アメリカ合衆国の奴隷制度の歴史
アメリカ合衆国の奴隷制度の歴史︵アメリカがっしゅうこくのどれいせいどのれきし、英:The history of slavery in the United States︶は、イギリスがバージニア植民地に初めて入植したすぐ後に始まり、1865年のアメリカ合衆国憲法修正第13条の成立で終わったことになっている。
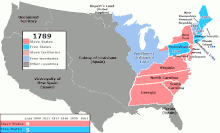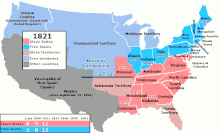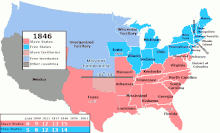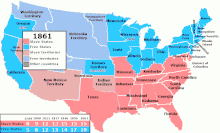
1789年から1865年までのアメリカ合衆国の領土内で奴隷制を禁 止または許可した地域を表している。

概要[編集]
動産としての奴隷制が拡がる前に、白人と黒人などの間に典型的なものでは4年から7年の間で続く﹁年季奉公﹂と呼ばれる労働契約の仕組みがあった。1662年までに、アメリカにおける奴隷制は法令の整備によって制度化され、主にアフリカ人とその子孫︵アフリカ系アメリカ人︶、および偶にアメリカ州の先住民族にも適用された。17世紀の終わりまでには、アメリカ植民地の南部において奴隷制が一般化されたが、北部との程度差があった。 1640年代から1865年まで、現在のアメリカ合衆国領域内ではアフリカ人とその子孫が合法的に奴隷化されていたが、その所有者は圧倒的に白人であり、ごく少数が先住民や自由黒人であった。この奴隷所有者の大多数は南部にいた。南北戦争の前の時点で南部の4家族に1軒が奴隷を所有していた[1]。黒人の95%は南部に住んでおり、南部の人口に対しては3分の1に達していた。これに対して北部における黒人の人口比率は1%に過ぎなかった[2]。 19世紀前半のアメリカ合衆国の富は黒人奴隷の労働の搾取に負うところが大きかった[3][4]。しかし、南北戦争における北軍の勝利により、南部の奴隷労働制は廃止され、南部の大規模綿花プランテーションはあまり利益を生まないものになった。北部の工業は南北戦争の前も戦争中も急速に成長を遂げ、南部の農業経済の落ち込みを補って余りあるものであった。アメリカ北東部の工業資本家が社会的および政治的事項を含め、国民生活の多くの面を支配するようになった。南部の農園主による貴族政治は影を潜め、南北戦争の後の急速な経済成長が近代におけるアメリカ合衆国産業経済の基盤となった。 17世紀から19世紀にかけて、およそ1,200万人のアフリカ黒人がアメリカ大陸に渡った[5][6]。このうち、5.4%︵645,000人︶が現在のアメリカ合衆国に連れて行かれた[7]。1860年のアメリカ合衆国の国勢調査では、奴隷人口は400万人に達していた。植民地アメリカ[編集]
植民地アメリカでは1619年に最初のアフリカ人奴隷の記録がある。オランダ船﹁ホワイトライオン﹂がメキシコへ向かうイスパニア船と交戦し50~60人の奴隷化されたアフリカ人を奪取した[8]。このイスパニア船はマニラで慶長遣欧使節から買い取ったサン・ファン・バウティスタ号であり、在英大使に譲渡された後に大使の親戚のマヌエル・メンデス・デ・アキューナに渡り、ルアンダから350人の奴隷を調達し輸送する途上だったという説が2018年に提唱されている[8]。ホワイトライオンは交戦で損傷しており、さらに晩夏の大きな嵐によってその程度がひどくなった状態でバージニアのジェームズタウン︵50km離れたハンプトンという説もある[8]︶に到着した。バージニア植民地は後に﹁大移住﹂ (1618-1623)と呼ばれる時期の最中にあり、住民は450人から4,000人にまで増えていたが、疫病、栄養失調、インディアンとの戦いによって極端に死亡率が高く、働ける労働者の比率は低いままであった[9]。ホワイトライオンは修理と補給物資を必要としており、植民地人は労働力を必要としていたので、奴隷20名と食料や用役とが交換された[8]。現代ではこの20名が北米大陸へ最初に上陸したアフリカ人奴隷と認識されている[8]。 アフリカ人奴隷に加えて、かなりの数のヨーロッパ人が特にイギリス領13植民地に年季奉公として連れてこられた[10]。イギリスから渡ってきていたジェームズタウンの白人は、バージニア植民地で最初のアフリカ人を年季奉公として扱うことに決めた。ヨーロッパからの奉公人と同様に、アフリカ人も一定期間の奉公が終われば解放され、前の主人から土地や物資の利用が認められた。少なくとも一人、アンソニー・ジョンソンは最終的にバージニアの東海岸で土地所有者となり、自分でも奴隷を所有した。年季奉公の主要な問題は時間が経てば解放しなければならないことであったが、解放された者もその後に富を築いたかと言えばそうでもなかった。バージニア植民地の肥沃な海岸地域は既に1650年までには富裕なプランテーションの一族に占められており、元奉公人は下層階級になった。1676年のベイコンの反乱は貧乏な労働者や農夫が金持ちの土地所有者にとって危険な存在であることを示した。純粋に動産としての奴隷制に移行することにより、新しい白人労働者や小農は自分で移民してきて自活していける者達にほとんど限られるようになった。 年季奉公から人種を区別した奴隷制への移行は徐々に進んだ。バージニア植民地の初期の歴史には奴隷制に関する法律もなかった。