前頭葉白質切截術
(精神外科から転送)
| 前頭葉白質切截術 | |
|---|---|
| 治療法 | |
| シノニム | ロイコトミー |
| 診療科 | 精神外科学 |
| ICD-9-CM | 01.32 |
| MeSH | D011612 |
前頭葉白質切截術︵ぜんとうようはくしつせっせつじゅつ︶、およびロボトミー︵英: lobotomy︶、またはロイコトミー︵英: leucotomy︶とは、精神外科の一術式で、脳の前頭前野の神経線維の切断を伴う脳神経外科的な精神障害の治療法である[2]。
概要[編集]
大脳の前頭葉の前部にある前頭前野へ交連する神経線維のほとんどがこの処置で切断される。重篤で頻繁な有害事象を伴う事が一般に知られていたにもかかわらず、20年以上にわたり西側諸国において精神障害や場合によっては、精神疾患以外を対象とした治療の主流として行われていた。 手術後、一部の患者はある程度改善することもあったが、合併症と機能低下︵時にそれは重篤なものとなる︶がしばしばみられた。この治療が登場した当初から、特にこの治療がもたらす利益と不利益については議論が絶えなかった。21世紀では、患者の権利を守る観点から、人道的な治療法としてはほとんどの場合認められなくなっている[3]。 この処置を最初に考案したポルトガルの神経学者エガス・モニスは﹁ある種の精神病症状に対するロイコトミーの治療的価値の発見﹂に対して1949年のノーベル生理学・医学賞[注 1]を共同受賞したが、この受賞にも議論があった[5]。しかし、アメリカのウォルター・フリーマンとジェームズ・ワッツ により術式が﹁発展﹂されたこともあり、難治性の精神疾患患者に対して、熱心に施術された。 1940年代前期から1950年代にかけて、この処置の使用頻度は劇的に増加し、イギリスではアメリカよりも多く行われ、最盛期には年間1000件を越えた[6]。 実施例の多くは女性であった。1951年のアメリカの病院の調査では60%近いロボトミー患者が女性であり、1948-52年のカナダオンタリオ州で行われた症例では、限られたデータではあるが74%が女性であった[7]。1950年代に入ると、ソビエト社会主義共和国連邦やヨーロッパなどでは[8]、ロボトミーは行われなくなった[9]。 この単語はギリシア語が語源であり、葉を意味するギリシア語: λοβός lobos と切る、薄切りにするという意味のτομή tomē に由来する。治療効果[編集]
﹁私はこの手術は彼女の精神状態にはわずかしか作用しないことを十分理解していたが、手術後、彼女がより平穏になり、看護しやすくなるのではないかという期待を込めて、この手術を実施した。﹂
“
”
歴史的には、ロボトミー実施直後の患者には、昏迷、不穏、そして失禁が見られた。一部の患者は食欲亢進や体重増加をきたすこともあった。けいれん発作もまたロボトミー術後にはよく見られる合併症であった。術後の数週間―数か月にかけて行われるリハビリテーションが重視された[11]。
ロボトミーは精神障害の症状を緩和するために行われ、それは患者の人格と知性を犠牲にすることで達成されていた。イギリスの精神科医であるモーリス・パートリッジは、ロボトミー300症例の経過を追跡し、ロボトミーは﹁患者の精神生活の複雑さを減少させることで﹂効果をもたらしていることを報告した。ロボトミー後は自発性、外界への反応性、自己認識、自律性が損なわれた。活動は惰性にとって代わられ、感情的に鈍麻し、術前のような知性を持つことはなかった[12]。
この手術の成績についての記載は賛否が混在している[13]。何人かは手術により死亡し、何人かは後に自殺した。また何人かは脳に深刻な損傷を与えられただけに終わった。手術によって退院できた人たちや、より管理しやすくなった患者もいた[13]。責任ある職業へ再就職を果たした人たちがいる一方、その対極には手術によって深刻な損傷と障害が残った患者もいた[14]。大半の患者はそのどちらでもない、精神病症状に一定の改善は認めるものの、感情や知的能力は低下し、その結果社会適応が良くなることもあれば悪くなることもあった[14]。1940年代の手術に伴う平均死亡率は約5%であった[14]。
ロボトミーによる処置は患者の人格や自律性を大きく損ねうるものであった[15]。ロボトミー後の患者には著明な自発性低下や行動の抑制がしばしば見られた[16]。認知機能低下と社会からの疎外のために、患者たちは集団に参画することが難しくなっていた[17]。
ウォルター・フリーマンは﹁外科的に誘発された子供時代﹂という単語を創造し、ロボトミーの結果を表現するために絶えず使用した。ロボトミーによって﹁幼稚な人格﹂を持つ人々が生み出された。フリーマンによれば成熟のための期間が回復へとつながることになっていた。未出版の伝記において、フリーマンは﹁患者が受けざるをえない社会的圧力に対して、より適合的に変化するよう期待して人格を変化させたと記載した。ある29歳の女性患者について、ロボトミー後の変化についてこのように述べている。﹁牡蠣のような性格を持った、笑みを浮かべ、怠惰だが満足げな患者﹂で、彼女はフリーマンの名前を想起することはできず、空っぽのポットからいつまでもコーヒーを注ぎ続けていた。彼女の両親が患者の問題行動への対応に困ったときは、フリーマンは報酬︵アイスクリーム︶と罰︵打擲︶を使い分けるように助言した[18]。
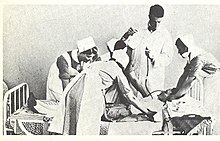
1950年代のヘルシンキで実施されていたインスリンショック療法
20世紀の初め、精神疾患に対する効果的治療がほとんどない一方で[注 2]、精神科病院に入院する患者は顕著に増加していた[注 3][24]。
19世紀末以来蔓延していた精神医学における治療的ニヒリズム―人為的介入を避け自然経過に委ねる姿勢―の打破を告げる嚆矢となった、西欧に出現した根本的かつ侵襲的な治療法の一つとしてロボトミーは生まれた[25]。梅毒第4期に出現する進行麻痺に対するマラリア療法︵1917︶[26]、深睡眠療法︵1920年︶、インスリン・ショック療法︵1933年︶、カルディアゾール︵cardiazol︶けいれん療法︵1934年︶、電気けいれん療法︵1938年︶[27]等を含む、実験的時代において出現した﹁英雄的﹂な物理的治療手段[28]は、治療手段がないために沈滞し意欲を失っていた精神医学の専門家たちに狂気を治療しうるという楽観と精神医学が持ちうる潜在的可能性を再認識させた[29]。かなりの危険性を伴うものではあったが、ショック療法の成功もまた、精神科医たちにロボトミーを含むさらに劇的な医学的介入へ踏み切らせる下地を作った[28]。
臨床医でもあり歴史家でもあるジョエル・ブラスローは、マラリア療法からロボトミーに至るまで、物理的な精神医学的治療法は﹁脳の核心へと螺旋を描きながらますます近づいて﹂いて、脳は﹁今や精神疾患の原因、治療の中心的存在となっている﹂と主張した[30]。
医史学のかつての大家であるロイ・ポーターは[31]、1930年代から40年代にかけて開発されたしばしば暴力的で侵襲的な精神科領域の物理的治療は、膨大な数に上る入院患者の苦痛を和らげる何らかの医学的手段を見つけたいという善意に根差した精神科医の願望と、次第に増加していた急進的な、時には無謀ともいえる医師たちの介入に対して患者たちの社会的抵抗力が相対的に不足していた[32]ことを示唆するものであることを指摘している。この時代の多くの医師、患者、そして家族は、破局的な結果におわる危険が潜んでいたとはいえ、ロボトミーの結果は多くの場合においてみたところは有用であり、少なくとも、ロボトミー以外の明白な代替策である長期の施設入所と比べればましなものだと信じられていた[33]。ロボトミーには議論が絶えなかったが、その時代の標準的医学において、ロボトミー以外の治療では絶望視されている患者に対して合法的に行える最終手段として特別扱いさえされていた。今日では、ロボトミーは処置としての評価を失い、ロボトミーという単語自体が、医学がもつ非人間的な側面や、医学による患者の人権侵害の代名詞となっている[3]。

ゴットリープ・ブルクハルト︵1836年–1907年︶
1930年代以前は、個々の医師が精神障害とみなされた患者の脳に対して実験的に新奇な外科手術を加えることはまれなことであった。その中にあってもっとも特筆すべきは、1888年にスイスの精神科医ゴットリーブ・ブルクハルトの行った一連の試行で、近代精神外科としての体系的な試行としては世界で最初の報告であった[34]。
ブルクハルトはスイスのプレファルジエ精神病院に収容していた6人の慢性患者に手術を行い大脳皮質上の領域を切除した。ブルクハルトの手術、精神疾患の特性と脳との相関性についての、3つの広く知られた視点から着想を得て実行に移された。
精神疾患は本質として器質的なもので、神経病理学上の変化を反映してのものであるという発想、神経系は神経系への入力を行う求心系︵感覚系︶、求心系と遠心系の間を連絡し、情報処理を担う場である連合野、出力を行う遠心系︵運動系︶からなるとする連合主義的概念、そして精神活動はそれぞれ脳の具体的な領域と関連しているとする機能局在論である[35]。
意図的に大脳のある領域に侵襲を加えることで、行動を変容する原因となる連合野を同定できる可能性がある、とブルクハルトは仮定した[35]。この仮説によれば、精神疾患の患者は、質、量、強度の点で、異常な神経興奮が感覚野で生じていて、この異常な刺激が運動野に伝達されることで、精神病理学的変化をきたすことになる[36]。しかしながらブルクハルトはまた、感覚野や運動野を担う神経組織への侵襲は、重篤な機能障害を引き起こしうることも想定していた[36]。彼はその代りに、連合野を対象とし、側頭葉の運動野との間に溝をつくることで、双方の情報伝達を遮断し、その結果精神障害に伴う精神症状や病的体験を緩和しようと試みた[37]。

ルートヴィヒ・プーセップ、1920年頃。
暴力的で対応困難なこれらの患者の治癒というよりは症状緩和を目的として[38]、1888年12月にブルクハルトは執刀を開始したが[39]、術式と装備のどちらもが未熟であったため、成功とも失敗とも言い難い結果であった[36]。合計6人の患者に手術を行い、ブルクハルト自身評価によれば、うち2例は不変、2例はより平穏となり、1例はてんかん発作を発症し術後数日で死亡し、1例は有効との結果であった[注 4]。術後合併症には運動神経麻痺、てんかん発作、感覚性失語と言語聾が含まれる[41]。有効率50%[42]であったことを1889年ベルリンで開催された国際医学会議で発表し報告を行ったが、当時の医学界の反応は否定的で、ブルクハルトはそれ以上の執刀を断念した[43]。
1912年、サンクトペテルブルクで活動している二人の医師、ロシアを代表する精神科医のウラジーミル・ベヒテレフとエストニア人の若い同僚である神経外科医ルートヴィヒ・プーセップは、精神病患者を対象とした外科的侵襲の範囲に関しての論文を発表した[44]。この論文は好意的に受け止められたが、精神外科の考察の部分では、ブルクハルトが1888年に行った外科的実験への軽蔑と、訓練を受けた医師がそのような不健全な処置に加担することは異常であるとの見解が述べられている[45]。
我々がこのデータを引用したのは、ブルクハルトの理論が根拠に乏しいだけでなく、非常に危険であることを示すためである。この著者が、医学士の称号を持つ人物が、この手術をなぜ実施できたのか、我々には説明できない[46]。
しかしながら著者自身、意図的に、1910年プーセップ自身が3人の精神病患者に前頭葉と頭頂葉をつなぐ皮質を切開する手術[47]を行っていた[注 5][49]ことを伏せていた。
この試行結果が思わしくなかったこと、その経験が、1912年の論文におけるブルクハルトへの非難につながったのかもしれない[45]。プーセップは初期にブルクハルトを非難していたにもかかわらず、次第に精神外科は精神病患者への医学的介入として正当化されると考えるようになっていた[注 6][51]。
1930年代後半、トリノ近郊のラッコニージの病院の脳神経外科チームと連携し、イタリアでのロイコトミー導入、普及の中心となった[52]。

エガス・モニス
ロイコトミー︵白質切截術︶は﹁精神外科﹂という単語の発案者でもあるポルトガルの脳神経内科医のエガス・モニスによって1935年初めて実施された[注 7][56]。1930年代初頭、精神疾患とその器質的治療への関心を持ち始めたエガス・モニスは[57]、精神疾患を対象とした脳の外科的治療法を開発することで評価を得ようと考えていたようである[38]。

脳のアニメーション‥左前頭葉が赤で強示されている。モニスは193 3年に白質切截術を初めて着想した際、前頭葉を対象とした。
この会議のわずか3か月後にモニスがロイコトミーに関する実験を開始したことも、フルトンとヤコブセンの発表と前頭葉切截術への決意との間に因果関係があることを支持する[64]。フルトンは、時にロボトミーの父とされることもあるが、この報告の著者であったため、後になってロボトミーの真の起源が彼の研究所にあると記録することができた[65]。1949年ハーバード大学の神経学者スタンレー・コブはアメリカ神経学会の会長講演において﹁研究室での観察がこれほど迅速かつ劇的に治療的手段へ転換を遂げたことはめったにない﹂と述べ、フルトンの意義を支持した。 しかしながら第2回国際神経学会議での発表から10年後作成されたフルトン自身による報告は、史料の裏付けを欠き、彼が以前作成した未出版の記述との類似性はほとんどない。その報告ではモニスとの偶然に個人的なやり取りをしたことについても言及しているが、フルトンが発表した公的な場での会話内容には証拠がない可能性が高い[66]。実際、モニスは最初にロボトミーを着想したのは1935年の会議以前としており、彼の精神外科的アイデアについて、後輩の脳神経外科医ペドロ・アルメイダ・リマに1933年の時点で精神外科手術のアイデアについて秘密裡に話している[67]。従来の説はモニスが前頭葉へ外科手術を行う決心をした原因として、フルトンとヤコブセンの重要性を強調しすぎ、モニスやモニス以外の脳神経内科医、脳神経外科医たちが、同時代の詳細な神経学的研究によって、前頭葉に手術を施すこと精神神障害者の人格を大きく変える可能性があることを認識していたことも省略されている[68]。
