真骨類
| 真骨類 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 様々な真骨類 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 分類 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 英名 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Teleost[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 下位分類群 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(本文参照)
|
真骨類︵しんこつるい︶は魚類の系統群。真骨魚類とも呼ばれる。分類階級は真骨亜区︵Teleostei︶。現生魚類の中の多数を占めるグループで、約40目と25,000以上の種を含む。体長7 mを超えるリュウグウノツカイ、体重2トンを超えるウシマンボウから、成熟しても全長6.2 mmにしかならないヒカリオニアンコウの雄まで、大きさは様々である。形態も多様で、速く泳ぐ流線型の魚、縦扁や側扁した魚、細長い円筒型の魚、タツノオトシゴのように特殊な魚などがある。
真骨類と他の硬骨魚類との違いは主に顎の骨にあり、可動性の前上顎骨とそれに付随する筋肉により、顎を突き出す事ができる。これにより、獲物を掴んで口に引き込む事が可能になる。より派生した分類群では上顎骨がレバーの役割を果たし、口を開閉する際に前上顎骨を動かす。また口の奥にある骨により、食べ物を磨り潰して飲み込むことが出来る。もう一つの違いは尾鰭にあり、尾鰭の上葉と下葉がほぼ等しく、脊椎は尾柄で終わり、尾鰭の上側に少しだけ伸びている。
殆どの種は体外受精を行い、子育てはしない。雌雄同体の種も多く、その中でも雌性先熟の種が多い。胎生の種や、親が卵を守る種も知られている。
人間にとっては経済的に重要であり、漁獲されて食用にされたり、スポーツフィッシングの対象になったりする。また養殖も盛んに行われている。水族館で飼育されたり、遺伝学や発生生物学の研究対象にもなる。

頭部骨格
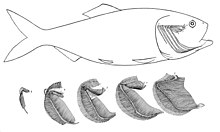
真骨類の際立った特徴として、可動性の上顎骨、尾鰭前部の細長い椎弓、非対称の鰓にある咽頭歯板がある[4]。前上顎骨は脳函と離れており、口を突き出して円形の開口部を作り出す。これにより口内の圧力が下がり、獲物が吸い込まれる。その後下顎と上顎を引いて口を閉じ、獲物を掴む。単に顎を閉じるだけでは食べ物が口から出てしまうため、より進化した分類群では、前上顎骨が肥大し、歯が存在している。対して上顎骨に歯は無い。上顎骨は前上顎骨と下顎を前方に押し出す役割がある。口を開く際は筋肉によって上顎上部が引かれ、下顎が前方に押し出される。また上顎骨が僅かに回転することで、骨突起が前上顎骨と噛み合って、前上顎骨が押し出される[5]。
咽頭顎は咽頭にある第2の顎で、鰓を支える5つの鰓弓から成る。前方3つの鰓弓は下鰓骨、角鰓骨、上鰓骨、咽鰓骨をそれぞれ2つずつ、基鰓骨を1つ含む。中央の基鰓骨は歯板で覆われる。4つ目の鰓弓は角鰓骨と上鰓骨2つずつから成り、咽鰓骨と基鰓骨を含む場合もある。下顎基部は5つ目の鰓弓から成り、上顎基部は2 - 4つ目の鰓弓から成る。より原始的な真骨類では、咽頭顎は脳函、肩帯、舌骨に付属しており、遊離した薄い部分となっている。その機能は食物の運搬のみで、多くは下顎の活動に頼る。より派生した分類群では、顎がより強力であり、左右の角鰓骨が融合している。咽鰓骨が融合して脳函と結合し、大きな上顎を形成している。また咽鰓骨が食物を運ぶだけでなく、粉砕することができるように、筋肉が発達している[6]。

尾鰭は対称的
尾は正形尾で、多くは尾軸下骨を持つ。脊椎は尾柄で終わり、古生代の魚類のように尾鰭上葉まで伸びたりはしない。椎弓は伸長し、上葉を支える部位を形成する[5]。椎骨の後端で尾骨が発達し、尾鰭を支えている[7]。
原始的な魚類と比べて、体の柔軟性が高く、より素早い。体骨格は完全に化骨し、その骨は軽量化されている。骨は石灰化しているが、全骨類のような緻密な海綿骨では無い。さらに下顎は歯骨、角骨、後関節骨から成る[8]。鱗は菱形の硬鱗ではなく軽量化された薄い円鱗となっている。
解剖学的特徴[編集]


進化と分類[編集]
分類[編集]
真骨類は1845年、ドイツの魚類学者であるヨハネス・ペーター・ミュラーによって独自の分類群として位置づけられた[9]。その名の由来はギリシア語の﹁Teleios (完全な) ﹂+ ﹁osteon (骨)﹂である[10]。ミュラーは特定の軟組織に基づき真骨類を定義したが、化石分類群の特徴は考慮していなかった。1966年、Greenwoodらにより新たに定義され、より確実な分類が行われた[9][11]。真骨類のステムグループであるteleosteomorphsの最古の化石は三畳紀に遡り、Prohalecites やフォリドフォルスが知られている[12][13]。しかし、真骨類は古生代には既に生まれていた可能性がある[14]。中生代と新生代の間に多様化し、現存する魚類の96 %を占めるまでになった[15]。 以下の系統樹は、真骨類とその他硬骨魚類の系統を示しており[14]、デボン紀に分化した四肢動物についても示してある[16][17]。分化年代についてはNear et al. (2012)を参考[14]。| Euteleostomi/ |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 硬骨魚類 |
下位分類[編集]
真骨類の内部分類は、DNAをベースとした系統分析が導入されるまで、長い間議論の対象となっていた。Near et al. (2012) は232種の非連鎖遺伝子のDNA配列を解析し、全ての主要な系統発生と、その分岐時期を調査した。彼らは化石記録から得られた信頼出来る36個の測定値に基づき、実際の分岐年代の値を設定した[14]。真骨類は以下に示す分岐群に分けられる[18]。分岐年代はNear et al. (2012) による[14]。より最新の研究では、真骨類の中でもアロワナ上目とカライワシ下区は他の分類群と離れているという[19][20]。
| Teleostei |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 310 mya |
現在、最も多様な硬骨魚類のグループはスズキ系で、マグロ、タツノオトシゴ、ハゼ、シクリッド、カレイ、ベラ、スズキ、アンコウ、フグなどが含まれる[21]。特にスズキ系は新生代に繁栄した。化石記録から、白亜紀と古第三紀の間の大量絶滅の直後に、真骨類の大きさや数が大幅に増加したことが分かっている[22]。

