呼吸困難
| 呼吸困難 | |
|---|---|
| 別称 | 息切れ |
 | |
| 発音 | Dyspnea: /dɪspˈniːə/; #語源・発音も参照 |
| 概要 | |
| 診療科 | 呼吸器学 |
| 分類および外部参照情報 | |
| Patient UK | 呼吸困難 |
呼吸困難︵こきゅうこんなん︶は、一般的には息切れ︵Shortness of Breath: SOB︶とも呼ばれ、十分に呼吸ができていない不快な感覚を指す。アメリカ英語では、"dyspnea" 、イギリス英語では"dyspnoea" と綴りが異なる。アメリカ胸部疾患学会は、呼吸困難の定義を﹁強さは様々だが、いつもと違う感覚より成る、主観的な呼吸愁訴﹂
A subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity
—American Thoracic Society
とし、呼吸困難の評価として、そのいつもと違う感覚の強度、苦痛や不快感の程度、患者の日常生活動作 ︵ADL︶に対する負担や影響を評価することを推奨している。﹁いつもと違う﹂感覚には、呼吸自体に努力が要る、胸の締め付け感や痛み、﹁空気飢餓感﹂︵酸素が足りないという感覚︶などがある[1]。前傾で肩で息をしている状態︵三脚位、tripod position︶は、しばしばその徴候であると想定される。
呼吸困難は、激しい肉体運動の際に生じる正常な症状でもあるが、予期せぬ状況、安静時や軽い運動時に生じると病的なものとなる[2]。85%の症例では、喘息、肺炎、心筋虚血、間質性肺疾患、うっ血性心不全、慢性閉塞性肺疾患、またはパニック障害や不安[3]などの心因性原因に起因する[2][4]。息切れを緩和し、あるいは取り除くための最善の治療法は通常、根本原因により異なる[5][6]。
定義[編集]
呼吸困難とは、﹁息切れ﹂を意味する医学用語である。アメリカ胸部疾患学会は、呼吸困難を﹁強さは様々だが、いつもと違う感覚より成る、主観的な呼吸愁訴﹂と定義している[7]。 他の定義では、﹁息をするのが難しい﹂︵difficulty in breathing︶[8]、﹁乱れたまたは不十分な呼吸﹂︵disordered or inadequate breathing︶[9]、﹁呼吸不快感の自覚﹂︵uncomfortable awareness of breathing︶[4]、または﹁息切れ﹂︵breathlessness︶の経験であり、急性、慢性、いずれもあり得ると記述されている[2][6][10]。鑑別診断[編集]
「呼吸困難の原因一覧」を参照
呼吸困難は一般的に循環器系や呼吸器系の障害によって引き起こされるが、神経系[11]、筋骨格系、内分泌系、造血系、精神系などの他の疾患が原因となっている場合もある[12]。オンライン医療エキスパートシステムであるDiagnosisProは2010年10月に497の異なる原因を挙げている[13]。最も一般的な心血管系の原因は急性心筋梗塞とうっ血性心不全であり、一般的な肺の原因は慢性閉塞性肺疾患、喘息、気胸、肺水腫、肺炎である[2]。病態生理学的には、原因は、︵1︶不安発作などの通常の呼吸に対する意識の高まり、︵2︶呼吸努力の増大、︵3︶換気または呼吸器系の異常[11]に分けることができる。
呼吸困難の病因を知るには、発症の速さと呼吸困難の持続時間が有用である。急性の呼吸困難は、通常、喉頭浮腫、気管支痙攣、心筋梗塞、肺塞栓症、気胸などの急激な生理的変化と関連している。COPDや特発性肺線維症︵IPF︶の患者は、労作時の呼吸困難が軽度から徐々に進行し、呼吸困難の急性増悪に至る。一方、喘息患者の多くは日常的な症状はないが、呼吸困難、咳、胸部圧迫感などの間欠的なエピソードがあり、通常、上気道感染やアレルゲンへの暴露などの特定の誘因に関連している[14]。
急性冠症候群︵Acute Coronary Syndrome: ACS︶[編集]
急性冠症候群は、後胸部不快感や息苦しさを訴えることが多いが[2]、非典型的に呼吸困難だけで発症することもある[15]。危険因子は、高齢、喫煙、高血圧、高脂血症、糖尿病である[15]。診断と治療の方向付けには、心電図と心筋酵素が重要である[15]。 治療には心臓の酸素要求量を下げる対策と冠血流量を増やす努力が含まれる[2]。COVID-19[編集]
詳細は「COVID-19」を参照
COVID-19に感染した人は、発熱、乾性咳嗽、嗅覚や味覚の低下といった症状を呈し、中等度から重度の場合は呼吸困難などの症状がある場合がある。
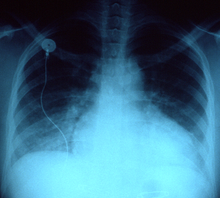
