微生物叢
微生物叢︵びせいぶつそう、英: microbiota︶とは、生態系における生きた微生物の集合のことであり、それらの遺伝情報を含意してマイクロバイオーム︵英: microbiome︶と呼ばれることもある。微生物叢は細菌をはじめとした多様な微生物によって構成されており、これら構成成分の組成構造は、微生物叢が定着する環境ごとに異なっている。微生物叢は動植物の体表面や体内に共生的に定着している他、土壌や海中から地下鉄の車内に至るまで、様々な環境に存在している。
ヒトの体にも微生物は定着しており、ヒトの微生物叢はヒトの健康状態と密接に関連している。そのため、特に腸内細菌は医学的な観点からも、古くから研究されてきた。地球上におけるバイオマスとして、細菌は植物に次ぐ重量を占めていると推定されており、環境中の微生物叢に関連した全世界規模の研究も実施されている。
古典的には分離培養に依存した研究が行われていたが、16S rRNA遺伝子の配列に基づく系統分類法が提唱されてからは、分離培養を伴わない方法により未培養の微生物を含めた解析が行われるようになった。近年のDNAシークエンス技術の発展に伴い、微生物叢の研究は急速に進展しており、様々な疾患との関連性が明らかにされている。

ミリメートル単位の原核生物から数十ナノメートル単位のウイルスまで、 様々な微生物が微生物叢を構成する。
微生物叢は、生きた微生物集団の全体を指す用語であり、また微生物集団が有する遺伝情報の全体を指してマイクロバイオーム (microbiome) と呼ばれることもある[1]。また、マイクロバイオームは微生物叢の遺伝情報のみならず、その集団が置かれる環境の状態も含有する[2]。従来は微生物叢を意味する用語として、生態学において叢︵くさむら、多くのものが集まっている︶を意味する用語であるフローラ︵flora︶の語が用いられてきたが、マイクロバイオーム解析の興隆と共に微生物叢 (microbiota) が支配的に用いられるようになった[1][3]。歴史的な背景によってフローラの語は用いられてきたが、現代において学術的に微生物叢を表す単語としてフローラを用いるべきではないと言われている[2]。また、微生物叢研究はメタゲノム解析と呼ばれる解析技術によって発展してきた。メタゲノムとはギリシャ語で﹁高次﹂や﹁超越﹂を意味する﹁メタ﹂と、すべての遺伝子全体を意味する﹁ゲノム﹂を組み合わせた造語である。メタゲノム解析においては微生物群集の遺伝子全体を、DNAの混合物として培養を行わずに網羅的に解析する[4][5][6]。微生物が細菌、古細菌、真菌、蠕虫などの寄生虫、及びウイルスを内包するように、微生物叢もまた細菌をはじめとした様々な微生物によって構成される。一方で、微生物叢の研究の多くは腸内細菌をはじめとした細菌に焦点を当てており[6]、マイクロバイオームが常在細菌と同義的に用いられることもある[7]。ヒト微生物叢の遺伝情報はヒトそのものの遺伝情報よりも大規模であり、それ故に﹁第二のゲノム﹂と称されることもある[8][9]。

シュードモナス属16S rRNAの超可変領域。細菌の16S rR NAには9か所の多様性の大きい部位が存在し、その領域を挟むようにプライマーを設計することで、菌種ごとに異なる配列をPCR法により増幅することができる。
細菌叢の組成を明らかにするためには、様々な生物で保存されており、適度に系統間では配列が異なる16S rRNA遺伝子のDNA配列をマーカー遺伝子として解析し、その存在比から細菌叢を構成する菌種の特定や組成を推定することが一般に行われる。また、その手法のことをメタ16S解析と呼ぶ[10]。この手法は比較的簡単、安価に行える、真正細菌だけでなく古細菌も同時に評価できるといった利点をもつ。ただし、ポリメラーゼ連鎖反応︵PCR︶によりDNA配列のコピー数を増幅する作業が必要であり、この過程で特定の分類群に対してその組成を過大/過少に評価してしまうようなバイアスが生じる[6]。また、古くから行われてきた手法であり、データベースに登録された既存データや解析ツールが充実している[11]。
一方で全メタゲノム解析は、試料に含まれる全てのDNA配列を解析する手法であり、微生物叢の遺伝情報を詳細に解析できる上、細菌のみならず真菌やDNAウイルスについても同時に評価できるという利点を持つ。しかしながら比較的高価で複雑な解析が必要であり、一般性は劣る[6][11]。
また、メタトランスクリプトーム解析は試料に含まれる全RNAを解析するもので、死んだ細菌内でも比較的安定した物質であるDNAを解析するメタ16S解析や全メタゲノム解析と異なり、原則的に生きている細菌の遺伝情報だけを解析できる。ただし、上記の手法に比べるとrRNAの除去が必要など、実験系が複雑であり、解析により多額の費用がかかる[11]。
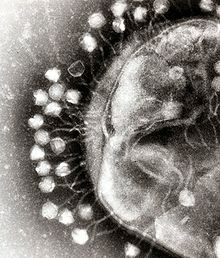
大腸菌に吸着するバクテリオファージの透過型電子顕微鏡像。縮尺はお よそ200,000倍。
他の微生物と同様にウイルスもまた人体に普遍的に常在しており、DNAウイルスやRNAウイルスを含むすべてのウイルスの集合をウイローム︵ヴァイローム、virome︶と呼ぶ[13][14]。ウイルスは細菌や真菌と異なり、全てのウイルスで共通して存在するような保存配列を持たない。そのため、ウイルス叢の解析においてはしばしば試料に含まれる全ての遺伝情報を解析するメタゲノム解析が用いられる。また、人体に生息するDNAウイルスの多くは、常在細菌に感染しているバクテリオファージであり、ウイルス叢の研究は細菌叢との関連で扱われることが多い[6]。ただし、ウイルスのゲノムは一般に細菌や哺乳類のゲノムに比べ小さく、メタゲノム解析で得られるウイルスDNA配列はメタゲノム全体の小さな割合を占めるに過ぎない。また、ファージのDNA配列は溶原化と呼ばれる過程を経て、細菌のゲノムに取り込まれて存在していることがあり、配列情報だけではウイルス粒子として存在する配列と細菌ゲノムに取り込まれた配列とを区別できない。そのため、厳密にウイルス粒子として存在するウイルスの遺伝情報を定量的に評価するためには、事前に細菌の菌体より孔の目が細かい膜を用いたろ過、ウイルス粒子外のDNAを分解する酵素処理、遠心分離による分画などを行うことで、ウイルス粒子内のDNAを抽出する手法が採用されることがある[15][16]。ファージは宿主となる細菌を殺したり、新しい遺伝子を付与することで、細菌叢に影響を及ぼしていると考えられている[17]。環境中にもウイルスは存在しており、最初期のウイルス叢研究は海水中のウイルス叢を解析したものであった[18][19]。
定義と語源[編集]

微生物叢の構成要素とその解析手法[編集]
細菌叢[編集]
細菌叢は微生物集団が有する遺伝情報の全体がマイクロバイオームと呼ばれるように、細菌︵バクテリア︶集団が有する遺伝情報の全体をバクテリオーム (bacteriome) と呼ぶ[注釈 1]。先述の通り、微生物叢を構成する要素の中でも、細菌の成分は特に重点を置かれて研究が進められてきた[6]。
真菌叢[編集]
カビや酵母といった真菌もまた微生物叢の構成要素として注目されている[6]。真菌の研究は19世紀から行われてきたが、環境中の真菌全体を捉える真菌叢の研究の歴史は浅く、mycobiologyとmicrobiomeを組み合わせた造語であるmycobiomeの語が提案されたのは2010年のことである[12]。また、真菌叢解析に関する報告は細菌叢解析に関するものに比べると格段に少ない。しかしながら、解析の手法に大きな差はない[10]。細菌叢の解析には16S rRNA遺伝子の配列がマーカーとして利用されるが、真菌叢の解析においてはリボソームRNA遺伝子を隔てる内部転写スペーサー (internal transcribed spacer, ITS) 領域や、細菌の16S rRNA遺伝子に相当する18S rRNA遺伝子がマーカー遺伝子として用いられる。ただし、真菌叢の解析はデータベースの不足から細菌叢の解析と比べ困難である。ヒトの身体の場合、粘膜においてはカンジダ属が優位だが、皮膚ではマラセチア属が優占する[6]。ウイルス叢[編集]

宿主や環境と微生物叢[編集]
ヒトと微生物叢[編集]
詳細は「ヒトマイクロバイオーム」を参照

腸内をはじめヒトの体には微生物が定着している。大腸には特に多数の細菌が生息しており、重量は体重70kgの成人男性で0.2kgに過ぎないが、細胞数では約40兆に及ぶと推定されている。この数は個人の全細胞の数を超える[21]。ヒトの微生物叢は特にヒトマイクロバイオームと呼ばれ、疾病等との関連性から重点的に研究が進められてきた。その中でも腸内細菌叢に関する研究が特に焦点を当てられてきており、腸管に沿って腸内細菌叢の構造が変化することや、様々な疾病との関連が明らかにされている。同様に、口腔、皮膚、膣などの微生物叢も疾患との関連などから研究されてきた[6]。また、ヒトの微生物叢の大規模な調査として、アメリカのHuman Microbiome ProjectやヨーロッパのMetaHITなどの国家規模のプロジェクトが実施されている[22][23]。
ヒトの微生物叢は腸管、口腔、皮膚、膣といった部位ごとに、構成する細菌種が異なり、例えば他者間のヒト腸管の微生物叢を比べた場合と、同一個人で腸管と口腔の微生物叢を比較した場合、前者の方が互いに類似性が高い[24][25]。

動物の腸管マイクロバイオーム多様性の主座標分析。腸管マイクロバイ オームはその分類毎に異なる。コウモリは哺乳類でありながら他の哺乳類よりもむしろ鳥類と類似した腸管マイクロバイオームを持ち、バクテロイデーテスが少なく、プロテオバクテリアが多い[26]。
ヒトと同様に様々な動物が微生物と共生関係にあり、固有の微生物叢を持つ。微生物叢はそれを保持する動物の行動によって構成が変化し、また微生物叢が宿主となる動物の行動に影響を与えるとされる[27]。一方でアリなどの一部の動物は、病的な状態や一過性に微生物が寄生することを除くと、共生関係にある微生物叢が存在しない場合もあると指摘する研究もある[28]。