デボン紀から現在までの条鰭類の進化。Benton, M. J. (2005)による。

中期ジュラ紀に出現した原始的な真骨類、アスピドリンクスの化石
初期の真骨類は前期三畳紀に出現し、前期白亜紀までの1億5000万年間で、様々な形質を獲得した[23]。
現生魚類の中でも原始的な分類群は、カライワシ下区とアロワナ上目である。カライワシ下区(上目)には800種が分類されており、幼生はレプトケファルスと呼ばれ、薄く葉のような形をしている。ウナギは体が細長く、骨盤帯と肋骨を欠き、上顎の骨は融合している。アロワナ上目には200種が含まれ、舌骨とその後方にある基鰓骨に歯がある。ニシン・骨鰾下区はニシン目と骨鰾上目から成る。ニシン目は350種が分類されており、腹部の稜鱗と下尾骨が特徴で、鰾には聴覚の役割がある。骨鰾系にはほとんどの淡水魚が含まれ、独自の聴覚を持った種もいる[5]。一つはウェーバー器官で、音波を内耳に届けている。また怪我をした場合、警戒物質を水中に分泌する[24]。
真骨類の大部分は正真骨類に分類され、頭と背鰭の間にある上神経棘の発生、尾の神経弓付近の骨の成長、尾の中央の軟骨が尾鰭基部の下尾軸骨の間に位置するといった特徴がある。さらに正真骨類の大部分は新真骨類に分類され、新真骨類は咽頭の顎を制御する筋肉が特徴であり、食物を粉砕する役割がある。その中でも棘鰭上目は、棘条から成る背鰭を持つ[25]。背鰭は移動時の推進力を生み[26]、防御の役割も果たす可能性がある。Acanthomorpha は円鱗でなく櫛鱗を持ち、歯のある前上顎骨を発達させ、より高速で泳ぐための形態となっている[5]。
脂鰭を持つ種は6,000種を超えるが、その系統の中で一度進化し、機能が限られているために何度も失われたと考えられていた。 2014年の研究はこの考えに疑問を呈し、脂鰭が収斂進化の一例であることを示唆した。カラシン目では脂鰭は幼魚の鰭のひだの縮小後に発達するが、サケ目では脂鰭はひだの残骸である[27]。

肉食魚のピラニアには、肉を切り裂く鋭い歯がある。
約40目、448科に26,000種以上が存在し[28]、現存する全魚種の96%を占めている[15]。26,000種のうち約12,000種が淡水に生息する[29]。ほぼすべての水生環境に生息しており、肉食、草食、濾過摂食、寄生など様々な摂食方法がある[30]。最長の現生種はリュウグウノツカイで、体長は7.6 m以上と報告されているが[31]、絶滅種を含めればリードシクティスは体長27.6 mと推定されている[32]。最も重い種はウシマンボウであり、2003年に水揚げされた標本の推定体重は2.3トンであった[33]。ヒカリオニアンコウの雄は体長わずか6.2 mmだが、雌の体長は50 mmで、はるかに大きい[31]。Schindleria brevipinguis は最も小さく、世界最小の脊椎動物とも言われる。雌の体長は8.4 mm、雄の体長はわずか7 mmである[34]。

1996年に捕獲されたリュウグウノツカイ
外洋の魚は通常、水中を移動する際の抵抗を最小限に抑えるために、魚雷のように流線形の体をしている。サンゴ礁に生息する魚は、複雑で比較的限られた水中環境に生息しており、スピードよりも動作性を優先させており、その多くはダートや方向転換の能力を最適化した体になっている。多くは側扁した体を持ち、亀裂に収まり、狭い隙間を泳ぐことができる。胸鰭を移動に使用する種もあれば、背鰭と尻鰭を波打たせて泳ぐ種もある[35]。カモフラージュのために皮膚の付属器官を発達させた種もいる。ヒゲハギは海藻に擬態し、オオウルマカサゴは海底に潜んで獲物を待ち伏せする。スギアヤチョウチョウウオのように、天敵を驚かせたり騙したりするための眼状紋を持つ種や、ミノカサゴなど毒棘を警告する模様を持つ種もいる[36]。
カレイ目は縦扁した体を持ち、仔魚は左右対称だが、成長の過程で変態が起こり、片方の目が頭の反対側に移動し、同時に横向きに泳ぎ始める。この形態には海底に横たわっているときに両目が上にあり、広い視野が得られるという利点がある。背面は擬態のために斑点があり、腹面は淡い色である[37]。
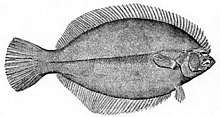
Pseudopleuronectes americanus など のカレイの仲間は左右非対称で、両目が同じ面にある。

コバンザメは頭の吸盤のような器官で他の生物に付着する。
寄生性の種もおり、コバンザメは額の大きな吸盤で、クジラ、ウミガメ、サメ、エイなどの大型動物に付着している。この場合コバンザメは宿主の寄生虫や皮膚を捕食しているため、コバンザメと宿主の両方が利益を得ており、寄生というよりは相利共生である[38]。カンディルは魚の鰓に潜り込み、血液や組織を食べる[39]。コンゴウアナゴは通常腐肉を食べるが、魚の肉に穴を開けることもあり、アオザメの心臓の内部で発見されたこともある[40]。

ジムナーカスは弱い電波を発生させ、濁った水の中でも獲物を見つける。
デンキウナギなどの一部の種は、強力な電流を流して獲物を気絶させる。ジムナーカスなどの他の魚は、弱い電場を生成して獲物を感知する。彼らは電場の歪みを避けるために背鰭を伸ばして泳ぐ。これらの電流は筋肉細胞または神経細胞が発達した細胞によって生成される[24]。

デザートパプフィッシュは砂漠の中の水たまりに生息する。
主要なグループのうち、カライワシ上目、ニシン上目、およびスズキ系はすべて世界中に分布しており、主に海産である。骨鰾上目とアロワナ上目は世界中に分布しているが、主に淡水に生息し、後者は主に熱帯に分布する。トウゴロウイワシ目やカダヤシ目、ダツ目は世界中の海水と淡水に分布し、主に表層に生息する。カワカマス目は北半球の淡水に、サケ目は全球の温帯の淡水で見られ、一部の種は海に出入りする。側棘鰭上目は北半球の淡水と海水に分布する[42]。
渡りをする種もおり、特定の淡水種は毎年河川内を移動する。サケなどの遡河魚は一生を海で過ごし、産卵のために内陸に移動する。ウナギなどはその逆である[44]。ヨーロッパウナギは、成体になると大西洋を渡ってサルガッソ海の浮遊海藻で繁殖する。成魚はここで産卵して死に、仔魚は成長しながらメキシコ湾流に乗ってヨーロッパに向かって流される。到着した稚魚は河口に入って川を遡上し、途中にある障害物を乗り越えて小川や池にたどり着き、そこで成魚になって一生を過ごす[45]。
ブラウントラウトやScaly osmanなどは、標高3,819 mもの高さにあるカシミールの山地の湖でも見られる[46]。またシンカイクサウオは水深7,700 mで見られ、近縁種が水深8,145 mで見られている[47][48]。
鰓
他のほとんどの魚類と同様、真骨類の主な呼吸手段は、水を口から吸い込み、鰓から送り出すときに、鰓の表面で空気を移動させることである。少量の空気を含む鰾を除けば、体には酸素の貯蔵量が無く、生涯にわたって呼吸を続ける必要がある。一部の真骨類は、停滞した水や湿った泥など、酸素の少ない場所に生息する。それらの種は呼吸のための特殊な器官を発達させている[49]。
いくつかの属は独自に空気呼吸能力を発達させており、水陸両用の種もいる。イソギンポ科の一部は餌を食べるために陸上に上がり、ウナギは湿った皮膚から酸素を吸収できる。トビハゼ類は長い間陸に留まることができ、口や咽頭の皮膚や粘膜を通してガス交換を行う。タウナギ科も同様に口の粘膜に血管が発達しており、何日も泥の中で休息状態に入ることができる[50]。キノボリウオ亜目は上鰓器官という呼吸補助器官が発達しており、これを用いて空気中の酸素を取り入れることができる。ヒレナマズ科も同様に上鰓器官を用いて空気呼吸を行う。ロリカリア科などは、消化管に溜めた空気を用いて呼吸することができる[51]。

