アルバートサウルス
| アルバートサウルス | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 全身骨格化石のレプリカ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 地質時代 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 約7060万年前 - 約6604.3万年前 [1] マーストリヒチアン中葉 - 末期 中生代白亜紀後期(後期白亜紀)末期 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 分類 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 学名 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albertosaurus Osborn, 1905 [2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| タイプ種 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Albertosaurus sarcophagus Osborn, 1905[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| シノニム | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 和名 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| アルバートサウルス | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 下位分類(種) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
アルバートサウルス︵学名‥Albertosaurus、意‥アルバータのトカゲ︶は、約7060万年前から約6604.3万年前にかけて[1]、すなわち、中生代白亜紀後期︵後期白亜紀︶末期にあたるマーストリヒチアン︵半ばから末期まで︶に、ララミディア大陸および北アメリカ大陸︵cf. #本属が棲息していた陸地︶に棲息していた肉食恐竜である。竜盤目獣脚亜目ティラノサウルス科に分類される。
タイプ種である A. sarcophagus 種︵サルコパグス種 / サルコファグス種︶の産出地は現代のカナダのアルバータ州に限定されており、属名はこの地名に由来する。ただし、属内の分類は一致しておらず、一部の研究者︵提唱者はローレンス・ラム︶は Gorgosaurus libratus︵ゴルゴサウルス・リブラトゥス︶を本属の種とみなしている。
他のティラノサウルス科の属と同様に、アルバートサウルスは小さな二本指の前肢を有する二足歩行の捕食動物であり、大型で鋭い歯が多く並ぶ巨大な頭部を持つ。棲息地域一帯における頂点捕食者であった可能性がある。アルバートサウルスは獣脚類としては大型であったが、一般知名度の高い近縁属のティラノサウルスとの比較では遥かに小型であり、成体の全長は9メートルから10メートル、体重は2トン未満と推定される。
1884年に初めて発見されて以来、30個体を超えるアルバートサウルスの化石が発見されていることから、他の大半のティラノサウルス科恐竜よりも解剖学の研究がより詳細に展開されている。特定地域に集中して25個体が発見されており、群れで行動していたと断定されている。さらにこの事実発見により、オントロジーや集団生物学といった研究分野も他の恐竜以上に発展を遂げている。
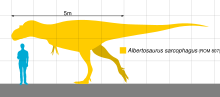
ヒトとの大きさ比較
アルバートサウルスはティラノサウルスやタルボサウルスといった他のティラノサウルス科よりも小型である。典型的なアルバートサウルスの成体は最大で全長9メートルに達するも[6][7]、希に10メートル超まで成長する個体もあった[8]。複数の成体のアルバートサウルスをそれぞれいくつかの手法を組み合わせて検証した結果、体重は1.3トン[9] から1.7トンの範囲と推定されている[10]。
アルバートサウルスの外見上の特徴は、他のティラノサウルス科と共通点が多い。獣脚類の典型的特徴である二足歩行であり、長い尾を使って重い頭部や胴部とバランスを取っていた。しかし、ティラノサウルス科の前肢は体サイズに対して極端に小さく、指も2本だけである。後肢は長く、4本の指を持ち、そのうち第1趾は地面に届かないほどに短い。第3趾は他の足の指よりも長い。アルバートサウルスの歩行速度は時速14 - 21キロメートルに達した可能性がある[11]。ただし幼体に限定すると、歩行速度はこの数値を上回っていた可能性も指摘されている[12]。
アルバートサウルスの皮膚は、部位によって異なる形状の鱗︵うろこ︶で覆われており、これまで2種類の印象化石 (鱗の形がプリントされた跡) が発見されている[13]。このうち1種は、腹肋骨や未確認の長い骨とともに発見されており、腹部の鱗と考えられている。この鱗はゴツゴツとした六角形に近い形で、徐々に大きさを増す。また、4 - 5センチメートル間隔で並ぶ大型の鱗の印象化石も発見されている[13]。もう1種類は、どの部位の鱗か特定できていないが、小型のダイヤモンド型をなして直線状に整列している[13]。

標本 TMP 1981 010 0001 / Albertosa urus 頭蓋骨雄型︵キャスト︶
S字型の短い頸︵くび︶に具わったアルバートサウルスの頭蓋骨は巨大で、成体の頭骨長は最大約1メートルである[14]。頭蓋骨には広く孔が開いていて頭蓋骨の軽量化に寄与するとともに、筋肉や感覚器官のためのスペースが形成されていた。長い顎には両側を合計して58本以上のバナナ状の歯が並んだ。近縁なゴルゴサウルスの歯が最低62本である一方、より大型のティラノサウルス科の歯はアルバートサウルスの歯よりも少なかった。大半の獣脚類と違い、アルバートサウルスや他のティラノサウルス科恐竜は口の中の場所によって歯の形状が異なるという異歯性を示した。上顎先端に位置する前上顎骨歯は左右それぞれに4本生え、これらは他の歯より小型で、密に並び、断面はD字型をなした[7]。ティラノサウルスと同様にアルバートサウルスの上顎骨歯は逃れようとしてもがく獲物による水平方向の運動力に耐えられる形状であった。しかし、アルバートサウルスの咬合力は格段に強いわけではなく、奥歯でも最大で3413ニュートンであった[15]。ただし、2012年に発表された研究論文によると、アルバートサウルスの咬合力は約4万2000ニュートンであった[16]。眼の上には骨質の突起があるが、これは、生きていた頃には鮮やかな色で交尾相手を惹き付ける繁殖用ディスプレイとして機能していた可能性もある[17]。