ペットとして、ヒトと生活空間を共にするイヌはそこで生活するヒトと同じ大腸菌を共有することがある[29]。また、イヌの皮膚の微生物叢は飼育するヒトの皮膚の微生物叢と類似し、ヒトの皮膚の微生物叢はイヌを飼育することで多様性を増す[30]。
一般に動物の腸内細菌叢は食性によって変わり、系統学的に近い種であっても食性が異なると腸内細菌叢の構造は異なったものとなる[31]。食性の違いによって生じる腸内細菌叢の差異は、腸内細菌叢の機能にも影響を及ぼすとさせる。2011年に公表された研究では、草食動物の糞便においてアミノ酸や糖の生合成に関わる酵素の遺伝子が増加していた一方、肉食動物ではアミノ酸や糖の分解に関わる酵素の遺伝子が増加していた[32]。レッサーパンダとジャイアントパンダは食性と腸内細菌叢の関連性における例外的存在であり、これらの動物は草食動物であるが、その腸内細菌叢はむしろ肉食動物のものである。これはパンダが最近になって食性を肉食から草食へと変化させたことを反映させているのかもしれない[33]。
ウシに代表される反芻動物は、胃が4つの部屋に分画されており、食道から直接つながる第一胃は食物の発酵槽として働く。草食動物であるウシは草本を栄養源として利用するが、一般に植物の葉は果実や動物の肉と比べて栄養の利用効率が低い。これは植物の葉がセルロースに代表される不溶性の多糖類から構成されるためであるが、反芻動物はこの不溶性の多糖類を第一胃の微生物による発酵で分解し、最終生産物として得られる酢酸、酪酸、プロピオン酸などの短鎖脂肪酸︵揮発性脂肪酸とも呼ばれる︶を吸収する。反芻動物はこの短鎖脂肪酸を材料に糖新生、脂肪新生という過程を経て糖や脂肪を合成している[33]。反芻動物の飼料利用効率は農業において重要であり、第一胃の微生物叢と飼料利用効率の相関が調査されている。それによると、ウシの飼料利用効率は第一胃にフィルミクテスが多い場合に高いとされている[34]。
細菌叢や特定の細菌が、それを保持する宿主に及ぼす生理作用を明らかにするために、ノトバイオート技術が用いられる。ヒトの細菌叢がヒトの健康に及ぼす影響を明らかにするためには、ヒトそのものを研究材料とすることがもっとも直接的な方法だが、遺伝的、環境的な背景を揃えた実験群を用意することは困難であり、また、健康を害するおそれのある処置を伴う実験は倫理的に行うことができない。そのため、ヒトの腸内細菌の研究であっても実験動物を用いた実験が必要となる。既知の細菌のみが腸内などに定着しているノトバイオート動物の作製においては、細菌の株やその混合物を何の微生物も定着していない無菌動物に接種する。さらに、細菌を移植されたノトバイオート動物の病態や健康状態の変化を観察することで、移植した細菌叢が宿主に与える生理作用を調べる。現在広く用いられる無菌動物はマウスとラットだが、無菌動物を用いた初期の研究ではモルモットが多く用いられた。他にもウサギ、ブタ、ヤギ、ヒツジ、ウシ、ウマ、イヌ、ニワトリなどの動物でも無菌化が行われている[10]。
ヒト以外の動物と微生物叢[編集]

植物と微生物叢[編集]

植物の各部位における典型的な微生物ネットワーク
土壌、空気中、根圏、葉圏、そして植物組織内における微生物群集の模式図。各種の生息地において、微生物︵色で塗られた小円(ノード)で示される︶は互いに共生的・競合的に関わったり︵線が引かれているペア︶、無関係であったりする︵線が引かれていないペア)。﹁ハブ﹂として現れる特定の種︵太線で示されるノード︶は、ネットワーク内で各微生物との関係性が強く、微生物叢の構造に強く影響を与えている。(a) 根圏の微生物は主に土壌に由来する。(b) 葉圏の微生物は、エアロゾル、昆虫、塵などの多様な外部環境に由来する。(c) 植物の地上部と地中部との間での微生物叢の移動も存在する[35]。
様々な栄養素を提供する植物は微生物にとって魅力的な宿主である。植物に寄生する微生物はエピファイト︵植物の表面に存在する微生物︶またはエンドファイト︵植物の組織内に存在する微生物︶として存在している[36][37]。卵菌と真菌は収斂進化の果てに類似した形態を持つようになり、生態学的ニッチを共有するようになった。これらの生物は菌糸を持っており、その脚を宿主の細胞へと浸透させる。共生的関係において植物は菌根菌とも呼ばれる共生真菌と物質交換を行っており、植物は光合成により産生した糖の代わりに、土壌中から吸収された無機リン酸を得ている。この共生関係は古代から続いていると考えられており、これが植物の地上進出を助けたと推測されている[38][39]。最古の菌根菌は3億5000万年から4億6000万年前には存在しており、陸生植物と同時期に進化した。現在の植物も24万8000種のうち90%が菌根菌との共生関係にあり、植物から独立した菌根菌は発見されていない[40]。植物成長促進根圏細菌︵plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria‥PGPR︶は植物の成長を促進する働きを持つ根圏微生物で、窒素固定、リンなどの無機物の可溶化、植物ホルモンの合成、無機物の取り込み、病原体からの防御といった植物に必須な機能を提供する[41][42]。PGPRは生態学的ニッチや基質の獲得を病原体と競合したり、アレロケミカルを産生したり、全身的な抵抗性誘導 (induced systemic resistance: ISR) を引き起こすことで、植物を病原体から守る[43][44]。

ソテツの珊瑚状の根粒切片を光学顕微鏡で観察すると、共生菌であるシ アノバクテリアの層が観察される。

1 mLの海水には50万個の細菌が含まれているとされる。中でもシア ノバクテリアが主要な成分の一つである[53]。
初期の微生物叢を確認できる化石として、ストロマトライトがある。これはシアノバクテリアによる堆積物であり、先カンブリア時代の地層で主に発見される。シアノバクテリアによる光合成が、地球の大気に酸素が含まれる原因になったと推測されており、ストロマトライトはその痕跡でもある。現在でも、塩分濃度が高く捕食者のいない浅瀬にストロマトライトが現生し、オーストラリアのシャーク湾には1万年前からストロマトライトが形成されている。外観は岩石のようだが、スポンジ状の部分もある[54][55]

イルミナ社製のDNAシーケンサーであるMiSeq。微生物叢解析に 用いられる次世代シーケンサーの代表例である。
古典的には腸内細菌叢をはじめとする微生物叢の研究には分離培養法を基礎とした手法が用いられてきた。しかしながら、今日において実験室で分離培養が可能な細菌は集団中の極一部に過ぎないことが知られており、分離培養に頼った手法で微生物叢の全体像を把握することは困難である[64][22][65][66]。
1977年、カール・ウーズとジョージ・E・フォックスは16S rRNA遺伝子の配列に基づく系統分類の手法を提示する[67][20]。
さらに1990年には、当時開発されたPCR法を用いて、キャサリン・G・フィールドらのグループが16S rRNAを増幅し、分離培養を介さずに海洋の微生物叢を構成する細菌の分類を試みる[64][68][63]。
1990年代における微生物叢解析の主な手法は、遺伝情報を含んだDNA配列を大腸菌に導入する必要があるクローニングを前提とした手法であった[64]。
メタゲノムの語が提唱されたのは1998年である[69]。また、マイクロバイオームという概念を初めて提唱したのはノーベル生理学・医学賞を受賞したジョシュア・レーダーバーグとされており、これは2001年のことであった[22]。
この頃までの微生物叢解析は古典的なDNAシークエンシング法であるサンガー法に依存していたため、出力されるデータ量に限りがあり、希少な種の遺伝情報を見過ごしてしまう可能性があった。この課題を解決したのが2010年頃からの次世代シーケンサーの登場である。454をはじめとした第二世代シーケンサーとも呼ばれるDNAシーケンサーはサンガー法に比べ、圧倒的に多数の配列を同時に解析することができる。このDNAシーケンサーの技術革新により、より網羅的に微生物叢を解析することが可能となった。[63][69]
これに伴って研究の規模も巨大化しており、例えば2006年に公表された初期のメタゲノム解析は、サンガー法による2人の被験者の腸内細菌を対象としたものであったが、2016年に公表された研究では、イルミナ社製の次世代シーケンサーが用いられ、解析対象者の数は1135人に及ぶ[10][70][71]。
また、Oxford Nanopore Technologies社のMinIONやPacific Biosciences社の1分子リアルタイムシーケンサーは第三世代シーケンサーやロングリードシーケンサーとも呼ばれ、解析時のエラーが多いという欠点と引き換えに、ショートリードシーケンサーとも呼ばれる第二世代シーケンサーに比べ長い配列を読むことができる。この利点を活かし、2010年代後半からは第三世代シーケンサーも微生物叢解析に用いられている[72][73][74]。

環境と微生物叢[編集]