イトヨの感覚器官
真骨類は高度に発達した感覚器官をもつ。ほとんどの昼行性種は、少なくとも人間と同程度の色覚を持っている。また多くの種が味覚と嗅覚を司る化学受容体も持っている。さらに側線により流れや振動を感知し、近くの魚や獲物の動きを知ることができる[52]。側線、鰾、および一部の種ではウェーバー器官を使用して、様々な方法で音を感知する。周りの風景から自分自身の位置を特定し、複数の風景に基づいて自分の中で地図を作ることができる。迷路を使った実験では、それに必要な空間記憶能力を持っていることが示された[53]。

アメリカウナギは海で産卵する
真骨類の皮膚はほとんど水を通さず、体とその周囲の主な境界面は鰓である。浸透によって淡水では水が鰓に流入し、海水では水が流出する。同様に、塩分は淡水では鰓から拡散し、海水では鰓から流入する。ヨーロッパヌマガレイは海水魚だが、河口や川に移動することもある。海中では1時間で、遊離ナトリウム総量の40%に相当するナトリウムイオンを獲得できる。このうち75%は鰓から入り、残りは水を飲むことで摂取している。対照的に川では、1時間あたり体内のナトリウムイオンの2%が交換されるのみである。交換される塩分と水分を制限するだけでなく、海水中では塩分を除去し、淡水中では体に取り込むための活発なメカニズムが鰓全体に存在している[54]。

鰾
真骨類の体は水よりも密度が高いため、その差を補わなければ沈んでしまう。軟質亜綱、全骨類、真骨類に共通する特徴は鰾である[62][63]。元々は真骨類の共通祖先に存在していたが、その後鰾を持たない種がいる425科のうち、少なくとも79科で少なくとも30 - 32回独立して失われている。マグロやサバなど、泳ぎの速い魚にはこの欠如がよく見られる[64]。鰾は魚が気体を操作して浮力を調整するのに役立ち、これにより魚は泳ぐ際にエネルギーを無駄にすることなく、現在の水深に留まったり、上昇または下降したりすることができる。鰾内の気体は奇網によって調節され、原始的な分類群では気道のある有気管鰾、それ以外は気道の無い無気管鰾である[65]。

トビウオは大きな胸鰭を広げ、尾をくねらせて空中を滑空する。
典型的に素早く泳ぐための流線型の体をしており、移動運動は通常、胴体の最後部と尾部の横方向のうねりによって行われ、水中で体を推進させる[66]。この移動方法には多くの例外があり、素早く動く必要がない場合は移動方法が異なる。岩の間やサンゴ礁では、優れた操作性でゆっくりと泳ぐことが必要とされる[67]。ウナギは体全体をくねらせて移動する。海草や藻類の中に生息するタツノオトシゴは直立姿勢をとって胸鰭を羽ばたかせて移動し、近縁のヨウジウオは細長い背鰭を波立たせて移動する。ハゼは、胸びれで体を支えて推進しながら、底を飛び跳ねるように移動する[68]。トビハゼは地上でもほぼ同じように動く[69]。一部の種では腹鰭の吸盤を用いており、Hawaiian freshwater gobyは滝を登る[68]。ホウボウの胸鰭には感覚機能を持つ3対の遊離軟条があり、底に沿って歩く[70]。トビウオは空中に飛び上がり、大きな胸鰭で数百m滑空することができる[71]。
サケは生涯に一度産卵し、そのあとすぐに死んでしまう。
ほとんどの真骨類は卵生であり、卵と精子の両方が受精のために水中に放出される体外受精を行う。500 - 600 種が体内受精を行うことが知られているが、軟骨魚類や多くの四肢動物ではより典型的である。体内受精を行うには、雄が生殖器を用いて雌に受精する必要がある[75]。受精卵のうち、成魚になるまで生き残るのは 100万個に1個未満であるが、胎生の種ではより生存率が高い。これらの種では卵子が雌の体内で受精し、ある程度成長するためである。カダヤシ目などには卵胎生の種もいる。卵には発育中の胚に栄養を与える卵黄嚢があり、これが使い果たされると、卵が孵化し、仔魚が水中に放たれる。グーデア科には真胎生の種もおり、発育中の胚は子宮内の胎盤のような構造を介して母親から栄養の供給を受ける。Nomorhamphus ebrardtiiなどは未受精卵を子宮内で食べて成長するが、一部のサヨリでは子宮内で共食いすることが報告されている[76]。
ほとんどの真骨類は生涯に複数回繁殖を行うが[77]、タイヘイヨウサケ属や一部のウナギ、キュウリウオ科魚類は一度繁殖すると死んでしまう。サケは淡水で生まれて海に降り、数年後に生まれた川に戻って産卵し、そこで死ぬ[78]。

クマノミ類は雌雄同体で、雌が死ぬと雄が新たな雌になる。
真骨類の88%は雌雄異体であり、生涯を通じて雄雌のどちらか一方を維持する。個体の性別は鳥類や哺乳類のように遺伝的に決定されることもあれば、爬虫類のように環境的に決定されることもある。一部の真骨類では、遺伝と環境の両方が性別の決定に役割を果たす[79]。遺伝によって性決定される種の場合、3つの形態に分けられる。まずは単一遺伝子座が性別を決定する場合がある。さらにXY型とZW型が存在する。サザンプラティフィッシュなどの一部の種は両方のシステムを備えており、個体群に応じてXYまたはZWを使用する[80]。
XY型とZW型の両方が関与するシステムは新熱帯区の種に多く、性染色体と常染色体の再構成が含まれる。たとえば、Apareiodon affinisの雌はZW1W2によって決定され、雄はZZによって決定される。Hoplias malabaricusの雌はX1X1X2X2によって決定され、雄はX1X2Yによって決定される[81]。ゼブラフィッシュなどは性別を決定する遺伝子が複数ある[82]。環境依存性の性決定は、少なくとも70種で記録されている。温度が主な要因だが、pH、成長速度、密度、社会環境も影響する可能性がある。Atlantic silversideでは、冷たい水域では雌が多く生まれ、暖かい水域では雄が多く生まれる[83]。

雌に求愛するChlamydogobius eremiusの雄
いくつかの繁殖形態があり、無差別型は雄と雌の両方が複数のパートナーと繁殖し、明らかな配偶者の選択が無い。グッピー、タイセイヨウニシンのバルト海亜種、ナッソーハタ、ヨスジリュウキュウスズメダイ、シクリッド、クレオールラスで記録されている。一妻多夫型では、1匹の雌と複数の雄が繁殖する。この形態をとる種は多くは無いが、クマノミ類やアンコウ目魚類に知られている。 一夫多妻型がはるかに多く、雄の縄張りを複数の雌が訪れるタイプは、サンフィッシュ科、カジカ上科、パーチ科の一部、スズメダイ科、シクリッドで記録されている。複数の雌の縄張りを雄が守るタイプは、スズメダイ、ベラ、ブダイ、ニザダイ科、モンガラカワハギ、アマダイなどのサンゴ礁の種に多い[77]。
カワスズメ科のCyrtocara eucinostomusなどは、雄が集まって雌にアピールする、レックに似た繁殖システムが記録されている。雄と雌がつがいを作り、パートナーとのみ繁殖する一夫一妻型は、北米の淡水ナマズ、多くのチョウチョウウオ、タツノオトシゴなどが行う[77]。求愛は、種の認識、つがいの結合の強化、産卵場所の位置決定、配偶子の放出の同期などの役割を果たす。体色の変化、音の発生、鰭の動きや泳ぎ方などが含まれ、これらは大抵雄によって行われる。雄が強い縄張り意識を持つ場合、雌が求愛することもある[88]。