生態復元想像図︵2015年作︶
ウィリアム・エイブラーは2001年にアルバートサウルスの歯を観察し、歯の鋸歯状構造が肥大部 (ampulla) [18]と呼ばれる丸い空洞で末端を迎える歯の割れ目に似ていると発表した[19]。ティラノサウルス科の歯は肉を引き剥がす道具として用いられていたため、﹁彼らが肉を剥ぎ取る際に純粋な張力で歯全体に割れ目のような鋸歯状構造が広がった﹂と彼は考えた[19]。しかし、肥大部が存在することで張力は表面全体に拡散され、歯が損傷する危険は軽減していた[19]。空洞で終わる切れ込みは人間の工学にも共通する。ギター職人も同様の切れ込みを用いており、歯が柔軟性と剛性を交互に使って機能していたと、エイブラーは記載した[19]。航空機産業においては、ドリルを使用して肥大部を作り、素材に亀裂が走ることを防いでいる[19]。また、切れ込みと穴のあるプレキシグラスの棒が通常のものよりも25パーセント強度を増すことをエイブラーは実証した[19]。ティラノサウルス科とは違い、植竜類やディメトロドンといったさらに古い時代の捕食動物は鋸歯状構造を具えてはおらず、摂食時に受ける歯のダメージを軽減する適応を示さない[19]。

ホロタイプ︵正基準標本︶CMN 5600 / カナダ自然博物館 所蔵。
ヘンリー・フェアフィールド・オズボーンは1905年にティラノサウルスを記載した際、論文の最後の1ページでアルバートサウルスも命名した[2]:265。
属名 Albertosaurus の構成要素 "Albert" は、本種の化石の産出地である "Alberta"﹁アルバータ州﹂の名から採用された。アルバータ州はアルバートサウルスが記載されたのと同じ1905年にカナダ自治領への加入を果たして正式に設立された州である。"-saurus" のほうは﹁爬虫類﹂を意味する分類学用新ラテン語名詞接尾辞であり、恐竜の属名を造るのに用いられることが多いため、ここでは﹁恐竜﹂と意訳して[20]差し支えない。その語源は、﹁トカゲ﹂を意味する古代ギリシア語の "σαῦρος︵ラテン翻字: sauros、日本語音写例: サウロス︶" [20] である。
タイプ種 Albertosaurus sarcophagus の種小名である sarcophagus は、古代ギリシア語で﹁肉食の﹂という意味をもつ "σαρκοφάγος︵ラテン翻字: sarkophagos、日本語音写例: サルコパゴス、サルコファゴス︶" に由来し、古代エジプトや古代ギリシアの石棺やその材である大理石を意味する "sarcophagus (stone sarcophagus)"︵日本語名‥サルコファガス︶[21] と同根語の関係にある[2]。

アルバータ州ドラムヘラー付近のレッドディア川。アルバートサウルス の化石の約4分の3が両側の露頭で川沿いに発見されている。
あらゆる年齢の30を超える標本が学術的に知られている[8][22]。タイプ標本は頭頂部の骨で、1884年の夏にアルバータ州レッドディア川沿いのホースシューキャニオン累層の露頭から収集された。この標本は地質学者ジョセフ・ティレル率いるカナダ地質調査所の発掘調査により1884年6月9日に発見されたが、特殊装備がなかったため彼らはほぼ完全な頭蓋骨を部分的にしか確保できなかった。1889年、ティレルとともに研究していたトーマス・チェスマー・ウェストンは、いくつかの骨格要素と繋がった小型の頭蓋骨を近くの産地で発見した[23]。2つの頭蓋骨は既に存在していた種 Laelaps incrassatus にエドワード・ドリンカー・コープが1892年に割り当てた[24] が、ラエラプスという属名は既にダニに使われており、オスニエル・チャールズ・マーシュが1877年にドリプトサウルス Dryptosaurus へ改名した。ライバルであるマーシュの作った名前にされることをコープは拒絶したが、ローレンス・ラムは1903年と1904年に化石を詳細に記載したときに Laelaps incrassatus ではなく1902年にオリバー・ペリー・ヘイが新組合せ[注釈 1]を作った[25] Dryptosaurus incrassatus という表記を採用した[26][27]。その直後、オズボーンは D. incrassatus が一般的なティラノサウルス科の歯に基づいており、ホースシューキャニオン累層の2つの頭蓋骨が本種に確実には分類できないことを指摘した。また、ホースシューキャニオン累層の頭蓋骨はドリプトサウルスのタイプ種 D. aquilunguis と大きく異なっており、オズボーンは1905年にこれらの化石を Albertosaurus sarcophagus と命名した。彼は化石を特に詳しくは記載せず、前年のラムによる完全な記載を参照した[2]。ホロタイプ標本 CMN 5600 とパラタイプ標本 CMN 5601 のいずれもがオタワのカナダ自然博物館に所蔵されている。21世紀初頭には、ホロタイプ標本の損傷状態が酷かったため他の標本を割り当てることができず、アルバートサウルスはタイプ標本だけを示す疑問名ではないかという意見も飛び出した。しかし2010年には、ホロタイプやパラタイプおよび後に発見された比較可能な標本が、ユニークな特徴を共有するあるいは固有派生形質を持つことを、トーマス・カールが明らかにした。具体的には、それは口蓋骨のサイドの背側縁に広がる含気性の孔の存在であり、これはアルバートサウルスが有効な分類群であることを証明した[28]。

標本 TMP 1999 050 0067, 0074, 0084 / ドライアイランドとドラムヘラーから産出した歯の化石。
1910年8月11日、アメリカの古生物学者バーナム・ブラウンはアルバートサウルスの大規模な群れの化石をレッドディア川沿いの産地で発見した。骨が余りにも多く、時間も限られていたため、ブラウンらは全ての標本を回収はしなかったが、ボーンベッドで区別可能な全ての個体から骨を収集した。ニューヨークのアメリカ自然史博物館のコレクションにある骨は、7本の右中足骨とそれに大きさの合わない乖離した2つの趾骨のものであり、これにより少なくとも9体が産地に眠っていたことが示唆された。ロイヤル・ティレル古生物学博物館の古生物学者フィリップ・J・カリーは1997年にボーンベッドを再発見し、現在のドライ・アイランド・バッファロー・ジャンプ州立公園でフィールドワークを行った[12]。1997年から2005年に行われたさらなる発掘調査では、さらに13体の様々な年齢の個体の化石が発見され、この中にはわずか2歳の個体や全長10メートルを超えると推定される非常に高齢の個体もあった。いずれも完全な骨格ではなく、大半は両博物館の化石に代表される[8][9]。発掘調査は2008年まで続いた。その年には、骨格に一つだけ保存された骨に基づくと個体数は最少で12体、類似する骨が個体発生において大きさが変わっただけの相同な骨であるとすれば26体とされた。合計で1128本のアルバートサウルスの骨が確保されており、白亜紀の大型獣脚類では最も化石が集中している[29]。