2018年に発表された研究によると、地球上にはおよそ550ギガトン (Gt) の炭素が生体物質︵バイオマス︶として存在し、70Gtのバイオマスを占める細菌は450 Gtを占める植物に次いでいる。真菌、古細菌、原生生物もそれぞれ12 Gt、7 Gt、4 Gtのバイオマスを占めるが、ヒトを含めた動物のそれは2 Gtに過ぎない。細菌や古細菌のバイオマスはおよそ9割が海底や陸上の地下8 m以深に定義される地下生物圏に存在する [45]。また、海洋のバイオマスは約70%が微生物によって占められる。その多くが細菌と原生生物で、細菌の細胞数は海洋全体で1029を超えるとされる。また、数で言えばウイルスはさらに多く、その粒子数は海洋全体で1030を超える[45][46]。 環境の微生物叢を地球規模で調査することを目的として設立されたプロジェクトとしてEarth Microbiome Project (EMP) が知られる。このプロジェクトは﹁地球の微生物叢を丸ごと調査する﹂ことを目的にしており、ヒトの体、土壌、海水、空気などありとあらゆる試料を含む200,000個の試料を調査することで、地球全体の微生物叢を網羅的に明らかにすることを試みている。実際に、2010年8月に始まったこのプロジェクトは、2014年までに30,000の試料を解析してきた[47]。同プロジェクトは世界各国の様々なグループが行った微生物叢解析の研究結果を統合することで実施される。しかし、以前の微生物叢研究は実験手技からデータ解析の手法に至るまで、各々の研究グループが独自の方法を開発していたため、比較することが困難であった。そのため、同プロジェクトは微生物叢解析実験の標準化を進めており、DNA抽出などの実験室で用いられる手技から、得られた塩基配列データのデータ解析に用いるソフトウェアまで、様々な段階における標準化を試みている。QIIME︵チャイムと発音する︶と呼ばれるデータ解析環境はその代表例である[47][48][49][50]。土壌[編集]
土壌は一様ではなく、pHや塩分濃度、酸素濃度などの勾配が存在し、土壌微生物叢は土壌環境によって構成を変化させる。土壌の微生物叢では細菌と真菌が多数を占め、その比率は他の成分である古細菌、ウイルス、原生生物の100倍から10000倍に及ぶ[51]。 地球の窒素循環には微生物叢が関わっている。窒素固定細菌は、マメ科などの植物の根に塊を作ることで土壌に窒素を蓄積する。マメ科の樹木は砂漠、半砂漠やサバンナ、熱帯雨林の紅葉樹などにも生育して土壌の窒素を保っている。他方で土壌の窒素は、脱窒素細菌の無気呼吸によって窒素ガスに変わり、空気中に送られる。この効果で、窒素が硝酸塩に変わって海に流出することを防ぎ、窒素固定細菌と脱窒素細菌による循環が作られている[52]海岸[編集]

地下生物圏[編集]
陸上で地下8m以深、海底で海底下10cm以深などの地下に存在する生物圏を地下生物圏という[56]。地下深部には海底下約800 mまでは1 cm3あたり100万細胞以上の微生物が存在するが、地下で微生物が持続的に生存するためには水やエネルギー基質の供給が重要と考えられている。八戸沖の掘削では海底下約1.2 km以深で1cm3あたり100細胞以下に減少し、海底下2.5 km近辺では生命は存在しないと考えられた。深くなるにつれて微生物が減少するのは、圧密によって間隙が減少し、水や栄養源の供給が失われるためとされる[57]。このような地下生物圏には、堆積した有機物を栄養源とする従属栄養の原核生物や、還元型無機物である硫化水素、水素、アンモニア、二価鉄を酸化することで有機物を同化するための化学エネルギーを獲得する化学合成無機独立栄養の原核生物が生息している[56]。 海底では、1970年代から1980年代にかけて深海底の熱水噴出孔や冷水湧出帯について研究が進められ、多くの微生物叢が発見された。海底から噴出する水には、摂氏4度から20度の温水︵湧水︶と、摂氏300度を超える熱水に大きく分かれており、いずれの水中にも微生物叢が存在し、熱水には好気性と嫌気性の微生物がともに生息していた。1990年代には、北海の海底やアラスカの永久凍土の地下3キロメートルなどの石油採掘孔で微生物叢が発見され、地球内部に一般的に生息していることが確認された。コロンビア川の玄武岩台地の地下900メートルにいた微生物叢は、玄武岩と地下水が反応した水素からエネルギーを得ており、発見者たちはこうした深地下の微生物をSLiME︵subsurface lithoautotrophic miceobial ecosystem: 表層岩石従属栄養微生物生態系︶と名付けた。深地下の微生物は多くが嫌気性で好熱性であり、酸素が多く気圧の低い地上では生存できない[58]。 SLiMEをはじめとする地下の無機栄養生物の発見は、宇宙探査計画に影響を与えた。火星の地下には玄武岩、水、二酸化炭素ガスがあると推測されているため、アメリカ航空宇宙局︵NASA︶は火星に生命が存在する可能性のモデルとして無機栄養生物を参考にしている[59]。建造環境[編集]
建造環境は人工的に造られた環境の事をいい、建造物や交通機関を含む全ての人工的な環境を言う。建造環境は地球上の他の環境と比較して微生物の生息には適さず、選択圧により一部の微生物しか生息しないため、自然環境と比べると独特の微生物群集を保持する。建造環境の微生物は主にヒトの皮膚や口腔微生物叢に由来すると考えられているが、一方で農村においては動物由来の微生物などより多様な微生物が生息する[60]。コーネル大学のグループはニューヨークの地下鉄の駅構内と地下鉄車両の車内を綿棒でぬぐい、地下鉄の微生物叢の調査を行った。およそ半分の配列は未知の配列であり、残りの大半は細菌のものであった。ニューヨークの地下鉄は世界でも最大規模であり、多数のヒトが利用するにもかかわらず、この研究から得られたヒトDNA配列は0.2%を占めるに過ぎなかった[61]。食品と微生物叢[編集]
食品の発酵と微生物群集の関係性については、チーズを含めた乳製品や酒類をはじめとした多数の食品・飲料で調査がなされてきた。発酵に影響を及ぼす外的要因としてはpH、水分活性、塩濃度、温度等が知られる。発酵食品の中には真菌が重要な役割を果たすものもあるが、発酵食品中の微生物についても真菌に関連する研究は数が少ない[62]。また、食品中の微生物は食品衛生の観点からも注目されており、例えば牛乳中の腐敗菌や病原細菌、野菜の表面に付着した病原細菌などが調べられている[63]。歴史[編集]

注釈[編集]
- ^ 昆虫類が持つ共生細菌を保持するための器官(共生器官)もbacteriomeと呼ばれる。
出典[編集]
(一)^ ab 実験医学別冊 もっとよくわかる!シリーズ もっとよくわかる!腸内細菌叢 健康と疾患を司る“もう1つの臓器”. 福田真嗣. 羊土社. ISBN 978-4-7581-2206-1. OCLC 1122630567
(二)^ abMarchesi, Julian R.; Ravel, Jacques (2015-12). “The vocabulary of microbiome research: a proposal” (英語). Microbiome 3 (1): 31, s40168-015-0094-5. doi:10.1186/s40168-015-0094-5. ISSN 2049-2618. PMC 4520061. PMID 26229597.
(三)^ 本間 央之 (2014). “医療イノベーションに向けた 腸管微生物叢研究の展開 ―微生物叢移植とその発展型を巡る研究開発と実用化の動向―”. 科学技術動向研究 (146).
(四)^ Inoue, Ryo (2019-03-14). “ABCs for analysis of gut microbiota”. Japanese Journal of Lactic Acid Bacteria 30 (1): 27-31. doi:10.4109/jslab.30.27. ISSN 1343-327X.
(五)^ Kusumoto, Ken-Ichi (2011). “Metagenomic Analysis”. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 58 (3): 136-136. doi:10.3136/nskkk.58.136. ISSN 1341-027X.
(六)^ abcdefghiRowan-Nash, Aislinn D.; Korry, Benjamin J.; Mylonakis, Eleftherios; Belenky, Peter (2019-01-09). “Cross-Domain and Viral Interactions in the Microbiome” (英語). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 83 (1): e00044-18, /mmbr/83/1/e00044-18.atom. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00044-18. ISSN 1092-2172. PMC 6383444. PMID 30626617.
(七)^ Moyes, David L.; Naglik, Julian R. (2012-06-14). “The Mycobiome: Influencing IBD Severity” (English). Cell Host & Microbe 11 (6): 551-552. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2012.05.009. ISSN 1931-3128. PMID 22704612.
(八)^ Zhao, Liping (2010-06). “The tale of our other genome” (英語). Nature 465 (7300): 879-880. doi:10.1038/465879a. ISSN 1476-4687.
(九)^ Grice, Elizabeth A.; Segre, Julia A. (2012). “The human microbiome: our second genome”. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics 13: 151-170. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-090711-163814. ISSN 1545-293X. PMC 3518434. PMID 22703178.