カンムリブダイは雄(上側)の頭が突出する
性的二型はいくつかの種に存在する。通常雄の形態が繁殖に有利な方向に変化する。シイラでは、オスの頭はメスよりも大きくて鈍い。一部の淡水魚は雄の顔に追星という突起が現れる[89]。カンムリブダイの雄は頭が隆起し、儀式的な頭突きを行う[90]。体色が変化する場合は通常雄が派手で、卵生メダカ、レインボーフィッシュ、ベラは恒常的だが、コイ目、トゲウオ、パーチ科の一部、サンフィッシュなどは繁殖期に婚姻色として変化する。派手な体色は目立つので捕食の危険性があるが、それよりも繁殖の成功率を優先させている[89]。
雌にうまく求愛できなかった雄は別の戦略をとる。ブルーギルなどのサンフィッシュ科では、雌に求愛することに成功した大きくて年をとった雄が、受精させた卵のために巣を作る。小さな雄は雌の行動や体色を模倣して巣に近づき、卵を受精させる。スニーカー雄として知られる他のオスは近くに潜んでいて、素早く巣に近づいて受精させる。これらの雄は求愛に成功した雄より小さい。スニーカー雄はタイヘイヨウサケ属にも存在し、優勢な大型の雄が雌と産卵している間に、雌の近くに小さな雄が突進して繁殖する[91]。

腹の赤いイトヨの雄は巣を作って雌を呼び、産卵後は卵を守る。187 9年、アレクサンダー・フランシス・ライドン作
真骨類は水中、一般的には底質に産卵する。水中に放出するものはサンゴ礁に生息することがほとんどである。水面に向かって突進し、配偶子を放出する。これにより、卵が一部の捕食者から保護され、海流に乗って広範囲に分散できると考えられる。その方式の場合、親の世話を受けない。さらに、群れで孵化することが多い。底質に産卵する場合は通常岩や巣穴に産み付けられる。植物、木材、貝殻などの表面に付着することもある[92]。

卵を育児嚢に抱えたタツノオトシゴの雄
卵生の真骨類のうち、79%は親の世話を受けない[93]。世話をする場合は一般的に雄が行う[93][94]。進化の過程で雄の縄張り意識が卵の世話に繋がった可能性がある[95][96]。ディスカスは雌が子育てをし、発育中の仔魚に粘液の形で栄養を与える[97]。一部の種では、卵や仔魚が体に付着しているか、体内で育つ。ハマギギ科、テンジクダイ科、アゴアマダイ科などでは口内保育を行い、口の中で卵を守る。一部のアフリカンシクリッドでは、卵がそこで受精する場合がある。Bujurquina vittata では、仔魚は孵化した後に保護され、両親が行なう場合がある。仔魚が放たれるタイミングは種によって異なり、孵化したばかりの子を放す者もいれば、幼魚になるまで保護する者もいる。口内保育のほかにも保護の形態は知られており、コモリウオは頭部のフックに卵を掛け、孵化するまで保護する。タツノオトシゴの場合、雄は育児嚢を持っており、雌はそこに受精卵を産み、稚魚になるまでそこに留まる。アスプレド科の雌は腹部に卵が付着する構造物を持つ[98]。
一部の種では成長した仔が親の子育てを手伝うヘルパーとなる。この行動はタンガニーカ湖の約19種のシクリッドで発生する。これらのヘルパーは、卵や仔魚の掃除、巣の掃除、縄張りの保護などに参加する。成長率は低下するが、捕食者からの保護が得られる。托卵を行う種もおり、ミノーはサンフィッシュ科や他のミノーの種の巣に卵を産む。カッコウナマズは、口内保育を行うシクリッドに托卵することで卵を守ってもらう。一部の種は共食いを行い、飢餓に対して進化した可能性がある[99]。
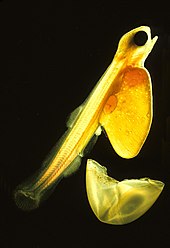
卵黄嚢を持つ孵化したばかりのタイセイヨウサケ
卵、仔魚、稚魚、成魚という4つの主要な生活段階がある。多くは遠洋または海底付近で生活を始める。ほとんどの仔魚は軽くて透明で浮力があり、薄い膜を持った遠洋性の卵から孵化する。遠洋性の卵は海流に頼って分散し、親の世話を受けない。孵化した仔魚は浮遊性で泳ぐことができない。卵黄嚢が付いており、そこから栄養が供給される。ほとんどの淡水種は、厚く、色素があり、比較的重く、底質に付着する底生卵を産む。淡水魚では親の世話が一般的である。遠洋性の仔魚とは異なり、底生の仔魚は孵化するとすぐに泳いで摂食することができる[84]。海洋種に多いが、仔魚は成魚と見た目が大きく異なり、別種と判断されることもあった。仔魚の死亡率は高く、ほとんどは生後1週間以内に飢餓または捕食により死亡する。成長につれて生存率が上昇し、生理学的耐性と感受性、生態学的および行動的能力が高まる[100]。
稚魚は形態的に成魚に似ており、基本的な骨格、内臓、鱗、色素沈着、鰭が完全に発達する。仔魚から稚魚への移行は、一部のスズメダイのように数分または数時間で終わる、短く非常に単純な場合もあるが、サケ科、イットウダイ科、ハゼ、カレイ目などでは、移行はより複雑で、完了までに数週間かかる[101]。成魚は生殖のために配偶子を生み出すことができる。多くの魚と同様、生涯を通じて成長し続ける。寿命は種によって異なり、ヨーロピアンパーチやオオクチバスなどのゲームフィッシュは最長25年生きる。メバル科には100年以上生きる種もいる[102]。

カタクチイワシ科の群れとカスミアジの群れ
多くの真骨類は群れを形成し、その目的は多様である。時には捕食者に対する適応となり、捕食者に対する警戒心を強化する。多くの場合、群れで食物を集める方が効率的であり、個々の魚は群れに参加するか群れから離れるかを選択することで戦略を最適化する。捕食者に気づくと防御反応を示し、群れの集団行動が発生する。隠れたり逃げたりしようとするだけではなく、分散と再集合を行い、産卵のために群れを作る種もいる[103]。