しかし、1640年までに、バージニア植民地の裁判所は少なくとも一人の黒人従僕を奴隷と宣告していた。1654年、ノーザンプトン郡の裁判所はアンソニー・ジョンソンの奴隷であったジョン・ケイサーに終生資産︵奴隷︶であると宣言する判決を下した。アフリカ生まれの者は生まれつきイギリスの市民ではないので、イギリスの慣習法で必ずしも保護されていなかった。 1705年のバージニア奴隷法で奴隷の条件を明らかにした。イギリス植民地の時代、各植民地に奴隷制があった。北部の場合は主に家の従僕であった。南部の初期の奴隷は農園やプランテーションで働き、アイ、米およびタバコを栽培した。綿花は1790年代以降、主要作物になった[11]。サウスカロライナ植民地では1720年に人口の65%が奴隷であった[12]。奴隷は海外との交易を行っているような裕福な農園主やプランテーション所有者に使われていた。僻地の必要最低限の生活をしているような農夫では滅多に奴隷を持てなかった。 イギリス領植民地の幾つかは新しいアフリカ人が秩序を乱すことを恐れて奴隷貿易を廃止させようとした。その効果を狙ったバージニア植民地の法案はイギリス本国の枢密院によって拒否された。ロードアイランド植民地は1774年に奴隷の輸入を禁止した。ジョージア植民地を除いて、全ての植民地は1786年までにアフリカ人奴隷貿易を禁止するか制限するかした。ジョージア植民地も1798年にそれに倣ったが、幾つかの州の法はその後撤廃された[13]。1776年から1850年[編集]
第二次中間経路[編集]
アメリカ合衆国が西に拡がるに連れて、綿花の栽培も西に拡がって行き[14]、歴史家のピーター・コルチンは﹁既存の家族を引き裂いて、彼らが知っている人や物とは遠く離れた場所に移動させた﹂この移民は大西洋奴隷貿易の﹁多くの恐怖を︵程度は低いかもしれないが︶思い出させた﹂と書いた[15]。同じく歴史家のアイラ・バーリンはこの移動を第二次中間経路と呼んだ。バーリンは、このことをアメリカ独立戦争と南北戦争の間で奴隷の生活における﹁中間的出来事﹂として特徴付け、奴隷達が自発的に動いたのかあるいは単純に彼らやその家族が意に反して移動させられる恐れの中で生きていたのであれば、﹁大量移送が奴隷であれ自由黒人であれ、黒人の意識に負担となっていた﹂と書いた[16]。 完全な統計ではないが、1790年から1860年の間に100万人の奴隷が西部に移動したと見積もられている。奴隷の大半はメリーランド州、バージニア州および両カロライナ州から移住した。最初の目的地はケンタッキー州とテネシー州であったが、1810年以降はジョージア州、アラバマ州、ミシシッピ州、ルイジアナ州およびテキサス州が多くを受け入れた。1830年代におよそ30万人が移住し、アラバマ州とミシシッピ州はそれぞれ10万人を受け入れた。1810年から1860年の間の10年間毎に少なくとも10万人の奴隷が生まれた土地を離れた。南北戦争前の最後の10年間、25万人が移住した。マイケル・タッドマンは1989年の著書﹃投機家と奴隷‥古南部の奴隷所有者、貿易業者および奴隷﹄で、移住した奴隷の60ないし70%は奴隷売買の結果だったとしている。1820年にアッパー・サウスにいた子供は30%の確率で1860年代までに売られた[17]。 奴隷貿易業者は西部に移住した奴隷の大半に責任があった。極少数はその家族やそれまでの所有者と共に移住した。奴隷貿易業者は奴隷の家族をそのまま購入することや運ぶことではあまり利益がなかったが、運ばれる男女と同数の﹁自己繁殖する労働力﹂を生むことには利益があった。バーリンは、﹁国内の奴隷貿易はプランテーション以外では南部で最大の事業になった。おそらく新しい輸送方法、財務および宣伝力を採用することでも最も進歩していた﹂と書いた。奴隷貿易産業は﹁最上の働き手、元気のいい若者、繁殖用の女および上等の女の子﹂といった特有の言葉を発展させ一般に使われるようになった[18]。州間奴隷貿易の拡大は、売りに出される奴隷の価格が上昇するに連れて、﹁一度落ち込んだ海岸州の経済的復活﹂に貢献した[19]。 貿易業者の中には、ノーフォークからニューオーリンズを通常経路としてその﹁動産﹂を船で運ぶ者もいたが、大半の奴隷は徒歩で移動することを強制された。通常の移動経路が確立され、奴隷が一時的に利用するための宿泊設備、囲い地および倉庫のネットワークが役に立った。移動が進むに連れてある奴隷は売られ、また新しい者が購入された。バーリンは﹁全体的に、奴隷貿易は中継点と地域の中心があり、横道や巡回路もあって、南部社会の隅々まで届けることができた。黒人であろうと白人であろうと南部の者達はほとんど関係しなかった﹂と結論づけた[20]。 行進中の奴隷の死亡率は大西洋奴隷貿易の当時に比べれば遙かに小さかったが、通常の死亡率よりは高かった。バーリンは次のように要約した。 …第二次中間経路は他にないくらい寂しく、衰弱させ、また気を落ち込ませるものだった。南部に向かう行進の陰気な様子を観察した者は﹁男も女も子供達までも葬式に向かう列に似ている﹂と表現した。実際に行進中に死に行く男や女、あるいは売られる者、再販される者がいて、奴隷は商品として扱われるだけでなく、あらゆる人間的な感情からも疎外されていた。 第二次中間経路は奴隷達に対するのと同様に貿易業者にとっても殺人や暴力で危険なものとなった。それが男達を鎖でしっかりと繋ぎ防御を図った理由であった。