19世紀末から前頭葉は科学的探究及び観察の対象であったため、フルトンの報告は論理的な支えとして機能したかもしれないが、それ自体は前頭葉に侵襲を加えるというモニスの決断を説明するには不必要かつ不十分ある[69]。
脳の発達についての進化的・階層的モデルでは、哺乳類の脳、とりわけ前頭葉のようなより新しい時代に出現した領域がより複雑な認知機能を担っていると仮定していた[70]。しかしこの仮説を支持する実験的裏付けは乏しかった。というのも19世紀に行われた前頭葉の外科的切除や電気刺激を加える実験では、動物の行動に変化はほとんど見られなかったからである[70]。第一次世界大戦が終わり、頭部外傷を負った退役軍人に関する症例報告が出現するようになると、前頭葉は機能を持たない﹁沈黙の野﹂であるとの図式は変わり始めた。脳神経外科技術が洗練されるにつれ、人間を対象にした脳腫瘍の摘出や焦点性てんかんの治療が試みられるようになり、その結果動物実験でもより精密な実験的脳神経外科手術が行われるようになった[70]。損傷を受けたり、疾患のために外科的に脳組織を除去した後に、精神症状が緩和する症例が報告されるようになった[47]。前頭葉の損傷に続く行動変化の医学的症例報告が蓄積する中、Witzelsucht︵多幸症、前頭葉症候群の一つ︶の疾患概念が確立された。多幸症は、ある種の気分高揚感や幼稚性を特徴とする神経学的状態像を意味する[70]。
こういった研究から浮かび上がってきた前頭葉機能の全体像は、左右どちらか単一の前頭葉の損傷による神経学的障害は、損傷を受けていない反対側の前頭葉によって補償できるとの観測結果から、さらに複雑なものになった[70]。
1922年、イタリアの神経学者レオナルド・ビアンキは動物における両側前頭葉切除術の結果について詳細な報告を出版し、前頭葉は左右とも知的機能に必要不可欠であり、その切除は人格の崩壊につながることを支持するものであった[71]。この報告は大きな影響をも与えたが、実験計画にある程度の瑕疵があることが指摘されていた[70]。
ヒトを対象とした最初の両側前頭葉切除術は1930年、アメリカの脳神経外科医ウォルター・ダンディー[注 9][72]によって実施された。神経学者リチャード・ブリックナーは1932年この症例について報告し [73]、この患者は﹁患者A﹂として知られるようになった。この症例では情動鈍麻がみられたが、知的能力に明らかな低下は見られず、少なくとも素人目には全く正常に見えた[74]。ブリックナーはこの知見から、﹁前頭葉は知性の﹃首座﹄ではない﹂と結論づけた[75]。
1934年、脳神経外科医ロイ・グレンウッド・スパーリングが行った類似の術式でも同様の臨床的知見が改めて確認され、精神科医スパフォード・アカリーにより報告された[76]。1930年代中葉までに、前頭葉の機能に対する関心は最高潮に達した。その関心の高さは、1935年のロンドンで開催された、第2回国際神経学会議[76]で開催された討議の一つである[76]、﹁前頭葉の機能に関する、注目すべきシンポジウム﹂においても反映されていた[77]。フランスの精神科医アンリ・クロードが議長をつとめ、前頭葉研究の現状の見直しからそのセッションは始まり、﹁前頭葉の変容はその患者の人格に大きな変容をもたらす﹂と結論付けた[75]。
このシンポジウムに用いられた文献には神経学者、脳神経外科医、精神科医が執筆した膨大な論文が含まれ、モニスに強い印象を与えた[74] 、ブリックナーが執筆した上述の﹁患者A﹂に関する詳細な報告[76]もその一つであった。フルトンとヤコブセンの論文も、この会議の実験的生理学部門の別のセッションで発表されており、前頭葉の機能について、動物を対象とした研究とヒトを対象とした研究を結びつけるものとして注目に値するものであった[76]。
つまり、1935年の第2回国際神経学会議の時点で、モニスは前頭葉の役割に関する研究に関して、フルトンとヤコブセンの観察結果をはるかに超える膨大な情報を活用できたのである[78]。
また、1930年代の臨床医家のなかで、前頭葉を直接対象とした処置を検討していたのはモニスだけではなかった[79]。究極的には脳を対象とした手術の実施には危険性が高すぎるために積極的に検討されることはなかったが、ウィリアム・メイヨー、ティエリー・デ・マルテル、リチャード・ブリックナー、レオ・ディヴィドフのような医師や神経学者は、1935年以前に、精神外科手術についての計画を持っていた[注 10][81]。
ユリウス・ワーグナー=ヤウレックによる神経梅毒のマラリア療法の開発に刺激され、1932年フランスの医師モーリス・デュコステは頭蓋骨を穿孔し、前頭葉に直接5mLのマラリア原虫感染血液を注入した100症例について報告した[79]。
彼は注入された神経梅毒患者に、﹁明白な精神的、身体的改善を認めた﹂と主張し、精神病患者に対して実施した場合の結果についても﹁有望である﹂とした[82]。前頭葉に発熱を誘発するマラリア原虫感染血液を注入する試みはイタリアのエットーレ・マリオッティやM. シュッティ、フランスのFerdièreやCoulloudonらによっても報告されるなど、1930年代通じて、繰り返された[83]。
スイスでは、モニスがロイコトミーに着手した時期とほぼ同時期に、脳神経外科医フランシス・オディが緊張性統合失調症患者の右前頭葉全体を除去する手術を行った[84]。
ルーマニアでは、オディの術式がブカレストのセントラル病院に勤務するディミトリ・バグダサールとコンスタンティネスコによって行われ、良好な結果を収めた[80]。オディは自分の執刀結果の発表を数年遅らせていたが、後になってモニスを﹁寛解が維持できているかどうか、十分な経過観察を行う事なしにロイコトミーを推進した﹂として非難するようになった[85]。
歴史[編集]

初期の精神外科[編集]


開発[編集]

前頭葉[編集]
精神外科を揺るがせたモニスの決断がどうして生まれたかについては、同時代と後代とでモニスの発言に矛盾が生じているため、曖昧なものになっている[58]。 モニスが前頭葉を対象にした理由について、従来はイェール大学の神経科学者であるジョン・フルトンの研究に帰されており、極端なものでは1935年のロンドンで開催された第2回国際神経学会議でフルトンの後輩であるカーライル・ヤコブセンと行った発表によるとされることもある[59]。 フルトンは類人猿脳の機能局在論を専門としており、1930年代初めにイェール大学にアメリカ初の類人猿神経生理学教室を設立した人物である[60]。1935年、モニスも参加していた神経学会議で[注 8]、フルトンとヤコブセンは前頭葉切除術を施されたベッキーとルーシーと名付けられた2頭のチンパンジーを供覧し、術後に行動と知的能力に変動が見られたことを報告した[61]。フルトンの発表によれば、2頭のチンパンジー、特に2頭でも感情的なベッキーは、一連の実験的課題での成績が悪く、報酬が与えられない場合は欲求不満の行動化―床に転がる、排便する等癇癪を示す行動―が見られていた[62]。前頭葉を外科的に除去した後、2頭の類人猿とも明らかに行動に変化が見られ、ベッキーはヤコブセンが﹁まるで幸福のカルト教団に入団した﹂と表現したぐらい、外見上平穏となった[61]。その論文の質疑応答の部分で、モニスはこの手技を精神疾患に苦しむ人間にまで拡張しうるかフルトンに尋ね、彼を驚かせたと主張している。フルトンはモニスに、﹁理論上は可能だが、人体に対する介入としては困難に過ぎるだろう﹂と返答したことを述べている[63]。
神経学的モデル[編集]
モニスの精神外科の根底にある理論的背景は、その多くが19世紀にブルクハルトが患者の大脳切除術を決断したときのものと共通していた。後に発表した手記では、モニスはラモン・イ・カハールのニューロン説や、イワン・パブロフの条件反射の両方に言及したが[86]、本質としてはその二つの神経学的研究を単に古い心理学モデルである連合主義―感覚と観念の結びつきから心理現象を説明する立場―によって解釈していた[58]。 しかしブルクハルトと違い、精神病患者の脳に器質的病理を想定せず、神経回路が固定化された破壊的回路に巻き込まれ、﹁優勢となる、強迫的な思考﹂に誘導されると考えていた点で、モニスの考えは全く異なっていた[注 11][88]。 1936年、モニスはこのように記載している: 精神病症状には必ず、程度に差はあるが固定化された、細胞レベルで連結された集団からなる回路と相関性があるに違いない。細胞体に異常はなく、軸索にも解剖学的変性を見いだせないかもしれない。しかし健常人では非常に多様である神経細胞間の構造が、多かれ少なかれ固定化し、そしてそれが、ある種の病的な精神状態像に見られる強迫観念やせん妄状態に関係している[89]。 モニスにとって、﹁精神病患者を治療するには﹂﹁特に前頭葉と交通している、脳の中に存在する多かれ少なかれ固定化された細胞間結合からなる構造を破壊する﹂ことが必要であり[90]、そのために固定化された病的な脳の回路を除去した。モニスはまた、大脳は外科的侵襲に適応し、機能を維持できるものと考えていた[91]。 ブルクハルトが採用していた理論モデルと異なり、1930年代当時の科学知識、技術水準では、脳の物理的病理学的変化と精神疾患の間には相関性がないとして、モニスの理論を反証することはできなかった[92]。最初のロイコトミー症例[編集]
ロイコトミーの根拠となる仮説については、疑義を呈されることもあるだろう。脳への外科的侵襲は無謀とみなされることもあるだろう。しかし、これらの手術により、患者の身体的、精神的生活能力を損なうことなく回復、ないし症状の緩和が得られることは明らかであり、それゆえにそのような論議は副次的なものである。 —エガス・モニス︵1937︶ 1935年11月12日、リスボンのサンタマリア病院で、モニスは精神病患者の脳を対象とした一連の外科手術を開始した[93]。初期の手術候補患者は、リスボンのミゲル・ボンバルダ精神科病院の医長であるジョゼ・デ・マトス・ソブラル・チドが選定していた[94]。モニスは脳神経外科領域の経験はなく、痛風の後遺症のため両手が思うように動かせなかったため、以前にモニスが脳血管造影の研究をしていた際に助手を務めたペドロ・アルメイダ・リマが全身麻酔下で執刀した[注 12][96]。 この手術は、前頭葉とほかの脳の主要領域との間を結合する長い線維のいくつかを切断することを意図していた[97]。この目的を達成するため、リマはトレフィンを用い頭蓋骨内に到達した後に、﹁前頭前野の皮質下白質[98]を対象にエタノールを注入し、連絡線維や連合神経路を破壊し[99]、モニスのいう﹁前頭葉の障壁﹂を生み出した[注 13][100]。最初の手術が完了した後、患者の抑うつ気分が改善したことをもってモニスはその症例については成功したと考え、患者は﹁治癒した﹂と宣言したが、実際には彼女が精神科病院から退院することはなかった[101]。 モニスとリマは、続く7人の患者でも前頭葉へのアルコール注入法に固執したが、彼らが望ましいと判断した結果を得るために多数のエタノール注入を要した症例が何例か見られたため、前頭葉を切開する方法へ変更した[101]。 9人目の患者から、ロイコトームと呼ばれる外科的器具を導入した。ロイコトームは長さ11センチメートル︵4.3インチ︶、直径2センチ︵0.79インチ︶の管状の器具である。 末端には収納可能なワイヤーの環があり、回転させると直径1センチ︵0.39インチ︶の環状の侵襲を前頭葉白質に生じさせた[102]。 典型的には、左右それぞれに6か所の侵襲を加えるが、結果が不満足なものである場合、リマはそれぞれが両側前頭葉に複数の侵襲を生み出す執刀を複数回行うこともあった[101]。 最初の一連のロイコトミーが終わる1936年2月までに、モニスとリマは平均週1回、20症例を執刀した。モニスは同年3月、ロイコトミーの知見について非常に速やかに報告した[103]。患者の年齢層は27歳から62歳であり、12例は女性、8例は男性であった。患者群のうち大うつ病は9人、統合失調症は6人、パニック障害は2人、躁病、緊張病、躁うつ病がそれぞれ1人ずつであり、主訴は不安と焦燥であった。術前り患期間は最短4週間、最長22年とばらつきが大きかったが、4例を除き少なくとも1年以上あった[104]。患者は通常、モニスの診療所を訪れた日に手術を受け、10日以内にミゲル・ボンバルダ精神科病院へ戻った[105]。 定型的な術後経過の評価が術後の1週間-10週間の間にかけて行われた[106]。ロイコトミーを実施した患者に見られた副作用は、以下が含まれる‥﹁体温の上昇、嘔吐、便失禁、尿失禁、下痢、そして眼瞼下垂や眼振のような眼球運動障害や、無気力、無動、嗜眠、時間および場所の見当識障害、窃盗癖、そして異常な飢餓の自覚といった精神症状﹂である[107]。 モニスはこれらの副作用は一過性であることを強調した[107]。彼が出版した評価によれば、最初の20人のうち、7人(35%)は著明に改善し、もう35%は一定の改善がみられ、残る6人(30%)は不変であった。周術期の死亡はなく、ロイコトミー実施後能力低下をきたした患者はいないものとモニスは考えていた[108]。受容[編集]
