編集]
味覚障害の症状は、その多くが自覚症状である。その症状は以下のように分類される[34]。
●味覚減退‥﹁味が薄くなった,味を感じにくい﹂
●味覚消失・無味症‥﹁全く味がしない﹂
●解離性味覚障害‥﹁甘みだけがわからない﹂
●異味症・錯味症‥﹁しょう油が苦く感じる﹂
●悪味症‥﹁何を食べても嫌な味になる﹂
●味覚過敏‥﹁味が濃く感じる﹂
●自発性異常味覚‥﹁口の中に何もないのに苦みや渋みを感じる﹂
●片側性味覚障害‥一側のみの味覚障害
原因[編集]
特定物質の欠乏 亜鉛の欠乏により味覚障害が引き起こされることが最も多い[35]が、薬剤の亜鉛のキレート作用が原因であると考えられる味覚障害は亜鉛欠乏症の味覚障害と区別されて薬剤性とされ[33][35]。また、ビタミンB2の欠乏が原因となっている可能性を指摘する報告がある[36]。「亜鉛欠乏症」も参照
薬剤性
ペニシラミン︵慢性リュウマチ治療︶[35]、アミトリプチリン︵向精神薬︶、ビンクリスチン︵抗がん剤︶、リトナビル︵AIDS治療薬︶、ACE阻害薬︵高血圧薬︶などいくつかの薬剤で味覚異常を示すものが知られている。
疾病
急性インフルエンザなども一過性の味覚異常を引き起こす。慢性関節リウマチで金化合物療法を受けている患者が金属味を愁訴するのは、口内炎の始まりを意味する。不愉快な甘味は肺の小細胞癌を示唆することがある。
口腔疾病
局所的原因に関しては、例えば歯科に関する原因の味覚異常として
●苦味 - 歯周あるいは歯槽膿瘍から発した膿
●塩味 - 炎症組織からの出血、組織液の漏出
●酸味 - 異種金属充填物間の電解質反応
などか知られており、これらの場合は歯科治療で原因が除去されると味覚異常が改善される。また、味覚閾値としては中学生頃が最も低く︵つまり味に対して鋭敏である︶、幼児・学童、成人、高齢者の順で高くなっていく。そのため高齢者では、健常者であってもある程度の味覚の変化が現れる。
味覚の個人差[編集]
味覚が通常よりも格段に鋭い人のことをスーパーテイスターと呼ばれる。エール大学のBartoshuk教授らによって1994年に発表された論文ではアメリカ人の約25%がスーパーテイスターであるとされている[37]。
イェール大学のリンダ・バートシュクはプロピルチオウラシル(PROP)を使った苦みの官能実験を行い、人間のPROPの味を感じられる能力について、25%の人はPROPの味を感じず︵PROP味盲︶、50%は適度に感じ、残りの25%は過敏に感じる︵味覚過敏︶という3つのグループに分けられることを示した[38]。バートシュクによれば、PROPに対する人間の味覚の違いは遺伝によるもので、PROP味盲の人と味覚過敏の人の舌の構造を比較すると、味蕾の味覚乳頭の密度に違いがあるという。この実験に対しては、特定の味覚物質を感知できない特異な無味覚症にすぎず、味覚全般に当てはめる事はできないという批判がある[38]。
味覚嫌悪
味覚嫌悪(条件性味覚嫌悪学習、味覚嫌悪学習、味覚嫌悪条件付け)とは、特定の食べ物を食べた後に腹痛、吐き気、嘔吐などを経験し嫌いになる現象で、発見者の心理学者ジョン・ガルシア[39]から名前が付けられ﹁ガルシア効果﹂とも呼ばれる。古典的条件づけの一種である。
研究[編集]
脳で味が処理される部位は﹁島皮質﹂であると判明した[40]。空腹に伴って生じる味覚の変化は視床下部AgRPニューロンを起点とした神経ネットワークにより調節される[41]。電気味覚[編集]
舌を電気的に刺激すると味覚の生じる現象は電気味覚と呼ばれる。1700年代には判明しており、1958年以降、Krarupによって味覚を定量的に評価する手段としてその閾値が臨床的に応用されるようになった[42][43]。2000年以降は味を強化したり、擬似的に再現する研究が進められる[44][45]。温度と味覚の関係[編集]
温度で味覚の感じ方が違う[46]。宇宙空間[編集]
宇宙空間では、Fluid Shifts︵体液シフト︶が起きて、地上で足に回る血液が頭へ向かい、うっ血して味覚が鈍る。また、宇宙船内は体臭や機械の臭いが強いため、これも味覚に影響を与える。このことから宇宙食では味の濃いものが求められた[47]。アクワイアード・テイスト[編集]
「単純接触効果」を参照
味覚には﹁経験値を重ねる事で好きになる臨界点﹂があり、アクワイアード・テイストと呼ばれる。
動物の味覚[編集]
魚は、甘味、酸味、辛味、苦味を感じ取るが、舌だけでなく口内やヒレ、ヒゲなどで感じ取る[48]。また、1960年代の実験で、有機化合物、殊にアミノ酸に対して顔面味覚系が反応することが確認された[49]。 草食動物には味蕾が多く、肉食動物には味蕾が少ない。また丸のみにする蛇なども少ない。鳥類やネコ、魚類は甘味に対して鈍感で、ペンギンの舌は酸味と塩味の2種類しか応答しない[50]。脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
- ^ なお、グルタミン酸あるいはグルタミン酸ナトリウム塩は違う味と認識される。
- ^ なお、英語でのうま味の表記は、以前は「デリシャス・テイスト」と表現されていたが、日本語の「うま味」が専門用語として採用され、現在では「ウマミ」が通用する。
- ^ 食品添加物への認定の要請者によると「「コク味」とは「五基本味では表せない、基本味および基本味の周辺の味の厚み・ひろがり・持続性・まとまりなどをも増強する効果を持つ」としている。