X線写真前後像上の拡大した心臓のシルエットは、慢性的な高血圧が左 心室に与える影響によるうっ血性心不全によるものである。心臓は肥大し、胸水が貯留し、肺うっ血を呈している。
うっ血性心不全は、労作時の呼吸困難、起坐呼吸︵寝ると息苦しくなるために座っている︶、発作性夜間呼吸困難などを頻繁に呈する[2]。米国の一般人口の1~2%が発症し、65歳以上では10%が発症している[2][15]。 急性非代償性心不全の危険因子には、食塩摂取過多、薬を処方通りに内服しない、心筋虚血、不整脈、腎不全、肺塞栓、高血圧、感染症などがある[15]。治療努力は肺うっ血の減少を目指すことになる[2]。
うっ血性心不全[編集]

慢性閉塞性肺疾患[編集]
慢性閉塞性肺疾患︵COPD︶、特に肺気腫や慢性気管支炎の患者は、慢性的な呼吸困難や湿性咳嗽を伴うことが多い[2]。急性増悪時は息切れが増悪し、喀痰が増える[2]。COPDは肺炎の危険因子であるため、この状態︵急性増悪︶を除外する必要がある[2]。急性増悪時の治療は、抗コリン薬、β2アドレナリン受容体作動薬、ステロイド、場合によっては人工呼吸器、これらを組み合わせることによる[2]。気管支喘息[編集]
喘息は、呼吸困難で救急外来を受診する最も一般的な理由である[2]。発展途上国・先進国共に最も多い肺疾患であり、人口の約5%が罹患している[2]。その他の症状には喘鳴、胸のつかえ、乾性咳嗽がある[2]。小児の治療には吸入コルチコステロイドが望ましい。しかしこれらの薬剤は成長速度を下げる[16]。急性症状は短作用性気管支拡張剤で治療する[17]。
気胸[編集]
詳細は「気胸」を参照
気胸は、典型的には急性発症の胸膜炎性胸痛と酸素吸入で改善しない呼吸困難を呈する[2]。 身体所見は、片側の胸部の呼吸音の消失、頚静脈怒張、気管の偏位がある[2]。
肺炎[編集]
肺炎の症状は、発熱、湿性咳嗽、呼吸困難、胸膜痛である[2]。診察時に吸気時の湿性ラ音が聞こえることがある[2]。肺炎とうっ血性心不全を区別するには、胸部X線が役に立つ[2]。原因は通常細菌感染なので、通常治療に抗生剤が用いられる[2]。肺塞栓症[編集]
肺塞栓症は、典型的には急性に発症する呼吸困難を呈する[2]。その他の症状としては、胸膜炎様の胸痛、咳、喀血、発熱などがある[2]。危険因子としては、深部静脈血栓症、最近の手術、がん、血栓塞栓症の既往が挙げられる[2]。 死亡リスクが高いため急性呼吸困難の発症時には必ず考慮しなければならない[2]。しかし診断は困難な場合もある[2]ので、ウェルズ・スコアを使った臨床確率の評価がよく行われている。治療は、症状の重症度に応じて、通常、抗凝固剤から開始する。危険な徴候︵低血圧︶がある場合は、血栓溶解療法が行われることがある[2]。貧血[編集]
徐々に進行する貧血は、通常、労作時呼吸困難、疲労、脱力、頻脈を呈する[18]。 心不全に至る場合もある[18]。貧血はしばしば呼吸困難の原因である。月経は、特に過多の場合、貧血の原因となり、女性では結果的に呼吸困難の原因となることがある。頭痛も貧血患者における呼吸困難の症状である。また、酸素と圧力の不足により目の奥が低血圧になり、視界がぼやけるという患者もいる。これらの患者はひどい頭痛を訴え、脳に障害を残すことすらある。症状としては、集中力の低下、疲労、言語能力障害、記憶力の低下などがある[19]。がん[編集]
呼吸困難は、がん患者にはよくあることで、多くの異なる要因によって引き起こされる可能性がある。進行がんの患者では、より継続的な呼吸困難の感覚とともに、激しい呼吸困難のエピソードがあることがある[20]。その他[編集]
呼吸困難の他の重要なまたは一般的な原因には、心タンポナーデ、アナフィラキシー、間質性肺炎、パニック発作[6][12][18]、肺高血圧症がある。また、女性の約2/3が正常な妊娠の症状の一部として息切れを経験する[9]。 心タンポナーデは、呼吸困難、頻脈、頸静脈圧上昇、奇脈︵吸気時の収縮期血圧低下が10mmHg以上となる︶を呈する[18]。診断のゴールドスタンダードは心臓超音波検査である[18]。 アナフィラキシーは通常、既往のある人に数分で発症する[6]。その他の症状としては、蕁麻疹、血管性浮腫︵上気道浮腫を伴う︶、胃腸の不調などがある[6]。主な治療法はエピネフリンである[6]。 間質性肺炎は、典型的には、素因となる環境暴露の既往があり、呼吸困難は緩徐に悪化していく[12]。 頻脈性不整脈を有する患者では、呼吸困難が唯一の症状であることが多い[15]。 パニック発作は、典型的には過呼吸、発汗、パレステジア︵異常感覚︶を呈する[6]が、これらは除外診断である[12]。 脊髄損傷、横隔神経損傷、ギラン・バレー症候群、筋萎縮性側索硬化症、多発性硬化症、筋ジストロフィーなどの神経疾患は、すべて呼吸困難の原因となり得る[11]。また、声帯機能障害の結果、呼吸困難が生じることもある[21]。 サルコイドーシスは、一般に乾性咳嗽、疲労、呼吸困難を呈する原因不明の炎症性疾患であるが、複数の臓器系が侵され、目、皮膚、関節などの部位が侵されることがある[22]。病態生理[編集]