南部に向かう奴隷の隊列は、その祖先を西方に運んだ奴隷船に似て、動く砦になり、そのような状況下になれば反抗するよりも戦う方が通常であった。奴隷達は重武装の権力者に直面するよりも、夜の闇に紛れ北極星に導かれて寓話の自由の土地を目指す方が容易であり、危険も少なかった。 — Berlin pg. 172-173 一旦移動が終わると、奴隷達は東部で経験したのとは全く異なる辺境の生活に直面した。樹木を取り払い、荒れ地に穀物を育て始めることは過酷な重労働であった。不適切な栄養、悪い水、さらに旅や仕事の疲れで消耗した体力の組み合わせは新しく到着したばかりの奴隷を弱らせ損失を生んだ。河床に近い新しいプランテーションに適した土地は蚊に襲われたり、他の自然環境の猛威に曝され、以前の土地では限られた免疫力しかなかった奴隷達の生存を脅かした。荒れ地からプランテーションを切り開いた最初の数年間の死亡率は凄まじいものがあり、農園主によっては自分の奴隷を所有するよりも、可能ならば奴隷を借りて使った方が良いと考える者もいた[21]。 辺境における過酷な環境のために奴隷の反抗が増え、奴隷所有者や監督者は以前にも増して暴力に頼るようになった。奴隷の多くは綿花畑の経験がなく、新しい生活に要求される﹁日の出から日没までの集団労働﹂に慣れていなかった。奴隷達は東部でタバコや小麦を栽培していた時よりも過酷な労働に駆り出された。奴隷達はまた自分達の消費のためあるいは交易のために、家に戻って家畜を飼ったり、野菜を育てたりすることでその生活水準を上げる時間も機会も少なかった[22]。 ルイジアナ州では主要な作物が綿花ではなく砂糖であった。1810年から1830年の間、奴隷の数は1万人以下のレベルから4万2千人以上にまで増加した。ニューオーリンズは国中でも重要な奴隷のための港となり、1840年代までには国でも最大の奴隷市場ができた。サトウキビを取り扱うことは綿花の栽培よりも体力を要し、購入される奴隷の3分の2を占めた若い男性が好まれた。若くて未婚の男性奴隷を集団で扱うことについて、その所有者は﹁特別野蛮な﹂暴力に頼る機会が増えた[23]。奴隷の処遇[編集]
詳細は「アメリカ合衆国における奴隷の扱い」を参照
歴史家のケネス・スタンプは奴隷制における強制力の役割について﹁州が奴隷所有者に与えた罰を与える権限がなければ、隷従は存在し得なかった。他の全ての管理方法と比較しても他の方法の重要さは2次的なものに過ぎなかった。﹂と述べている。スタンプはさらに、報酬を奴隷に与えることは奴隷が適切に成果を上げる役には立ったが、大半は次のアーカンソー州の奴隷所有者の言に同意したとも注釈している。
さて、私の知っていることを話そう。黒人を働くように説得しようとすることは﹁豚に真珠を投げること﹂に似ている。奴隷は働くように仕向けなければならないし、その義務を果たさなかったらそのために罰を受けることを常に理解させて置くべきである。 — Stampp, The Peculiar Institution pg. 171
ピュリッツァー賞受賞者の歴史家デイビッド・ブライオン・デイビスとマルクス主義者の歴史家ユージーン・ジェノヴェーゼによれば、奴隷の処遇は過酷で非人間的なものであった。働いているときも公衆の中を歩いているときも、奴隷として生きる人々は合法の暴力で規制された。デイビスは、奴隷制のある観点で﹁福祉的資本家﹂の見方を採り、次のように指摘している。
我々は、深南部のこれら同じ﹁福祉的資本家﹂のプランテーションが基本的に恐怖で支配されていたことを忘れてはならない。最も親切で人間的な所有者であっても暴力を恐れさせることだけが、当時の観察者が﹁正規の訓練された兵隊﹂と指摘したように、﹁規律を持って﹂朝から晩まで畑の集団を働かせる手段であった。度々公衆の前で笞打つことは不十分な労働、無秩序な行動、あるいは上位のものの権威を受け入れない行動に対する罰を全ての奴隷に思い出させた。 — Davis pg. 196
大規模プランテーションでは、奴隷の監督者が従わない奴隷を笞打ち、残忍に扱うことを認められていた。奴隷法は暴力を認め、免責にし、また要求すらしており、それが奴隷制度廃止運動家によって残忍と非難された。奴隷も自由黒人も﹁黒人法﹂︵英語: Black Codes︶によって規制され、その行動は白人から募集された奴隷警邏隊によって監視され、警邏隊は逃亡した奴隷に略式の罰を与えること、時には傷を負わせたり殺すことさえも許された。肉体的な虐待や殺人に加えて、奴隷達は、所有者が利益や、罰あるいは負債の償還のために売り渡すと決めた場合はその家族の一員を失う危険性をいつも抱えていた。主人や監督者を殺したり、納屋を燃やしたり、馬を殺したりあるいは仕事を鈍くしたりして報復する奴隷もいた[24]。スタンプは、ジェノヴェーゼの主張する奴隷が直面していた暴力や性的搾取に関しては異議を唱えず、主人と奴隷の関係の分析についてマルクス主義的アプローチをすることの適切さに疑問を投げ掛けた[25]。
ジェノヴェーゼは、奴隷がその所有者の合法的な財産であったので、奴隷にされた黒人女性がその所有者、所有者の家族の一員あるいは友人によって強姦されることは異常ではなかったと主張している。その結果として生まれる子供達は、奴隷所有者により解放されない限り、その母の状態を引き継ぎ奴隷のままであった。One drop ruleにより奴隷の血が少しでも混じっていればその人間は白人と同等の権利は認められなかった[26]。これは混血児でも父親が認知すれば相続権も認められた南米とは対照的である。