(十)^ abcd 今すぐ始める! メタゲノム解析 実験プロトコール ヒト常在細菌叢から環境メタゲノムまでサンプル調製と解析のコツ. 服部 正平. 羊土社. (2016). ISBN 978-4-7581-0197-4. OCLC 1089711913
(11)^ abcKnight, Rob; Vrbanac, Alison; Taylor, Bryn C.; Aksenov, Alexander; Callewaert, Chris; Debelius, Justine; Gonzalez, Antonio; Kosciolek, Tomasz et al. (07 2018). “Best practices for analysing microbiomes”. Nature Reviews. Microbiology 16 (7): 410-422. doi:10.1038/s41579-018-0029-9. ISSN 1740-1534. PMID 29795328.
(12)^ Cui, Lijia; Morris, Alison; Ghedin, Elodie (2013). “The human mycobiome in health and disease”. Genome Medicine 5 (7): 63. doi:10.1186/gm467. ISSN 1756-994X. PMC 3978422. PMID 23899327.
(13)^ 緒方靖哉・西山孝・土居克実﹁改訂 ウイルス分類‥話題のウイルスの知見と動向﹂﹃化学と生物﹄第58巻1号、日本農芸化学会、2020年、20-33頁。
(14)^ 小林大介﹁昆虫類のウイルス叢解析の実際と見出されたウイルスのユニークな進化生態﹂﹃蚕糸・昆虫バイオテック﹄第90巻1号、日本蚕糸学会、2021年、9-19頁。
(15)^ Mohiuddin, Mohammad; Schellhorn, Herb (2015). “Spatial and temporal dynamics of virus occurrence in two freshwater lakes captured through metagenomic analysis” (English). Frontiers in Microbiology 6. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00960. ISSN 1664-302X.
(16)^ Kleiner, Manuel; Hooper, Lora V.; Duerkop, Breck A. (2015-01-22). “Evaluation of methods to purify virus-like particles for metagenomic sequencing of intestinal viromes” (英語). BMC Genomics 16 (1): 7. doi:10.1186/s12864-014-1207-4. ISSN 1471-2164. PMC 4308010. PMID 25608871.
(17)^ Haynes, Matthew; Rohwer, Forest (2011). “The Human Virome”. In Nelson, Karen E. (英語). Metagenomics of the Human Body. New York, NY: Springer. pp. 63-77. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7089-3_4. ISBN 978-1-4419-7089-3. PMC 7122492
(18)^ Wylie, Kristine M.; Weinstock, George M.; Storch, Gregory A. (2012-10-01). “Emerging view of the human virome” (英語). Translational Research 160 (4): 283-290. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2012.03.006. ISSN 1931-5244.
(19)^ Breitbart, Mya; Salamon, Peter; Andresen, Bjarne; Mahaffy, Joseph M.; Segall, Anca M.; Mead, David; Azam, Farooq; Rohwer, Forest (2002-10-29). “Genomic analysis of uncultured marine viral communities”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99 (22): 14250-14255. doi:10.1073/pnas.202488399. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 137870. PMID 12384570.
(20)^ abByrd, Allyson L.; Belkaid, Yasmine; Segre, Julia A. (2018-03). “The human skin microbiome” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 16 (3): 143-155. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2017.157. ISSN 1740-1526.
(21)^ Sender, Ron; Fuchs, Shai; Milo, Ron (2016-08-19). “Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body” (英語). PLOS Biology 14 (8): e1002533. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002533. ISSN 1545-7885. PMC 4991899. PMID 27541692.
(22)^ abcNIH HMP Working Group; Peterson, Jane; Garges, Susan; Giovanni, Maria; McInnes, Pamela; Wang, Lu; Schloss, Jeffery A.; Bonazzi, Vivien et al. (2009-12). “The NIH Human Microbiome Project”. Genome Research 19 (12): 2317-2323. doi:10.1101/gr.096651.109. ISSN 1549-5469. PMC 2792171. PMID 19819907.
(23)^ Qin, Junjie; Li, Ruiqiang; Raes, Jeroen; Arumugam, Manimozhiyan; Burgdorf, Kristoffer Solvsten; Manichanh, Chaysavanh; Nielsen, Trine; Pons, Nicolas et al. (2010-03). “A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing” (英語). Nature 464 (7285): 59-65. doi:10.1038/nature08821. ISSN 1476-4687.
(24)^ Costello, Elizabeth K.; Lauber, Christian L.; Hamady, Micah; Fierer, Noah; Gordon, Jeffrey I.; Knight, Rob (2009-12-18). “Bacterial Community Variation in Human Body Habitats Across Space and Time” (英語). Science 326 (5960): 1694-1697. doi:10.1126/science.1177486. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 19892944.
(25)^ The Human Microbiome Project Consortium (2012-06). “Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome” (英語). Nature 486 (7402): 207-214. doi:10.1038/nature11234. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 3564958. PMID 22699609.
(26)^ Song, Se Jin; Sanders, Jon G.; Delsuc, Frédéric; Metcalf, Jessica; Amato, Katherine; Taylor, Michael W.; Mazel, Florent; Lutz, Holly L. et al. (2020-02-25). Graf, Joerg. ed. “Comparative Analyses of Vertebrate Gut Microbiomes Reveal Convergence between Birds and Bats” (英語). mBio 11 (1). doi:10.1128/mBio.02901-19. ISSN 2161-2129. PMC 6946802. PMID 31911491.
(27)^ Ezenwa, V. O.; Gerardo, N. M.; Inouye, D. W.; Medina, M.; Xavier, J. B. (2012-10-12). “Animal Behavior and the Microbiome” (英語). Science 338 (6104): 198-199. doi:10.1126/science.1227412. ISSN 0036-8075.
(28)^ Hammer, Tobin J.; Sanders, Jon G.; Fierer, Noah (2019-05-01). “Not all animals need a microbiome” (英語). FEMS Microbiology Letters 366 (10). doi:10.1093/femsle/fnz117. ISSN 0378-1097.
(29)^ Caugant, Dominique A.; Levin, B. R.; Selander, R. K. (1984-06). “Distribution of multilocus genotypes of Escherichia coli within and between host families” (英語). Journal of Hygiene 92 (3): 377-384. doi:10.1017/S0022172400064597. ISSN 0022-1724. PMC 2129322. PMID 6376625.
(30)^ Song, Se Jin; Lauber, Christian; Costello, Elizabeth K; Lozupone, Catherine A; Humphrey, Gregory; Berg-Lyons, Donna; Caporaso, J Gregory; Knights, Dan et al. (2013-04-16). Weigel, Detlef. ed. “Cohabiting family members share microbiota with one another and with their dogs”. eLife 2: e00458. doi:10.7554/eLife.00458. ISSN 2050-084X.
(31)^ Ley, R. E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P. J.; Ramey, R. R.; Bircher, J. S.; Schlegel, M. L.; Tucker, T. A. et al. (2008-06-20). “Evolution of Mammals and Their Gut Microbes” (英語). Science 320 (5883): 1647-1651. doi:10.1126/science.1155725. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 2649005. PMID 18497261.
(32)^ Muegge, Brian D.; Kuczynski, Justin; Knights, Dan; Clemente, Jose C.; González, Antonio; Fontana, Luigi; Henrissat, Bernard; Knight, Rob et al. (2011-05-20). “Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans”. Science (New York, N.Y.) 332 (6032): 970-974. doi:10.1126/science.1198719. ISSN 1095-9203. PMC 3303602. PMID 21596990.
(33)^ abKarasov, William H.; Douglas, Angela E. (2013-4). “Comparative Digestive Physiology”. Comprehensive Physiology 3 (2): 741-783. doi:10.1002/cphy.c110054. ISSN 2040-4603. PMC 4458075. PMID 23720328.
(34)^ Myer, Phillip R. (2019-06-25). “Bovine Genome-Microbiome Interactions: Metagenomic Frontier for the Selection of Efficient Productivity in Cattle Systems” (英語). mSystems 4 (3). doi:10.1128/mSystems.00103-19. ISSN 2379-5077. PMID 31219789.
(35)^ Hassani, M.A., Durán, P. and Hacquard, S. (2018) "Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont". Microbiome, 6(1): 58. doi:10.1186/s40168-018-0445-0.  Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
(36)^ Berlec, Aleš (2012-09-01). “Novel techniques and findings in the study of plant microbiota: Search for plant probiotics”. Plant Science 193-194: 96-102. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.05.010. PMID 22794922.
(37)^ Whipps, J.m.; Hand, P.; Pink, D.; Bending, G.d. (2008-12-01). “Phyllosphere microbiology with special reference to diversity and plant genotype” (英語). Journal of Applied Microbiology 105 (6): 1744-1755. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03906.x. ISSN 1365-2672. PMID 19120625.
(38)^ “Four hundred-million-year-old vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 (25): 11841-3. (1994). Bibcode: 1994PNAS...9111841R. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.25.11841. PMC 45331. PMID 11607500.
(39)^ “Common themes in nutrient acquisition by plant symbiotic microbes, described by the Gene Ontology”. BMC Microbiology 9(Suppl 1): S6. (2009). doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-S1-S6. PMC 2654666. PMID 19278554.
(40)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、131-134頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(41)^ Kloepper, J. W (1993). “Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biological control agents”. In Metting, F. B. Jr. Soil microbial ecology: applications in agricultural and environmental management. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. pp. 255-274. ISBN 978-0-8247-8737-0
(42)^ Bloemberg, G. V.; Lugtenberg, B. J. J. (2001). “Molecular basis of plant growth promotion and biocontrol by rhizobacteria”. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 4 (4): 343-350. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00183-7. PMID 11418345.