スコットランド沿岸での養殖
世界中で食用として捕獲されている。ニシン、タラ、ポラック属、カタクチイワシ、マグロ、サバなどの少数の種は年間数百万トンが食用にされるが、他の多くの種は漁獲量が少ない[104]。漁獲量の少ない種にはゲームフィッシュとされるものもいる[105]。商業漁業と娯楽漁業を合わせて、何百万人もの人々に雇用がもたらされている[106]。
コイ、サケ[107]、ティラピア、ナマズなどの少数の生産性の高い種が商業的に養殖されており、年間何百万トンものタンパク質が豊富な食料を生産している。国連食糧農業機関は、生産量が急激に増加し、2030年までにおそらく食用魚の62パーセントが養殖されると予想している[108]。
魚は新鮮に消費されるか、乾燥、燻製、塩漬け、発酵などの伝統的な方法で保存される[109]。現代の保存方法には、冷凍、凍結乾燥、および加熱処理︵缶詰など︶が含まれる。冷凍魚製品には、パン粉や衣をまぶした切り身、フィッシュフィンガー、フィッシュケーキなどが含まれる。魚粉は養殖魚や家畜の栄養補助食品として使用される。魚油は特にビタミンAとDが豊富な魚の肝臓、またはイワシやニシンなどの脂肪の多い魚の体から作られ、栄養補助食品として、またビタミン欠乏症の治療に使用される。
小さくカラフルな種は観賞魚として飼育されることもある。オオカミウオ科は皮革産業に使用される。アイシングラスは真骨類からも作られる[105]。
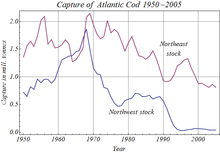
タイセイヨウダラの漁獲量
人間の活動は、乱獲[110]、汚染、地球温暖化などを通じて、多くの種類の真骨類の資源に影響を与えている。記録されている多くの事例の中でも、乱獲により1992年にニューファンドランド島沖のタイセイヨウダラの個体数が完全に激減し、カナダの漁業が無期限に中止されたことが挙げられる[111]。特に河川や海岸沿いでは、下水、殺虫剤、除草剤が水中に流入し、悪影響を及ぼしている。重金属、有機塩素、カルバミン酸塩などの多くの汚染物質は、内分泌系を混乱させることによって繁殖を妨げる。ローチでは、川の汚染により内分泌かく乱が起こっている。内分泌かく乱は人間にも影響を与えるため、真骨類が水中にそのような化学物質が存在することを示すために使用される。20世紀後半、水質汚染により北ヨーロッパの多くの湖で真骨類の個体群が局地的に絶滅した[112]。
真骨類に対する気候変動の影響は強力である可能性があるが、その関係性は複雑である。例えば冬の降水量の増加はノルウェーの淡水魚の個体数に悪影響を与える可能性があるが、夏の暖かさは成魚の成長を増加させる可能性がある[113]。海洋では、真骨類は温暖化に対処する可能性があるが、それは気候の自然変動の延長にすぎない[114]。二酸化炭素濃度の上昇によって引き起こされる海洋酸性化が真骨類にどのような影響を与えるのかは不明である[115]。

研究用に飼育されるゼブラフィッシュ
いくつかの種は人間にとって危険であり、ゴンズイ科、フサカサゴ科、オニオコゼ科などの一部の魚は、人間に重傷を負わせたり、死に至る可能性のある有毒な棘を持つ。デンキウナギやデンキナマズは、重度の感電を引き起こす可能性がある。ピラニアやカマスなどは強力な歯と顎を持ち、時には人間を襲うこともある[105]。報告によると、ナマズ目の一部の種は人間を捕食するのに十分な大きさになる可能性がある。
メダカとゼブラフィッシュは、遺伝学や発生生物学の研究においてモデル生物として使用される。ゼブラフィッシュは、最も一般的に使用される実験用脊椎動物であり[105]、哺乳類との遺伝的類似性、小さな体、必要な環境の簡単さ、非侵襲的イメージングを可能にする透明な仔魚、豊富な子孫、急速な成長、水中に追加された変異原を吸収する能力という利点がある[116]。

進化の傾向[編集]

多様性[編集]





分布[編集]
世界中で見られ、暖かい海と冷たい海、流水域と止水域、砂漠の中の孤立した、高温で塩分を含んだ水域を含むほとんどの水生環境に生息している[41][42]。種の多様性は、極高緯度では低い。例えば北緯82度までのゼムリャフランツァヨシファでは、年間の大部分の時期で氷に覆われ、水温が 0 °C未満であるため、種の数が制限される。そこで見つかった種の75 %は北極の固有種である[43]。
生理学[編集]
呼吸[編集]

感覚器[編集]

浸透圧調節[編集]

体温調節[編集]
真骨類は冷血動物であり、一般的に体温は周囲の温度と同じである。皮膚を通して熱を調節し、水温の変化に応じて鰓への血流を増減させることで循環を調節する。筋肉や腸で生成された代謝熱は鰓から放散され、寒さにさらされると血液は鰓から遠ざかる[55]。血液温度を操作する能力が低いため、ほとんどの真骨類は狭い範囲の水温にしか適応できない[56]。 冷水域に生息する種は、温水域の種と比較して脳細胞膜中の不飽和脂肪酸の割合が高く、そのため生息環境において適切な膜流動性を維持することができる[57]。 寒さに順応すると、真骨類はミトコンドリア密度や毛細血管密度の増加など、骨格筋に生理学的変化を示す[58]。これにより好気性ATPの生成が促進され、温度の低下による代謝率の低下を防ぐことができる。 マグロなどの速く泳ぐ外洋魚は、効率的に移動するために筋肉を環境よりも高い温度に維持している[59]。マグロは、筋肉によって生成され静脈血中に存在する代謝熱が動脈血を事前に温めるシステムを備えているため、筋肉の温度は周囲よりも11° C以上高い。さらにマグロは速度を高めるため、流線型の紡錘形の体、水の抵抗が少ない鰭[59]、より効率的に酸素を利用できるようにミオグロビン含有量が増加した筋肉などを持つ。これにより筋肉は赤みがかった色になり、より効率的に酸素を利用できるようになる[60]。水温の低い極地や深海では、メカジキ、カジキ、マグロなどの一部の大型魚は、脳と目の温度を上昇させる発熱機構を備えている。そのため、体温の低い獲物よりもはるかに優れた視力を得ている[61]。浮力[編集]

移動[編集]

発音[編集]
コミュニケーションのために音を出す能力は、いくつかの系統で独自に進化したようである[72]。体の一部を擦り合わせるか、鰾を振動させることで発音する。ニベ科では、筋肉が鰾を高速で振動させ、太鼓のような音を出す。ナマズ、タツノオトシゴ、イサキは、骨格や歯、棘を擦り合わせることで鳴く。これらの魚では、鰾が共鳴器として働くこともある。擦る音は主に1000 - 4000Hzであるが、鰾によって共鳴された音は1000Hzより低い周波数を持つ[73][74]。繁殖とライフサイクル[編集]
性決定[編集]

雌雄同体[編集]
一部の真骨類は雌雄同体であり、同時的と異時的という2つの形態がある。前者では、精子と卵子の両方が生殖腺内に存在する。同時雌雄同体は通常、配偶者がまばらに分散しているような深海魚である[84][85]。自家受精はまれで、Kryptolebias marmoratus と Kryptolebias hermaphroditus の2種でのみ記録されている[85]。異時雌雄同体では、初期には一方の性として機能し、後に切り替わる可能性がある。ブダイ、ベラ、ハタ、ハナダイ、コチ、タイ、ギンハダカ科などが知られる[84]。 雄性先熟の種は雄から雌に性転換し、雌性先熟の種はその逆であり、後者の方が一般的である。性転換はさまざまな状況で発生する可能性がある。ホンソメワケベラは、雄と最大10匹の雌から成るハーレムを形成しており、雄が不在になると、最大の雌が雄のような行動を示し、最終的には精巣を形成する。その雌が不在になると、次の雌が代わりになる。キンギョハナダイは大きな群れを作り、雌の数が圧倒的に多いが、群れに一定数の雄が不在になると、同じ数の雌が性転換して代わりになる。クマノミ類も群れを作り、群れの中で最大の雌と最大の雄の2匹だけが繁殖する。雌が死ぬと雄が性転換し、次に大きい雄が代わりになる[86]。 チョウチンアンコウ亜目では、はるかに小さい雄が雌に永久的に付着し、精子を生成する付着物に退化する。これにより雌とそれに付着した雄は同一個体になり、雌雄同体のような状態になる[87]。繁殖戦略[編集]