ネル・アーウィン・ペインターや他の歴史家は、南部の歴史が﹁人種差別を越えて﹂行ったとも記した。当時の農園主階級と結婚したメアリー・チェスナットやファニー・ケンブルの証言や、公共事業促進局の下に集まった元奴隷達の証言は、女奴隷が所有者や監督者階級の白人男性に虐待されたことを裏付けていた。
しかし、ノーベル経済学賞を受賞したロバート・フォーゲルは、奴隷の増殖と性的搾取が伝説としての黒人家族を破壊したと信じると述べることで議論を呼んでいる。家族は奴隷制の下の社会的組織で基本単位であり、農園主が奴隷家族の安定を奨励することは経済的利益にも繋がったので、多くの者がそうした。奴隷の大半は家族ごと売られるか、家族の元を離れても良いと考えられる年齢に達した個人が売られた[27]。
ジェノヴェーゼによれば、奴隷達は最小のやりかたで食べ物と着るものと家、それに医療を与えられた。クリスマスに少額のボーナスを渡すのが普通であり、奴隷所有者の中には奴隷達が稼ぎを貯めたり、賭け事をすることを認める者もいた。一人の奴隷、デンマーク・ビージーは宝くじに当たってその自由を買ったことで知られている。多くの家庭では、奴隷の肌の色によって扱いが変わることがあった。色の黒い奴隷は農園で働き、明るい色の奴隷は家の従僕となり、よりましな衣服、食物、住居を与えられた[24]。
トーマス・ジェファーソンの有名な家庭のように、肌の色という概念的な問題ではなかった。時として、農園主は肌の色が明るい奴隷は彼らが血が繋がっている親戚であるという理由で農作業を免じ家僕として使役した。ジェファーソン家の奴隷の何人かはその義父とジェファーソンの妻によって結婚させられた奴隷女性の子供達であった。若い奴隷の女性サリー・ヘミングスはトーマス・ジェファーソンと性的関係があり、ジェファーソンの妻が死んだ後の子供を生んだと言われており、ジェファーソンの妻にとっては異母妹であった。
しかし、フォーゲルは奴隷の生活における物質的条件は自由工場労働者のそれに比してかなり良かったとしている。現在の基準からすればそれほど良くはないにしても、この事実は19世紀前半の自由にしろ奴隷にしろ全ての労働者の厳しい運命を表している。典型的な農場奴隷はその全生涯で生産したものから得られる収入の90%近くを受け取ったと言われる[27]。
調査に拠れば58%の歴史家と42%の経済学者は、奴隷の生活における物質的条件は自由工場労働者のそれに比してかなり良かったという仮説に同意していない[27]。
奴隷が犯罪を犯した場合、法律的には非人間と考えられた。アラバマ州の裁判所は、奴隷が﹁分別のある存在であり、犯罪を犯すことができる、犯罪である行動に関しては奴隷は人間である、彼らは奴隷であるから公的な活動は出来ないのでそのような場合は、彼らは物であり、人間ではない﹂と主張した[28]。
女性の行動[編集]
1600年代初期、アフリカ人の女性も男性と同様に奴隷にするためにアメリカに連れてこられた。プランテーションや農場で働くときは、女も男も同じように働いた。しかし、厳しい労働の多くは男によるか、子供の出産適齢期を過ぎた女に渡された。女性に与えられた仕事は所有者の家や奴隷自身のための料理、縫い物、助産婦、樹木の刈り込み、その他の労働集約的な仕事であった。 また、奴隷を買うより、奴隷が子供を産んだ方が安上がりということもあり、性行為や強姦による強制妊娠や奴隷主のレイプもあった。[29] 1837年、ニューヨーク市で黒人、白人双方の女性の参加によるアメリカ女性の反奴隷制会議が開催された。ルクレティア・モットやエリザベス・キャディ・スタントンが会議で初めて会って、女性の権利のための運動を別に展開する必要性を認識した。ロンドンで行われた集会でスタントンはエミリー・ウィルソン、アビー・サウスウィック、エリザベス・ニール、メアリー・グルー、アビー・キンバーなど多くの他の女性代議委員とも会った。しかし、スタントンとウィンスローが参加したマサチューセッツ反奴隷制協会の会合では、主催者が女性代議員の参加を拒否した。その結果女性達は自分達で﹁女性の権利を提唱する協会﹂の設立のための会議を開いた。8年後、ニューヨーク州セネカフォールズで、スタントンとウィンスローは女性の権利運動を起ち上げ、アメリカの歴史の中でも異なった社会的勢力の一つになった。さらにこの運動が南北戦争の終わりや第一次世界大戦の直前に盛り上がった事実は間違いなく脅威であった[30]。奴隷制度廃止運動[編集]
詳細は「アメリカ合衆国における奴隷制廃止運動」を参照
1750年代に始まり、独立戦争の間に奴隷制は︵国全体と白人にとって︶社会的な悪であり、行く行くは廃止すべきという考え方が広まった。北部の諸州は1780年から1804年までに解放法を成立させたが、その大半は段階的解放であり、解放された者には特別の立場が用意されたので、1860年になってもニュージャージー州では﹁永久奉公﹂の者が1ダースほども残っていた[31]。
1780年のマサチューセッツ憲法は全ての人が﹁生まれながらにして自由かつ平等﹂を宣言した。奴隷のクウォーク・ウォーカーはこの憲法を根拠に自由を求めて告訴を行い自由を勝ち取って、マサチューセッツの奴隷制を廃止させた。