(43)^ “Use of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Biocontrol of Plant Diseases: Principles, Mechanisms of Action, and Future Prospects”. Appl Environ Microbiol 71 (9): 4951-9. (2005). doi:10.1128/AEM.71.9.4951-4959.2005. PMC 1214602. PMID 16151072.
(44)^ 百町満朗﹁生物防除研究の現状と展望﹂﹃日本植物病理學會報﹄第79巻第3号、日本植物病理學會、2013年8月、123-127頁、doi:10.3186/jjphytopath.79.123、ISSN 00319473、NAID 10031191400。
(45)^ abBar-On, Yinon M.; Phillips, Rob; Milo, Ron (2018-05-21). “The biomass distribution on Earth” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (25): 6506-6511. doi:10.1073/pnas.1711842115. ISSN 0027-8424.
(46)^ Blasiak, R.; Wynberg, R.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Thambisetty, S.; Bandarra, N. M.; Canário, A. V. M.; da Silva, J.; Duarte, C. M. et al. (2020-08). “The ocean genome and future prospects for conservation and equity” (英語). Nature Sustainability 3 (8): 588-596. doi:10.1038/s41893-020-0522-9. ISSN 2398-9629.
(47)^ abGilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2014-08-22). “The Earth Microbiome project: successes and aspirations”. BMC Biology 12 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s12915-014-0069-1. ISSN 1741-7007.
(48)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2018-06-26). “Earth Microbiome Project and Global Systems Biology” (英語). mSystems 3 (3). doi:10.1128/mSystems.00217-17. ISSN 2379-5077.
(49)^ Thompson, Luke R.; Sanders, Jon G.; McDonald, Daniel; Amir, Amnon; Ladau, Joshua; Locey, Kenneth J.; Prill, Robert J.; Tripathi, Anupriya et al. (2017-11). “A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity” (英語). Nature 551 (7681): 457-463. doi:10.1038/nature24621. ISSN 1476-4687.
(50)^ Caporaso, J Gregory; Kuczynski, Justin; Stombaugh, Jesse; Bittinger, Kyle; Bushman, Frederic D; Costello, Elizabeth K; Fierer, Noah; Peña, Antonio Gonzalez et al. (2010-05). “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data” (英語). Nature Methods 7 (5): 335-336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303. ISSN 1548-7091.
(51)^ Fierer, Noah (2017-10). “Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 15 (10): 579-590. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2017.87. ISSN 1740-1526.
(52)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、114-121頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(53)^ Whitman, William B.; Coleman, David C.; Wiebe, William J. (1998-06-09). “Prokaryotes: The unseen majority” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95 (12): 6578-6583. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 9618454.
(54)^ 伊津野, 郡平﹁ハメリンプール湾における現生ストロマトライトの形態形成について﹂﹃地質ニュース1995年8月号﹄第492巻、1995年8月、41-54頁。
(55)^ 山本純之、磯﨑行雄﹁ストロマトライト研究の歴史と今後の展望﹂﹃地學雜誌﹄第122巻第5号、東京地学協会、2013年、791-806頁、doi:10.5026/jgeography.122.791、ISSN 0022-135X、NAID 130003385928。
(56)^ abNAGANUMA, Takeshi (2004). “Deep Subsurface Biosphere: a New Look of Geo-Biological Resources”. Shigen-to-Sozai 120 (1): 1-9. doi:10.2473/shigentosozai.120.1. ISSN 0916-1740.
(57)^ Ijiri, Akira (2020-01-15). “Significance of biogeochemical processes in mud volcanoes”. The Journal of the Geological Society of Japan 126 (1): 29-37. doi:10.5575/geosoc.2019.0044. ISSN 0016-7630.
(58)^ スティーヴン・ジェイ・グールド 著、渡辺政隆 訳﹃フルハウス 生命の全容﹄早川書房、1998年、250-257頁。︵原書 Gould, Stephen Jay (1996), Full House: The Spread of Excellence from Plato to Darwin, Harmony Books︶
(59)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、72-74頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(60)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Stephens, Brent (2018-11). “Microbiology of the built environment” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 16 (11): 661-670. doi:10.1038/s41579-018-0065-5. ISSN 1740-1526.
(61)^ Afshinnekoo, Ebrahim; Meydan, Cem; Chowdhury, Shanin; Jaroudi, Dyala; Boyer, Collin; Bernstein, Nick; Maritz, Julia M.; Reeves, Darryl et al. (2015-07-29). “Geospatial Resolution of Human and Bacterial Diversity with City-Scale Metagenomics” (英語). Cell Systems 1 (1): 72-87. doi:10.1016/j.cels.2015.01.001. ISSN 2405-4712.
(62)^ Filippis, Francesca De; Parente, Eugenio; Ercolini, Danilo (2017). “Metagenomics insights into food fermentations” (英語). Microbial Biotechnology 10 (1): 91-102. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12421. ISSN 1751-7915. PMC 5270737. PMID 27709807.
(63)^ abcCao, Yu; Fanning, Séamus; Proos, Sinéad; Jordan, Kieran; Srikumar, Shabarinath (2017-09-21). “A Review on the Applications of Next Generation Sequencing Technologies as Applied to Food-Related Microbiome Studies”. Frontiers in Microbiology 8: 1829. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01829. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 5627019. PMID 29033905.
(64)^ abcAmann, R I; Ludwig, W; Schleifer, K H (1995-03). “Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation.”. Microbiological Reviews 59 (1): 143-169. ISSN 0146-0749. PMC 239358. PMID 7535888.
(65)^ SAKUDA, SHOHEI (2002). Kagaku To Seibutsu 40 (9): 600-605. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600. ISSN 0453-073X. https://doi.org/10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600.
(66)^ 平山 和宏 (2014). “シリーズ 腸内細菌叢1腸内細菌叢の基礎”. モダンメディア 60.
(67)^ Woese, Carl R.; Fox, George E. (1977-11-01). “Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 74 (11): 5088-5090. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 432104. PMID 270744.
(68)^ Giovannoni, Stephen J.; Britschgi, Theresa B.; Moyer, Craig L.; Field, Katharine G. (1990-05). “Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton” (英語). Nature 345 (6270): 60-63. doi:10.1038/345060a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
(69)^ abYAMADA, Takuji (2013). “Human Gut Metagenomic Analysis toward Clinical Studies”. KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU 51 (12): 802-808. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu.51.802. ISSN 0453-073X.
(70)^ Gill, S. R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R. T.; Eckburg, P. B.; Turnbaugh, P. J.; Samuel, B. S.; Gordon, J. I.; Relman, D. A. et al. (2006-06-02). “Metagenomic Analysis of the Human Distal Gut Microbiome” (英語). Science 312 (5778): 1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 3027896. PMID 16741115.
(71)^ Zhernakova, Alexandra; Kurilshikov, Alexander; Bonder, Marc Jan; Tigchelaar, Ettje F.; Schirmer, Melanie; Vatanen, Tommi; Mujagic, Zlatan; Vila, Arnau Vich et al. (2016-04-29). “Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity” (英語). Science 352 (6285): 565-569. doi:10.1126/science.aad3369. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 5240844. PMID 27126040.
(72)^ Frank, J. A.; Pan, Y.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Eijsink, V. G. H.; McHardy, A. C.; Nederbragt, A. J.; Pope, P. B. (2016-05-09). “Improved metagenome assemblies and taxonomic binning using long-read circular consensus sequence data” (英語). Scientific Reports 6 (1): 25373. doi:10.1038/srep25373. ISSN 2045-2322.
(73)^ Tsai, Yu-Chih; Conlan, Sean; Deming, Clayton; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Segre, Julia A.; Kong, Heidi H.; Korlach, Jonas; Oh, Julia (2016-02-09). “Resolving the Complexity of Human Skin Metagenomes Using Single-Molecule Sequencing”. mBio 7 (1): e01948–01915. doi:10.1128/mBio.01948-15. ISSN 2150-7511. PMC 4752602. PMID 26861018.
(74)^ Liu, Yong-Xin; Qin, Yuan; Chen, Tong; Lu, Meiping; Qian, Xubo; Guo, Xiaoxuan; Bai, Yang (2021-05-01). “A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data” (英語). Protein & Cell 12 (5): 315–330. doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00724-8. ISSN 1674-8018.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
(36)^ Berlec, Aleš (2012-09-01). “Novel techniques and findings in the study of plant microbiota: Search for plant probiotics”. Plant Science 193-194: 96-102. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.05.010. PMID 22794922.
(37)^ Whipps, J.m.; Hand, P.; Pink, D.; Bending, G.d. (2008-12-01). “Phyllosphere microbiology with special reference to diversity and plant genotype” (英語). Journal of Applied Microbiology 105 (6): 1744-1755. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03906.x. ISSN 1365-2672. PMID 19120625.
(38)^ “Four hundred-million-year-old vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 (25): 11841-3. (1994). Bibcode: 1994PNAS...9111841R. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.25.11841. PMC 45331. PMID 11607500.
(39)^ “Common themes in nutrient acquisition by plant symbiotic microbes, described by the Gene Ontology”. BMC Microbiology 9(Suppl 1): S6. (2009). doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-S1-S6. PMC 2654666. PMID 19278554.