標本 TMP 1985 098 0001 / 頭蓋骨化石
1911年にアルバータ州のアメリカ自然史博物館で運営の職に就いて2年目を迎えていたバーナム・ブラウンは、レッドディア川トルマン橋付近で断片的なアルバートサウルスの頭蓋骨化石 AMNH 5222 を発見した[30]。
ウィリアム・パークスは、1923年にレッドディア川付近でガス・リンドバルドとラルフ・ホーネルが発掘した頭蓋骨を欠く部分的骨格に基づき、1928年に新種 Albertosaurus arctunguis を記載した[31]が、この標本は1970年以降 A. sarcophagus であると考えられている[6]。パークスの標本 ROM 807 はトロントのロイヤルオンタリオ博物館に所蔵されている。
1926年から1972年の間アルバートサウルスの化石は全く発見されなかったが、70年代以降は着実に標本が増加している。ドライ・アイランドのボーンベッドとは別に6つの頭蓋骨と他の骨格がアルバータ州で発見され、カナダの様々な博物館に所蔵されている。アマチュア古生物学者マウリス・ステファンクが1978年に発見した標本 RTMP 81 010 001、彼が1985年6月16日に発見した RTMP 85 098 001、1985年12月に発見した RTMP 86 64 001 、1986年の RTMP 86 205 001、1996年の RTMP 97 058 0001、そして CMN 11315 である。しかしヴァンダリズムと事故によりこれらは全て損傷を受けることとなった[23]。また、アメリカ合衆国モンタナ州・ニューメキシコ州・ワイオミング州からも化石が報告されているが、これらは A. sarcophagus ではなく、アルバートサウルスですらない可能性がある[7][22]。

アイオワ科学センターの組み立てられた骨格
アルバートサウルスは獣脚亜目ティラノサウルス科アルバートサウルス亜科に分類される。最も近縁な種はわずかに古い時代に生息した Gorgosaurus libratus︵Albertosaurus libratus とする説あり︶である[42]。これら2種だけが唯一記載されたアルバートサウルス亜科であり、未記載種が存在する可能性もある[22]。トーマス・R・ホルツ・ジュニアはアパラチオサウルスをアルバートサウルス亜科に加える論文を2004年に発表した[7] が、彼は後の未発表の研究でアパラチオサウルスをティラノサウルス科の外に位置付けており[43]、これは他の研究者からも賛同された[34]。
ティラノサウルス科の別の亜科にはティラノサウルス亜科があり、ダスプレトサウルスやタルボサウルス、ティラノサウルスなどが属する。これら頑強なティラノサウルス亜科と比べ、アルバートサウルス亜科の体は細長く、頭蓋骨のプロポーションは小さく、脚の下部︵脛骨︶や足︵中足骨と趾骨︶が長い[14][42]。
以下のティラノサウルス科のクラドグラムは2013年のローウェンらの系統解析に基づく[44]。
概要[編集]

頭蓋骨と歯[編集]


発見と命名[編集]
命名[編集]

初期の発見[編集]

ボーンベッド[編集]

他の発見[編集]

ゴルゴサウルス[編集]
1913年に古生物学者チャールズ・ヘイゼリアス・スタンバーグが別のティラノサウルス科の骨格をやや古い時代のアルバータ州ダイナソーパーク累層から発見し、ローレンス・ラムが1914年にこの恐竜を Gorgosaurus libratus と命名した[32]。後にアルバータ州とモンタナ州で他の標本も発見された。主にアルバートサウルスの良い頭蓋骨が無く、両者を区別する重大な相違点もなかったため、デイル・ラッセルはゴルゴサウルスを先に命名されたアルバートサウルスのジュニアシノニムと提唱し、1970年には G. libratus は Albertosaurus libratus に改名された。標本の時代が違ったため種レベルでは区別されたままとなった。ゴルゴサウルスがアルバートサウルスに加えられたことでアルバートサウルスの生息した時代範囲は数百万年拡張され、地理範囲も数百キロメートル南方へ広がった[6]。 2003年にフィリップ・J・カリーは獣脚類の解剖学的知識の増大とより広範囲の発見に恩恵を受け、複数のティラノサウルス科の頭蓋骨を比較し、両者はかつて考えられていたよりも別個の動物であると結論付けた。両者は姉妹群で他のどの種よりも互いに近縁であったため、1属か2属かの決定は恣意的な面も否めなかった。しかしカリーはそれを承知した上で、常に別属に分類されるダスプレトサウルスとティラノサウルスほど両者が似ていないと結論付け、アルバートサウルスとゴルゴサウルスを別属にすべきであると推奨した。さらに、アラスカ州とニューメキシコ州から複数のアルバートサウルス亜科の標本が発見され、アルバートサウルスとゴルゴサウルスの状態はこれらが完全に記載されることで明確化すると提唱した[22]。大半の論文執筆者はカリーの意見に従った[7][9][33] が、そうでない研究者もいる[34]。他の種[編集]
A. sarcophagus、A. arctunguis、A. libratus︵ゴルゴサウルス︶の他に、複数のアルバートサウルスの種が命名されてきた。これらは今日では他の種の若年個体のシノニムか疑問名と見られており、アルバートサウルス属には分類されていない。 1930年、アナトリー・ニコラヴィッチ・リアビニンは中国から産出した歯に基づいて Albertosaurus pericolosus Riabinin, 1930 を命名したが、これはおそらくタルボサウルスに属する[35]。1932年にフリードリヒ・フォン・ヒューネは Dryptosaurus incrassatus (Cope, 1876) を本属に移動し、Albertosaurus incrassatus とした[36]。1970年にデイル・ラッセルはゴルゴサウルス属をアルバートサウルス属に内包し、Gorgosaurus sternbergi Matthew & Brown, 1922 を Albertosaurus sternbergi へ、Gorgosaurus lancensis Gilmore, 1946 を Albertosaurus lancensis へ改名した[6]。前者は今日では Gorgosaurus libratus の幼体と考えられており、後者はティラノサウルスかナノティラヌスとされた。1988年にグレゴリー・ポールはモンタナ州ヘルクリーク累層から産出した小型のティラノサウルス科骨格標本 LACM 28345 に基づいて Albertosaurus megagracilis Paul, 1988 を記載した[37]。これは1995年に新属ディノティラヌス Dinotyrannus Olshevsky, 1995 に移され、Dinotyrannus megagracilis (Paul, 1988) Olshevsky, 1995 とされた[38] が、現在ではティラノサウルス・レックスの幼体と考えられている[14]。また、1988年にポールが Alectrosaurus olseni Gilmore, 1933 を Albertosaurus olseni に改名した[37] が、一般に受け入れられなかった。1989年に Gorgosaurus novojilovi Maleev, 1955 をブリン・メダーとロバート・ブラッドレイが Albertosaurus novojilovi に改名し[39]、現在ではタルボサウルスのシノニムとみなされている。 有効なアルバートサウルスの骨格に基づいて他の属へ再分類された種も2例ある。1922年にウィリアム・ディラー・マシューは A. sarcophagus を Deinodon sarcophagus に改名し[40]、1939年にドイツの古生物学者オスカー・クーンは A. arctunguis を Deinodon arctunguis に改名した[41]。分類と系統[編集]