19世紀の前半を通じて、奴隷制を終わらせる運動がアメリカ合衆国中で強さを増していった。この闘争は、奴隷労働の仕組みから大きな利益を上げていた南部白人の強い奴隷制擁護派の中に反発を呼んだ。これらの奴隷所有者は奴隷制を他の強制労働とは区別して防衛しようとし、﹁特別の制度﹂と言い始めた。
大規模で資金もあるアメリカ植民地協会が、西アフリカのリベリアに作ったアメリカ植民地に戻りたいという元奴隷や自由黒人を船で運ぶ行動的な計画を作った。
1830年以降、ウィリアム・ロイド・ガリソンに指導された宗教的運動は奴隷制が個人の罪であると宣言し、奴隷所有者は即時に悔い改め、解放を始めるよう要求した。この運動は多くの議論を呼び、南北戦争の原因にもなった。
ジョン・ブラウンのような極少数の奴隷制度廃止運動家は、武器を取って奴隷の中からの蜂起を扇動したが、その他の者は法に添ったやり方を選んだ。

ルイジアナ州バトンルージュの奴隷ピーター。1863年撮影。背中の 傷は監督者によって笞打たれた結果。その後解放された。体力が回復するまでに2ヶ月を要した。
奴隷制度廃止運動 (1810-60) の影響力ある指導者
●ウィリアム・ロイド・ガリソン - ﹁ザ・リベレーター﹂紙を発刊
●ハリエット・ビーチャー・ストウ - アンクルトムの小屋の作者
●フレデリック・ダグラス - 最も力ある反奴隷制論説家、元奴隷。﹃フレデリック・ダグラスの人生の物語﹄でも有名。
●ハリエット・タブマン - 南部からの逃亡奴隷350人を援助。秘密結社﹁地下鉄道﹂の﹁指揮者﹂として知られた。
﹁武器﹂を取った奴隷の蜂起 (1700 - 1859)

- ニューヨークの反乱、1712年
- ストノの反乱、1739年、サウスカロライナ
- ニューヨーク奴隷反乱、1741年
- ガブリエルの反乱、1800年、バージニア州
- ルイジアナ準州奴隷反乱、チャールズ・デスランズが指導、1811年
- ジョージ・ボクスリーの反乱、1815年、バージニア州
- デンマーク・ヴィージーの反乱、1822年、サウスカロライナ州
- ナット・ターナーの反乱、1831年、バージニア州
- アミスタッド号事件、1839年、スペイン船での反乱
緊張の高まり[編集]
プランテーション奴隷制の経済的価値は、イーライ・ホイットニーによる1793年の綿繰り機の発明で拡大した。この機械は種殻や時には粘り着く種から綿繊維を分離するように工夫されたものだった。この発明で、綿糸生産量は従来の50倍にもなり、綿花栽培業に革命をもたらした。その結果、綿花産業の爆発的成長をもたらし、南部での奴隷労働に対する需要も高まった[32]。
同時期に北部諸州は奴隷制を禁止したが、アレクシス・ド・トクヴィルが﹃アメリカの民主主義﹄︵1835年︶で指摘しているように、奴隷制の禁止といっても常に奴隷が解放されることを意味しているのではなかった。トクヴィルは、北部諸州が段階的解放を決めたとき、州内での奴隷販売を違法としたと言っている。このことは解放する前に奴隷を売ろうとする唯一の方法は南部に移動することを意味していた。トクヴィルはそのような移動が実際にある規模で起こったという証拠は残さなかった[33]。実際に北部の奴隷解放は、北部の自由黒人の人口で見ると1770年代の700人から1810年の5万人という拡大に繋がった[34]。
奴隷の需要が増すにつれて、供給は制限された。1787年に採択されたアメリカ合衆国憲法は連邦議会が1808年まで奴隷の輸入を禁止することを妨げていた。1808年1月1日、連邦議会はそれ以降の輸入を禁止した。新しい奴隷はその時点で合衆国内にいる者の子孫でなければならなくなった。しかし、国内の奴隷貿易と合衆国市民による国際貿易への関与あるいは奴隷貿易船の艤装は禁じられていなかった。この法にも確かに違反はあったが、アメリカの奴隷制は多かれ少なかれ自己保持的になっていった。
バージニア州や両カロライナ州海岸地帯の農業の変化により、農園主は過剰な奴隷労働力を抱えていた。農園主は奴隷貿易業者に奴隷を売り、業者はジョージア州、アラバマ州、ミシシッピ州、アーカンソー州、ルイジアナ州およびテキサス州のいわゆる深南部で拡張するプランテーションのための市場に奴隷を連れて行った。この国内奴隷貿易と奴隷の強制移住はさらに半世紀も続いた。国内奴隷貿易の規模は深南部の富に貢献した。1840年、最大の奴隷市場であり、輸入港でもあったニューオーリンズは国でも3番目の大都市になり、最も富める町になった。
アメリカ合衆国憲法の5分の3条項により、奴隷所有者は連邦政府での勢力を伸ばし、議会で逃亡奴隷法を成立させた。南部を脱出した逃亡奴隷はオハイオ川や北部と南部を分けるメイソン=ディクソン線の他の場所を越え、秘密結社﹁地下鉄道﹂の支援により北部に入った。シンシナティやオバーリンなど北部の町にアフリカ系アメリカ人が存在することは北部白人を扇動し、他の者は元所有者から元奴隷を隠し、また他の者はカナダで自由になるのを助けた。1854年以降。共和党は奴隷勢力の力を弱め、特に連邦政府の2、3の部門を支配していた奴隷制擁護派の民主党を排除した。
中西部の諸州が1820年代に奴隷制を許さないと決めたので、また北東部の大半の州が部分解放で自由州となったので、北部の自由州が団結して地理的に連続した一つの地域となった。分割線はオハイオ川とメイソン=ディクソン線になった︵奴隷州のメリーランド州と自由州のペンシルベニア州の間︶。