モニスはロイコトミーの結果について、医学雑誌への投稿記事や1936年に執筆した論文を通じて速やかに広めた[100]。しかしながら当初、医学界はこの新しい処置に対して敵対的に見えた[109]。1936年7月26日、モニスの助手の一人ディオゴ・フルタドは、パリで開催された第2回医学心理学会で、リマがロイコトミーを実施した患者のうち第2群の結果を発表した[100]。彼自身の所属するリスボンにある病院から、最初の患者たちをモニスに紹介したソブラル・チドはその学会に参加したうえで、執刀について非難し[109]、手術後の患者は術前よりも﹁能力低下をきたし﹂、﹁人格の欠損﹂に苦しんでいると断言した[110]。彼はモニスが観察した患者の変化は頭部外傷と手術による衝撃と考えたほうがより合理的であると主張し、モニスが構築したロイコトミーの理論的背景は﹁大脳の神話﹂に過ぎないと嘲けった[110]。 同じ学会にいたパリの精神科医ポール・クールドンは、臨床的観察よりも理論的考察のみを根拠とする外科的処置には賛成できないと述べた[111]。クールドンはそれに加え、臓器の欠損によって機能が向上することはなく、ロイコトミーがもたらす大脳の損傷は髄膜炎、てんかん、脳膿瘍を慢性的に引き起こす危険性があることを指摘した[112]。にもかかわらず、外科的治療によって20人中14例に好ましい結果が得られたとするモニスの報告を受けて、実験的基礎を背景としたこの新しい処置は、1930年代のブラジル、キューバ、イタリア、ルーマニアの臨床医家たちに速やかに受け入れられていった[113]。イタリアにおけるロイコトミー[編集]
精神疾患を取り巻く現状において、治療に無思慮であることを非難する人がいる一方で、なんら手を打たず、無関心なままでいることや、些末な症候、精神病性に生じる病的好奇心への勉学に満足したり、もっと悪いことには、勉学さえもしないことは、嘆かわしく、許されないことである。
1930年代の後半、ロイコトミーを受容した国々での手術数は非常に低水準にとどまっていた。後にロイコトミーの中心となるイギリスでも[注 14]、1942年以前の手術数はわずか6例であった[116]。全体的に、ロイコトミーの実施を試みた臨床医家たちは慎重であり、1940年代以前に手術された患者はごくわずかであった。ロイコトミーを早くから採用し、その実施にも熱心だったイタリアの神経精神科医たちは、このような漸進的な採用を避けた点において例外的な存在であった[52]。
1936年、イタリアの医学界においてロイコトミーの最初の症例が発表され、その次の年にはモニスがロイコトミーに関するイタリア語の記事を投稿した[52]。1937年6月、モニスはイタリアに招聘され、ロイコトミーを実演するために2週間滞在しトリエステ、フェラーラ、そしてトリノに近いラッコニージ病院を訪問した。ラッコニージ病院では、イタリア人の精神科医たちにロイコトミーを指導したほか、彼自身も数例の執刀を監督した[52]。
1937年に開かれた2つのイタリアの精神科会議でロイコトミーは取り上げられ、その後の2年間でラッコニージ、トリエステ、ナポリ、ジェノヴァ、ミラノ、ピサ、カターニアとロヴィーゴの医療機関に所属するイタリア人臨床医によって、モニスの精神外科に関する医学論文が数多く発表された[52]。
イタリアでロイコトミーの中心となったのはラッコニージ病院で、熟練した脳神経外科医ルードウィヒ・プーセップの協力を得ていた[注 15][52]。
エミリオ・リザッティの医学的監督のもと、1939年までにラッコニージ病院でのロイコトミーの症例は少なくとも200例に達した[118]。イタリアの他の医療機関からのロイコトミーに関する報告はずっと少なかった[52]。
イタリアの臨床医たちによって、モニスのロイコトミーの実験的改良が始まったのはそれから間もなくのことだった[119]。その中でも最も特筆すべきものは、1937年ヴァレーゼの精神科病院の診療責任者であるアマッロ・フィアンベルティ[120]が初めて考案した、眼窩を通じて前頭葉への経路を確保する経眼窩法である[119]。フィアンベルティの方法は、眼窩上壁を構成する骨の薄層に穴をあけ、その穿孔を通じて前頭葉の白質にアルコールやホルマリンを注入する方法であった[121]。この方法によって、ロイコトームのための皮膚切開の代替として使う場合も含め、第二次世界大戦勃発までに100人の患者にロイコトミーを実施したものと推定されている[120]。モニスの方法に対するフィアンベルティの発明は、後にウォルター・フリーマンが開発した経眼窩的ロボトミーに示唆を与えた可能性がある[121]。

フリーマンとワッツらによって開発された、﹁標準前頭前野ロボトミー (ロイコトミー)﹂にのための穿孔部分の図示。
アメリカにおける最初の前頭葉ロイコトミーは、1936年9月14日、ジョージ・ワシントン大学病院で実施された、脳神経内科医ウォルター・フリーマンと、友人で同僚の脳神経外科医ジェームズ・ワッツらによるものである[122]。
フリーマンが最初にモニスと出会ったのは1935年のロンドンで開催された第2回国際神経学会議で、モニスは専門分野である脳血管造影についてのポスターを展示していた[123]。フリーマンは幸いにもモニスの隣の区域だったため、この偶然の出会いを喜び、モニスに対して、非常に好ましい印象を持ち、のちに彼の﹁全く非凡な才能﹂について言及することになった。
フリーマンは、もしもモニスと直接遭遇していなければ、フリーマン自身が前頭葉への精神外科領域に踏み出すことはほとんどなかっただろうとしている[123]。フリーマンは1924年、現在はセント・エリザベス病院としても通称されている連邦政府精神科病院の医長に任命されてから精神医学に関心を持つようになった[124]。野心的かつ才能ある研究者であったフリーマンは、精神疾患の原因を器質的原因に求めており、続く数年間、精神疾患を引き起こす神経病理学的根拠を徹底して調査したが、結果的には何の成果も得られなかった[125]。
1936年春、モニスの発表したロイコトミーに関する試験的な論文を偶然目にしたフリーマンは、その年の5月にモニスとの文通を開始した。フリーマンが以前精神外科手術の構想を持っていたことに触れ、モニスに﹁あなたの影響力なら実行に移せるものと強く期待している﹂と伝えた[126]。モニスは返答として、ロイコトミーについて近々発表予定の論文の別刷を送ることを約束し、フランスの業者からロイコトームを購入するよう勧めた[127]。
モニスの論文を受け取ったフリーマンは、Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry誌に匿名で批評を投稿した[127]。論文について、﹁この論文の重要性は計り知れない﹂としたうえで[127]、精神病患者の中枢神経細胞に病的変化は観測できないが、細胞間連絡には﹁さまざまな細胞群間での関係性が特定のパターンをとって固定化している﹂とし、その結果、強迫観念や妄想、精神病状態をもたらしていることを述べ、モニスの理論的基盤について要約を示した[128]。フリーマンはモニスの理論が不十分であることは認識していたが、モニスの理論を採用することで、精神疾患の原因について、精神病患者の大脳に病理学的変化を求めることなく、大脳に内在する神経回路に問題があること、そして問題を起こす精神的回路を切断することで、症状緩和がもたらされる可能性を提示できる利点があった[128]。
1937年、フリーマンとワッツはリマとモニスの外科的処置に慣熟し、フリーマン・ワッツ法、又はフリーマン・ワッツ標準前頭葉ロボトミーとしても知られる、﹁より精密な方法﹂を開発した[129]。
アメリカでのロイコトミー[編集]

経眼窩的ロボトミー[編集]
フリーマン・ワッツ標準前頭葉ロボトミーの実施には頭蓋骨の穿孔がいまだ必要であり、その実施には手術室と訓練を受けた脳神経外科医を必要とした。ウォルター・フリーマンは彼が必要と考えた手術室、外科医、麻酔器が無く、限られた予算しかない州立病院に入院している大多数の患者にとって、ロボトミーは利用できないと考えた。そのため、フリーマンは精神科病院に入院する精神科医単独で実施できるように、もっと簡便な処置とすることを求めた[130]。 イタリアの精神科医アマッロ・フィアンベルディの業績に着想を得て、フリーマンはある時点で頭蓋骨に穿孔する方法に代わって、眼窩を経由して前頭葉に到達する方法を考案した。1945年、彼はキッチンにあったアイスピック[注 16][注 17]を手に取り、グレープフルーツや献体を使い、このアイデアの実用化を試みた。この新しい﹁経眼窩的﹂ロボトミーは、上瞼を持ち上げ、その地点に︵orbitoclastまたはロイコトームと呼ばれるが、モニスの項目で登場したワイヤの環のあるロイコトームとはかなり異なる︶薄い手術器具の先端を上瞼の下、眼窩上縁に接触させる。木槌を使い、眼窩上縁の薄い骨層を通じて、鼻梁と平行に、大脳縦裂と15度の角度となるように脳内に進入する。この術式には、頭蓋骨を壊さず、外側から見える傷跡がないというメリットがあった。 Orbitoclastを木槌を使って前頭葉に5センチメートル︵2インチ︶挿入し、眼窩上縁から角度にして40度ずつ、水平、垂直に旋回させることで、鼻側から見て反対側の大脳半球にかけての神経線維を切断した。その後、器具を再び元合った位置まで戻し、さらに2センチメートル︵4/5インチ︶挿入し、左右とも28度ずつ水平、垂直に旋回させて両側を切除した。 より急進的な変法では、上述の切断後、Orbitclastを頭側に向け再度挿入し、大脳縦裂の側の白質を垂直方向に切断することもあった。﹁深部前頭葉切断法﹂と呼ばれる変法である︶。この切除はすべて、前頭前野と視床を連絡する白質線維の切断を目的としたものであった。切断が終わるとロイコトームはいったん抜き取られ、反対側に同様の手技を繰り返した。[要出典]。 フリーマンは1946年、初めて生きた患者に経眼窩的ロボトミーを実施した。手技が単純であることから、先行するより複雑な術式に求められる手術に必要な施設を持たない精神科単科病院でも実施できる可能性が示された︵フリーマンはまた、従来型の全身麻酔管理ができない場合は、患者の意識を消失させるために電気けいれん療法を利用することも提案していた︶[132]。 1947年、フリーマンとワトソンの協力関係は終了した。フリーマンの考案したロボトミーの変法が、外科手術を﹁事務作業のような﹂単純な手技に変えてしまったことを嫌ったためである[133]。 1940年から1944年までの間に、アメリカ合衆国では684例のロボトミーが実施された。しかしながら、フリーマンとワッツらがロボトミーの普及に熱心であったこともあり、1940年代末にかけて実施数は急速に増加した。1949年は1940年代で最高の件数を記録し、アメリカで5074例が実施されたが、1951年までにロボトミーの実施数は18608例以上に上った[134]。普及[編集]
アメリカ合衆国においてロボトミーが実施された人数は約40,000人である。イングランドでは17000人、デンマーク、ノルウェー、スウェーデンの北欧三か国合わせて約9300人である[135]。人口当たりロボトミー実施数でいえば、北欧の病院はアメリカ合衆国の病院より2.5倍多かった[136]。1944年から1966年までの間、スウェーデンでロボトミーが実施された人数は4500人で、多くが女性であった。この中には子供も含まれている[137]。 ノルウェーでは2005例の実施が知られている[138]。デンマークでのロボトミー実施数は4500例であった[139]。 日本で主に行動異常を伴う子供に対して実施されていた。ソビエト連邦では1950年に倫理面から禁止された[140]。ドイツでは数例が行われるに留まった[141]。1970年代後半までに、ロボトミーは次第に行われなくなったが、フランスでは1980年代になってもまだ実施されていた[142]。批判[編集]
早くも1944年のJournal of Nervous and mental Disease誌にロボトミーについての投稿が見られる。﹁前頭葉白質切截術の歴史は短く、波乱に満ちている。その歴史の中で、激烈な反発もあれば、特に疑問視されることもなく受け入れられることもあった。﹂ 1947年からスウェーデンの精神科医スノーレ・ウォルフハルトは、初期の実施について評価し、﹁統合失調症患者に対しての白質切截術の実施は明らかに有害である﹂と報告し、白質切截術は﹁その助けによって慢性精神疾患患者に対してあえて治療として試みるには不完全であり﹂、さらに﹁精神外科は正確な適応と禁忌を見いだせておらず、その手技は残念ながら多くの点でいまだかなり粗雑で危険に満ちたものとみなさなければならない﹂と言及した[143]。 1948年、﹁サイバネティックス――動物と機械における制御と通信﹂の著者であるノーバート・ウィーナーは﹁前頭葉ロボトミーは、最近一定の流行を見せているが、それはロボトミーによって多くの患者の養護が容易になる事実と無関係ではないだろう。私に言わせれば、彼らを殺せば、その養護はさらに容易なものとなる。﹂と述べた[144]。 ロボトミーに対する懸念は確実に増加しつつあった。ソビエト連邦の精神科医ヴァシリー・ギリャロフスキーはロボトミーと、ロボトミーの実施に使われている大脳機能局在論を批判した。前頭葉の白質の切断によって視床との連絡は失われ、視床からの刺激を受容することができなくなり、それが易怒性と精神機能全体の混乱につながると思われる。この説明は機械論的であり、アメリカの精神科医に特徴的な狭義の機能局在論によるものである。そしてロイコトミーはアメリカからもたらされたものである[145]。 ギリャロフスキーが主導し[146]、ソビエト連邦は1950年に前頭葉白質切截術を公式に禁止した[147] [146]。ソビエト連邦の医師たちは、この処置が﹁人道の原則に反しており﹂﹁ロボトミーによって、精神病患者は完全な白痴へと変えられてしまうだろう﹂と結論づけた[148]。1970年代までに多くの国で白質切截術は禁止され、いくつかのアメリカの州でも禁止された[149]。 1977年、ジミー・カーター在任中、ロボトミーを含む精神外科が、マイノリティーの統制と、個人の権利の制限に用いられているという疑惑を調査するため、アメリカ合衆国議会は生物医学および行動学研究の対象者保護のための国家委員会︵ベルモント委員会︶を立ち上げた。委員会は、一部の極めて特殊な、適切に実施された精神外科手術は有益であると結論付けられた[150]。 21世紀初頭、ノーベル財団がロボトミーの開発に対して与えたノーベル賞を撤回するよう要請が複数あった。ノーベル賞授与はその時代でも驚くべき誤りであるとみなされ、精神医学が学ぶべき点がいまだあるとみなされていたが、ノーベル財団は撤回を拒否し、白質切截術の成績を擁護する記事を掲載し続けている[151][5]。注目すべき事例[編集]