(40)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、131-134頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(41)^ Kloepper, J. W (1993). “Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biological control agents”. In Metting, F. B. Jr. Soil microbial ecology: applications in agricultural and environmental management. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. pp. 255-274. ISBN 978-0-8247-8737-0
(42)^ Bloemberg, G. V.; Lugtenberg, B. J. J. (2001). “Molecular basis of plant growth promotion and biocontrol by rhizobacteria”. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 4 (4): 343-350. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00183-7. PMID 11418345.
(43)^ “Use of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Biocontrol of Plant Diseases: Principles, Mechanisms of Action, and Future Prospects”. Appl Environ Microbiol 71 (9): 4951-9. (2005). doi:10.1128/AEM.71.9.4951-4959.2005. PMC 1214602. PMID 16151072.
(44)^ 百町満朗﹁生物防除研究の現状と展望﹂﹃日本植物病理學會報﹄第79巻第3号、日本植物病理學會、2013年8月、123-127頁、doi:10.3186/jjphytopath.79.123、ISSN 00319473、NAID 10031191400。
(45)^ abBar-On, Yinon M.; Phillips, Rob; Milo, Ron (2018-05-21). “The biomass distribution on Earth” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (25): 6506-6511. doi:10.1073/pnas.1711842115. ISSN 0027-8424.
(46)^ Blasiak, R.; Wynberg, R.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Thambisetty, S.; Bandarra, N. M.; Canário, A. V. M.; da Silva, J.; Duarte, C. M. et al. (2020-08). “The ocean genome and future prospects for conservation and equity” (英語). Nature Sustainability 3 (8): 588-596. doi:10.1038/s41893-020-0522-9. ISSN 2398-9629.
(47)^ abGilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2014-08-22). “The Earth Microbiome project: successes and aspirations”. BMC Biology 12 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s12915-014-0069-1. ISSN 1741-7007.
(48)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2018-06-26). “Earth Microbiome Project and Global Systems Biology” (英語). mSystems 3 (3). doi:10.1128/mSystems.00217-17. ISSN 2379-5077.
(49)^ Thompson, Luke R.; Sanders, Jon G.; McDonald, Daniel; Amir, Amnon; Ladau, Joshua; Locey, Kenneth J.; Prill, Robert J.; Tripathi, Anupriya et al. (2017-11). “A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity” (英語). Nature 551 (7681): 457-463. doi:10.1038/nature24621. ISSN 1476-4687.
(50)^ Caporaso, J Gregory; Kuczynski, Justin; Stombaugh, Jesse; Bittinger, Kyle; Bushman, Frederic D; Costello, Elizabeth K; Fierer, Noah; Peña, Antonio Gonzalez et al. (2010-05). “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data” (英語). Nature Methods 7 (5): 335-336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303. ISSN 1548-7091.
(51)^ Fierer, Noah (2017-10). “Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 15 (10): 579-590. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2017.87. ISSN 1740-1526.
(52)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、114-121頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(53)^ Whitman, William B.; Coleman, David C.; Wiebe, William J. (1998-06-09). “Prokaryotes: The unseen majority” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95 (12): 6578-6583. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 9618454.
(54)^ 伊津野, 郡平﹁ハメリンプール湾における現生ストロマトライトの形態形成について﹂﹃地質ニュース1995年8月号﹄第492巻、1995年8月、41-54頁。
(55)^ 山本純之、磯﨑行雄﹁ストロマトライト研究の歴史と今後の展望﹂﹃地學雜誌﹄第122巻第5号、東京地学協会、2013年、791-806頁、doi:10.5026/jgeography.122.791、ISSN 0022-135X、NAID 130003385928。
(56)^ abNAGANUMA, Takeshi (2004). “Deep Subsurface Biosphere: a New Look of Geo-Biological Resources”. Shigen-to-Sozai 120 (1): 1-9. doi:10.2473/shigentosozai.120.1. ISSN 0916-1740.
(57)^ Ijiri, Akira (2020-01-15). “Significance of biogeochemical processes in mud volcanoes”. The Journal of the Geological Society of Japan 126 (1): 29-37. doi:10.5575/geosoc.2019.0044. ISSN 0016-7630.
(58)^ スティーヴン・ジェイ・グールド 著、渡辺政隆 訳﹃フルハウス 生命の全容﹄早川書房、1998年、250-257頁。︵原書 Gould, Stephen Jay (1996), Full House: The Spread of Excellence from Plato to Darwin, Harmony Books︶
(59)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、72-74頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(60)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Stephens, Brent (2018-11). “Microbiology of the built environment” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 16 (11): 661-670. doi:10.1038/s41579-018-0065-5. ISSN 1740-1526.
(61)^ Afshinnekoo, Ebrahim; Meydan, Cem; Chowdhury, Shanin; Jaroudi, Dyala; Boyer, Collin; Bernstein, Nick; Maritz, Julia M.; Reeves, Darryl et al. (2015-07-29). “Geospatial Resolution of Human and Bacterial Diversity with City-Scale Metagenomics” (英語). Cell Systems 1 (1): 72-87. doi:10.1016/j.cels.2015.01.001. ISSN 2405-4712.
(62)^ Filippis, Francesca De; Parente, Eugenio; Ercolini, Danilo (2017). “Metagenomics insights into food fermentations” (英語). Microbial Biotechnology 10 (1): 91-102. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12421. ISSN 1751-7915. PMC 5270737. PMID 27709807.
(63)^ abcCao, Yu; Fanning, Séamus; Proos, Sinéad; Jordan, Kieran; Srikumar, Shabarinath (2017-09-21). “A Review on the Applications of Next Generation Sequencing Technologies as Applied to Food-Related Microbiome Studies”. Frontiers in Microbiology 8: 1829. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01829. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 5627019. PMID 29033905.
(64)^ abcAmann, R I; Ludwig, W; Schleifer, K H (1995-03). “Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation.”. Microbiological Reviews 59 (1): 143-169. ISSN 0146-0749. PMC 239358. PMID 7535888.
(65)^ SAKUDA, SHOHEI (2002). Kagaku To Seibutsu 40 (9): 600-605. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600. ISSN 0453-073X. https://doi.org/10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600.
(66)^ 平山 和宏 (2014). “シリーズ 腸内細菌叢1腸内細菌叢の基礎”. モダンメディア 60.
(67)^ Woese, Carl R.; Fox, George E. (1977-11-01). “Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 74 (11): 5088-5090. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 432104. PMID 270744.
(68)^ Giovannoni, Stephen J.; Britschgi, Theresa B.; Moyer, Craig L.; Field, Katharine G. (1990-05). “Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton” (英語). Nature 345 (6270): 60-63. doi:10.1038/345060a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
(69)^ abYAMADA, Takuji (2013). “Human Gut Metagenomic Analysis toward Clinical Studies”. KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU 51 (12): 802-808. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu.51.802. ISSN 0453-073X.
(70)^ Gill, S. R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R. T.; Eckburg, P. B.; Turnbaugh, P. J.; Samuel, B. S.; Gordon, J. I.; Relman, D. A. et al. (2006-06-02). “Metagenomic Analysis of the Human Distal Gut Microbiome” (英語). Science 312 (5778): 1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 3027896. PMID 16741115.
(71)^ Zhernakova, Alexandra; Kurilshikov, Alexander; Bonder, Marc Jan; Tigchelaar, Ettje F.; Schirmer, Melanie; Vatanen, Tommi; Mujagic, Zlatan; Vila, Arnau Vich et al. (2016-04-29). “Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity” (英語). Science 352 (6285): 565-569. doi:10.1126/science.aad3369. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 5240844. PMID 27126040.
(72)^ Frank, J. A.; Pan, Y.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Eijsink, V. G. H.; McHardy, A. C.; Nederbragt, A. J.; Pope, P. B. (2016-05-09). “Improved metagenome assemblies and taxonomic binning using long-read circular consensus sequence data” (英語). Scientific Reports 6 (1): 25373. doi:10.1038/srep25373. ISSN 2045-2322.
(73)^ Tsai, Yu-Chih; Conlan, Sean; Deming, Clayton; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Segre, Julia A.; Kong, Heidi H.; Korlach, Jonas; Oh, Julia (2016-02-09). “Resolving the Complexity of Human Skin Metagenomes Using Single-Molecule Sequencing”. mBio 7 (1): e01948–01915. doi:10.1128/mBio.01948-15. ISSN 2150-7511. PMC 4752602. PMID 26861018.
(74)^ Liu, Yong-Xin; Qin, Yuan; Chen, Tong; Lu, Meiping; Qian, Xubo; Guo, Xiaoxuan; Bai, Yang (2021-05-01). “A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data” (英語). Protein & Cell 12 (5): 315–330. doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00724-8. ISSN 1674-8018.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
(36)^ Berlec, Aleš (2012-09-01). “Novel techniques and findings in the study of plant microbiota: Search for plant probiotics”. Plant Science 193-194: 96-102. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.05.010. PMID 22794922.
(37)^ Whipps, J.m.; Hand, P.; Pink, D.; Bending, G.d. (2008-12-01). “Phyllosphere microbiology with special reference to diversity and plant genotype” (英語). Journal of Applied Microbiology 105 (6): 1744-1755. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03906.x. ISSN 1365-2672. PMID 19120625.
(38)^ “Four hundred-million-year-old vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 (25): 11841-3. (1994). Bibcode: 1994PNAS...9111841R. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.25.11841. PMC 45331. PMID 11607500.
(39)^ “Common themes in nutrient acquisition by plant symbiotic microbes, described by the Gene Ontology”. BMC Microbiology 9(Suppl 1): S6. (2009). doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-S1-S6. PMC 2654666. PMID 19278554.