酸感受性イオンチャネル化学受容器、機械受容器、肺内受容体など、異なる生理学的経路が呼吸困難に介在している可能性がある[15]。 呼吸困難は、求心性信号、遠心性信号、中枢の情報処理という3つの要素で構成されていると考えられている。脳の中央処理では、求心性信号と遠心性信号を比較し、換気の必要性︵求心性信号︶が実際の呼吸︵遠心性信号︶によって満たされない場合など、両者の間に﹁ミスマッチ﹂が生じた場合に呼吸困難を生じると考えられている[23][要ページ番号]。 求心性信号は、脳に到達する感覚神経信号である。呼吸困難に重要な求心性ニューロンは、頸動脈小体、延髄、肺、胸壁筋を含む多数の起点として生じる。頸動脈小体および延髄の化学受容体は、O2、CO2およびH+の血液ガス中の濃度に関する情報を提供する[24]。肺では、傍毛細血管受容体︵J受容体︶が肺の間質性浮腫に敏感で、伸張受容体は気管支収縮を知らせる。胸壁の筋紡錘は、呼吸筋の伸張と緊張を知らせるものである。したがって、高炭酸ガス血症につながる換気不良、肺の間質性浮腫︵ガス交換の障害︶につながる左心不全、気管支攣縮︵気流の制限︶につながる喘息、および呼吸筋の非効率な動作につながる筋肉疲労はすべて、呼吸困難の感覚の原因となる可能性がある[23][要ページ番号]。 遠心性信号は、呼吸筋に下降する運動神経信号である。呼吸筋の中で最も重要なのは横隔膜である。その他の呼吸筋には、外肋間筋と内肋間筋、腹筋、副呼吸筋がある[25]。 脳は換気に関する豊富な求心性情報を受け取ると、遠心性信号によって決定される現在の呼吸レベルと比較することができる。呼吸のレベルが身体の状態に対して不適切な場合、呼吸困難が生じる可能性がある。また、呼吸困難には心理的な要素もあり、そのような状況で呼吸を意識しても、呼吸困難の典型的な苦痛を感じない人もいる[23][要ページ番号]。診断[編集]
初期アプローチは、蘇生のABC、すなわち気道︵Airway︶、呼吸︵Breathing︶、循環︵Circulation︶の評価から始まり[注釈 1]、病歴聴取と身体診察を行う[2]。 重大な重症度を示す徴候や症状には、低血圧、低酸素血症、気管偏位、意識レベルの変化、循環動態不安定な不整脈、吸気時喘鳴、陥没呼吸、チアノーゼ、前傾で肩で息をしている状態︵三脚位、tripod position︶、呼吸補助筋︵胸鎖乳突筋、斜角筋︶への顕著な依存、呼吸音の消失などがある[12]。 呼吸困難の程度を定量化するために、多くの尺度が用いられている[26]。主観的に1から10までの尺度で評価し、その数値に関連する記述子を付けることもある︵修正ボルグスケール︶[26]。MRC息切れスケール[編集]
| グレード | 息切れの程度 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 激しい運動をしたときだけ息切れがある |
| 1 | 平坦な道を早足で歩く,あるいはゆるやかな 上り坂を歩くときに息切れがある |
| 2 | 息切れがあるので,同年代の人よりも平坦な 道を歩くのが遅い,
あるいは平坦な道を自分 のペースで歩いているとき,息切れのために 立ち止まることがある |
| 3 | 平坦な道を約100m,あるいは数分歩くと息 切れのため立ち止まる |
| 4 | 息切れがひどく家から出られない,あるいは 衣服の着替えをするときにも息切れがある |
MRC息切れスケールは、呼吸困難が生じる状況や重症度に基づき5段階の呼吸困難を提案するものである[28]。国際的に普及している呼吸困難の評価尺度であり、日本でも改訂版の修正MRC息切れスケールが近年多くのガイドラインに取り入れられてきているが、学会やガイドライン間で訳に違いがあるため、どの日本語版を用いるべきかで臨床現場に混乱が生じてもいる[29]。
ヒュー・ジョーンズ分類[編集]
| グレード | 息切れの程度 |
|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 同年代の健常者と同様の生活・仕事ができ、階段も健常者なみにのぼれる |
| Ⅱ | 歩行は同年代の健常者並にできるが、階段の上り下りは健常者なみにできない |