●ジョン・F・ケネディ大統領の妹であるローズマリー・ケネディは、先天性の軽い知的障害を患い、父親の命令で1941年にロボトミーを受けたが重度の後遺症を負った[152][153]。 ●ハワード・デュリは、12歳の時にロボトミー手術を施されたが存命。後に彼はそれらの回想録を本にまとめている[154]。 ●ニュージーランドの作家で詩人のジャネット・フレイムは、予定されたロボトミーが行われる前日の1951年に文学賞を受賞した。ロボトミーは行われなかった[155]。 ●ポーランドのヴァイオリニスト兼作曲家であるヨーゼフ・ハシッドは、統合失調症と診断されロボトミーを受けた後、26歳で他界した[156]。 ●スウェーデンのモダニスト画家シグリッド・イェルテンは、1948年 ロボトミーの後に他界した[157]。 ●アメリカの劇作家テネシー・ウィリアムズの姉のローズはロボトミーを受け、彼女は一生無力になった。このエピソードから、彼はある作品の登場人物やモチーフにインスピレーションを受けたと言われている[158]。 ●1848年、長い鉄の棒が誤ってフィニアス・ゲージの頭を貫通した。これにより彼の脳に﹁偶発的なロボトミー﹂が構成されたのではないか、またこの出来事が1世紀後の外科的ロボトミーの開発に何らかの影響を与えたのではないかとよく言われる。しかし彼に関する注意深い調査ではそのような関連性は発見されていない[159]。 ●1979年、日本の元スポーツライターがロボトミー手術を行った執刀医の母親と妻を殺害する事件を起こした。彼は1964年3月、親族間とのトラブルにより警察に現行犯逮捕されたのち、精神科病院に措置入院させられる。同年11月、執刀医が﹁肝臓検査﹂と偽り、彼にロボトミー手術を実施[160][161]。元スポーツライターはこの手術の影響により、ライター業を廃業。職を転々としたのち、執刀医を標的とした殺人事件を起こした[注 18]。「ロボトミー殺人事件」を参照
文学と映画の描写[編集]
日本の作品[編集]
●手塚治虫の漫画﹃ブラック・ジャック﹄では精神外科︵ホセ・デルガードの開発したスティモシーバー︶の描写がある第58話﹁快楽の座﹂が単行本未収録となっている[163]。他にも未収録の作品はあるが、文庫版や他の書籍での収録や改作などが行われていないのはこの作品のみである[要出典]。この話の中ではブラック・ジャックは脳に電気刺激を与えたのみにもかかわらずロボトミーという語の誤用に対して障害者団体である全国青い芝の会などから﹁ロボトミーを美化している﹂と抗議が来たためと一説では言われるが[164]、実際の漫画では手塚は精神外科に対し否定的な描写をしている[163]。また、単に言葉が使われているだけ、しかも誤用されているもの︵これは﹁快楽の座﹂も同様︶として、第41話﹁植物人間﹂がある。これは単行本︵旧版少年チャンピオン第4巻︶に収録されていたが、後に、﹁からだが石に…﹂に差し替えられた。
●医学博士で作家の渡辺淳一による﹃脳は語らず﹄は、1970年代に日本の大学で行われ、後で週刊誌などに取り上げられた﹁事件﹂に発展したロボトミー手術をドキュメンタリータッチで描いた小説である。
●映画﹁カッコーの巣の上で﹂では、ロボトミー手術を受け廃人になる登場人物の姿が描かれている。
●日本映画でも同時期に、ロボトミー手術により廃人化させられる描写が見られる。例として、1978年の﹁皇帝のいない八月﹂では自衛隊のクーデターを未然に防げなかった陸上幕僚監部幹部が、同年の﹁ブルークリスマス﹂では最初にUFOの実在を訴えた科学者が、機密保持のためにロボトミー手術を受けて廃人化される描写が描かれている。
●ガロ系作品である﹃夢の島で逢いましょう﹄に収録されている﹁DREAM ISLAND﹂では、犯罪者を収容する施設と化した﹁夢の島﹂で慰問目的で訪れていた聖歌隊を救助するため死刑囚の体にロボトミー手術を施したテロ鎮圧用兵器﹁D-4﹂が登場する。
海外の作品[編集]
原文と比べた結果、この節には多数の︵または内容の大部分に影響ある︶誤訳があることが判明しています。情報の利用には注意してください。︵2023年1月︶ |
ロボトミーは、いくつかの文学および映画のプレゼンテーションで取り上げられており、手順に対する社会の態度を反映し、時にはそれを変えた。作家や映画製作者は、ロボトミーに対する反対世論を変える上で極めて重要な役割を果たしてきた[5]。
●ロバート・ペン・ウォーレンの1946年の小説﹃すべて王の臣﹄は、ロボトミーを﹁スキャルピングナイフを持ったタイロのように見えるコマンチの勇者﹂と表現し、外科医を愛情を込めて﹁他人を変えることができない抑圧された男﹂として描写しているため、代わりに﹁高級大工仕事﹂と表現した[165]。
●テネシー・ウィリアムズは、﹃去年の夏 突然に﹄の中で、同性愛者を﹁道徳的に正気﹂にするためにロボトミーを行なう必要があったため、ロボトミーを批判した。 劇中、裕福な精神病院は、病院が姪にロボトミーを与える場合、地元の精神病院に多額の寄付を提供し、姪の息子に関する衝撃的な暴露を止めることができた[166]。ロボトミーは彼女の姪の﹁せせらぎ﹂を止めないかもしれないと警告し、彼女は﹁そうかもしれないし、そうではないかもしれないが、手術後、彼女を信じるだろう、ドクター?﹂と答えた[167]。
●ケン・キージーの1962年の小説﹃カッコーの巣の上で﹄とその映画版では、ロボトミーは﹁前頭葉去勢﹂と表現されている。﹁顔は無表情。まるで店に並ぶダミーのなかの1つと同じ﹂ようになる、人への罰と支配の一形態として描かれた。ある患者については﹁彼の目を見れば、そこで彼がどのように焼き尽くされたかがわかる。彼の目はすべて煙に包まれ、灰色になり、その中は空虚なものにされている﹂と語られた[165]。
●シルヴィア・プラスの1963年の小説﹃ベル・ジャー﹄では、主人公はロボトミー化された若い女性の﹁永遠の大理石の静けさ﹂に恐怖で反応する[165]。
●エリオット・ベイカーの1964年の小説と、その映画版である1966年の﹃素晴らしき狂気﹄は、女性化した喧嘩の詩人の人間性を奪うロボトミーを描き、外科医は非人道的なクラックポットとして描かれている[168]。
●1982年の伝記映画﹃女優フランシス﹄は、女優フランシス・ファーマー︵映画の主題︶が一線を越えたロボトミーを受けていることを描いている[169]ものの、事実上の根拠がほとんどまたはまったくないとして批判されている[170]。
●2006年の映画﹃グエムル-漢江の怪物-﹄には、怪物に奪い去られた娘を救出したいと望む父親が、在韓米軍の軍医によって精神錯乱とされ、薬物によっても沈静されず、頭蓋骨にドリルで孔を開ける米国式ロボトミー手術を受けても言動が変わらないというシーンが描かれている。[171]
●2018年の映画﹃The Mountain﹄は、1950年代アメリカの文脈でロボトミーの文化的意義、そして一般的にメンタルヘルスを取り巻く20世紀半ばの態度を中心に描いている。この映画は、亡くなった母親がロボトミーされた主人公である若い男性の経験を通じて、実践の倫理的および社会的影響を調査している。主人公は、ジェフ・ゴールドブラムが演じるウォレス・ファインズ博士の医療写真家としての仕事を引き受けた。ファインズは大まかにフリーマンの意見に基づいている[172][173]。
精神外科[編集]
精神外科︵せいしんげか︶とは、かつて精神疾患の治療法として流行した、大脳を切り取る外科手術を行うことにより、精神科医による患者治療が行えるとした医療分野であった。代表的なものに前頭葉白質切截術︵ロボトミー︶がある。
かつては、精神外科の名のもとに爆発性精神病質などの診断を受けた患者に対し、情動緊張や興奮などの精神障害を除去する目的で前頭葉白質を切除する手術︵ロボトミー︶が実施されていた[152]。
なお、﹁ロボトミー﹂という語は、"ロボット (robot)"から来ていると誤解されることがあるが、﹁ロボトミー︵lobotomy︶﹂は、肺や脳などで臓器を構成する大きな単位である﹁葉︵よう、lobe︶﹂[注 19]を切るすることを意味する外科分野の医学英語である[注 20]。
当項目のロボトミーでは﹁前頭葉切除﹂を意味し、﹁大脳葉にある神経路を1つ以上分断すること﹂と定義される[174]。
歴史[編集]
日本[編集]
日本では1942年︵昭和17年︶、新潟医科大学︵後の新潟大学医学部︶の中田瑞穂によって初めて行われ[信頼性要検証]、第二次世界大戦中および戦後しばらく、主に統合失調症患者を対象として各地で施行された。しかし、1975年︵昭和50年︶に﹁精神外科を否定する決議﹂が日本精神神経学会で可決され、それ以降は行われていない。[要出典] 名古屋大学医学部精神医学教室で、ロボトミーを受けた患者の病理解剖では、前頭葉全体が空洞化しており、スカスカだったという。当時解剖した患者で一番多かったのはアルコール依存症であった。なお、同教室の医師が他の医師と手術の統計をまとめようとしたところ、手術記録や診療録が、何処にも見当たらなかったという。これは前出のロボトミー否定の学会決議を受け、病院側が資料を破棄したものと見られている[信頼性要検証][175]。 日本精神神経学会の1975年︵昭和50年︶の精神外科を否定する決議でロボトミー手術の廃止が宣言された[176]ことから、日本の精神科において、精神疾患に対してロボトミー手術を行うことは、精神医学上禁忌である。しかし、精神障害者患者会の一つ、全国﹁精神病﹂者集団の声明︵2002年9月1日︶では﹃厚生省の﹁精神科の治療指針﹂︵昭和42年改定︶はロボトミーなど精神外科手術を掲げており、この通知はいまだ廃止されていない。﹄と主張した[177]。また2008年3月、衆議院議員の郡和子は、第169回国会において、本件に関する質問[178]および再質問[179]を行っているが、厚生労働省は答弁[180][181]において明確に﹁ロボトミー手術は禁止している﹂とはしていない。眼窩脳内側領域切除術[編集]
廣瀬貞雄日本医科大学名誉教授が開発した術式。年表[編集]
●1938年︵昭和13年︶- 新潟大学中田瑞穂、ロボトミー開始[要出典]。 ●1947年︵昭和22年︶- 東京都立松沢病院、東京大学医学部でロボトミー開始[182]。 ●1950年︵昭和25年) - 臺弘︵うてな ひろし︶の研究でロボトミー︵臺実験︶。 ●1957年︵昭和32年︶- A氏、横手興生病院でロボトミー[183]。 ●1963年︵昭和38年︶- S氏、チングレクトミー︵ロボトミーの一種︶を桜ヶ丘保養院︵=桜ヶ丘記念病院︶で受け[184]、1979年に﹁ロボトミー殺人事件﹂を起こす。 ●1968年︵昭和43年︶10月30日 - M氏(仮名)、香流病院︵守山十全病院→愛知医科大学附属病院→紘仁病院︶でロベクトミー[185]。 ●1971年︵昭和46年︶3月 - 東京大学精神科医師連合︵精医連︶実行委員長・東京大学講師︵当時︶の石川清が、臺が行った上述の﹃臺実験﹄を告発[186]。 ●1973年︵昭和48年︶5月 - 日本精神神経学会が﹃臺実験﹄を﹁医学実験として到底容認しえないものである﹂と決議する[186]。 ●1973年︵昭和48年︶9月 - 国際脳外科学会闘争︵精神外科問題提議︶[187]。 ●1973年︵昭和48年︶11月 - M氏、ロベクトミー裁判開始︵守山十全病院︶、M氏支援会、ロベクトミー糾弾[188]。 ●1974年︵昭和49年︶7月 - A支会(準)結成︵横手興生病院ロボトミー糾弾︶[188]。 ●1975年︵昭和50年︶5月13日 - 日本精神神経学会が精神外科を否定する決議を可決︵賛成473票、反対0票、保留39票︶。ロボトミー手術の廃止を宣言[176]。 ●1978年︵昭和53年︶9月29日 - 北全病院ロボトミー判決[189]︵院長と執刀医に賠償金の支払いが命じられた︶。 ●1979年︵昭和54年︶9月30日 - ロボトミー糾弾全国共闘会議︵ロ全共︶結成[190]。脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
この項目﹁前頭葉白質切截術﹂は途中まで翻訳されたものです。︵原文‥英語版ウィキペディア Lobotomy
︵04:48, 2 August 2021)版︶
翻訳作業に協力して下さる方を求めています。ノートページや履歴、翻訳のガイドラインも参照してください。要約欄への翻訳情報の記入をお忘れなく。︵2023年7月︶ |