1845年、南部バプテスト連盟の設立で北部と南部はさらに別々になっていった。福音や旧約聖書には神や主が奴隷制度を容認していると解せる文脈の記述[35] があることに注目した人びとがいた。当然、これらの聖書の記述は古代社会であるにもかかわらず、彼らはこれを文字通り近代社会に当て嵌めうるとの強引な解釈を行った。この会議はこのように聖書が奴隷制を認めているという解釈を採用し、キリスト教徒でも奴隷を所有できるとする解釈を打ち出した。初めは多くの教会や聖職者はこの強引なこじつけの解釈を黙認したが、やがて南部バプテスト会議はその後この解釈を明確に否定するようになった。この分裂は北部バプテストが奴隷制に反対することで深刻になり、特に1844年までに家庭伝道教会が奴隷を資産として保っている者は宣教師たりえないと宣言することで決定的となった。メソジストと長老派教会は同様に北部と南部で分裂したので、1850年代までに民主党だけが国全体の組織となり、それも1860年アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙で分裂した。

| 統計年 | 奴隷 | 自由 黒人 |
黒人計 | 自由 黒人比 |
全人口 | 黒人 比率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1790 | 697,681 | 59,527 | 757,208 | 7.9% | 3,929,214 | 19% |
| 1800 | 893,602 | 108,435 | 1,002,037 | 10.8% | 5,308,483 | 19% |
| 1810 | 1,191,362 | 186,446 | 1,377,808 | 13.5% | 7,239,881 | 19% |
| 1820 | 1,538,022 | 233,634 | 1,771,656 | 13.2% | 9,638,453 | 18% |
| 1830 | 2,009,043 | 319,599 | 2,328,642 | 13.7% | 12,860,702 | 18% |
| 1840 | 2,487,355 | 386,293 | 2,873,648 | 13.4% | 17,063,353 | 17% |
| 1850 | 3,204,313 | 434,495 | 3,638,808 | 11.9% | 23,191,876 | 16% |
| 1860 | 3,953,760 | 488,070 | 4,441,830 | 11.0% | 31,443,321 | 14% |
| 1870 | 0 | 4,880,009 | 4,880,009 | 100% | 38,558,371 | 13% |
| Source: http://www.census.gov/population/documentation/twps0056/tab01.xls | ||||||
ナット・ターナー、反教育法[編集]
1831年、バージニア州サザンプトン郡で奴隷による流血反乱が起こった。ナット・ターナーという奴隷は読み書きができ、「幻視」を見て、ナット・ターナーの反乱あるいはサザンプトン反乱と呼ばれる反乱を指導した。ナット・ターナーとその追随者は自分や他の奴隷を自由にするという目標をもって決起し、子供を含むおよそ50名の白人の男女殺害したが、結果的には白人民兵に鎮圧された。
ナット・ターナーは絞首刑になり体皮を剥かれた。その仲間として戦った連中も絞首刑にされた。白人民兵はナット・ターナーやその仲間を殺すだけで治まらず、反乱には関わっていなかった無実の100人以上の奴隷を殺害した。その反乱の後は、南部中で厳しい法律が制定され、アフリカ系アメリカ人の既に制限されていた権利をさらに抑えることになった。典型的なものはバージニア州で制定された奴隷、自由黒人および白人と黒人の混血児に対する教育を制限する法であった。だがしかし、これらの法を個人的に拒む者もいた。その中でも著名な者は後に南軍の将軍となったストーンウォール・ジャクソンであった。
1850年代から南北戦争へ[編集]
血を流すカンザス[編集]
詳細は「血を流すカンザス」を参照
1854年のカンザス・ネブラスカ法の成立後、境界戦争がカンザス準州で勃発した。そこでは、奴隷州と自由州のどちらで合衆国に加盟するかという判断を住民に委ねられていた。奴隷制度廃止運動家のジョン・ブラウンは積極的に反抗し、﹁血を流すカンザス﹂では多くの白人南部人と同様に殺人も行った。同時に、奴隷勢力が連邦政府を席捲するという恐れが反奴隷制を掲げる共和党を強くさせ議会に送り込んだ。

サイモン・レグリーとアンクルトム。﹃アンクル・トムの小屋﹄の1シー ン。
新しく作られたアリゾナ準州では、1863年2月24日のアリゾナ基本法で奴隷制を廃止した。ケンタッキー州を除きテネシー州などの境界州は1865年早くまでに奴隷制を廃止した。北軍が南部に侵攻するにつれて解放宣言が執行され解放された奴隷がいた。残る南部の州に解放が実際に訪れたのは1865年春のアメリカ連合国軍の降伏の後であった。当時テキサス州には25万人以上の奴隷が残っていた。連合国崩壊の知らせが届いた所から奴隷が解放されていった。決定的な日は1865年6月19日であった。テキサス州やオクラホマ州などでは、その知らせがガルベストンの最後の奴隷まで届いた日として6月10日を記念して祝っている。