| ティラノサウルス科 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
古生物学[編集]
成長パターン[編集]

アルバートサウルスはほぼ全ての年齢の個体が化石記録に残っている。骨の組織学を利用すると大抵の場合それぞれの個体が死亡したときの年齢を決定でき、成長率を推定して他の種と比較することも可能となる。これまで知られている中で最も若いアルバートサウルスはドライ・アイランドのボーンベッドで発見された2歳の個体で、体重は50キログラムに達し、全長は2メートルを超えたと考えられている。同じ産地から産出した全長10メートルの標本は知られている中で最高齢の28歳である。中間の年齢とサイズの標本をグラフにプロットするとS字型のカーブが現れ、12 - 16歳ごろに最も急激な成長を見せており、これは他のティラノサウルス科にも見られるパターンである。急成長期の成長率は1.3トンの成体に基づくと、年間122キログラムであった。他の研究ではさらに成体の体重が重いことが示唆されているが、これは成長率の大きさには影響しても、全体的なパターンを左右することは無い。ティラノサウルス科はアルバートサウルスに近い成長率と体格を示したが、より大型のティラノサウルスは最大で年間601キログラムという5倍ほどの成長率を示した[8]。急成長段階の終わりはアルバートサウルスの性成熟の始まりを示唆するが、その後も生涯を通じて緩やかな成長は続いていた[8][9]。まだ活発に成長している時期に性成熟が起こるのは、小型恐竜[45] と大型恐竜[46]、そしてヒトやゾウといった大型哺乳類に共通する傾向である[46]。この比較的早期に性成熟が起こるというパターンは、成長が完了する後まで性成熟を遅らせる鳥類のパターンとは大きく異なる[33][46]。
成長の間に歯が厚くなって形態が大きく変化したため、ドライ・アイランドのボーンベッドの若い個体と成体の骨格が同じ分類群に属することを証明できなくなり、幼体の歯は系統解析により別種のものと同定された可能性が高い[47]。

ブライアン・クーレイが2007年にデザインした、群れるアルバート サウルスのブロンズ像
バーナム・ブラウンらが発見したドライ・アイランドのボーンベッドには26体のアルバートサウルスが保存されており、一ヶ所から産出した白亜紀の大型獣脚類としては世界最多であり、大型獣脚類全体においてもユタ州の Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry から産出したアロサウルスに次いで2番目である。この群れは非常に高齢の個体1頭、17 - 23歳の成体8頭、12 - 16歳の急成長期真っ只中の亜成体7頭、2 - 11歳の急成長期に至っていない幼体6頭から構成されている[8]。
アルバートサウルスのボーンベッドからは植物食性動物の化石がほぼ産出しておらず、また多くの個体の保存状態が似ているため、 カリフォルニア州のラ・ブレア・タールピットのような捕食者トラップではなく、さらに保存されている死んだ動物たちは全て同時に死亡したとカリーは結論付けた。彼はこれを群れで行動していたことの根拠であると主張した[12]。他の科学者は懐疑的であり、アルバートサウルスは干ばつや洪水などの理由で一緒に運ばれた可能性があると意見した[8][48][50]。

模型
角竜やハドロサウルス科など植物食恐竜には群れで行動していた証拠が豊富にあるが[51]、同じ場所で肉食恐竜が数多く発見されることも稀にある。ディノニクス[52] やコエロフィシス[53] といった小型獣脚類は群れで発見されており、アロサウルスやマプサウルスといった大型の捕食動物にも例はある[54]。他のティラノサウルス科にも群居性の証拠がある。シカゴのフィールド自然史博物館で化石が組み立てられたスーの近くで小型個体の断片化石が発見されているほか、モンタナ州ツーメディスン累層のボーンベッドには、数頭のハドロサウルス科の傍に少なくとも3つのダスプレトサウルスの標本が保存されていた[55]。これらの発見は、一時的あるいは異様な集合時の化石である可能性が否定できないものもあるが、アルバートサウルスの社会的行動の証拠と結びつけられる可能性がある[12]。社会的集団ではなく、コモドオオトカゲのように死体の周りに群がり、激しく争って殺し合いや共食いに発展したと推測する研究者もいる[48]。
また、アルバートサウルスは群れで狩りを行っていたとカリーは推論している。小型個体の脚のプロポーションはおそらく最速の恐竜の一つであるオルニトミムス科に匹敵する。若いアルバートサウルスは同程度に俊足、あるいは少なくとも獲物よりも速かったとみられている。獲物を強力だが動作の襲い成体の方へ群れの若いメンバーが追い込んでいた、とカリーは仮説を立てた[12]。また、幼体は成体と異なる生活スタイルを送っており、アルバートサウルスよりも体重が2桁軽いような同時代の小型獣脚類の捕食者と巨大な成体との間の生態的地位を埋めていた[7]。同様の状況は現代のコモドオオトカゲでも確認できる。彼らは彼らは木を這って虫を捕食するところから始まって、島の支配的な捕食動物へ成長する[56]。しかし、行動が化石記録に保存されることは極めて稀であり、このアイディアは容易に確かめられなかった。2010年には、いまだ群れで狩りをしていた説をカリーは支持していたが、洪水でゆっくり水位が上昇したなどの他の要因で化石が集中した可能性があると認めた[57]。