(一)^ Walter Rudolf Hess, who was the joint winner with Moniz of the Nobel Prize in 1949 for his work on the function of the midbrain, had no involvement with leucotomy.[4]
(二)^ A 1937 report detailed that in the United States there were then 477 psychiatric institutions with a total population of approximately 451,672 patients, almost half of whom had been resident for a period of five years or more.[19] The report also observed that psychiatric patients occupied 55 per cent of all hospital beds in America.[19] Conditions within US mental hospitals became the subject of public debate as a series of exposes were published in the 1940s.[20] A 1946 Life magazine article remarked that the nation's system of mental hospitals resembled "little more than concentration camps on the Belsen pattern";[21] a point the piece emphasized with documentary photography that depicted patient neglect and dilapidated material conditions within psychiatric institutions.[22]
(三)^ Ugo Cerletti, the Italian psychiatrist and joint inventor with Lucio Biniofelectroconvulsive therapy, described psychiatry during the interwar period as a "funereal science".[23] Likewise Egas Moniz, the inventor of leucotomy, referred to the﹃impotência terapeutica﹄(therapeutic impotence) of existing therapeutic remedies during the 1930s.[24]
(四)^ The patient he thought improved subsequently committed suicide.[40]
(五)^ According to Puusepp, the three patients were suffering from manic depression or considered "epileptic equivalents".[48]
(六)^ Puusepp admitted to his 1910 experimentation with psychosurgery in a 1937 publication.[50] At that point he had completed a series of 14 leucotomies to relieve aggressive symptoms in patients. Convinced that the results had been positive in these cases, he felt that further research into psychosurgery was warranted.[47]
(七)^ Professor of neurology at the University of Lisbon from 1911 to 1944, Moniz was also for several decades a prominent parliamentarian and diplomat. He was Portugal's ambassador to Spain during World War I and represented Portugal at the postwar Versailles Treaty negotiations,[53] but after the Portuguese coup d'état of 1926, which ushered in the Ditadura Nacional (National Dictatorship), the Republican Moniz, then 51 years old, devoted his considerable talents and energies to neurological research entirely. Throughout his career he published on topics as diverse as neurology, sexology, historical biography, and the history of card games.[54] For his 1927 development of cerebral angiography, which allowed routine visualisation of the brain's peripheral blood vessels for the first time, he was twice nominated, unsuccessfully, for a Nobel Prize. Some have attributed his development of leucotomy to a determination on his part to win the Nobel after these disappointments.[55]
(八)^ The American neuropsychiatrist Walter Freeman also attended the Congress where he presented his research findings on cerebral ventriculography. Freeman, who would later play a central role in the popularisation and practice of leucotomy in America, also had an interest in personality changes following frontal lobe surgery.[47]
(九)^ The patient suffered from meningioma, a rare form of brain tumour arising in the meninges.[72]
(十)^ Brickner and Davidoff had planned, before Moniz's first leucotomies, to operate on the frontal lobes to relieve depression.[80]
(11)^ Moniz wrote in 1948: 'sufferers from melancholia, for instance, are distressed by fixed and obsessive ideas ... and live in a permanent state of anxiety caused by a fixed idea which predominates over all their lives ... in contrast to automatic actions, these morbid ideas are deeply rooted in the synaptic complex which regulates the functioning of consciousness, stimulating it and keeping it in constant activity ... all these considerations led me to the following conclusion: it is necessary to alter these synaptic adjustments and change the paths chosen by the impulses in their constant passage so as to modify the corresponding ideas and force thoughts along different paths ...'[87]
(12)^ Lima described his role as that of an "instrument handled by the Master".[95]
(13)^ Before operating on live subjects, they practised the procedure on a cadaver head.[81]
(14)^ It was estimated by William Sargant and Eliot Slater that 15,000 leucotomies had been performed in the UK by 1962.[115]
(15)^ The 14 leucotomies reported by Puusepp in his 1937 paper were performed at the Racconigi Hospital.[117]
(16)^ Frank Freeman, Walter Freeman's son, stated in an interview with Howard Dully that: "He had several ice-picks that just cluttered the back of the kitchen drawer. The first ice-pick came right out of our drawer. A humble ice-pick to go right into the frontal lobes. It was, from a cosmetic standpoint, diabolical. Just observing this thing was horrible, gruesome." When Dully asked Frank Freeman, then a 79-year-old security guard, whether he was proud of his father, he replied: "Oh yes, yes, yeah. He was terrific. He was really quite a remarkable pioneer lobotomist. I wish he could have gotten further."[131]
(17)^ Rodney Dully, whose son Howard Dully had had a transorbital lobotomy performed on him by Walter Freeman when he was twelve years old, stated in an interview with his son that: "I only met him [Freeman] I think the one time. He described how accurate it [transorbital lobotomy] was and that he had practised the cutting on, literally, a carload of grapefruit, getting the right move and the right turn. That's what he told me."[131]
(18)^ 執刀医は同僚医師の送別会に出席していたため、元スポーツライターが予想していた帰宅時間に自宅に戻らず、元スポーツライターは拘束していた母親と妻を殺害した。
(19)^ 葉とは、大脳では前頭葉や側頭葉、頭頂葉などから構成され、肺では上葉、下葉などから構成される。
(20)^ 語義の上では,-otomyは切断,離断を意味し,-ectomyは切除,摘除を意味する。物理的に切り離されるところまでは同じだが,-otomyでは切り離すのみで,-ectomyは切り離した部分を除去するところが異なる。すなわち、切断した部分を取り去ればlobectomy,基本の位置を動かさなければlobotomyになり,手技そのものの違いである。肺の場合は癌や感染症に侵された肺を取り去るのが目的なのでlobectomyになる。
出典[編集]
(一)^ Kaempffert 1941, p. 18.