- ^ 組織・構造については舌の項に詳しい。
- ^ グルメ探偵漫画『喰いタン』ではこの効果を採り上げたことがあり、作者・寺沢大介による検証も行われたが、その結果は効く人もいれば効かない人もいるというものだった。
出典[編集]
(一)^ “Why do two great tastes sometimes not taste great together?” (英語). Scientific American. 2022年4月18日閲覧。
(二)^ Miller, Greg (2011-09-02). “Sweet Here, Salty There: Evidence for a Taste Map in the Mammalian Brain” (英語). Science 333 (6047): 1213–1213. doi:10.1126/science.333.6047.1213. ISSN 0036-8075.
(三)^ Witt, Martin (2019-01-01), Doty, Richard L., ed. (英語), Chapter 10 - Anatomy and development of the human taste system, Smell and Taste, 164, Elsevier, pp. 147–171, doi:10.1016/b978-0-444-63855-7.00010-1 2022年4月18日閲覧。
(四)^ abChiras, Daniel D. (2005) (英語). Human Biology. Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN 978-0-7637-2899-1
(五)^ Trivedi, Bijal P. (2012-06). “Gustatory system: The finer points of taste” (英語). Nature 486 (7403): S2–S3. doi:10.1038/486S2a. ISSN 1476-4687.
(六)^ Schacter, Daniel L. (2011). Psychology. Daniel Todd Gilbert, Daniel M. Wegner (2nd ed ed.). New York, NY: Worth Publishers. ISBN 978-1-4292-3719-2. OCLC 755079969
(七)^ Boron, W.F., E.L. Boulpaep. 2003. Medical Physiology. 1st ed. Elsevier Science USA.
(八)^ Seidel, Henry M., MD (2011). Mosby's Guide to Physical Examination.. Henry M., MD Seidel (Seventh edition ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-323-07357-8. OCLC 830351369
(九)^ “The Animals That Taste Only Saltiness” (英語). Nautilus | Science Connected (2014年6月9日). 2022年4月18日閲覧。
(十)^ taste map
(11)^ ﹁世界の食文化百科事典﹂p524 野林厚志編 丸善出版 令和3年1月30日発行
(12)^ Tordoff, Michael G.; Shao, Hongguang; Alarcón, Laura K.; Margolskee, Robert F.; Mosinger, Bedrich; Bachmanov, Alexander A.; Reed, Danielle R.; McCaughey, Stuart (2008-08). “Involvement of T1R3 in calcium-magnesium taste”. Physiological Genomics 34 (3): 338–348. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.90200.2008. ISSN 1094-8341.
(13)^ Tordoff, Michael G.; Alarcón, Laura K.; Valmeki, Sitaram; Jiang, Peihua (2012-07-06). “T1R3: A human calcium taste receptor”. Scientific Reports 2 (1). doi:10.1038/srep00496. ISSN 2045-2322.
(14)^ abLapis, T. J.; Penner, M. H.; Lim, J. (2014-10-17). “Evidence that Humans Can Taste Glucose Polymers”. Chemical Senses 39 (9): 737–747. doi:10.1093/chemse/bju031. ISSN 0379-864X.