トリコモナス症型の病変を起こしたティラノサウルス科の顎の骨。Dが アルバートサウルス
アルバートサウルスなどティラノサウルス科恐竜の顎化石に見られる滑らかな縁の穴は、現代の鳥にも感染するトリコモナスのような寄生虫により生じたものである、と研究者が2009年に仮説を立てた[58]。彼らは、ティラノサウルス科恐竜が互いに噛み合って感染症を伝播し、感染により摂食能力が低下したと提唱した[58]。
2001年にブルース・ロスチャイルドらは獣脚類の疲労骨折と腱断裂の証拠を調べる研究を発表した。319本のアルバートサウルスの骨のうち疲労骨折が確認できたものは1本のみで、手の骨には見られなかった。また、研究者はアルバートサウルスの疲労骨折はカルノサウルス類のアロサウルスよりも非常に少ないとした[59]。A. arctunguis のホロタイプ ROM 807 は現在 A. sarcophagus に割り当てられており、これには腸骨に2.5×3.5センチメートルの深い穴があったが、本種の記載者はこれを病変と判断しなかった。また、標本には外骨腫が左第4中足骨に複数存在した。1970年には Albertosaurus sarcophagus の標本5つのうち2つに病理的損傷が見られるとデイル・ラッセルが報告した[60]。
2010年にドライ・アイランドのアルバートサウルスの群れの健康状態が報告された。大半の標本に病気の兆候はなかったが、3本の趾骨に腱の異常な骨化で構成される奇妙な骨の突起、すなわち靭帯付着部増殖体が存在し、その原因は不明とされた。2本の肋骨と腹肋骨には破損と治癒の兆候が見られた。ある成体の標本は左の下顎に刺創があり、治癒済みの噛み跡と未治癒の噛み跡の両方が確認できた。2007年に調査されたマジュンガサウルスの群れの健康状態と比較して、病変を示す個体は19%と少ないことが明らかになった[61]。

アルバータ州 ホースシューキャニオンのタイプ産地に露出した ホースシューキャニオン累層
Albertosaurus sarcophagus の大半の化石はアルバータ州の上部ホースシューキャニオン累層から産出しており、これらの新しい地層のユニットは7000万年前から6800万年前の後期白亜紀末期にあたるマーストリヒチアンに属する。この層の直下には西部内陸海路を代表する海成層であるベアパウ頁岩が横たわる。西部内陸海路は白亜紀末に向けて気候が寒冷化するとともに海退が起こり、かつて海中であった陸地が露出することとなった。ただしこの過程はスムーズに進んだわけではなく、完全な海退が起こるまでに海路は海面上昇を起こして周期的にホースシューキャニオンの一部領域を覆っていた。海水面変動のため、ホースシューキャニオン累層の環境は目まぐるしく変化し、沖合や沿岸の海洋生息域、ラグーン、河口、干潟などが出現した。また、無数の炭層の存在から、当時炭田湿地が存在したことが示唆されている。同じ層から産出する他の大半の脊椎動物化石と同様に、アルバートサウルスの化石はホースシューキャニオンの後半の時代に三角州と氾濫原に堆積したと判明している[62]。
恐竜を含む脊椎動物化石が極めて一般に産出するため、ホースシューキャニオン累層の動物相は研究が進んでいる。サメ、エイ、チョウザメ、アミア・カルヴァ、ガー、ガーに似たアスピドリンクスが魚類相を形成した。哺乳類には多丘歯目や有袋類のディデルフォドンがいた。首長竜のレウロスポンディルスがホースシューキャニオンの海洋堆積物から発見されている一方、淡水環境にはカメやチャンプソサウルス、レイディオスクスやスタンゲロチャンプサといったワニが生息していた。恐竜は動物相を支配し、特にエドモントサウルスやサウロロフス、ヒパクロサウルスといったハドロサウルス科恐竜は全ての恐竜の半分を占めた。角竜とオルニトミムス科もまた非常にありふれており、合計で動物相の三分の一を占めた。アンキロサウルス科やパキケファロサウルス科はこれらと比較すれば希少であり、これらの動物は全てトロオドン科、ドロマエオサウルス科、カエナグナトゥス科を含む多様な肉食性獣脚類の餌食になっていたと考えられている[62][63]。ドライ・アイランドのボーンベッドにはアルバートサウルスの化石とともに小さなアルバートニクスの骨が発見されている[64]。成体のアルバートサウルスはこの環境における頂点捕食者で、小型獣脚類との中間的な生態的地位はおそらくアルバートサウルスの幼体が占めていた[62]。
生活史[編集]
これまで知られているアルバートサウルスの個体の大半は14歳前後で死亡している。幼体は滅多に化石として発見されないが、これは主に幼体の小さな骨は成体の大きな骨よりも化石化により保存されにくいという保存バイアス、小さな骨歯フィールドで収集者が気付きにくいという収集バイアスによる[48]。若いアルバートサウルスは動物の幼体としては比較的大型であるが、成体と比較すると化石記録はそれでも希少である。この現象はバイアスではなくアルバートサウルスの生活史によるもので、単純に幼体が成体ほど頻繁に死ぬことはなかったからであるとする見解もある[8]。 群れで大量死したものの、幼体は体が小さく繊細な構造であったため化石記録に保存されなかった、とする生活史仮説もある。わずか2年後には、幼体は成体のアルバートサウルスを除いてその地域のどの捕食動物よりも大型で、大半の獲物より俊足の捕食動物に成長した。これにより幼体の脂肪質が劇的に低下し、そのまま化石の希少性に繋がったという。死亡率は12歳で倍加するが、これはおそらく急成長段階の生理的要求の結果である。14歳から16歳の間の性成熟を迎えるとともに死亡率は再び倍増した。成体はその後も死亡率が上昇し、これはおそらく交配や資源を巡る種内競争で受けるストレスや負傷などの生理的要求、最終的には老化の影響である。成体の死亡率が高いと、化石が多く保存されていることにも説明がつく。非常に大型の動物はそのような体躯に達するまで生き残る個体が少ないため希少である。まとめると、生まれた直後の死亡率が高く、幼体の時期に死亡率が低下し、成体で急激に増大し、ごく少数のみが最大サイズに達するということになる。そのような動物にはゾウやアフリカスイギュウやサイなどの大型哺乳類が該当する。同様のパターンはティラノサウルス科でも確認できる。現生哺乳類と他のティラノサウルス科の比較はこの生活史仮説を支持しているが、全てのアルバートサウルスの三分の二を超える数が同じ産地から産出している以上、化石記録のバイアスもまだ大きな要因の一つである[8][33][49]。群れ[編集]