法的にはケンタッキー州[37] の奴隷約4万人が解放されたのが最後だった。これは1865年12月、アメリカ合衆国憲法修正第13条の批准が成立した時であった。
ドレッド・スコット[編集]
ドレッド・スコットが、奴隷制の禁じられている領土に住んでいたことを理由にその解放を求めて訴訟を起こしたときは62歳であった。その領土とはルイジアナ買収で得た土地の北部であり、ミズーリ妥協の条項で奴隷制は排除されていた。最高裁はスコットの自由を否定する判決を下し、この判決が合衆国を南北戦争に導くことになった。この判決は、スコットが連邦裁判所に訴訟を起こす権利のある市民ではないとし、連邦議会がミズーリ妥協を成立させるには憲法で権限を与えられていないとした。 1857年の﹁ドレッド・スコット対サンフォード事件﹂の判決は、6対3の評決で、自由州に連れて行かれた奴隷は自由にならないとした。連邦議会は領土から奴隷制を禁じることができないし、黒人は市民になり得ないとした。この判決はエイブラハム・リンカーンを含め多くの共和党員に不公平と見なされ、奴隷勢力が最高裁を支配している証拠とも見なされた。裁判長ロジャー・トーニーによって書かれた判決文は奴隷とその子孫から市民権を取り上げた。この判決は奴隷制度廃止運動家を激怒させ、奴隷所有者を勇気づけた[36]。1860年アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙[編集]
国の分裂は1860年アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙で際だって露呈された。選択肢は4つに分かれた。一つの党︵南部民主党︶が奴隷制を裏書きした。一つ︵共和党︶はそれを否定した。一つ︵北部民主党︶は民主主義で住人が地域ごとに奴隷制の採用を決めればよいと言った。4つめの党派︵立憲連合党︶は合衆国が存続の節目に立っており、他の全てのことは妥協すべきと言った。 共和党のリンカーンが一般投票で最多票を獲得し、選挙人投票では過半数を得た。しかし、リンカーンは南部の10州の候補者名簿にも載らなかった。リンカーンの選出は必然的に分割線で国を2つに分けた。南部の多くの奴隷所有者は共和党の実際の意図が奴隷制の存在する州でのその廃止であり、400万人の奴隷の突然の解放は無報酬で働く労働力から大きな利益を得ていた奴隷所有者とその経済にとって問題となることを恐れた。 奴隷所有者は、新しい州で奴隷制を禁じることが自由州と奴隷州の微妙な平衡関係と見ていたものを破壊するとも論じた。この平衡関係を終わらせることは製造業の発達した北部の支配を許し、輸入品に高い関税を課することになるのを恐れた。これらの要素が結びついて南部は合衆国からの脱退を選択し南北戦争が始まった。リンカーンのような北部指導者は奴隷制の利益を政治的脅威と見なしており、南部の脱退については新しい南部連合、アメリカ連合国がミシシッピ川と西部を支配する可能性があり、政治的にも軍事的にも認めがたいものとした。戦争と解放[編集]
1861年に始まった南北戦争の結果はアメリカにおける動産としての奴隷制の終焉であった。戦争が勃発して間もなく、弁護士を職業とする北軍の将軍ベンジャミン・F・バトラーに信託された法的な操作により、北部の﹁所有﹂となった奴隷は﹁戦争の禁制品﹂と考えられ、それ故に、戦争前の南部の所有者の元に帰る必要はないとされた。すぐにその噂が広まり、多くの奴隷は﹁禁制品﹂と宣言されることを願って北部の領土内に逃亡した。﹁禁制品﹂の多くが北軍の労働者あるいは兵隊として参加し、黒人だけで構成されるアメリカ有色人種連隊も結成された。他のものはモンロー砦の近くのグランド・コントラバンド・キャンプのような避難民キャンプに行くか北部の都市に逃れた。バトラー将軍の解釈は連邦議会が1861年の没収法を通して補強された。この没収法は南軍に使われていた財産は、奴隷を含み、すべて北軍に没収されることを宣言した。 1863年1月1日のリンカーンによる奴隷解放宣言は北軍が南部に到着すればすぐに南部の奴隷に自由を約束する強力な動きであり、また、北軍にアフリカ系アメリカ人を徴兵することも認めた。しかし、奴隷解放宣言は南部と境界を接し、北軍に付いている奴隷所有州の奴隷を解放しなかった。連合国の諸州はリンカーンの権威を認めず、奴隷解放宣言は境界州に適用されなかったので、最初に解放された者は北部の領域に逃げ込んだ少数の奴隷だけであった。それでも奴隷制の廃止が公式の戦争目的とされ、北軍が南部から奪った領土には強制された。1860年の国勢調査によれば、この政策で400万人近い奴隷、すなわち全人口の12%以上の者を解放することであった。
レコンストラクションから現在[編集]
レコンストラクションの間、奴隷制が永久に廃止されるのか、あるいは北軍がいなくなれば奴隷制に近いような形が現れるのかが重大な問題であった。分益小作制度[編集]
1867年の連邦法で、ニューメキシコ準州に残っていたスペイン領時代以来の分益小作制度[38] あるいは借金による束縛は奴隷制の名残であるとして禁じられた。1903年から1944年まで最高裁は黒人の借金による束縛に関する幾つかの事件に判決を下し、そのような状態を違憲とした。しかし、実際には分益小作制度が南部の黒人にも白人農夫にも日雇いの形で残っていた。教育問題[編集]