(15)^ Ueda, Yoichi; Yonemitsu, Muneaki; Tsubuku, Takako; Sakaguchi, Makoto; Miyajima, Ryuichi (1997-01). “Flavor Characteristics of Glutathione in Raw and Cooked Foodstuffs”. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 61 (12): 1977–1980. doi:10.1271/bbb.61.1977. ISSN 0916-8451.
(16)^ Running, Cordelia A.; Craig, Bruce A.; Mattes, Richard D. (2015-07-03). “Oleogustus: The Unique Taste of Fat”. Chemical Senses 40 (7): 507–516. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjv036. ISSN 0379-864X.
(17)^ abYasumatsu, Keiko; Iwata, Shusuke; Inoue, Mayuko; Ninomiya, Yuzo (2019-5). “Fatty acid taste quality information via GPR120 in the anterior tongue of mice” (英語). Acta Physiologica 226 (1): e13215. doi:10.1111/apha.13215. ISSN 1748-1708.
(18)^ 温度を感じる仕組み-富永真琴
(19)^ “Could your mouth charge your iPhone?” (英語). Holistic Dentistry - KC Dental Works - Dr. John Humphrey. 2022年4月18日閲覧。
(20)^ Riera, Céline E.; Vogel, Horst; Simon, Sidney A.; Coutre, Johannes le (2007-08-01). “Artificial sweeteners and salts producing a metallic taste sensation activate TRPV1 receptors”. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 293 (2): R626–R634. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00286.2007. ISSN 0363-6119.
(21)^ (英語) Progress: A Monthly Journal Devoted to Medicine and Surgery. Progress Publishing Company. (1905)
(22)^ Monosson, Emily (2012-03-29) (英語). Evolution in a Toxic World: How Life Responds to Chemical Threats. Island Press. ISBN 978-1-59726-976-6
(23)^ Goldstein, E. Bruce (2009-10-15) (英語). Encyclopedia of Perception. SAGE. ISBN 978-1-4129-4081-8
(24)^ “That Tastes ... Sweet? Sour? No, It's Definitely Calcium!”, Science Daily, (21 August 2008) 2010年9月14日閲覧。
(25)^ Laugerette, F; Passilly-Degrace, P; Patris, B; Niot, I; Febbraio, M; Montmayeur, J. P.; Besnard, P (2005). “CD36 involvement in orosensory detection of dietary lipids, spontaneous fat preference, and digestive secretions”. Journal of Clinical Investigation 115 (11): 3177–84. doi:10.1172/JCI25299. PMC 1265871. PMID 16276419.
(26)^ 油脂のおいしさの科学 社団法人 日本酪農乳業協会
(27)^ Cartoni, C.; Yasumatsu, K.; Ohkuri, T.; Shigemura, N.; Yoshida, R.; Godinot, N.; le Coutre, J.; Ninomiya, Y. et al. (2010-06-23). “Taste Preference for Fatty Acids Is Mediated by GPR40 and GPR120”. Journal of Neuroscience 30 (25): 8376–8382. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0496-10.2010. ISSN 0270-6474.
(28)^ Ozdener, Mehmet Hakan; Subramaniam, Selvakumar; Sundaresan, Sinju; Sery, Omar; Hashimoto, Toshihiro; Asakawa, Yoshinori; Besnard, Philippe; Abumrad, Nada A. et al. (2014-04). “CD36- and GPR120-Mediated Ca2+ Signaling in Human Taste Bud Cells Mediates Differential Responses to Fatty Acids and Is Altered in Obese Mice”. Gastroenterology 146 (4): 995–1005.e5. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.006. ISSN 0016-5085.
(29)^ Lapis, Trina J.; Penner, Michael H.; Lim, Juyun (2016-11-01). “Humans Can Taste Glucose Oligomers Independent of the hT1R2/hT1R3 Sweet Taste Receptor”. Chemical Senses 41 (9): 755–762. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjw088. ISSN 0379-864X.
(30)^ Pullicin, Alexa J.; Penner, Michael H.; Lim, Juyun (2017-08-29). “Human taste detection of glucose oligomers with low degree of polymerization” (英語). PLOS ONE 12 (8): e0183008. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0183008. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5574539. PMID 28850567.