古病理学[編集]

古生態学[編集]

論文[編集]
記載論文[編集]
- Osborn, Henry F. (1905). “Tyrannosaurus and other Cretaceous carnivorous dinosaurs”. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History (American Museum of Natural History) 21 (3): 259–265. doi:10.5281/ZENODO.1038222. hdl:2246/1464.

- Parks, William A. (1928). “Albertosaurus arctunguis, a new species of therapodous dinosaur from the Edmonton Formation of Alberta”. University of Toronto Studies, Geological Series 25: 1–42.
脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
- ^ ある種の属を移動し、種小名と移動後の属名を組み合わせて作られた、新たな学名(種名)
出典[編集]
(一)^ abFossilworks, Age range: 70.6 to 66.043 Ma.
(二)^ abcdeOsborn, 1905.
(三)^ GBIF: A. arctunguis.
(四)^ GBIF: Gorgosaurus libratus.
(五)^ GBIF: A. libratus.
(六)^ abcdRussell, Dale A. (1970). “Tyrannosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of western Canada”. National Museum of Natural Sciences Publications in Paleontology 1: 1–34.
(七)^ abcdefHoltz, Thomas R. (2004). “Tyrannosauroidea”. In David B. Weishampel; Peter Dodson; Osmólska, Halszka. The Dinosauria (Second ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 111–136. ISBN 978-0-520-24209-8
(八)^ abcdefghiErickson, Gregory M.; Currie, Philip. J.; Inouye, Brian D.; Wynn, Alice A. (2006). “Tyrannosaur life tables: an example of nonavian dinosaur population biology”. Science 313 (5784): 213–217. doi:10.1126/science.1125721. PMID 16840697. オリジナルの2010-07-18時点におけるアーカイブ。 2010年8月29日閲覧。.
(九)^ abcdErickson, Gregory M.; Makovicky, Peter J.; Currie, Philip J.; Norell, Mark A.; Yerby, Scott A.; Brochu, Christopher A. (2004). “Gigantism and comparative life-history parameters of tyrannosaurid dinosaurs”. Nature 430 (7001): 772–775. doi:10.1038/nature02699. PMID 15306807. オリジナルの2011-10-06時点におけるアーカイブ。 2010年8月29日閲覧。.
(十)^ Christiansen, Per; Fariña, Richard A. (2004). “Mass prediction in theropod dinosaurs”. Historical Biology 16 (2–4): 85–92. doi:10.1080/08912960412331284313.
(11)^ Thulborn, Richard A. (1982). “Speeds and gaits of dinosaurs”. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 38 (3–4): 227–256. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(82)90005-0.
(12)^ abcdeCurrie, Philip J. (1998). “Possible evidence of gregarious behaviour in tyrannosaurids”. Gaia 15: 271–277. オリジナルの2009-03-26時点におけるアーカイブ。 2009年5月3日閲覧。.
(13)^ abcBell, Phil; E. Campione, Nicolás; Scott Persons, W; J. Currie, Philip; Larson, Peter; Tanke, Darren; T. Bakker, Robert (2017-06-01). “Tyrannosauroid integument reveals conflicting patterns of gigantism and feather evolution”. Biology Letters 13 (6): 20170092. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2017.0092. PMC 5493735. PMID 28592520.
(14)^ abcCurrie, Philip J. (2003). “Allometric growth in tyrannosaurids (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of North America and Asia”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 40 (4): 651–665. doi:10.1139/e02-083.
(15)^ Reichel, Miriam (2010). “The heterodonty of Albertosaurus sarcophagus and Tyrannosaurus rex: biomechanical implications inferred through 3-D models”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1253–1261. doi:10.1139/e10-063.
(16)^ Jovanelly, Tamie J.; Lane, Lesley (September 2012). “Comparison of the Functional Morphology of Appalachiosaurus and Albertosaurus”. The Open Geology Journal 6 ((1)): 65–71. doi:10.2174/1874262901206010065.
(17)^ "Albertosaurus." In: Dodson, Peter; Britt, Brooks; Carpenter, Kenneth; Forster, Catherine A.; Gillette, David D.; Norell, Mark A.; Olshevsky, George; Parrish, J. Michael; & Weishampel, David B. The Age of Dinosaurs. Lincolnwood, Illinois: Publications International, Ltd., 1993. pp. 106–107. ISBN 0-7853-0443-6.
(18)^ “歯科英語” (PDF). 千葉大学大学院医学研究院 腔内科学講座、千葉大学医学部付属病院 歯科・顎・口腔外科. p. 262. 2021年5月23日閲覧。
(19)^ abcdefgAbler, W.L. 2001. A kerf-and-drill model of tyrannosaur tooth serrations. p. 84–89. In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life. Ed.s Tanke, D. H., Carpenter, K., Skrepnick, M. W. Indiana University Press.
(20)^ ab“-saurus” (English). Online Etymology Dictionary. 2021年5月16日閲覧。
(21)^ “sarcophagus”. 英辞郎 on the WEB. アルク. 2021年5月16日閲覧。
(22)^ abcdCurrie, Philip J. (2003). “Cranial anatomy of tyrannosaurids from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta”. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 48 (2): 191–226.
(23)^ abTanke, Darren H.; Currie, Philip J. (2010). “A history of Albertosaurus discoveries in Alberta, Canada”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1197–1211. doi:10.1139/e10-057.
(24)^ Cope, Edward D. (1892). “On the skull of the dinosaurian Laelaps incrassatus Cope”. American Philosophical Society, Proceedings 30: 240-245.
(25)^ Hay, Oliver Perry (1902), “Bibliography and Catalogue of the Fossil Vertebrata of North America”, Bulletin of the United States Geological Survey (Government Printing Office) (117): 868
(26)^ Lambe, L.M. (1903). “On the lower jaw of Dryptosaurus incrassatus (Cope)”. Ottawa Naturalist 17: 134.
(27)^ Lambe, Lawrence M. (1904). “On Dryptosaurus incrassatus (Cope) from the Edmonton Series of the Northwest Territory”. Contributions to Canadian Palaeontology 3: 1–27 2010年8月29日閲覧。.
(28)^ Carr, Thomas D. (2010). “A taxonomic assessment of the type series of Albertosaurus sarcophagus and the identity of Tyrannosauridae (Dinosauria, Coelurosauria) in the Albertosaurus bonebed from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation (Campanian–Maastrichtian, Late Cretaceous”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1213–1226. doi:10.1139/e10-035.
(29)^ Eberth, David A.; Currie, Philip J. (2010). “Stratigraphy, sedimentology, and taphonomy of the Albertosaurus bonebed (upper Horseshoe Canyon Formation; Maastrichtian), southern Alberta, Canada”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1119–1143. doi:10.1139/e10-045.
(30)^ Carpenter, K., 1992, "Tyrannosaurids (Dinosauria) of Asia and North America", In: N. Mateer and P.-J. Chen (eds.) Aspects of nonmarine Cretaceous geology. China Ocean Press, Beijing, China, pp. 250–268
(31)^ Parks, 1928.
(32)^ Lambe, Lawrence M. (1914). “On a new genus and species of carnivorous dinosaur from the Belly River Formation of Alberta, with a description of the skull of Stephanosaurus marginatus from the same horizon”. Ottawa Naturalist 28: 13–20.
(33)^ abcRicklefs, Robert E. (2007). “Tyrannosaur ageing”. Biology Letters 3 (2): 214–217. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2006.0597. PMC 2375931. PMID 17284406.
(34)^ abCarr, Thomas D.; Williamson, Thomas E.; Schwimmer, David R. (2005). “A new genus and species of tyrannosauroid from the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian) Demopolis Formation of Alabama”. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 25 (1): 119–143. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0119:ANGASO]2.0.CO;2.
(35)^ Riabinin, A.N. (1930). “[In Russian] "On the age and fauna of the dinosaur beds on the Amur River”. Memoirs of the Russian Mineralogical Society 59 (2): 41–51.