(二)^ “Lobotomy: Definition, Procedure & History”. Live Science 2018年6月28日閲覧。
(三)^ abRaz 2009, p. 116.
(四)^ Nobelprize.org 2013.
(五)^ abcSutherland 2004.
(六)^ Levinson, Hugh (2011年11月8日). “The strange and curious history of lobotomy”. BBC News (BBC)
(七)^ Johnson, Jenell (17 October 2014). American Lobotomy: A Rhetorical History. University of Michigan Press. pp. 50–60. ISBN 978-0472119448 2017年8月12日閲覧。 El-Hai (2016年12月21日). “Race and Gender in the Selection of Patients for Lobotomy”. Wonders & Marvels. 2017年8月12日閲覧。 “Lobotomies”. Western University. 2017年8月12日閲覧。
(八)^ Zajicek, Benjamin (2017). “Banning the Soviet Lobotomy: Psychiatry, Ethics, and Professional Politics during Late Stalinism”. Bulletin of the History of Medicine 91 (1): 33–61. doi:10.1353/bhm.2017.0002. ISSN 1086-3176. PMID 28366896. Gallea, Michael (Summer 2017). “A brief reflection on the not-so-brief history of the lobotomy”. BCMedical Journal 59: 302–04 2019年2月4日閲覧。.
(九)^ Kalat, James W. (2007). Biological psychology (9th ed.). Belmont, California: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning. p. 101. ISBN 9780495090793 2015年12月21日閲覧。
(十)^ Quoted in Pressman 2002, p. 48
(11)^ Noyes & Kolb 1962, pp. 550–55.
(12)^ Partridge 1950, pp. 470–71.
(13)^ abCooper 2014, pp. 143–54.
(14)^ abcValenstein 1997, pp. 499–516.
(15)^ Szasz 2007, pp. 151–72.
(16)^ Freberg 2010, pp. 416–17.
(17)^ Shutts 1982.
(18)^ Raz 2013, pp. 101–13.
(19)^ abFeldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 650; Mashour, Walker & Martuza 2005, p. 411
(20)^ Maisel 1946; Wright 1947; Deutsch 1948;Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 650; Pressman 2002, pp. 148–50
(21)^ Albert Q. Maisel, "Bedlam 1946, Most U.S. Mental Hospitals are a Shame and a Disgrace", Life 20 (1946), pp. 102–03, quoted in Pressman 2002, p. 149
(22)^ Pressman 2002, pp. 148–49.
(23)^ Shorter 1997, p. 218.
(24)^ abGross & Schäfer 2011, p. 5.
(25)^ Swayze 1995, pp. 505–15;Hoenig 1995, p. 337; Meduna 1985, p. 53
(26)^ Brown 2000, pp. 371–82.
(27)^ Shorter 1997, pp. 190–225; Jansson 1998
(28)^ abPressman 2002, p. 200.
(29)^ Healy 2000, p. 404; Braslow 1995, pp. 600–05; Braslow 1997, pp. 89, 93
(30)^ Braslow 1997, p. 3.
(31)^ Cooter 2012, p. 216.
(32)^ Porter 1999, p. 520.
(33)^ Pressman 2002, p. 428; Raz 2009, pp. 116, 129
(34)^ Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 1; Heller et al. 2006, p. 727; Joanette et al. 1993, pp. 572, 575; Kotowicz 2008, p. 486; Manjila et al. 2008, p. 1; Noll 2007, p. 326; Reevy, Ozer & Ito 2010, p. 485; Steck 2010, pp. 85–89; Stone 2001, pp. 79–92; Suchy 2011, p. 37; Mareke & Fangerau 2010, p. 138; Ford & Henderson 2006, p. 219; Green et al. 2010, p. 208; Sakas et al. 2007, p. 366; Whitaker, Stemmer & Joanette 1996, p. 276
(35)^ abBerrios 1997, p. 68.
(36)^ abcBerrios 1997, p. 69.
(37)^ Berrios 1997, pp. 69, 77.
(38)^ abTierney 2000, p. 26.
(39)^ Whitaker, Stemmer & Joanette 1996, p. 276; Berrios 1997, p. 69
(40)^ Stone 2001, p. 80.
(41)^ Berrios 1997, p. 70.
(42)^ Manjila et al. 2008, p. 1.
(43)^ Kotowicz 2005, pp. 77–101.
(44)^ Bechterev & Puusepp 1912; Kotowicz 2008, p. 486
(45)^ abKotowicz 2005, p. 80; Kotowicz 2008, p. 486
(46)^ Quoted in Berrios 1997, p. 71
(47)^ abcdFeldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 649.
(48)^ Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 149.
(49)^ Kotowicz 2005, p. 80; Kotowicz 2008, p. 486; Berrios 1997, p. 71
(50)^ Puusepp 1937
(51)^ Kotowicz 2008, p. 486.
(52)^ abcdefgKotowicz 2008, p. 477.
(53)^ Tierney 2000, p. 23
(54)^ Tierney 2000, p. 25; Tierney 2000, pp. 22–23; Kotowicz 2005, p. 78
(55)^ Shorter 1997, p. 226; Tierney 2000, pp. 25
(56)^ Doby 1992, p. 2; Tierney 2000, pp. 25
(57)^ El-Hai 2005, p. 100.
(58)^ abBerrios 1997, p. 72.
(59)^ Pressman 2002, pp. 13–14, 48–51, 54–55; Berrios 1997, pp. 72–73; Shorter 1997, p. 226; Heller et al. 2006, p. 721
(60)^ Heller et al. 2006, p. 721.
(61)^ abPressman 2002, p. 48.
(62)^ Pressman 2002, p. 48; Heller et al. 2006, p. 721
(63)^ Pressman 2002, p. 48; Berrios 1997, p. 73
(64)^ Berrios 1997, p. 73.
(65)^ Pressman 2002, pp. 48–50.
(66)^ Pressman 2002, p. 50.
(67)^ Berrios 1997, pp. 72–73.
(68)^ Pressman 2002, pp. 48–55; Valenstein 1997, p. 541
(69)^ Pressman 2002, pp. 51, 55.
(70)^ abcdefPressman 2002, p. 51.
(71)^ Bianchi 1922; Pressman 2002, p. 51; Levin & Eisenberg 1991, p. 14
(72)^ abPressman 2002, p. 52; Kotowicz 2005, p. 84
(73)^ Brickner 1932.
(74)^ abKotowicz 2005, p. 84.
(75)^ abQuoted in Pressman 2002, p. 52
(76)^ abcdePressman 2002, p. 52.
(77)^ Quoted in Freeman & Watts 1944, p. 532
(78)^ Pressman 2002, p. 53.
(79)^ abValenstein 1990, p. 541.
(80)^ abValenstein 1997, p. 503.
(81)^ abFeldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 650.
(82)^ Quoted in Valenstein 1990, p. 541
(83)^ Valenstein 1990, p. 541; Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 650; Kotowicz 2008, p. 478
(84)^ Berrios 1997, p. 77; Valenstein 1990, p. 541; Valenstein 1997, p. 503
(85)^ Quoted in Valenstein 1997, p. 503
(86)^ Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 1.
(87)^ Quoted in Berrios 1997, p. 74
(88)^ Kotowicz 2005, p. 99; Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 1
(89)^ Quoted in Kotowicz 2005, p. 88
(90)^ Quoted in Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 651
(91)^ Berrios 1997, p. 74.
(92)^ Kotowicz 2005, p. 89.
(93)^ Kotowicz 2005, pp. 80–81; Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 650
(94)^ Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 2; Kotowicz 2008, p. 482
(95)^ , Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 2
(96)^ Tierney 2000, p. 29; Kotowicz 2005, pp. 80–81; Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 2
(97)^ Pressman 2002, p. 54.
(98)^ Moniz 1994, p. 237.
(99)^ Finger 2001, p. 292.
(100)^ abcKotowicz 2005, p. 81.
(101)^ abcFeldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 651.
(102)^ Jansson 1998; Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 2; Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 651. For Moniz's account of the procedure see, Moniz 1994, pp. 237–39
(103)^ Kotowicz 2005, p. 81; Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 651; Valenstein 1997, p. 504
(104)^ Berrios 1997, p. 75.
(105)^ Kotowicz 2005, p. 92.
(106)^ Berrios 1997, p. 75; Kotowicz 2005, p. 92
(107)^ abGross & Schäfer 2011, p. 3.
(108)^ Berrios 1997, p. 74; Gross & Schäfer 2011, p. 3
(109)^ abKotowicz 2008, p. 482.
(110)^ abQuoted in Kotowicz 2008, p. 482
(111)^ Kotowicz 2008, pp. 482–83.
(112)^ Kotowicz 2008, p. 483.
(113)^ Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 652; Kotowicz 2005, p. 81
(114)^ Quoted in El-Hai 2005, p. 182
(115)^ Kotowicz 2008, pp. 486 n.1; Sargant & Slater 1963, p. 98
(116)^ Kotowicz 2008, pp. 476–77.
(117)^ Puusepp 1937; Kotowicz 2008, pp. 477, 486
(118)^ Kotowicz 2008, pp. 477, 487.
(119)^ abKotowicz 2008, p. 478.
(120)^ abEl-Hai 2005, p. 182.
(121)^ abEl-Hai 2005, p. 182; Finger 2001, p. 293; Weiss, Rauch & Price 2007, p. 506
(122)^ Shorter 1997, p. 227; Pressman 2002, p. 78
(123)^ abPressman 2002, p. 76; Feldman & Goodrich 2001, p. 649
(124)^ Pressman 2002, p. 73.
(125)^ Pressman 2002, pp. 73–75.
(126)^ Quoted in Pressman 2002, p. 76
(127)^ abcPressman 2002, p. 76.
(128)^ abPressman 2002, p. 77.
(129)^ Finger 2001, p. 293.
(130)^ El-Hai 2005, p. 184.
(131)^ abDully 2005.
(132)^ El-Hai 2005.
(133)^ Caruso, James P.; Sheehan, Jason P. (2017). “Psychosurgery, ethics, and media: a history of Walter Freeman and the lobotomy.”. Neurosurgical Focus 43 (3): E6. doi:10.3171/2017.6.FOCUS17257. PMID 28859561.
(134)^ Shorter 1997, pp. 227–28.
(135)^ Tranøy & Blomberg 2005, p. 107
(136)^ Tranøy 1996, pp. 1–20
(137)^ Ogren & Sandlund 2005, pp. 353–67.
(138)^ Goldbeck-Wood 1996, pp. 708–09.
(139)^ “Jesper Vaczy Kragh:﹃Sidste udvej? Træk af psykokirurgiens historie i Danmark﹄(Dansk Medicinhistorisk Årbog 2007)”. 2016年3月5日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2018年1月20日閲覧。
(140)^ “Banning the Soviet Lobotomy: Psychiatry, Ethics, and Professional Politics during Late Stalinism”. Benjamin Zajicek. Bull Hist Med. ︵National Library of Medicine︶ (2017年1月1日). 2024年2月16日閲覧。
(141)^ Bangen, Hans: Geschichte der medikamentösen Therapie der Schizophrenie. Berlin 1992, ISBN 3-927408-82-4
(142)^ “La neurochirurgie fonctionnelle d'affections psychiatriques sévères” (フランス語). Comité Consultatif National d'Ethique. (2002年4月25日). オリジナルの2011年7月20日時点におけるアーカイブ。 (French national consultative committee on ethics, opinion #71: Functional neurosurgery of severe psychiatric conditions)
(143)^ Ogren & Sandlund 2005.