(31)^ Hamzelou, Jessica (2016年9月2日). “There is now a sixth taste – and it explains why we love carbs” (英語). New Scientist. 2022年4月18日閲覧。
(32)^ ﹁世界の食文化百科事典﹂p525 野林厚志編 丸善出版 令和3年1月30日発行
(33)^ abc鄒ら
(34)^ 重篤副作用疾患別対応マニュアル 平成23年3月厚生労働省
(35)^ abc川口ら
(36)^ 生井明浩、池田稔ほか、﹃味覚障害患者に対するビタミンB2内服療法﹄口腔・咽頭科 Vol.12 (1999-2000) No.3 P369-372, doi:10.14821/stomatopharyngology1989.12.369
(37)^ “偏食家は﹁スーパーテイスター﹂?”. (2013年11月12日) 2016年12月24日閲覧。
(38)^ abジェイミー・グッド﹃新しいワインの科学﹄梶山あゆみ訳 河出書房新社 2014年 ISBN 9784309253145 pp.312-314.
(39)^ Garcia J, Kimeldorf DJ, Koelling RA. Conditioned aversion to saccharin resulting from exposure to gamma radiation. Science 1955; 122(3160): 157-8
(40)^ “人体の不思議。人は舌ではなく頭で味わっている。脳の中の味覚の位置が特定される︵米研究︶”. (2019年3月28日) 2019年9月16日閲覧。
(41)^ “空腹になると味覚を調節する神経ネットワークを発見-生理研ら”. (2019年10月11日) 2019年10月22日閲覧。
(42)^ 三吉康郎、吉浦禎二、木村知郎、中根英晴、臨床味覚検査法の一つとして電気性味覚検査法Krarup氏法の検討 日本耳鼻咽喉科学会会報 1968年71巻10号 p.1477-1483, doi:10.3950/jibiinkoka.71.1477
(43)^ 高橋祥一郎、後藤昌昭、岡増一郎 ほか、電気味覚の正常値について 日本口腔外科学会雑誌 1979年25巻5号 p.967-972, doi:10.5794/jjoms.25.967
(44)^ 日本放送協会. “味覚研究の最前線 ~塩味が増強されるお箸!?~ | NHK | WEB特集”. NHKニュース. 2022年7月25日閲覧。
(45)^ 中村裕美、宮下芳明、電気味覚メディア構築のための生理学的知見 コンピュータ ソフトウェア 2016年33巻2号 p.2_43-2_55, doi:10.11309/jssst.33.2_43
(46)^ Cruz, Alberto; Green, Barry G. (2000-02). “Thermal stimulation of taste” (英語). Nature 403 (6772): 889–892. doi:10.1038/35002581. ISSN 1476-4687.
(47)^ Taste in Space NASA
(48)^ “魚に味覚はありますか。‥農林水産省”. www.maff.go.jp. 2024年2月11日閲覧。
(49)^ 大須賀, 謙二、丸井, 隆之﹁魚類の味覚受容(<総説特集>水棲動物の化学受容)﹂2003年、doi:10.18965/tasteandsmell.10.1_29。
(50)^ “﹁味覚﹂の真実をどれだけ知っていますか”. 東洋経済オンライン (2017年5月2日). 2024年2月11日閲覧。
参考文献[編集]
●相場 覚、鳥居修晃 ﹃知覚心理学1997﹄ 放送大学教育振興会 ISBN 4-595-52379-3
●山内昭雄、鮎川武二 ﹃感覚の地図帳2001﹄ 講談社 ISBN 4-06-206148-1
●都甲潔 ﹃味覚を科学する﹄ 角川選書 角川書店 ISBN 4-04-703345-6
●都甲潔 ﹃感性の起源﹄ヒトはなぜ苦いものが好きになったか 中公新書 中央公論新社 ISBN 4121017722
●佐藤昌康、小川尚 編 ﹃味覚の科学﹄ 朝倉書店 ISBN 4254101392
●ピュイゼ、ジャック 三国清三 監修 鳥取絹子 訳 ﹃子どもの味覚を育てる﹄ピュイゼ・メソッドのすべて 紀伊国屋書店 ISBN 4314009691
●鄒天皓、明石昌也 著﹁20味覚障害への対応﹂、古森孝英 編﹃こんな患者さんが歯科に来たときは? 全身疾患・口腔外科疾患に対する診療マニュアル﹄︵初版第1刷︶第一歯科出版、東京都品川区、2011年12月1日、159-164頁。ISBN 978-4-924858-58-9。
●川口充、澤木康平、大久保みぎわ、坂井隆之、四宮敬史、小菅康弘﹁薬物治療と口腔内障害﹂﹃日本薬理学雑誌﹄第127巻第6号、日本薬理学会、2006年6月1日、447-453頁、doi:10.1254/fpj.127.447、ISSN 1347-8397、NAID 10018061177。
●メルクマニュアル 万有製薬 Merck︵オリジナル版︶
関連項目[編集]
|
|
|
評価:Degustation、利き酒、闘茶、グルメリポーター、ガストロノミー(美食学)