J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 U s e s
2 M e c h a n i s m o f a c t i o n
3 S y n t h e s i s
4 T o x i c i t y
5 E n v i r o n m e n t a l e f f e c t s
6 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
P r o f e n o f o s
2 l a n g u a g e s
● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Profenofos is an organophosphate insecticide . It is a liquid with a pale yellow to amber color and a garlic -like odor .[1] [3] : 1 European Union .[4]
Uses
[ edit ]
Profenofos can be used on a variety of crops including cotton and vegetables such as maize , potato , soybean , and sugar beet .[5] : 404 lepidopteran insects.[3] : 1
Mixed with phoxim , cypermethrin , beta-cypermethrin imidacloprid and deltamethrin , profenofos can be used against Cotton MealyBug, cabbage caterpillar , Plutella xylostella asparagus caterpillars , as well as against wheat and cabbage aphids .[citation needed
Mechanism of action
[ edit ]
Like other organophosphates, the profenofos mechanism of action is via the inhibition of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme . Although it is used in the form of a racemate , the S(-) isomer is a more potent inhibitor.[5] : 404
Synthesis
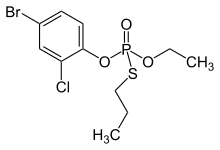
[ edit ] One route to chemical synthesis of profenofos.
Profenofos can be synthesized by reacting phosphorus oxychloride with sodium ethoxide and sodium 1-propanethiolate , followed by treatment with 4-bromo-2-chlorophenol .[6] : 332
Toxicity
[ edit ]
A 2007 World Health Organization report found no adverse effects to workers of routine exposure to profenofos and no teratogenicity or carcinogenicity .[5] : 435–8
Based on a study of patients poisoned with profenofos and its close chemical relative prothiofos , the compound has been described as "of moderately severe toxicity ", causing respiratory failure . Differences in chemical structure that distinguish these two compounds from more common organophosphate pesticides - namely, the presence of the S alkyl group on the phosphorus atom where most OP compounds possess a methoxy or ethoxy group - underlie differences in their behavior as acetylcholinesterase enzyme inhibitors compared to the rest of the OP class.[7]
In one study of a patient who died of profenofos poisoning, the major metabolites of profenofos were identified as des-S propylated profenofos, two isomers of despropylated propenofos, and desethylated propenofos.[8] biomarker for exposure.[9]
Environmental effects
[ edit ]
A United States Environmental Protection Agency report identified profenofos as toxic to birds , small mammals , bees , fish , and aquatic invertebrates , noting several fish kill incidents in which profenofos exposure, primarily due to runoff , was implicated as a probable cause.[3] : 2–3
References
[ edit ]
^ Profenofos in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook , NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69MD ) (retrieved 2015)
^ a b c "Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Profenofos" (PDF) . United States Environmental Protection Agency . US Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pesticide Programs. Retrieved 18 July 2015 .
^ "EU Pesticides database" . European Commission . Retrieved 18 July 2015 .
^ a b c Pesticide residues in food--2007: toxicological evaluations . Geneva: World Health Organization. 2009. ISBN 9789241665230
^ Braun, David B. (1995). Pharmaceutical manufacturers an international directory . Park Ridge, N.J., U.S.A.: Noyes Publications. ISBN 9780815518532
^ Eddleston, M; Worek, F; Eyer, P; Thiermann, H; Von Meyer, L; Jeganathan, K; Sheriff, MH; Dawson, AH; Buckley, NA (November 2009). "Poisoning with the S-Alkyl organophosphorus insecticides profenofos and prothiofos" . QJM . 102 (11 ): 785–92. doi :10.1093/qjmed/hcp119 . PMC 2766103 PMID 19737786 .
^ Gotoh, M; Sakata, M; Endo, T; Hayashi, H; Seno, H; Suzuki, O (15 February 2001). "Profenofos metabolites in human poisoning". Forensic Science International . 116 (2–3): 221–6. doi :10.1016/s0379-0738(00 )00377-7 . PMID 11182275 .
^ Dadson, OA; Ellison, CA; Singleton, ST; Chi, LH; McGarrigle, BP; Lein, PJ; Farahat, FM; Farahat, T; Olson, JR (5 April 2013). "Metabolism of profenofos to 4-bromo-2-chlorophenol, a specific and sensitive exposure biomarker" . Toxicology . 306 : 35–9. doi :10.1016/j.tox.2013.01.023 . PMC 4751995 PMID 23415833 .
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Profenofos&oldid=1203022655 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● A c e t y l c h o l i n e s t e r a s e i n h i b i t o r s ● O r g a n o p h o s p h a t e i n s e c t i c i d e s ● C h l o r o b e n z e n e d e r i v a t i v e s ● B r o m o b e n z e n e d e r i v a t i v e s ● P h e n o l e s t e r s ● E t h y l e s t e r s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● P u b C h e m I D ( C I D ) s a m e a s W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t E B I s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t K E G G s o u r c e ● E C H A I n f o C a r d I D f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● A l l a r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s f r o m J u l y 2 0 1 5
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 4 F e b r u a r y 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 1 : 3 7 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w