(144)^ Wiener 1948, p. 148.
(145)^ Gilyarovsky 1950
(146)^ abGilyarovsky 1973, p. 4.
(147)^ Lichterman 1993, pp. 1–4; USSR Ministry of Health 1951, pp. 17–18
(148)^ Diefenbach et al. 1999, pp. 60–69.
(149)^ Wood & Wood 2008, p. 153.
(150)^ DHEW 1977.
(151)^ Jansson. “Controversial Psychosurgery Resulted in a Nobel Prize, first published 29 October 1998”. Official website of the Nobel Prize. www.Nobelprize.org. 2013年3月21日閲覧。
(152)^ ab安達和俊﹃現代社会の健康科学﹄エンタプライズ、2008年、345頁
(153)^ Henley, Jon (2009年8月12日). “The Forgotten Kennedy”. 2023年12月8日閲覧。
(154)^ Day 2008.
(155)^ Martin 2004.
(156)^ Prior 2008.
(157)^ Snyder & Steffen-Fluhr 2012, p. 52.
(158)^ Kolin 1998, pp. 50–51.
(159)^ Macmillan 2000, p. 250.
(160)^ “ロボトミー殺人事件の現場を歩く︵1︶”. 月刊﹃記録﹄. 株式会社アストラ (2008年7月7日). 2021年9月19日閲覧。
(161)^ “ロボトミー殺人事件の現場を歩く︵2︶”. 月刊﹃記録﹄. 株式会社アストラ (2008年7月21日). 2021年9月19日閲覧。
(162)^ Nijensohn 2012, p. 582.
(163)^ ab“ブラック・ジャック 快楽の座 ︻単行本未収録&唯一の完全封印作品︼”. premium-goma.com. 2023年8月29日閲覧。
(164)^ ﹃封印作品の謎 少年・少女マンガ編﹄彩図社、2017年1月24日。ISBN 978-4801302006。
(165)^ abcGrenander 1978, pp. 42–44.
(166)^ Bigsby 1985, p. 100.
(167)^ Williams 1998, p. 15.
(168)^ Gabbard & Gabbard 1999, pp. 119–20.
(169)^ Arnold 1982.
(170)^ Bragg 2005, pp. 72–75; El-Hai 2005, pp. 241–42
(171)^ https://lwlies.com/articles/why-i-love-song-kang-hos-performance-in-the-host/
(172)^ Lapin, Andrew (2019年7月25日). “A Lobotomist Struggles To Hang On In The Brilliant, Blistering 'The Mountain'”. NPR 2020年11月8日閲覧。
(173)^ Kohn, Eric (2018年8月30日). “'The Mountain' Review: Jeff Goldblum and Tye Sheridan Are Lost Souls in Rick Alverson's Beautiful, Fractured America”. IndieWire 2020年11月8日閲覧。
(174)^ ステッドマン医学大辞典改訂第5版︵メディカルレビュー︶
(175)^ 精神科がおかしい―﹁医者﹂も﹁患者﹂も大混乱ありのまま!︿宝島社﹀2001年
(176)^ ab富田三樹生 2000, p. 38.
(177)^ ﹃精神保健従事者団体懇談会特別フォーラムに参加された皆様へ﹄︵2010年1月25日付アーカイブ︶[1]全国﹁精神病﹂者集団 2023年8月28日閲覧
(178)^ 平成二十年三月十七日提出
質問第一八五号 ﹁脳切截術﹂の診療報酬収載に関する質問主意書[2]衆議院
(179)^ 平成二十年三月二十七日提出質問第二二八号 ﹁脳切截術﹂の診療報酬収載に関する再質問主意書[3]衆議院
(180)^ https://www.shugiin.go.jp/internet/itdb_shitsumon.nsf/html/shitsumon/b169185.htm
(181)^ https://www.shugiin.go.jp/internet/itdb_shitsumon.nsf/html/shitsumon/b169228.htm
(182)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 28.
(183)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 29.
(184)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 30.
(185)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 31.
(186)^ ab﹃封印作品の謎﹄安藤健二 太田出版 ISBN 978-4872338874
(187)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 36.
(188)^ ab富田三樹生 2000, p. 37.
(189)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 42.
(190)^ 富田三樹生 2000, p. 43.
参考文献[編集]
●Acharya, Hernish J. (2004). “The Rise and Fall of Frontal Leucotomy”. In Whitelaw, W.A. (ed). The Proceedings of the 13th Annual History of Medicine Days. Calgary. pp. 32–41 ●Arnold, William (1982). Shadowland. Berkley Books. ISBN 0-425-05481-0 ●Bechterev, V.; Puusepp, L. (1912). “La chirugie des aliénes [Surgery of the Insane]”. Archives Internationales de Neurologie 34: 1–17, 69–89. ●Berrios, German E. (1997). “The Origins of Psychosurgery: Shaw, Burckhardt and Moniz”. History of Psychiatry 8 (1): 61–81. doi:10.1177/0957154X9700802905. PMID 11619209. ●Bianchi, Leonardo (1922). The Mechanism of the Brain and the Function of the Frontal Lobes. translated by James Hogg MacDonald. New York & Edinburgh: William Wood & Co; E.S Livingstone ●Bigsby, C.W.E. (1985). A Critical Introduction to Twentieth-Century American Drama: Volume 2. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27717-4 ●Bragg, Lynn (2005). Myths and Mysteries of Washington (1st ed.). TwoDot. ISBN 978-0-7627-3427-6 ●Braslow, Joel T. (May 1995). “Effect of therapeutic innovation on perception of disease and the doctor-patient relationship: a history of general paralysis of the insane and malaria fever therapy, 1910–1950”. American Journal of Psychiatry 152 (2): 660–65. PMID 7726304. ●Braslow, Joel T. (1997). Mental Ills and Bodily Cures: Psychiatric Treatment in the First Half of the Twentieth Century. University of California. ISBN 0-520-20547-2 ●Brickner, Richard M. (1932). “An interpretation of frontal lobe function based upon the study of a case of partial bilateral frontal lobotomy”. Research Publications – Association for Research for Nervous end Mental Disease 13: 259–351. ●Brown, Edward M. (2000). “Why Wagner-Jauregg won the Nobel Prize for discovering malaria therapy for General Paresis of the Insane”. History of Psychiatry 11 (4): 371–82. doi:10.1177/0957154X0001104403. オリジナルの4 January 2013時点におけるアーカイブ。. ●Cooper, Rachel (2014). “On deciding to have a lobotomy: either lobotomies were justified or decisions under risk should not always seek to maximise expected utility”. Medicine, Health Care and Philosophy 17 (1): 143–54. doi:10.1007/s11019-013-9519-8. ●Cooter, Roger (2012). “Neuropatients in Historyland”. In Jacyna, Stephen J.; Casper, Stephen T. (eds). The Neurological Patient in History. Rochester, NY: University of Rochester Press. pp. 215–22. ISBN 978-1-58046-412-3 ●Day, Elizabeth (2008年1月12日). “He was bad, so they put an ice pick in his brain..”. The Guardian 2010年3月31日閲覧。 ●Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (23 May 1977). “Protection on Human Subjects: Use of Psychosurgery in Practice and Research: Report and Recommendations for Public Comment. Part 3”. Federal Register 42 (99): 26317–32. オリジナルの18 June 2013時点におけるアーカイブ。. ●Deutsch, Albert (1948). Shame of the States. New York: Harcourt, Brace ●Diefenbach, Gretchen; Diefenbach, Donald; Baumeister, Alan; West, Mark (April 1999). “Portrayal of lobotomy in the popular press: 1935–1960”. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences 8 (1): 60–69. doi:10.1076/jhin.8.1.60.1766. PMID 11624138. オリジナルの23 March 2010時点におけるアーカイブ。. ●Doby, T (1992). “Cerebral Angiography and Egas Moniz”. American Journal of Roentgenology 359 (2): 364.[リンク切れ] ●El-Hai, Jack (2005). The Lobotomist: A Maverick Medical Genius and His Tragic Quest to Rid the World of Mental Illness. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-23292-0 ●Feldman, Burton (2001). The Nobel prize: a history of genius, controversy, and prestige. Arcade Publishing. ISBN 1-55970-592-2 ●Feldman, Robert P.; Goodrich, James T. (March 2001). “Psychosurgery: A Historical Overview”. Neurosurgery 48 (3): 647–57; discussion 657–59. doi:10.1097/00006123-200103000-00041. PMID 11270556. ●Finger, Stanley (2001). Origins of Neuroscience: A History of Explorations into Brain Function. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-514694-3 ●Ford, Paul J.; Henderson, Jaimie M. (2006). “Functional neurosurgical intervention: neuroethics in the operating rooms”. In Illes, Judy (ed.). Neuroethics: defining the issues in theory, practice, and policy. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-856721-9 ●Freberg, Laura A. (2010). Discovering Biological Psychology (2nd ed.). Belmont, California: Wadsworth. ISBN 0-547-17779-8 ●Freeman, Walter; Watts, James W. (1944). “Psychosurgery: An Evaluation of Two Hundred Cases over Seven Years”. Journal of Mental Science 90 (379): 532–37. doi:10.1192/bjp.90.379.532. ●Gabbard, Glen O.; Gabbard, Krin (1999). Psychiatry and the Cinema (2nd ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.. ISBN 978-0-88048-964-5 ●Gilyarovsky, Vasily [Гиляровский, Василий] (14 September 1950). “Учение Павлова – основа психиатрии [Pavlov's teaching is the basis of psychiatry]” (Russian). Медицинский работник [Health Worker] (37). ●Gilyarovsky, Vasily [Гиляровский, Василий] (1973) (Russian). Избранные труды [Selected Works]. Moscow: Медицина [Medicine]. p. 4 ●Goldbeck-Wood, Sandra (21 September 1996). “Norway compensates lobotomy victims”. British Medical Journal 313 (7059): 708–09. doi:10.1136/bmj.313.7059.708a. PMC 2352081. PMID 11644825. ●Green, Alexander; Astradsson, A.; Stacey, R.J.; Aziz, T.Z. (2010). “Functional and epilepsy neurosurgery”. In Johnson, Reuben; Green, Alexander (eds). Landmark Papers in Neurosurgery. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-959125-1 ●Grenander, M.E. (1978). “Of Graver Import Than History: Psychiatry In Fiction”. Journal of Libertarian Studies 2 (1): 29–44. PMID 11614766 2008年1月22日閲覧。. ●Gross, Dominik; Schäfer, Gereon (2011). “Egas Moniz (1874–1955) and the "invention" of modern psychosurgery: a historical and ethical reanalysis under special consideration of Portuguese original sources”. Neurosurgical Focus 30 (2): 8. doi:10.3171/2010.10.FOCUS10214. PMID 21284454. ●Healy, David (January 2000). “Some continuities and discontinuities in the pharmacotherapy of nervous conditions before and after chlorpromazine and imipramine”. History of Psychiatry 11 (44): 393–412. doi:10.1177/0957154X0001104405. ●Heller, A. C.; Amar, A.P.; Liu, C.Y.; Apuzzo, M.L.J. (2006). “Surgery of the mind and mood: A mosaic of issues in time and evolution”. Neurosurgery 59 (4): 727. ●Hoenig, J. (1995). “Schizophrenia”. In Berrios, German E.; Porter, Roy (eds). A History of Clinical Psychiatry: The Origin and History of Psychiatric Disorders. Athlone. ISBN 0-485-24011-4 ●Joanette, Yves; Stemmer, Brigitte; Assal, Gil; Whitaker, Harry (1993). “From theory to practice: the unconventional contribution of Gottlieb Burckhardt to psychosurgery”. Brain and Language 45 (4): 572–87. doi:10.1006/brln.1993.1061. PMID 8118674. ●Kaempffert, Waldemar (24 May 1941). “Turning the Mind Inside Out”. Saturday Evening Post 213 (47): 18–19, 69–74. ●Kolin, Philip (Spring 1998). “Something Cloudy, Something Clear: Tennessee Williams's Postmodern Memory Play”. Journal of Dramatic Theory and Criticism 12 (2): 35–55. ●Kondratev, Fedor [Фёдор Кондратьев] (2010) (Russian). Судьбы больных шизофренией: клинико-социальный и судебно-психиатрический аспекты [The fates of the ill with schizophrenia: clinico-social and forensico-psychiatric aspects]. Moscow: ЗАО Юстицинформ [Closed joint-stock company Justitsinform] ●Kotowicz, Zbigniew (2005). “Gottlieb Burckhardt and Egas Moniz – Two Beginnings of Psychosugery”. Gesnerus 62 (1/2): 77–101. オリジナルの15 December 2011時点におけるアーカイブ。 