| Ⅲ | 健常者なみに歩けないが、自分のペースで1km(または1マイル)程度の歩行が可能 |
| Ⅳ | 休みながらでなければ50m以上の歩行が不可能 |
| Ⅴ | 会話や着物の着脱で息がきれ、外出ができない |
日本で古くから利用されているものに、ヒュー・ジョーンズ分類︵Hugh-Jones分類︶がある[30][31]が、そもそもFletcherらが使っていた[30]ものなので、名称に疑義があるために国際的に通用しない分類であり、MRCスケールの使用が推奨されるようになってきている[29]。
血液検査[編集]
呼吸困難の原因を特定するために、多くの検査項目が参考になることがある。Dダイマーは、リスクの低い人の肺塞栓症を除外するのに有用であるが、呼吸困難につながる多くの疾患で陽性となる可能性があるため、陽性であってもあまり参考にならない[15]。脳性ナトリウム利尿ペプチド︵BNP︶の低値は鬱血性心不全を除外するのに効果があるが、高値は診断を支持するが、高齢、腎不全、急性冠症候群、大きな肺塞栓による可能性もある[15]。画像診断[編集]
胸部X線撮影は、気胸、肺水腫、肺炎の確認または除外に有用である[15]。放射線造影剤を静脈内投与するスパイラルCTは、肺塞栓症の評価に選択される画像検査である[15]。治療[編集]
呼吸困難の主な治療は、その根本的な原因に向けられる[6]。 低酸素症の患者には追加の酸素補給が有効であるが、血中酸素飽和度が正常な患者には効果がない[4][32]。理学療法[編集]
理学療法による介入も有益である[33]。神経/神経筋異常がある人は、換気に必要な肋間筋、腹筋および/またはその他の筋肉が弱いか麻痺しているために呼吸困難がある[34]。この集団に対するいくつかの理学療法介入には、積極的咳嗽補助[35]、息継ぎなどの換気量の増強[36]、体位と換気パターンに関する教育[37]、呼吸促進の動作戦略[36]などがある。呼吸器リハビリテーションは、COPD患者など一部の人の症状を緩和することはあるが、基礎疾患を治癒することはない[38][39]。顔面への扇風機療法︵手持ちの小型扇風機を顔に向ける︶は、がんを含むさまざまな進行性疾患の患者の呼吸困難を緩和することが示されている[40]。その作用機序は三叉神経への刺激と考えられている。緩和医療[編集]
全身投与の即放型オピオイドは、がんおよびがん以外の原因による呼吸困難の症状の重症度を迅速に軽減するのに有効である[4][41]。長時間作用型/徐放型オピオイドは、緩和領域における呼吸困難の予防/治療継続のためにも用いられる。ミダゾラム、ネブライザーによるオピオイド、混合ガスの使用、認知行動療法を推奨するエビデンスはまだない[42]。非薬物療法的手法[編集]
非薬理学的介入は呼吸困難の管理に重要な手段となる[20]。潜在的に有益なアプローチとしては、心理社会的問題︵不安、抑うつなど︶の積極的な管理、および自己管理戦略の実施、例えば、身体的および精神的リラックス法、ペーシング法、エネルギー節約法、呼吸制御エクササイズの学習、健康教育などがある[20]。扇風機の使用はおそらく有益と思われる[20]。認知行動療法も有益かもしれない[20]。薬物療法[編集]
重度、慢性、または制御不能な呼吸困難のある人には、呼吸困難を治療するための非薬理学的アプローチを薬物と併用することがある。呼吸困難の原因となっているがんを持つ患者に対しては、オピオイド、ベンゾジアゼピン、酸素、ステロイドなどの薬物療法が提案されている[20]。最近のシステマティック・レビューおよびメタアナリシスでは、オピオイドは進行がん患者の治療において必ずしも高い有効性と関連していないことがわかった[43][44]。 薬による副作用や有害作用と、薬による改善の可能性のバランスを、薬を処方する前に慎重に検討する必要があることを確認する[20]。がん患者の緩和ケアにおいて、副腎皮質ホルモンの全身投与はよく行われているが、成人がん患者におけるこのアプローチの有効性と潜在的な有害作用は十分に研究されていない[20]。疫学[編集]
米国では、救急外来を受診する人の3.5%が呼吸困難を主な原因としている。このうち約51%が入院し、13%が1年以内に死亡している[45]。入院患者の最大27%が呼吸困難を発症し[46]、死にゆく患者では75%が呼吸困難を経験するという研究もある[23] [要ページ番号]。急性呼吸困難は、姑息的治療を要する人が救急外来を訪れる最も多い理由である[4] 。進行がんの成人の最大70%も呼吸苦を呈する[20]。語源・発音[編集]