産卵と世話[編集]


成長[編集]

群れ[編集]

人との関わり[編集]
経済的重要性[編集]

株価への影響[編集]

その他の影響[編集]

芸術において[編集]
少なくとも14,000年にわたり、その経済的重要性を反映して、芸術の頻繁な主題となってきた。それらは古代エジプトでパターンとして一般的に加工され、古代ギリシャとローマで神話的な重要性を獲得し、そこから宗教的シンボルとしてキリスト教に入った。中国と日本の芸術家も同様に魚のイメージを象徴的に使用している。真骨類はルネサンス美術で一般的になり、17世紀にはオランダで静物画が人気のピークに達した。20世紀には、クレー、マグリット、マティス、ピカソなどのさまざまな芸術家が、魅力的なものから暴力的なものまで、根本的に異なるテーマを表現するために真骨類の表現を使用した[117]。動物学者であり芸術家でもあるエルンスト・ヘッケルは、 1904年の﹃Kunstformen der Natur﹄で真骨類やその他の動物を描いた。ヘッケルは、ゲーテとアレクサンダー・フォン・フンボルトから、深海などの未知の自然形態を正確に描写することによって、﹁その起源と進化の法則を発見できるだけでなく、その秘密の部分に迫ることもできる﹂と確信していた[118]。-
紀元前1400年ごろ、エジプトの壁画
-
イタリア・ルネサンス、1610-1630年、ポッジョ・ア・カイアーノにあるメディチ家の別荘にて
-
オランダ黄金時代の絵画、1636年
-
18世紀、清朝の絵画
-
1886年、フィンセント・ファン・ゴッホの作品
-
エルンスト・ヘッケル著 Kunstformen der Natur (1904)より
-
ヘッケルによるハコフグ科魚類の図
-
1925年、パウル・クレーの作品
脚注[編集]
出典[編集]
(一)^ Palmer, Douglas (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs & Prehistoric Animals. Marshall Editions Developments. ISBN 978-1-84028-152-1
(二)^ Müller, Johannes (1845). “Über den Bau und die Grenzen der Ganoiden, und über das natürliche System der Fische”. Archiv für Naturgeschichte 11 (1): 129.
(三)^ "teleost". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(四)^ Patterson, C.; Rosen, D. E. (1977). “Review of ichthyodectiform and other Mesozoic teleost fishes, and the theory and practice of classifying fossils”. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 158 (2): 81–172. hdl:2246/1224.
(五)^ abcdBenton, Michael (2005). “The Evolution of Fishes After the Devonian”. Vertebrate Palaeontology (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 175–184. ISBN 978-1-4051-4449-0
(六)^ Vandewalle, P.; Parmentier, E.; Chardon, M. (2000). “The branchial basket in Teleost feeding”. Cybium 24 (4): 319–342.
(七)^ Moriyama, Y.; Takeda, H. (2013). “Evolution and development of the homocercal caudal fin in teleosts”. Development, Growth & Differentiation 55 (8): 687–98. doi:10.1111/dgd.12088. PMID 24102138.
(八)^ Bone, Q.; Moore, R. (2008). Biology of Fishes. Garland Science. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-415-37562-7
(九)^ abGreenwood, P.; Rosen, D.; Weitzman, S.; Myers, G. (1966). “Phyletic studies of teleostean fishes, with a provisional classification of living forms”. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 131: 339–456.
(十)^ “Teleost”. メリアム=ウェブスター. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(11)^ Arratia, G. (1998). “Basal teleosts and teleostean phylogeny: response to C. Patterson”. Copeia 1998 (4): 1109–1113. doi:10.2307/1447369. JSTOR 1447369.
(12)^ Arratia, G. (2015). “Complexities of early teleostei and the evolution of particular morphological structures through time.”. Copeia 103 (4): 999–1025. doi:10.1643/CG-14-184.
(13)^ Romano, Carlo; Koot, Martha B.; Kogan, Ilja; Brayard, Arnaud; Minikh, Alla V.; Brinkmann, Winand; Bucher, Hugo; Kriwet, Jürgen (February 2016). “Permian-Triassic Osteichthyes (bony fishes): diversity dynamics and body size evolution”. Biological Reviews 91 (1): 106–147. doi:10.1111/brv.12161. PMID 25431138.
(14)^ abcdeNear, Thomas J. (2012). “Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification”. PNAS 109 (34): 13698–13703. Bibcode: 2012PNAS..10913698N. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206625109. PMC 3427055. PMID 22869754.
(15)^ abBerra, Tim M. (2008). Freshwater Fish Distribution. University of Chicago Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-226-04443-9
(16)^ Betancur-R., Ricardo (2013). “The Tree of Life and a New Classification of Bony Fishes”. PLOS Currents: Tree of Life 5. doi:10.1371/currents.tol.53ba26640df0ccaee75bb165c8c26288. hdl:2027.42/150563. PMC 3644299. PMID 23653398.
(17)^ Laurin, M.; Reisz, R.R. (1995). “A reevaluation of early amniote phylogeny”. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 113 (2): 165–223. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1995.tb00932.x.
(18)^ Betancur-R (2016年). “Phylogenetic Classification of Bony Fishes Version 4”. Deepfin. 2017年7月11日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年12月30日閲覧。
(19)^ Study Resolves 50-Year Dispute of Teleost Fishes Ancestral Lineage
(20)^ Genome structures resolve the early diversification of teleost fishes
(21)^ Betancur-R, Ricardo; Wiley, Edward O.; Arratia, Gloria; Acero, Arturo; Bailly, Nicolas; Miya, Masaki; Lecointre, Guillaume; Ortí, Guillermo (6 July 2017). “Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes”. BMC Evolutionary Biology 17 (1): 162. Bibcode: 2017BMCEE..17..162B. doi:10.1186/s12862-017-0958-3. ISSN 1471-2148. PMC 5501477. PMID 28683774.
(22)^ Sibert, E. C.; Norris, R. D. (2015-06-29). “New Age of Fishes initiated by the Cretaceous−Paleogene mass extinction”. PNAS 112 (28): 8537–8542. Bibcode: 2015PNAS..112.8537S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1504985112. PMC 4507219. PMID 26124114.
(23)^ Clarke, John T.; Friedman, Matt (August 2018). “Body-shape diversity in Triassic–Early Cretaceous neopterygian fishes: sustained holostean disparity and predominantly gradual increases in teleost phenotypic variety”. Paleobiology 44 (3): 402–433. Bibcode: 2018Pbio...44..402C. doi:10.1017/pab.2018.8.
(24)^ abHelfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen pp. 268–274
(25)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen pp. 274–276
(26)^ Drucker, E. G.; Lauder, G. V. (2001). “Locomotor function of the dorsal fin in teleost fishes: experimental analysis of wake forces in sunfish”. The Journal of Experimental Biology 204 (Pt 17): 2943–2958. doi:10.1242/jeb.204.17.2943. PMID 11551984.
(27)^ Steward, T. A.; Smith, W. L.; Coates, M. I. (2014). “The origins of adipose fins: an analysis of homoplasy and the serial homology of vertebrate appendages”. Proceedings of the Royal Society|Proceedings of the Royal Society B 281 (1781): 20133120. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.3120. PMC 3953844. PMID 24598422.
(28)^ Miller, Stephen; Harley, John P. (2007). Zoology (7th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 297
(29)^ Lackmann, Alec R.; Andrews, Allen H.; Butler, Malcolm G.; Bielak-Lackmann, Ewelina S.; Clark, Mark E. (2019-05-23). “Bigmouth Buffalo Ictiobus cyprinellus sets freshwater teleost record as improved age analysis reveals centenarian longevity” (英語). Communications Biology 2 (1): 197. doi:10.1038/s42003-019-0452-0. ISSN 2399-3642. PMC 6533251. PMID 31149641.
(30)^ Dorit, R. L.; Walker, W. F.; Barnes, R. D. (1991). Zoology. Saunders College Publishing. pp. 67–69. ISBN 978-0-03-030504-7
(31)^ ab Guinness World Records 2015. ギネス世界記録. (2014). p. 60. ISBN 978-1-908843-70-8