2009年11月26日閲覧。. ●Kotowicz, Zbigniew (December 2008). “Psychosurgery in Italy, 1936–39”. History of Psychiatry 19 (4): 476–89. doi:10.1177/0957154X07087345. ISSN 0957-154X. PMID 19397090. ●Kragh, J.V. (2010). “Shock Therapy in Danish Psychiatry”. Medical History 54 (3): 341–64. doi:10.1017/S0025727300004646. PMC 2889500. PMID 20592884. ●Levin, Harvey S.; Eisenberg, Howard M. (1991). Frontal Lobe Function and Dysfunction. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-506284-7 ●Lichterman, B.L. (1993). “On the history of psychosurgery in Russia”. Acta Neurochirugie 125 (1–4): 1–4. doi:10.1007/BF01401819. PMID 8122532. ●Maisel, Albert Q. (1946年5月6日). “Bedlam 1946, Most U.S. Mental Hospitals are a Shame and a Disgrace”. Life 20 ●Manjila, S.; Rengachary, S.; Xavier, A.R.; Parker, B.; Guthikonda, M. (2008). “Modern psychosurgery before Egas Moniz: a tribute to Gottlieb Burckhardt”. Neurosurgery Focus 25 (1): 1–4. ●Macmillan, M. (2000). An Odd Kind of Fame: Stories of Phineas Gage. MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-13363-6 ●Mareke, Arends; Fangerau, Heiner (2010). “Deep brain stimulation in psychiatric disorders”. In Fangerau, Heiner; Jörg, Fegert; Mareke, Arends (eds). Implanted Minds: The Neuroethics of Intracerebral Stem Cell Transplantation and Deep Brain Stimulation. Verlag. ISBN 978-3-8376-1433-6 ●Martin, Douglas (2004年1月30日). “Janet Frame, 79, Writer Who Explored Madness”. The New York Times 2007年11月17日閲覧。 ●Mashour, George A.; Walker, Erin E.; Martuza, Robert L. (2005). “Psychosurgery: Past, Present, and Future”. Brain Research Reviews 48 (3): 409–19. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.09.002. PMID 15914249. オリジナルの17 January 2013時点におけるアーカイブ。. ●Meduna, L.J. (1985). “Autobiography of L.J. Meduna”. Convulsive Therapy 1 (1): 43–57. PMID 11940805. ●Moniz, Egas (1994). Prefrontal Leucotomy in the Treatment of Mental Disorders (1937) American Journal of Psychiatry 1844–1944. American Psychiatric Publishing. pp. 237–39. ISBN 978-0-89042-275-5 ●Nijensohn, DE (2012). “New evidence of prefrontal lobotomy in the last months of the illness of Eva Perón”. World Neurosurgery 77 (3-4): 582–90. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2011.02.036. PMID 22079825. ●Noll, Richard (January 2007). The encyclopedia of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8160-6405-2 ●Noyes, A.P.; Kolb, L.C. (1962). Modern clinical psychiatry. Philadelphia and London: W.B. Saunders ●Ogren, K.; Sandlund, M. (2005). “Psychosurgery in Sweden 1944–1964”. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences 14 (4): 353–67. doi:10.1080/096470490897692. PMID 16338693. ●Partridge, Maurice (1950). Pre-frontal leucotomy:. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications ●Pressman, Jack D. (2002). Last Resort: Psychosurgery and the Limits of Medicine. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-52459-8 ●Prior, Alex (2008年2月6日). “Music's boy wonder: Composer, conductor, singer ... and he's only fifteen”. The Independent 2010年7月11日閲覧。 ●Porter, Roy (1999). The Greatest Benefit to Mankind: A Medical History of Humanity from Antiquity to the Present. Fontana Press. ISBN 0-00-637454-9 ●Puusepp, L. (1937). “Alcune considerazioni sugli interventi chirurgici nelle malattie mentali [Some Considerations about Surgery in Mental Illness]”. G Accad Med Torino 100: 3–16. ●Raz, Mical (2009). “Psychosurgery, Industry and Personal Responsibility, 1940–1965”. Social History of Medicine 23 (1): 116–33. doi:10.1093/shm/hkp061. ●Raz, Mical (2013). The lobotomy letters: the making of American psychosurgery. University of Rochester Press. ISBN 9781580464499 ●Reevy, Gretchen; Ozer, Yvette Malamud; Ito, Yuri (2010). Encyclopedia of Emotion. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-0-313-34576-0 ●Sakas, Damianos E.; Panourias, L.G.; Singounas, E.; Simpson, B.A. (2007). “Neurosurgery for psychiatric disorders: from the excision of brain tissue to the chronic electrical stimulation of neural networks”. In Sakas, D.E.; Simpson, B.A. (eds). Operative Neuromodulation. Functional Neuroprosthetic Surgery. Volume II: Neural Networks Surgery. 2. Springer. pp. 365–74. ISBN 978-3-211-33081-4 ●Shorter, Edward (1997). A History of Psychiatry: From the Era of the Asylum to the Age of Prozac. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-24531-3 ●Snyder, John; Steffen-Fluhr, Nancy (2012). Overcoming Depression Without Drugs: Mahler's Polka With Introductory Funeral March. AuthorHouse. ISBN 1-4685-4962-6 ●Shutts, David (1982). Lobotomy: resort to the knife. Van Nostrand Reinhold. ISBN 978-0-442-20252-1 ●Sargant, William; Slater, Elliot (1963). An Introduction to Physical Methods of Treatment in Psychiatry. Williams & Wilkins ●Steck, A.J. (2010). “Milestones in the development of neurology and psychiatry in Europe”. Schweizer Archiv für Neurologie und Psychiatrie 161 (3): 85–89. doi:10.4414/sanp.2010.02153. ●Stone, James L. (2001). “Gottlieb Burckhardt – The Pioneer of Psychosurgery”. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences 10 (1): 79–92. doi:10.1076/jhin.10.1.79.5634. PMID 11446267. ●Suchy, Yana (2011). Clinical Neuropsychology of Emotion. Guilford Press. ISBN 978-1-60918-072-0 ●Swayze, V.W. (1995). “Frontal leukotomy and related psychosurgical procedures in the era before antipsychotics (1935–1954): a historical overview”. American Journal of Psychiatry 152 (4): 505–15. doi:10.1176/ajp.152.4.505. PMID 7900928. ●Szasz, Thomas (2007). Coercion as Cure: A Critical History of Psychiatry. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Transaction. ISBN 0-7658-0379-8 ●Tierney, Ann Jane (April 2000). “Egas Moniz and the Origins of Psychosurgery: A Review Commemorating the 50th Anniversary of Moniz's Nobel Prize”. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences 9 (1): 22–36. doi:10.1076/0964-704X(200004)9:1;1-2;FT022. PMID 11232345. ●Tranøy, Joar (Winter 1996). “Lobotomy in Scandinavian psychiatry”. The Journal of Mind and Behavior 17 (1): 1–20. オリジナルの26 May 2008時点におけるアーカイブ。. ●Tranøy, Joar; Blomberg, Wenche (March 2005). “Lobotomy in Norwegian Psychiatry”. History of Psychiatry 16 (1): 107–10. doi:10.1177/0957154X05052224. オリジナルの3 December 2007時点におけるアーカイブ。. ●USSR Ministry of Health (1951). “Приказ МЗ СССР 1003 (9 декабря 1950) [Order 1003 (9 December 1950)]” (Russian). Невропатология и психиатрия [Neuropathology and Psychiatry] 20 (1): 17–18. ●Valenstein, Elliot S. (1990). “The Prefrontal Area and Psychosurgery”. In Uylings, H.B.M.; Van Eden, C.G.; De Bruin, J.P.C.; Corner, M.A.; Feenstra, M.G.P. (eds). The Prefrontal Cortex: Its Structure, Function and Pathology. Progress in Brain Research, Volume 85. Amsterdam & New York: Elsevier. pp. 539–54. ISBN 978-0-444-81124-0 ●Valenstein, Elliot A. (1997). “History of Psychosurgery”. In Greenblatt, Samuel H. (ed.). A History of Neurosurgery: In Its Scientific and Professional Contexts. Park Ridge, IL: The American Association of Neurological Surgeons. pp. 499–516. ISBN 978-1-879284-17-3 ●Weiss, Anthony P.; Rauch, Scott L.; Price, Bruce H. (2007). “Neurosurgical intervention for psychiatric illness: past, present and future”. In Miller, Bruce L.; Cummings, Jeffrey L. (eds). The Human Frontal Lobes: Functions and Disorders. Guilford Press. pp. 505–17. ISBN 978-1-59385-329-7 ●Whitaker, H.A.; Stemmer, B.; Joanette, Y. (1996). “A psychosurgical chapter in the history of cerebral localization: the six cases of Gottlieb Burkhardt”. In Code, Christopher; Wallesch, C.-W.; Joanette Y.; Roch A. (eds). Classic Cases in Neuropsychology. Hove: Psychology Press. pp. 275–304. ISBN 978-0-86377-395-2 ●Wiener, Norbert (1948). Cybernetics. MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-73009-X ●Williams, Tennessee (1998). Suddenly Last Summer. Dramatists Play Service. ISBN 978-0-8222-1094-8 ●Wood, Jeffrey C.; Wood, Minnie (September 2008). Therapy 101: A Brief Look at Modern Psychotherapy Techniques & How They Can Help. New Harbinger Publications. ISBN 978-1-57224-568-6 ●Wright, Frank Leon (1947). Out of Sight, Out of Mind: A Graphic Picture of Present-day Institutional Care of the Mentally Ill in America, Based on More Than Two Thousand Eye-witness Reports. Philadelphia: Mental Health Foundation ●富田三樹生﹃東大病院精神科の30年…宇都宮病院事件・精神衛生法改正・処遇困難者専門病棟問題﹄青弓社、2000年︵原著2000年1月︶。ISBN 9784787231680。 オンライン文献 ●Dully, Howard (2005年11月16日). “"My Lobotomy": Howard Dully's Journey” (podcast). NPR. 2009年11月28日閲覧。 ●Jansson, Bengt (1998年10月29日). “Controversial Psychosurgery Resulted in a Nobel Prize”. Nobel Media. 2012年1月24日閲覧。 ●Macmillan, Malcolm (1999–2012). “The Phineas Gage Information Page: Lobotomy”. The Center for the History of Psychology, University of Akron, Ohio. 2009年3月21日閲覧。 ●“The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1949 Walter Hess, Egas Moniz”. Nobel Media (2013年). 2013年1月24日閲覧。 ●Sutherland, John (2004年8月5日). “Should they de-Nobel Moniz?”. The Guardian. 2011年12月22日閲覧。関連項目[編集]
●精神科医 - 精神保健の歴史 ●ヨーゼフ・ハシッド ●HM (患者) ●精神障害 ●生命倫理学 ●ブレイン・マシン・インタフェース(BMI,BCI) ●カッコーの巣の上で ●ハンニバル ●シャッター アイランド ●エンジェル ウォーズ ●テネシー・ウィリアムズ ●﹃ロボトミー﹄ - コトバンク ウィキメディア・コモンズには、前頭葉白質切截術に関するカテゴリがあります。
ウィキメディア・コモンズには、前頭葉白質切截術に関するカテゴリがあります。