呼吸困難を意味する英語のdyspneaはラテン語のdyspnoea、ギリシャ語のdyspnoiaに由来し、文字通り﹁呼吸の乱れ﹂を意味する[12][47]。その結合辞︵dys- + -pnea︶は、機能障害dysfunction︵dys- + function︶や無呼吸 apnea︵a- + -pnea︶といった他の医学英語でおなじみである。医学英語での最も一般的な発音は、 [dɪspˈniːə] disp-NEE-əで、pが発音され、niː音節が強く発音される。しかし、pnのpが黙字である発音︵pneumo-も同様︶は一般的であり︵[dɪsˈniːə] または [ˈdɪsniə] ︶[48]、 また、最初に強音節があるもの︵[ˈdɪspniə]or[ˈdɪsniə] ︶もある[48]。 英語では、医学でよく用いられる様々な"-pnea"を接尾辞とする単語は、niːの音節とその前の音節のどちらが強調されるかについて、一つの明確なパターンに従っていない。pは通常発音されるが、単語によっては黙字となることがある。以下の照合表は、主要な辞書がどのように発音・表記しているかを示したものである︵あまり用いられない表記は省略︶。| 分類 | 医学用語 | 結合辞 | 主要辞書における主な発音 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 良い good | 正常呼吸 | eu- + -pnea | [juːpˈniːə] yoop-NEE-ə[49][50][48][51] |
| 悪い bad | 呼吸困難 | dys- + -pnea | [dɪspˈniːə] disp-NEE-ə,[50][51][52] [ˈdɪspniə] DISP-nee-ə[49][48] |
| 速い ast | 頻呼吸 | tachy- + -pnea | [ˌtækɪpˈniːə] TAK-ip-NEE-ə[49][50][48][51][52] |
| 遅い brady | 徐呼吸 | brady- + -pnea | [ˌbreɪdɪpˈniːə] BRAY-dip-NEE-ə[50][48][51] |
| 坐位の upright | 起坐呼吸 | ortho- + -pnea | [ɔːrˈθɒpniə] or-THOP-nee-ə,[50][48][52][49]:audio [ɔːrθəpˈniːə] or-thəp-NEE-ə[48][49]:print |
| 仰臥位の supine | 扁平呼吸 | platy- + -pnea | [pləˈtɪpniə] plə-TIP-nee-ə[49][50] |
| 前屈みの bent over | 前屈呼吸苦 | bend + -o- + -pnea | [bɛndˈɒpniə] bend-OP-nee-ə |
| 過度の excessive | 過呼吸 | hyper- + -pnea | [ˌhaɪpərpˈniːə] HY-pərp-NEE-ə[49][50][48][51] |
| 不十分な insufficient | 呼吸低下 | hypo- + -pnea | [haɪˈpɒpniə] hy-POP-nee-ə,[49][50][51][52] [ˌhaɪpəpˈniːə] high-pəp-NEE-ə[48][51] |
| 欠落した absent | 無呼吸 | a- + -pnea | [ˈæpniə] AP-nee-ə,[49][50][48][51][52]:US [æpˈniːə] ap-NEE-ə[48][51][52]:UK |
脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
- ^ 一般的な蘇生のアプローチは2023年現在はC、A、Bの順に変わってきているが、呼吸を原因とした急変に対する優先度はA、B、Cで良いであろう。
出典[編集]
(一)^ Donald A. Mahler; Denis E. O'Donnell (2014). Dyspnea: Mechanisms, Measurement, and Management, Third Edition. CRC Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4822-0869-6
(二)^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaaabac“Dyspnea”. Med. Clin. North Am. 90 (3): 453–79. (May 2006). doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2005.11.006. PMID 16473100.