(32)^ Martill, D.M. (1988). “Leedsichthys problematicus, a giant filter-feeding teleost from the Jurassic of England and France”. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie 1988 (11): 670–680. doi:10.1127/njgpm/1988/1988/670.
(33)^ Roach, John (2003年5月13日). “World's Heaviest Bony Fish Discovered?”. National Geographic News. オリジナルの2003年5月17日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2016年1月9日閲覧。
(34)^ “Scientists Describe the World's Smallest, Lightest Fish”. Scripps Institution of Oceanography (2004年7月20日). 2016年3月5日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年4月9日閲覧。
(35)^ Maddock, L.; Bone, Q.; Rayner, J.M.V. (1994). The Mechanics and Physiology of Animal Swimming. Cambridge University Press. pp. 54–56. ISBN 978-0-521-46078-1
(36)^ Ross, David A. (2000). The Fisherman's Ocean. Stackpole Books. pp. 136–138. ISBN 978-0-8117-2771-6
(37)^ Schreiber, Alexander M. (2006). “Asymmetric craniofacial remodeling and lateralized behavior in larval flatfish”. The Journal of Experimental Biology 209 (Pt 4): 610–621. doi:10.1242/jeb.02056. PMID 16449556.
(38)^ Jackson, John (2012年11月30日). “How does the Remora develop its sucker?”. National History Museum 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(39)^ Combes, Claude (2001). Parasitism: The Ecology and Evolution of Intimate Interactions. University of Chicago Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-226-11446-0
(40)^ Caira, J.N.; Benz, G.W.; Borucinska, J.; Kohler, N.E. (1997). “Pugnose eels, Simenchelys parasiticus (Synaphobranchidae) from the heart of a shortfin mako, Isurus oxyrinchus (Lamnidae)”. Environmental Biology of Fishes 49 (1): 139–144. Bibcode: 1997EnvBF..49..139C. doi:10.1023/a:1007398609346.
(41)^ Dudek and ICF International (2012). Desert Renewable Energy Conservation Plan (DRECP) Baseline Biology Report. California Energy Commission.
(42)^ ab“Actinopterygii - ray-finned fishes”. University College, London. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(43)^ Chernova, N. V.; Friedlander, A. M.; Turchik, A.; Sala, E. (2014). “Franz Josef Land: extreme northern outpost for Arctic fishes”. PeerJ 2: e692. doi:10.7717/peerj.692. PMC 4266852. PMID 25538869.
(44)^ “What is an anadromous fish? A catadromous fish?”. Fish FAQ. NOAA. 2016年1月20日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年1月12日閲覧。
(45)^ “Anguilla anguilla (Linnaeus, 1758)”. Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme. Food and Agriculture Organization: Fisheries and Aquaculture Department (2004年1月1日). 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(46)^ “Coldwater Fish and Fisheries in the Indian Himalayas: Lakes and Reservoirs”. Food and Agriculture Organization. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(47)^ Morelle, Rebecca (2008年10月7日). “'Deepest ever' living fish filmed”. BBC News 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(48)^ Morelle, Rebecca (2014年12月19日). “New record for deepest fish”. BBC News 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(49)^ Meurant, Gerard (1984). Fish Physiology V10A. Academic Press. pp. 263–. ISBN 978-0-08-058531-4
(50)^ Liem, Karel F. (1998). Paxton, J.R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.. eds. Encyclopedia of Fishes. Academic Press. pp. 173–174. ISBN 978-0-12-547665-2
(51)^ Armbruster, Jonathan W. (1998). “Modifications of the digestive tract for holding air in loricariid and scoloplacid catfishes”. Copeia 1998 (3): 663–675. doi:10.2307/1447796. JSTOR 1447796.
(52)^ Orr, James (1999). Fish. Microsoft Encarta 99. ISBN 978-0-8114-2346-5
(53)^ Journal of Undergraduate Life Sciences. “Appropriate maze methodology to study learning in fish”. 2011年7月6日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2009年5月28日閲覧。
(54)^ Bentley, P.J. (2013). Endocrines and Osmoregulation: A Comparative Account in Vertebrates. Springer. p. 26. ISBN 978-3-662-05014-9
(55)^ Whittow, G. Causey (2013). Comparative Physiology of Thermoregulation: Special Aspects of Thermoregulation. Academic Press. p. 223. ISBN 978-1-4832-5743-3
(56)^ McFarlane, Paul (1999年1月1日). “Warm-blooded fish”. Monthly Bulletin. Hamilton and District Aquarium Society. 2013年5月15日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年1月6日閲覧。
(57)^ Logue, J. A.; Vries, A. L. de; Fodor, E.; Cossins, A. R. (2000-07-15). “Lipid compositional correlates of temperature-adaptive interspecific differences in membrane physical structure”. Journal of Experimental Biology 203 (14): 2105–2115. doi:10.1242/jeb.203.14.2105. ISSN 0022-0949. PMID 10862723.
(58)^ Johnston, I. A.; Dunn, J. (1987). “Temperature acclimation and metabolism in ectotherms with particular reference to teleost fish”. Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology 41: 67–93. ISSN 0081-1386. PMID 3332497.
(59)^ abMartin, R. Aidan (1992年4月). “Fire in the Belly of the Beast”. ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(60)^ Brown, W. Duane (1962). “The concentration of myoglobin and hemoglobin in tuna flesh”. Journal of Food Science 27 (1): 26–28. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1962.tb00052.x.
(61)^ Fritsches, Kerstin (2005年1月11日). “Warm eyes give deep-sea predators super vision”. University of Queensland 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(62)^ Molecular developmental mechanism in polypterid fish provides insight into the origin of vertebrate lungs
(63)^ Changes in Nkx2.1, Sox2, Bmp4, and Bmp16 expression underlying the lung-to-gas bladder evolutionary transition in ray-finned fishes
(64)^ Twenty ways to lose your bladder: common natural mutants in zebrafish and widespread convergence of swim bladder loss among teleost fishes
(65)^ Kardong, K. (2008). Vertebrates: Comparative anatomy, function, evolution (5th ed.). Boston: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-304058-5
(66)^ Numerical Studies of Hydrodynamics of Fish Locomotion and Schooling by a Vortex Particle Method. (2008). pp. 1–4. ISBN 978-1-109-14490-1
(67)^ Kapoor, B.G.; Khanna, Bhavna (2004). Ichthyology Handbook. Springer. pp. 149–151. ISBN 978-3-540-42854-1
(68)^ abPatzner, Robert; Van Tassell, James L.; Kovacic, Marcelo; Kapoor, B.G. (2011). The Biology of Gobies. CRC Press. pp. 261, 507. ISBN 978-1-4398-6233-9
(69)^ Pace, C. M.; Gibb A. C. (2009). “Mudskipper pectoral fin kinematics in aquatic and terrestrial environments”. The Journal of Experimental Biology 212 (Pt 14): 2279–2286. doi:10.1242/jeb.029041. PMID 19561218.
