

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Banzel, Inovelon |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a609001 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 85% (under fed conditions); tmax = 4–6 hours |
| Protein binding | 34% |
| Metabolism | Carboxylesterase-mediated hydrolysis (CYP not involved) |
| Metabolites | Inactive |
| Elimination half-life | 6–10 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (85%)[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
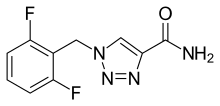
| Formula | C10H8F2N4O |
| Molar mass | 238.198 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Rufinamide is an anticonvulsant medication. It is used in combination with other medication and therapy to treat Lennox–Gastaut syndrome[3] and various other seizure disorders. Rufinamide, a triazole derivative, was developed in 2004 by Novartis Pharma, AG, and is manufactured by Eisai.
Rufinamide was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2008, as adjunctive treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in children four years and older and adults. Its official FDA-approved labeling does not mention use in the treatment of partial seizures inasmuch as clinical trials submitted to the FDA were marginal. However, several recent clinical trials suggest that the drug has efficacy for partial seizures [4] It is marketed under the brand name Banzel.[5] It is also marketed in the European Union under the brand name Inovelon.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[7]
The mechanism of action of rufinamide is not fully understood. There is some evidence that rufinamide can modulate the gating of voltage-gated sodium channels,[8][9] a common target for antiepileptic drugs.[10] A recent study indicates subtle effects on the voltage-dependence of gating and the time course of inactivation in some sodium channel isoforms that could reduce neuronal excitability.[11] However, this action cannot explain the unique spectrum of activity of rufinamide.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chloride |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Transient receptor potential channel modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||