(三)^ Mukerji, Vaskar (1990). “11”. Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea. Butterworth Publishers. ISBN 9780409900774. PMID 21250057. オリジナルの27 April 2018時点におけるアーカイブ。 2014年8月15日閲覧. "In addition, dyspnea may occur in febrile and hypoxic states and in association with some psychiatric conditions such as anxiety and panic disorder."
(四)^ abcde“Emergencies in palliative care”. Cancer J 16 (5): 514–20. (2010). doi:10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181f28a8d. PMID 20890149.
(五)^ Kelvin, Joanne Frankel (2011). 100 questions & answers about cancer symptoms and cancer treatment side effects. Leslie B. Tyson (2nd edition ed.). Sudbury, Massachusetts: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7637-7760-9. OCLC 499179391
(六)^ abcdefghZuberi, T. et al. (2009). “Acute breathlessness in adults”. InnovAiT 2 (5): 307–15. doi:10.1093/innovait/inp055.
(七)^ American Heart Society (1999). “Dyspnea mechanisms, assessment, and management: a consensus statement”. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 159 (1): 321–40. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.159.1.ats898. PMID 9872857.
(八)^ TheFreeDictionary Archived 2019-06-05 at the Wayback Machine., retrieved on Dec 12, 2009. Citing: The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition by Houghton Mifflin Company. Updated in 2009. Ologies & -Isms. The Gale Group 2008
(九)^ ab“Approach to the adult with dyspnea in the emergency department”. www.uptodate.com. UpToDate (2022年9月16日). 2023年4月12日閲覧。
(十)^ “Dyspnea – General Practice Notebook”. 2011年6月13日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2011年6月13日閲覧。
(11)^ abcFrownfelter, Donna; Dean, Elizabeth (2006). “8”. In Willy E. Hammon III. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy. 4. Mosby Elsevier. p. 139
(12)^ abcdef“Evaluation of the dyspneic patient in the office”. Prim. Care 33 (3): 643–57. (September 2006). doi:10.1016/j.pop.2006.06.007. PMID 17088153.