(70)^ Jamon, M.; Renous, S.; Gasc, J.P.; Bels, V.; Davenport, J. (2007). “Evidence of force exchanges during the six-legged walking of the bottom-dwelling fish, Chelidonichthys lucerna”. Journal of Experimental Zoology 307 (9): 542–547. doi:10.1002/jez.401. PMID 17620306.
(71)^ Dasilao, J.C.; Sasaki, K. (1998). “Phylogeny of the flyingfish family Exocoetidae (Teleostei, Beloniformes)”. Ichthyological Research 45 (4): 347–353. Bibcode: 1998IchtR..45..347D. doi:10.1007/BF02725187.
(72)^ Rice, A. N. (2022). “Evolutionary Patterns in Sound Production across Fishes”. Ichthyology & Herpetology 110 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1643/i2020172.
(73)^ “How do fish produce sounds?”. Discovery of Sound in the Sea. 2017年2月15日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2017年2月17日閲覧。
(74)^ Lobel, P. S.. “Fish Courtship and Mating Sounds”. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 2018年1月10日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2017年2月17日閲覧。
(75)^ Wootton and Smith p. 5.
(76)^ Springer, Joseph; Holley, Dennis (2012). An Introduction to Zoology. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 370. ISBN 978-0-7637-5286-6
(77)^ abcHelfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen p. 457
(78)^ Wootton and Smith p. 4.
(79)^ Wootton and Smith p. 2.
(80)^ Wootton and Smith pp. 14, 19.
(81)^ Wootton and Smith p. 20.
(82)^ Wootton and Smith pp. 21–22.
(83)^ Wootton and Smith p. 21–22.
(84)^ abcLaying, E.. “Fish Reproduction”. 2014年11月14日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年1月7日閲覧。
(85)^ abWootton and Smith p. 2–4.
(86)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen p. 458
(87)^ Wootton and Smith p. 320
(88)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen p. 465
(89)^ abHelfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen p. 463
(90)^ Muñoz, R.; Zgliczynski, B.; Laughlin, J.; Teer, B. (2012). “Extraordinary aggressive behavior from the giant coral reef fish, Bolbometopon muricatum, in a remote marine reserve”. PLOS ONE 7 (6): e38120. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...738120M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038120. PMC 3368943. PMID 22701606.
(91)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen p. 473
(92)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen p. 465–68
(93)^ abReynolds, John; Nicholas B. Goodwin; Robert P. Freckleton (19 March 2002). “Evolutionary Transitions in Parental Care and Live Bearing in Vertebrates”. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 357 (1419): 269–281. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0930. PMC 1692951. PMID 11958696.
(94)^ Clutton-Brock, T. H. (1991). The Evolution of Parental Care. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press
(95)^ Werren, John; Mart R. Gross; Richard Shine (1980). “Paternity and the evolution of male parentage”. Journal of Theoretical Biology 82 (4): 619–631. doi:10.1016/0022-5193(80)90182-4. PMID 7382520 2013年9月15日閲覧。.
(96)^ Baylis, Jeffrey (1981). “The Evolution of Parental Care in Fishes, with reference to Darwin's rule of male sexual selection”. Environmental Biology of Fishes 6 (2): 223–251. Bibcode: 1981EnvBF...6..223B. doi:10.1007/BF00002788.
(97)^ Wootton and Smith p. 280
(98)^ Wootton and Smith pp. 257–61
(99)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen pp. 472–73
(100)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen pp. 146–47
(101)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen pp. 149
(102)^ Helfman, Collette, Facey and Bowen pp. 153–56
(103)^ Pitcher, Tony J. (1986). “12. Functions of Shoaling Behaviour in Teleosts”. The Behaviour of Teleost Fishes. Springer. pp. 294–337. doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-8261-4_12. ISBN 978-1-4684-8263-8
(104)^ “Capture production by principal species in 2012”. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics 2012. Food and Agriculture Organization. p. 12. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(105)^ abcdKisia, S. M. (2010). Vertebrates: Structures and Functions. CRC Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-1-4398-4052-8
(106)^ “New Economic Report Finds Commercial and Recreational Saltwater Fishing Generated More Than Two Million Jobs”. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(107)^ Scottish Fish Farm Production Survey 2014. The Scottish Government/Riaghaltas na h-Alba. (September 2015). ISBN 978-1-78544-608-5
(108)^ “Fish to 2030 : prospects for fisheries and aquaculture (Report 83177)”. Food and Agriculture Organization; World Bank Group. pp. 1–102 (2013年12月1日). 2016年2月2日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年1月3日閲覧。
(109)^ “Fish and fish products”. Food and Agriculture Organization. 2019年2月8日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2016年4月8日閲覧。
(110)^ Vince, Gaia (2012年9月20日). “How the world's oceans could be running out of fish”. BBC. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(111)^ Kunzig, R. (April 1995). “Twilight of the Cod”. Discover: 52.
(112)^ Wootton and Smith 2014, pp. 123–125
(113)^ Kernan, Martin; Battarbee, Richard W.; Moss, Brian R. (2011). Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Ecosystems. John Wiley & Sons. p. 93. ISBN 978-1-4443-9127-5
(114)^ Fisheries Management and Climate Change in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean and the Baltic Sea. Nordic Council of Ministers. (2008). p. 48. ISBN 978-92-893-1777-1
(115)^ Committee on the Review of the National Ocean Acidification Research and Monitoring Plan, Ocean Studies Board, Division on Earth and Life Studies, National Research Council (2013). Review of the Federal Ocean Acidification Research and Monitoring Plan. National Academies Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-309-30152-7
(116)^ “Five reasons why zebrafish make excellent research models”. NC3RS (2014年4月10日). 2024年4月29日閲覧。
(117)^ Moyle, Peter B.; Moyle, Marilyn A. (May 1991). “Introduction to fish imagery in art”. Environmental Biology of Fishes 31 (1): 5–23. Bibcode: 1991EnvBF..31....5M. doi:10.1007/bf00002153.
(118)^ “The Tragic Sense of Ernst Haeckel: His Scientific and Artistic Struggles”. University of Chicago. 2024年4月29日閲覧。
参考文献[編集]
- E.H.コルバート 『脊椎動物の進化』 築地書館 2004 ISBN 4806712957
- Helfman, G.; Collette, B. B.; Facey, D. E.; Bowen, B. W. (2009). The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution, and Ecology (2nd ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-2494-2
- Wootton, Robert J.; Smith, Carl (2014). Reproductive Biology of Teleost Fishes. Wiley. ISBN 978-1-118-89139-1