(36)^ Von Huene, F., 1932 Die fossile Reptil-Ordnung Saurischia: ihre Entwicklung und Geschichte. Monographie für Geologie und Palaeontologie, Parts I and II, ser. I, 4: 1-361
(37)^ abPaul, Gregory S. (1988). Predatory Dinosaurs of the World. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-61946-6
(38)^ Olshevsky, George. (1995). “(The origin and evolution of the tyrannosaurids.)” (Japanese). Kyoryugaku Saizensen (Dino Frontline) 9: 92–119.
(39)^ Mader, B.; Bradley, R. (1989). “A redescription and revised diagnosis of the syntypes of the Mongolian tyrannosaur Alectrosaurus olseni”. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 9 (1): 41–55. doi:10.1080/02724634.1989.10011737.
(40)^ Matthew, W.D.; Brown, B. (1922). “The family Deinodontidae, with notice of a new genus from the Cretaceous of Alberta”. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 46 (6): 367–385.
(41)^ Kuhn, O., 1939 Saurischia — Fossilium catalogus I, Animalia, Pars 87. 's-Gravenhage, W. Junk, 1939, 124 pp
(42)^ abCurrie, Philip J.; Hurum, Jørn H; Sabath, Karol (2003). “Skull structure and evolution in tyrannosaurid phylogeny”. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 48 (2): 227–234. オリジナルの26 March 2009時点におけるアーカイブ。 2009年5月3日閲覧。.
(43)^ Holtz, Thomas R. (2005年9月20日). “RE: Burpee Conference (LONG)”. 2007年6月18日閲覧。
(44)^ Loewen, M.A.; Irmis, R.B.; Sertich, J.J.W.; Currie, P. J.; Sampson, S. D. (2013). Evans, David C. ed. “Tyrant Dinosaur Evolution Tracks the Rise and Fall of Late Cretaceous Oceans”. PLoS ONE 8 (11): e79420. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079420. PMC 3819173. PMID 24223179.
(45)^ Erickson, Gregory M.; Curry Rogers, Kristi; Varricchio, David J.; Norell, Mark.; Xu, Xing (2007). “Growth patterns in brooding dinosaurs reveals the timing of sexual maturity in non-avian dinosaurs and genesis of the avian condition”. Biology Letters 3 (5): 558–561. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2007.0254. PMC 2396186. PMID 17638674.
(46)^ abcLee, Andrew H.; Werning, Sarah (2008). “Sexual maturity in growing dinosaurs does not fit reptilian growth models”. PNAS 105 (2): 582–587. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708903105. PMC 2206579. PMID 18195356.
(47)^ Buckley, Lisa G.; Larson, Derek W.; Reichel, Miriam; Samman, Tanya (2010). “Quantifying tooth variation within a single population of Albertosaurus sarcophagus (Theropoda: Tyrannosauridae) and implications for identifying isolated teeth of tyrannosaurids”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1227–1251. doi:10.1139/e10-029.
(48)^ abcRoach, Brian T.; Brinkman, Daniel T. (2007). “A reevaluation of cooperative pack hunting and gregariousness in Deinonychus antirrhopus and other nonavian theropod dinosaurs”. Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History 48 (1): 103–138. doi:10.3374/0079-032X(2007)48[103:AROCPH]2.0.CO;2.
(49)^ Erickson, Gregory M.; Currie, Philip J.; Inouye, Brian D.; Winn, Alice A. (2010). “A revised life table and survivorship curve for Albertosaurus sarcophagus based on the Dry Island mass death assemblage”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1269–1275. doi:10.1139/e10-051.
(50)^ Eberth, David A.; McCrea, Richard T. (2001). “Were large theropods gregarious?”. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 21 (Supplement to 3 – Abstracts of Papers, 61st Annual Meeting of the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology): 46A. doi:10.1080/02724634.2001.10010852.(published abstract only)
(51)^ Horner, John R. (1997). “Behavior”. In Philip J. Currie; Padian, Kevin. Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 45–50. ISBN 978-0-12-226810-6
(52)^ Maxwell, W. Desmond; Ostrom, John H. (1995). “Taphonomy and paleobiological implications of Tenontosaurus-Deinonychus associations”. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 15 (4): 707–712. doi:10.1080/02724634.1995.10011256.
(53)^ Raath, Michael A. (1990). “Morphological variation in small theropods and its meaning in systematics: evidence from Syntarsus rhodesiensis”. In Kenneth Carpenter; Currie, Philip J.. Dinosaur Systematics: Approaches and Perspectives. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 91–105. ISBN 978-0-521-43810-0
(54)^ Coria, Rodolfo A.; Currie, Philip J. (2006). “A new carcharodontosaurid (Dinosauria, Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of Argentina”. Geodiversitas 28 (1): 71–118. オリジナルの2009-03-26時点におけるアーカイブ。 2009年5月3日閲覧。.
(55)^ Currie, Philip J.; Trexler, David; Koppelhus, Eva B.; Wicks, Kelly; Murphy, Nate (2005). “An unusual multi-individual tyrannosaurid bonebed in the Two Medicine Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) of Montana (USA)”. In Kenneth Carpenter. The Carnivorous Dinosaurs. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. pp. 313–324. ISBN 978-0-253-34539-4
(56)^ Auffenberg, Walter (2000). The Behavioral Ecology of the Komodo Monitor. Gainesville: University Press of Florida. ISBN 978-0-8130-0621-5
(57)^ Currie, Philip J.; Eberth, David A. (2010). “On gregarious behavior in Albertosaurus”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1277–1289. doi:10.1139/e10-072.
(58)^ abWolff, Ewan D. S.; Salisbury, Steven W.; Horner, John R.; Varricchio, David J. (2009). Hansen, Dennis Marinus. ed. “Common avian infection plagued the tyrant dinosaurs”. PLoS ONE 4 (9): e7288. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007288. PMC 2748709. PMID 19789646.
(59)^ Rothschild, B., Tanke, D. H., and Ford, T. L., 2001, Theropod stress fractures and tendon avulsions as a clue to activity: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 331–336.
(60)^ Molnar, R. E., 2001, Theropod paleopathology: a literature survey: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 337–363.
(61)^ Bell, Phil R. (2010). “Palaeopathological changes in a population of Albertosaurus sarcophagus from the Upper Cretaceous Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1263–1268. doi:10.1139/e10-030.
(62)^ abcEberth, David A. (1997). “Edmonton Group”. In Philip J. Currie; Padian, Kevin. Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 199–204. ISBN 978-0-12-226810-6
(63)^ Larson, Derek W.; Brinkman, Donald B.; Bell, Phil R. (2010). “Faunal assemblages from the upper Horseshoe Canyon Formation, an early Maastrichtian cool-climate assemblage from Alberta, with special reference to the Albertosaurus sarcophagus bonebed”. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (9): 1159–1181. doi:10.1139/e10-005.
(64)^ Longrich, Nicholas R.; Currie, Philip J. (2009). “Albertonykus borealis, a new alvarezsaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Early Maastrichtian of Alberta, Canada: Implications for the systematics and ecology of the Alvarezsauridae”. Cretaceous Research 30 (1): 239–252. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2008.07.005.