(13)^ “Differential Diagnosis for Dyspnea: Poisoning (Specific Agent)”. 2010年11月16日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2012年8月23日閲覧。
(14)^ D. L. Kasper et al. (ed), Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th edition (2018), p. 1943
(15)^ abcdefghijk“Evaluation of the acutely dyspneic elderly patient”. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 23 (2): 307–25, vi. (May 2007). doi:10.1016/j.cger.2007.01.007. PMID 17462519.
(16)^ “How Is Asthma Treated and Controlled?”. 2012年9月4日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2012年9月4日閲覧。
(17)^ Pollart, Susan M.; Compton, Rebekah M.; Elward, Kurtis S. (2011-07-01). “Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations” (英語). American Family Physician 84 (1): 40–47.
(18)^ abcde“Pitfalls in the evaluation of shortness of breath”. Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am. 28 (1): 163–81, ix. (February 2010). doi:10.1016/j.emc.2009.09.011. PMID 19945605.
(19)^ “Anemia Affects Body...And Maybe The Mind”. Johns Hopkins medicine (2006年). 2020年5月15日閲覧。
(20)^ abcdefghiHaywood, Alison; Duc, Jacqueline; Good, Phillip; Khan, Sohil; Rickett, Kirsty; Vayne-Bossert, Petra; Hardy, Janet R. (2019-02-20). “Systemic corticosteroids for the management of cancer-related breathlessness (dyspnoea) in adults”. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2: CD012704. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012704.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6381295. PMID 30784058.
(21)^ Ibrahim, Wanis H.; Gheriani, Heitham A.; Almohamed, Ahmed A.; Raza, Tasleem (2007-03-01). “Paradoxical vocal cord motion disorder: past, present and future” (英語). Postgraduate Medical Journal 83 (977): 164–72. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2006.052522. ISSN 1469-0756. PMC 2599980. PMID 17344570. オリジナルの2016-11-08時点におけるアーカイブ。.
(22)^ Bokhari, SRA; Zulfiqar, H; Mansur, A (January 2021). Sarcoidosis in StatPearls. PMID 28613460
(23)^ abcdHarrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Longo DL, et al. (eds)) (16th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
(24)^ “Dyspnea”. www.mywhatever.com. 2022年4月21日閲覧。
(25)^ “Unit V - Respiration”. www3.nd.edu. 2022年4月21日閲覧。
(26)^ abSaracino A (October 2007). “Review of dyspnoea quantification in the emergency department: is a rating scale for breathlessness suitable for use as an admission prediction tool?”. Emerg Med Australas 19 (5): 394–404. doi:10.1111/j.1742-6723.2007.00999.x. PMID 17919211.
(27)^ 中村 健、岡村正嗣、佐伯拓也 (2017). “特集 息切れのリハビリテーション 2 息切れの評価法”. The Japanese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 54: 941-946.
(28)^ Williams, N (2017-08-01). “The MRC breathlessness scale.”. Occupational Medicine (Oxford, England) 67 (6): 496–97. doi:10.1093/occmed/kqx086. PMID 28898975.
(29)^ ab宮本顕二 (2008). “MRC息切れスケールをめぐる混乱-いったいどのMRC息切れスケールを使えばよいのか?-”. 日本呼吸器学会雑誌 46: 593-600.
(30)^ abFletcher CM. The clinical diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema; an experimental study. Proc Royal Soc Med 45: 577-584, 1952.
(31)^ Hugh-Jones P, Lambert AV. A simple standard exercise test and its use for measuring exertion dyspnoea. Brit Med J 1: 65-71, 1951.
(32)^ Abernethy AP; McDonald CF; Frith PA et al. (September 2010). “Effect of palliative oxygen versus medical (room) air in relieving breathlessness in patients with refractory dyspnea: a double-blind randomized controlled trial”. Lancet 376 (9743): 784–93. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61115-4. PMC 2962424. PMID 20816546.