(40)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、131-134頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(41)^ Kloepper, J. W (1993). “Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biological control agents”. In Metting, F. B. Jr. Soil microbial ecology: applications in agricultural and environmental management. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. pp. 255-274. ISBN 978-0-8247-8737-0
(42)^ Bloemberg, G. V.; Lugtenberg, B. J. J. (2001). “Molecular basis of plant growth promotion and biocontrol by rhizobacteria”. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 4 (4): 343-350. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00183-7. PMID 11418345.
(43)^ “Use of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Biocontrol of Plant Diseases: Principles, Mechanisms of Action, and Future Prospects”. Appl Environ Microbiol 71 (9): 4951-9. (2005). doi:10.1128/AEM.71.9.4951-4959.2005. PMC 1214602. PMID 16151072.
(44)^ 百町満朗﹁生物防除研究の現状と展望﹂﹃日本植物病理學會報﹄第79巻第3号、日本植物病理學會、2013年8月、123-127頁、doi:10.3186/jjphytopath.79.123、ISSN 00319473、NAID 10031191400。
(45)^ abBar-On, Yinon M.; Phillips, Rob; Milo, Ron (2018-05-21). “The biomass distribution on Earth” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (25): 6506-6511. doi:10.1073/pnas.1711842115. ISSN 0027-8424.
(46)^ Blasiak, R.; Wynberg, R.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Thambisetty, S.; Bandarra, N. M.; Canário, A. V. M.; da Silva, J.; Duarte, C. M. et al. (2020-08). “The ocean genome and future prospects for conservation and equity” (英語). Nature Sustainability 3 (8): 588-596. doi:10.1038/s41893-020-0522-9. ISSN 2398-9629.
(47)^ abGilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2014-08-22). “The Earth Microbiome project: successes and aspirations”. BMC Biology 12 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s12915-014-0069-1. ISSN 1741-7007.
(48)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2018-06-26). “Earth Microbiome Project and Global Systems Biology” (英語). mSystems 3 (3). doi:10.1128/mSystems.00217-17. ISSN 2379-5077.
(49)^ Thompson, Luke R.; Sanders, Jon G.; McDonald, Daniel; Amir, Amnon; Ladau, Joshua; Locey, Kenneth J.; Prill, Robert J.; Tripathi, Anupriya et al. (2017-11). “A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity” (英語). Nature 551 (7681): 457-463. doi:10.1038/nature24621. ISSN 1476-4687.
(50)^ Caporaso, J Gregory; Kuczynski, Justin; Stombaugh, Jesse; Bittinger, Kyle; Bushman, Frederic D; Costello, Elizabeth K; Fierer, Noah; Peña, Antonio Gonzalez et al. (2010-05). “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data” (英語). Nature Methods 7 (5): 335-336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303. ISSN 1548-7091.
(51)^ Fierer, Noah (2017-10). “Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 15 (10): 579-590. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2017.87. ISSN 1740-1526.
(52)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、114-121頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(53)^ Whitman, William B.; Coleman, David C.; Wiebe, William J. (1998-06-09). “Prokaryotes: The unseen majority” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95 (12): 6578-6583. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 9618454.
(54)^ 伊津野, 郡平﹁ハメリンプール湾における現生ストロマトライトの形態形成について﹂﹃地質ニュース1995年8月号﹄第492巻、1995年8月、41-54頁。
(55)^ 山本純之、磯﨑行雄﹁ストロマトライト研究の歴史と今後の展望﹂﹃地學雜誌﹄第122巻第5号、東京地学協会、2013年、791-806頁、doi:10.5026/jgeography.122.791、ISSN 0022-135X、NAID 130003385928。
(56)^ abNAGANUMA, Takeshi (2004). “Deep Subsurface Biosphere: a New Look of Geo-Biological Resources”. Shigen-to-Sozai 120 (1): 1-9. doi:10.2473/shigentosozai.120.1. ISSN 0916-1740.
(57)^ Ijiri, Akira (2020-01-15). “Significance of biogeochemical processes in mud volcanoes”. The Journal of the Geological Society of Japan 126 (1): 29-37. doi:10.5575/geosoc.2019.0044. ISSN 0016-7630.
(58)^ スティーヴン・ジェイ・グールド 著、渡辺政隆 訳﹃フルハウス 生命の全容﹄早川書房、1998年、250-257頁。︵原書 Gould, Stephen Jay (1996), Full House: The Spread of Excellence from Plato to Darwin, Harmony Books︶
(59)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、72-74頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(60)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Stephens, Brent (2018-11). “Microbiology of the built environment” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 16 (11): 661-670. doi:10.1038/s41579-018-0065-5. ISSN 1740-1526.
(61)^ Afshinnekoo, Ebrahim; Meydan, Cem; Chowdhury, Shanin; Jaroudi, Dyala; Boyer, Collin; Bernstein, Nick; Maritz, Julia M.; Reeves, Darryl et al. (2015-07-29). “Geospatial Resolution of Human and Bacterial Diversity with City-Scale Metagenomics” (英語). Cell Systems 1 (1): 72-87. doi:10.1016/j.cels.2015.01.001. ISSN 2405-4712.
(62)^ Filippis, Francesca De; Parente, Eugenio; Ercolini, Danilo (2017). “Metagenomics insights into food fermentations” (英語). Microbial Biotechnology 10 (1): 91-102. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12421. ISSN 1751-7915. PMC 5270737. PMID 27709807.
(63)^ abcCao, Yu; Fanning, Séamus; Proos, Sinéad; Jordan, Kieran; Srikumar, Shabarinath (2017-09-21). “A Review on the Applications of Next Generation Sequencing Technologies as Applied to Food-Related Microbiome Studies”. Frontiers in Microbiology 8: 1829. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01829. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 5627019. PMID 29033905.
(64)^ abcAmann, R I; Ludwig, W; Schleifer, K H (1995-03). “Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation.”. Microbiological Reviews 59 (1): 143-169. ISSN 0146-0749. PMC 239358. PMID 7535888.
(65)^ SAKUDA, SHOHEI (2002). Kagaku To Seibutsu 40 (9): 600-605. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600. ISSN 0453-073X. https://doi.org/10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600.
(66)^ 平山 和宏 (2014). “シリーズ 腸内細菌叢1腸内細菌叢の基礎”. モダンメディア 60.
(67)^ Woese, Carl R.; Fox, George E. (1977-11-01). “Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 74 (11): 5088-5090. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 432104. PMID 270744.
(68)^ Giovannoni, Stephen J.; Britschgi, Theresa B.; Moyer, Craig L.; Field, Katharine G. (1990-05). “Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton” (英語). Nature 345 (6270): 60-63. doi:10.1038/345060a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
(69)^ abYAMADA, Takuji (2013). “Human Gut Metagenomic Analysis toward Clinical Studies”. KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU 51 (12): 802-808. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu.51.802. ISSN 0453-073X.
(70)^ Gill, S. R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R. T.; Eckburg, P. B.; Turnbaugh, P. J.; Samuel, B. S.; Gordon, J. I.; Relman, D. A. et al. (2006-06-02). “Metagenomic Analysis of the Human Distal Gut Microbiome” (英語). Science 312 (5778): 1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 3027896. PMID 16741115.
(71)^ Zhernakova, Alexandra; Kurilshikov, Alexander; Bonder, Marc Jan; Tigchelaar, Ettje F.; Schirmer, Melanie; Vatanen, Tommi; Mujagic, Zlatan; Vila, Arnau Vich et al. (2016-04-29). “Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity” (英語). Science 352 (6285): 565-569. doi:10.1126/science.aad3369. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 5240844. PMID 27126040.
(72)^ Frank, J. A.; Pan, Y.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Eijsink, V. G. H.; McHardy, A. C.; Nederbragt, A. J.; Pope, P. B. (2016-05-09). “Improved metagenome assemblies and taxonomic binning using long-read circular consensus sequence data” (英語). Scientific Reports 6 (1): 25373. doi:10.1038/srep25373. ISSN 2045-2322.
(73)^ Tsai, Yu-Chih; Conlan, Sean; Deming, Clayton; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Segre, Julia A.; Kong, Heidi H.; Korlach, Jonas; Oh, Julia (2016-02-09). “Resolving the Complexity of Human Skin Metagenomes Using Single-Molecule Sequencing”. mBio 7 (1): e01948–01915. doi:10.1128/mBio.01948-15. ISSN 2150-7511. PMC 4752602. PMID 26861018.
(74)^ Liu, Yong-Xin; Qin, Yuan; Chen, Tong; Lu, Meiping; Qian, Xubo; Guo, Xiaoxuan; Bai, Yang (2021-05-01). “A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data” (英語). Protein & Cell 12 (5): 315–330. doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00724-8. ISSN 1674-8018.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
(36)^ Berlec, Aleš (2012-09-01). “Novel techniques and findings in the study of plant microbiota: Search for plant probiotics”. Plant Science 193-194: 96-102. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.05.010. PMID 22794922.
(37)^ Whipps, J.m.; Hand, P.; Pink, D.; Bending, G.d. (2008-12-01). “Phyllosphere microbiology with special reference to diversity and plant genotype” (英語). Journal of Applied Microbiology 105 (6): 1744-1755. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03906.x. ISSN 1365-2672. PMID 19120625.
(38)^ “Four hundred-million-year-old vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 (25): 11841-3. (1994). Bibcode: 1994PNAS...9111841R. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.25.11841. PMC 45331. PMID 11607500.