関連項目[編集]
●1905年の古生物学 - 本属が記載された年における古生物学上の事象。 ●本属および模式種の記載者 - ヘンリー・フェアフィールド・オズボーン。 ●本属が生存した地質年代 - マーストリヒチアン。 ●本属が棲息していた陸地 (1) 西部内陸海路︵ナイオブララ海︶消滅以前 - ララミディア大陸︵アラスカを含む現在の北アメリカ大陸西部地域の前身︶。 (2) 西部内陸海路が閉じてゆく時代 - 北アメリカ大陸。約4000万年ぶりに陸続きになっていった旧ララミディア大陸︵現・北アメリカ大陸西部地域︶・旧アパラチア大陸︵現・北アメリカ大陸南東部地域︶・旧フランクリニア大陸﹇Franklinia. 現・北アメリカ大陸北部地域︶。 ●本属の化石を産出した地層 - ホースシューキャニオン累層、ほか。 ●恐竜の一覧 ●絶滅した動物一覧外部リンク[編集]
●“†Albertosaurus Osborn 1905 (Alberta lizard)”. Fossilworks. John Alroy. 2021年5月18日閲覧。 ●“†Albertosaurus sarcophagus Osborn 1905 (Alberta lizard)”. Fossilworks. 2021年5月18日閲覧。 ●“†Albertosaurus Osborn 1905 (Alberta lizard)”. Paleobiology Database(PBDB). 2021年5月18日閲覧。 ●“†Albertosaurus sarcophagus Osborn 1905 (Alberta lizard)”. PBDB. 2021年5月18日閲覧。 ●“Albertosaurus Osborn, 1905”. 地球規模生物多様性情報機構 (GBIF). 2021年5月22日閲覧。 ●“Albertosaurus arctunguis Parks”. GBIF. 2021年5月22日閲覧。※ただし、タイプ種と同定するのが現在の定説。 ●“Albertosaurus libratus Lambe, 1914”. GBIF. 2021年5月22日閲覧。※Gorgosaurus libratus を本属の1種とする説に基づく。 ●cf. ** “Gorgosaurus libratus Lambe, 1914”. GBIF. 2021年5月22日閲覧。 ●“Albertosaurus sarcophagus Osborn, 1905”. GBIF. 2021年5月22日閲覧。※タイプ種。 ●“Genus †Albertosaurus Osborn, 1905 (dinosaur)”. Taxonomicon. 2021年5月22日閲覧。 ●“Albertosaurus†”. Mindat.org. Hudson Institute of Mineralogy. 2021年5月18日閲覧。