(33)^ Frownfelter, Donna; Dean, Elizabeth (2006). “8”. In Willy E. Hammon III. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy. 4. Mosby Elsevier
(34)^ Frownfelter, Donna; Dean, Elizabeth (2006). “22”. In Donna Frownfelter; Mary Massery. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy. 4. Mosby Elsevier. p. 368
(35)^ Frownfelter, Donna; Dean, Elizabeth (2006). “22”. In Donna Frownfelter; Mary Massery. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy. 4. Mosby Elsevier. pp. 368–71
(36)^ abFrownfelter, Donna; Dean, Elizabeth (2006). “32”. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy. 4. Mosby Elsevier. pp. 569–81
(37)^ Frownfelter, Donna; Dean, Elizabeth (2006). “23”. In Donna Frownfelter; Mary Massery. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy. 4. Mosby Elsevier
(38)^ Puhan, Milo A.; Gimeno-Santos, Elena; Cates, Christopher J.; Troosters, Thierry (2016-12-08). “Pulmonary rehabilitation following exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 12: CD005305. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005305.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6463852. PMID 27930803.
(39)^ Zainuldin, Rahizan; Mackey, Martin G.; Alison, Jennifer A. (2011-11-09). “Optimal intensity and type of leg exercise training for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014 (11): CD008008. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008008.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 8939846. PMID 22071841.
(40)^ Matsushima, Eisuke; Inoguchi, Hironobu; Uchitomi, Yosuke; Zenda, Sadamoto; Ogawa, Asao; Kinoshita, Hiroya; Sekimoto, Asuko; Kobayashi, Masamitsu et al. (2018-10-01). “Fan Therapy Is Effective in Relieving Dyspnea in Patients With Terminally Ill Cancer: A Parallel-Arm, Randomized Controlled Trial” (英語). Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 56 (4): 493–500. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.07.001. ISSN 0885-3924. PMID 30009968.
(41)^ “Evidence-based review of interventions to improve palliation of pain, dyspnea, depression”. Geriatrics 64 (8): 8–10, 12–14. (August 2009). PMID 20722311.
(42)^ DiSalvo, WM.; Joyce, MM.; Tyson, LB.; Culkin, AE.; Mackay, K. (Apr 2008). “Putting evidence into practice: evidence-based interventions for cancer-related dyspnea”. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 12 (2): 341–52. doi:10.1188/08.CJON.341-352. PMID 18390468.
(43)^ Feliciano, Josephine L.; Waldfogel, Julie M.; Sharma, Ritu; Zhang, Allen; Gupta, Arjun; Sedhom, Ramy; Day, Jeff; Bass, Eric B. et al. (2021-02-25). “Pharmacologic Interventions for Breathlessness in Patients With Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis” (英語). JAMA Network Open 4 (2): e2037632. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37632. ISSN 2574-3805. PMC 7907959. PMID 33630086.
(44)^ Dy, Sydney M.; Gupta, Arjun; Waldfogel, Julie M.; Sharma, Ritu; Zhang, Allen; Feliciano, Josephine L.; Sedhom, Ramy; Day, Jeff et al. (2020-11-19). Interventions for Breathlessness in Patients With Advanced Cancer. doi:10.23970/ahrqepccer232.
(45)^ Stephen J. Dubner; Steven D. Levitt (2009). SuperFreakonomics: Tales of Altruism, Terrorism, and Poorly Paid Prostitutes. New York: William Morrow. pp. 77. ISBN 978-0-06-088957-9
(46)^ Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 4th Ed. Robert J. Mason, John F. Murray, Jay A. Nadel, 2005, Elsevier
(47)^ “dyspnea” (英語), Wiktionary, (2022-04-21) 2022年4月21日閲覧。
(48)^ abcdefghijklMerriam-Webster, Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster.
(49)^ abcdefghiElsevier, Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary, Elsevier.
(50)^ abcdefghiWolters Kluwer, Stedman's Medical Dictionary, Wolters Kluwer, オリジナルの2015-09-25時点におけるアーカイブ。.
(51)^ abcdefghiHoughton Mifflin Harcourt, The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, オリジナルの2015-09-25時点におけるアーカイブ。.
(52)^ abcdefOxford Dictionaries, Oxford Dictionaries Online, Oxford University Press, オリジナルの2014-10-22時点におけるアーカイブ。.
参考文献[編集]
- medtoolz『レジデント初期研修資料 内科診療ヒントブック』(改訂第2版)オーム社、2012年11月25日。ISBN 9784274069048。
- Paul L. Marino 著、稲田英一 訳『ICUブック』(第4版)メディカルサイエンスインターナショナル、2015年11月30日。ISBN 4895928314。
関連項目[編集]
外部リンク[編集]
| 分類 | |
|---|---|
| 外部リソース(外部リンクは英語) |
