

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Shenyang Mandarin" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2006) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Shenyang Mandarin | |
|---|---|
| 瀋陽話 / 沈阳话 Shěnyánghuà | |
| Native to | China |
| Region | Shenyang |
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
cmn-she | |
| Glottolog | shen1252 |
Shenyang Mandarin (Chinese: 沈阳话) is a dialect of Northeastern Mandarin used by people in and around Shenyang, the capital of Liaoning province and the largest city in Northeast China. It is very close to Standard Chinese but has some notably distinctive words. Some people consider it a strong accent rather than a distinct dialect. Because of its similarity to the standard language, pinyin can be used to represent its pronunciation. Its usage is dwindling as schools in Shenyang teach only the standard language.
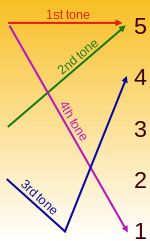
The most distinctive aspect of the Shenyang dialect is the much lower pitch of the first tone than in Standard Mandarin. It would be positioned at 2, rather than 5, on the chart shown (right). As a result, it can sound rather like the third tone.
Like the Beijing dialect, the Shenyang dialect is characterized by erhua (儿化).
Some of the words in the Shenyang dialect come from other languages like the Manchu language. One example is 旮旯儿 gālár 'corner'.
Examples of words in various Northeastern dialects (not necessarily specific to Shenyang) include:
| Northeastern Mandarin | pinyin | Standard Mandarin | pinyin | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不赶趟儿 | bù gǎntàngr | 来不及 | lái bù jí | too late |
| 波楞盖儿 | bōlingàr | 膝盖 | xīgài | kneecap |
| 疙瘩、圪塔[citation needed] | gāda | 地方 | dìfang | place (noun) |
| 得瑟 | dèse | 卖弄 | màinòng | to show off |
| 老鼻子(了) | lǎobízi(le) | 很多 | hěnduō | a lot |
| 驲驲地 | rírídi | (象声词:车速度快) | N/A | onomatopoeia: fast car |
| 埋汰 | máitai | 脏 | zāng | dirty, filthy |
| 嘎哈 | gàhá | 干什么 、干嘛 | gànshénme, gànmá | What are you doing? |
| 砢碜 | kēchen, kēzhen | 丑、难看 | chǒu, nánkàn | ugly, hideous |
| 老 | lǎo | 很 | hěn | very |
| 贼 | zéi | 特别 | tèbié | exceedingly |
| 毙 | bì | 棒 | bàng | good, excellent |
| 蚂蛉 | māling | 蜻蜓 | qīngtíng | dragonfly |
| 嘎赌 | gàdu | 打赌 | dǎdǔ | to bet |
Shenyang dialect has 19 initial consonants, as opposed to the 21 in Standard Mandarin. Notably, the retroflex consonants [ʈ͡ʂ], [ʈ͡ʂʰ] and [ʂ] in Standard Mandarin are pronounced as [t͡s], [t͡sʰ] and [s], respectively, while [ɻ] is omitted. While lost in Standard Mandarin, Middle Chinese [ɳ] is preserved in the Shenyang dialect. [v] also exists in the Shenyang dialect.[1]
| Labial | Alveolar | Dental sibilants | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stops | unaspirated | p | t | t͡s | t͡ɕ | k |
| aspirated | pʰ | tʰ | t͡sʰ | t͡ɕʰ | kʰ | |
| Nasals | m | n | ɳ | |||
| Fricatives | f | v | s | ɕ | x | |
| Approximants | l | |||||
Standard Mandarin diphthongs tend to be pronounced as monophthongs in the Shenyang dialect. For example, [ai] becomes [æ], and [au] becomes [ɔ].[1]
|
Sino-Tibetan branches
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Himalayas (Himachal, Uttarakhand, Nepal, Sikkim) |
| ||||
| Eastern Himalayas (Tibet, Bhutan, Arunachal) |
| ||||
| Myanmar and Indo-Burmese border |
| ||||
| East and Southeast Asia |
| ||||
| Dubious (possible isolates) (Arunachal) |
| ||||
| Proposed groupings |
| ||||
| Proto-languages |
| ||||
Italics indicates single languages that are also considered to be separate branches. | |||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major groups |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard forms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phonology |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grammar |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Idioms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Input |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literary forms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scripts |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This Sino-Tibetan languages-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |