

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
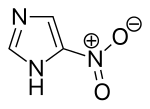
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Nitro-1H-imidazole | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.296 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H3N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 113.076 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 303 °C (577 °F; 576 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Nitroimidazoles are the group of organic compounds consisting of an imidazole ring with at least one nitro group substituent. The term also refers to the class of antibiotics that have nitroimidazole in their structures.[2] These antibiotics commonly include the 5-nitroimidazole positional isomer.

Imidazole undergoes a nitration reaction with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to give 5-nitroimidazole.

From the chemistry perspective, nitroimidazole antibiotics can be classified according to the location of the nitro functional group. Structures with names 4- and 5-nitroimidazole are equivalent from the perspective of drugs since these tautomers readily interconvert. Drugs of the 5-nitro variety include metronidazole, tinidazole, nimorazole, dimetridazole, pretomanid, ornidazole, megazol, and azanidazole. Drugs based on 2-nitroimidazoles include benznidazole and azomycin.[3]
Nitroimidazole antibiotics have been used to combat anaerobic bacterial and parasitic infections.[4] Perhaps the most common example is metronidazole. Other heterocycles such as nitrothiazoles (thiazole) are also used for this purpose. Nitroheterocycles may be reductively activated in hypoxic cells, and then undergo redox recycling or decompose to toxic products.[5]

|
| |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entamoeba |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Acanthamoeba |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antifolates (inhibit bacterial purine metabolism, thereby inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Quinolones (inhibit bacterial topoisomerase and/or DNA gyrase, thereby inhibiting DNA replication) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Anaerobic DNA inhibitors |
| ||||||||||||||||
| RNA synthesis |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||