(39)^ “Common themes in nutrient acquisition by plant symbiotic microbes, described by the Gene Ontology”. BMC Microbiology 9(Suppl 1): S6. (2009). doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-S1-S6. PMC 2654666. PMID 19278554.
(40)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、131-134頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(41)^ Kloepper, J. W (1993). “Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biological control agents”. In Metting, F. B. Jr. Soil microbial ecology: applications in agricultural and environmental management. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. pp. 255-274. ISBN 978-0-8247-8737-0
(42)^ Bloemberg, G. V.; Lugtenberg, B. J. J. (2001). “Molecular basis of plant growth promotion and biocontrol by rhizobacteria”. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 4 (4): 343-350. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00183-7. PMID 11418345.
(43)^ “Use of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Biocontrol of Plant Diseases: Principles, Mechanisms of Action, and Future Prospects”. Appl Environ Microbiol 71 (9): 4951-9. (2005). doi:10.1128/AEM.71.9.4951-4959.2005. PMC 1214602. PMID 16151072.
(44)^ 百町満朗﹁生物防除研究の現状と展望﹂﹃日本植物病理學會報﹄第79巻第3号、日本植物病理學會、2013年8月、123-127頁、doi:10.3186/jjphytopath.79.123、ISSN 00319473、NAID 10031191400。
(45)^ abBar-On, Yinon M.; Phillips, Rob; Milo, Ron (2018-05-21). “The biomass distribution on Earth” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (25): 6506-6511. doi:10.1073/pnas.1711842115. ISSN 0027-8424.
(46)^ Blasiak, R.; Wynberg, R.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Thambisetty, S.; Bandarra, N. M.; Canário, A. V. M.; da Silva, J.; Duarte, C. M. et al. (2020-08). “The ocean genome and future prospects for conservation and equity” (英語). Nature Sustainability 3 (8): 588-596. doi:10.1038/s41893-020-0522-9. ISSN 2398-9629.
(47)^ abGilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2014-08-22). “The Earth Microbiome project: successes and aspirations”. BMC Biology 12 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s12915-014-0069-1. ISSN 1741-7007.
(48)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Jansson, Janet K.; Knight, Rob (2018-06-26). “Earth Microbiome Project and Global Systems Biology” (英語). mSystems 3 (3). doi:10.1128/mSystems.00217-17. ISSN 2379-5077.
(49)^ Thompson, Luke R.; Sanders, Jon G.; McDonald, Daniel; Amir, Amnon; Ladau, Joshua; Locey, Kenneth J.; Prill, Robert J.; Tripathi, Anupriya et al. (2017-11). “A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity” (英語). Nature 551 (7681): 457-463. doi:10.1038/nature24621. ISSN 1476-4687.
(50)^ Caporaso, J Gregory; Kuczynski, Justin; Stombaugh, Jesse; Bittinger, Kyle; Bushman, Frederic D; Costello, Elizabeth K; Fierer, Noah; Peña, Antonio Gonzalez et al. (2010-05). “QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data” (英語). Nature Methods 7 (5): 335-336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303. ISSN 1548-7091.
(51)^ Fierer, Noah (2017-10). “Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 15 (10): 579-590. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2017.87. ISSN 1740-1526.
(52)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、114-121頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(53)^ Whitman, William B.; Coleman, David C.; Wiebe, William J. (1998-06-09). “Prokaryotes: The unseen majority” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95 (12): 6578-6583. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.12.6578. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 9618454.
(54)^ 伊津野, 郡平﹁ハメリンプール湾における現生ストロマトライトの形態形成について﹂﹃地質ニュース1995年8月号﹄第492巻、1995年8月、41-54頁。
(55)^ 山本純之、磯﨑行雄﹁ストロマトライト研究の歴史と今後の展望﹂﹃地學雜誌﹄第122巻第5号、東京地学協会、2013年、791-806頁、doi:10.5026/jgeography.122.791、ISSN 0022-135X、NAID 130003385928。
(56)^ abNAGANUMA, Takeshi (2004). “Deep Subsurface Biosphere: a New Look of Geo-Biological Resources”. Shigen-to-Sozai 120 (1): 1-9. doi:10.2473/shigentosozai.120.1. ISSN 0916-1740.
(57)^ Ijiri, Akira (2020-01-15). “Significance of biogeochemical processes in mud volcanoes”. The Journal of the Geological Society of Japan 126 (1): 29-37. doi:10.5575/geosoc.2019.0044. ISSN 0016-7630.
(58)^ スティーヴン・ジェイ・グールド 著、渡辺政隆 訳﹃フルハウス 生命の全容﹄早川書房、1998年、250-257頁。︵原書 Gould, Stephen Jay (1996), Full House: The Spread of Excellence from Plato to Darwin, Harmony Books︶
(59)^ デヴィッド・W・ウォルフ 著、長野敬, 赤松眞紀 訳﹃地中生命の驚異 -秘められた自然誌﹄青土社、2016年、72-74頁。︵原書 Wolfe, David W. (2001), Tales From The Underground: A Natural History Of Subterranean Life︶
(60)^ Gilbert, Jack A.; Stephens, Brent (2018-11). “Microbiology of the built environment” (英語). Nature Reviews Microbiology 16 (11): 661-670. doi:10.1038/s41579-018-0065-5. ISSN 1740-1526.
(61)^ Afshinnekoo, Ebrahim; Meydan, Cem; Chowdhury, Shanin; Jaroudi, Dyala; Boyer, Collin; Bernstein, Nick; Maritz, Julia M.; Reeves, Darryl et al. (2015-07-29). “Geospatial Resolution of Human and Bacterial Diversity with City-Scale Metagenomics” (英語). Cell Systems 1 (1): 72-87. doi:10.1016/j.cels.2015.01.001. ISSN 2405-4712.
(62)^ Filippis, Francesca De; Parente, Eugenio; Ercolini, Danilo (2017). “Metagenomics insights into food fermentations” (英語). Microbial Biotechnology 10 (1): 91-102. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12421. ISSN 1751-7915. PMC 5270737. PMID 27709807.
(63)^ abcCao, Yu; Fanning, Séamus; Proos, Sinéad; Jordan, Kieran; Srikumar, Shabarinath (2017-09-21). “A Review on the Applications of Next Generation Sequencing Technologies as Applied to Food-Related Microbiome Studies”. Frontiers in Microbiology 8: 1829. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01829. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 5627019. PMID 29033905.
(64)^ abcAmann, R I; Ludwig, W; Schleifer, K H (1995-03). “Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation.”. Microbiological Reviews 59 (1): 143-169. ISSN 0146-0749. PMC 239358. PMID 7535888.
(65)^ SAKUDA, SHOHEI (2002). Kagaku To Seibutsu 40 (9): 600-605. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600. ISSN 0453-073X. https://doi.org/10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu1962.40.600.
(66)^ 平山 和宏 (2014). “シリーズ 腸内細菌叢1腸内細菌叢の基礎”. モダンメディア 60.
(67)^ Woese, Carl R.; Fox, George E. (1977-11-01). “Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms” (英語). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 74 (11): 5088-5090. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 432104. PMID 270744.
(68)^ Giovannoni, Stephen J.; Britschgi, Theresa B.; Moyer, Craig L.; Field, Katharine G. (1990-05). “Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton” (英語). Nature 345 (6270): 60-63. doi:10.1038/345060a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
(69)^ abYAMADA, Takuji (2013). “Human Gut Metagenomic Analysis toward Clinical Studies”. KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU 51 (12): 802-808. doi:10.1271/kagakutoseibutsu.51.802. ISSN 0453-073X.
(70)^ Gill, S. R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R. T.; Eckburg, P. B.; Turnbaugh, P. J.; Samuel, B. S.; Gordon, J. I.; Relman, D. A. et al. (2006-06-02). “Metagenomic Analysis of the Human Distal Gut Microbiome” (英語). Science 312 (5778): 1355-1359. doi:10.1126/science.1124234. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 3027896. PMID 16741115.
(71)^ Zhernakova, Alexandra; Kurilshikov, Alexander; Bonder, Marc Jan; Tigchelaar, Ettje F.; Schirmer, Melanie; Vatanen, Tommi; Mujagic, Zlatan; Vila, Arnau Vich et al. (2016-04-29). “Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity” (英語). Science 352 (6285): 565-569. doi:10.1126/science.aad3369. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 5240844. PMID 27126040.
(72)^ Frank, J. A.; Pan, Y.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Eijsink, V. G. H.; McHardy, A. C.; Nederbragt, A. J.; Pope, P. B. (2016-05-09). “Improved metagenome assemblies and taxonomic binning using long-read circular consensus sequence data” (英語). Scientific Reports 6 (1): 25373. doi:10.1038/srep25373. ISSN 2045-2322.
(73)^ Tsai, Yu-Chih; Conlan, Sean; Deming, Clayton; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Segre, Julia A.; Kong, Heidi H.; Korlach, Jonas; Oh, Julia (2016-02-09). “Resolving the Complexity of Human Skin Metagenomes Using Single-Molecule Sequencing”. mBio 7 (1): e01948–01915. doi:10.1128/mBio.01948-15. ISSN 2150-7511. PMC 4752602. PMID 26861018.
(74)^ Liu, Yong-Xin; Qin, Yuan; Chen, Tong; Lu, Meiping; Qian, Xubo; Guo, Xiaoxuan; Bai, Yang (2021-05-01). “A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data” (英語). Protein & Cell 12 (5): 315–330. doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00724-8. ISSN 1674-8018.