1832年以降の反教育法は、その35年後の南北戦争と奴隷解放の後も、解放された者や他のアフリカ系アメリカ人の識字率が上がるにつれて、疑いもなく大きな影響を残した。解放後、レコンストラクション以降に無学の者が資本主義的な仕組みに加わろうとしたり自立しようとしたりするときに、無学であることが大きな障壁となったので、それらの法律の不公平さに注意が引き付けられることになった。 結果的に、多くの宗教組織、元北軍の士官や兵士および富裕な慈善家が立ち上がり、特に南部のアフリカ系アメリカ人の学力を上げるために教育機関を創設したり資金を作ったりした。彼らは教師を育てるための師範学校を作り、それが後にハンプトン大学やタスケギー大学になった。ブッカー・T・ワシントン博士のような教育者の働きに刺激を受けて、20世紀の初めの3分の1までに、5,000校以上の学校が南部の黒人のために作られた。そのための資金としてヘンリー・H・ロジャーズ、アンドリュー・カーネギー、および最も有名なところではジュリアス・ローゼンウォルドのような個人によってもたらされた私的マッチングファンドが使われた。これらの篤志家は下層階級から出て、富を築いた者が多かった。謝罪[編集]
2007年2月24日、バージニア州議会は共同決議案第728号を成立させ、﹁アフリカ人の不本意な奉仕およびアメリカ州の先住民に対する搾取に深い後悔の念を表し、あらゆるバージニア州住民の間の和解を提案﹂した[39]。この決議案の成立により、バージニア州はアメリカ合衆国50州の中で初めて、州の政体を通じて奴隷制に後ろ向きに関わったことを認めた。この決議案成立は、アメリカ植民地の初期奴隷貿易港の一つであったジェームズタウンの開設400周年を祝ったすぐ後のことだった。奴隷制を正当化するために使われた議論[編集]
19世紀、奴隷制を擁護する者はしばしば﹁必要悪﹂として制度を弁護した。奴隷制を続けるよりも解放することの方が社会的また経済的に害を及ぼすという恐れが言われた。1820年、トーマス・ジェファーソンは奴隷制について手紙に次のように書いた。 我々は難局に立っており、奴隷制を維持することもできないし、奴隷を安全に去らせることもできない。公平さは一つの釣り合いであり、自己保存は別のものである。 — Jefferson, Thomas. "Like a fire bell in the night" Letter to John Holmes, April 22, 1820. Library of Congress. Retrieved October 24, 2007. ロバート・E・リーは1856年に次のように記した。 この啓蒙の時代に、奴隷制が制度として道徳的また政治的悪であることを認めようとしない人はほとんどいないと、私は信じる。その短所を長々と述べるのはつまらない。私は有色人種よりも白人にとって大きな悪だと思う。私の感覚が有色人種のために強く働く一方で、私の同情は白人の方に深く向かっている。黒人は、道徳的、肉体的および社会的にアフリカよりもここの方が遙かに良い暮らしをしている。彼らが経験している苦痛を伴う規律は人種としてさらに教導するために必要であり、より良い状態に進むための準備だと私は願う。彼らの奉仕がどのくらい長く必要かは、慈愛深い神意によって知らされ告げられるであろう。 — Lee, R.E. "Robert E. Lee's opinion regarding slavery", フランクリン・ピアース大統領への手紙, December 27, 1856. civilwarhome.com. Retrieved October 24, 2007.﹁肯定的善﹂としての奴隷制[編集]
しかし、奴隷制度廃止運動が進み、プランテーションが拡大するに連れて、奴隷制に対する南部の弁明は影を潜めていった。当時の弁明は、奴隷制が労働者管理には恩恵のある仕組みだという主張に置き換えられた。ジョン・カルフーンは、1837年の上院における有名な演説で、奴隷制は﹁悪ではなく善である、肯定的善である﹂と宣言した。カルフーンはその見解を次のような理由で補強した。 あらゆる文明化した社会では、社会の一部は他人の労働に頼って生きなければならない。学問、科学および芸術は余暇の上に成り立つ。アフリカ人奴隷がその主人や女主人にやさしく扱われ、老年になって面倒を見て貰えば、ヨーロッパの自由労働者よりも良い生活ができる。奴隷制の下では資本家と労働者の紛争が避けられる。この点での奴隷制の長所は﹁干渉によって妨げられず、国が富み人が増えれば、より一層と明らかになってくる。﹂ — Beard C.A. and M.R. Beard. 1921. History of the United States. No copyright in the United States, p. 316.先住民族[編集]
先住民族の奴隷化[編集]
17世紀、ヨーロッパからの植民者によって先住民族を奴隷化することが通常であった。これら先住民族奴隷の多くは海外に輸出され、特にカリブ海の﹁砂糖の島﹂では顕著であった。歴史家のアラン・ギャレイは1670年から1715年まで、イギリスの奴隷貿易業者が24,000人ないし51,000人の先住民を現在のアメリカ合衆国南部から輸出したと見積もった[40]。 先住民の奴隷制はフランシスコ会伝道所を通じてバハ・カリフォルニアとアルタ・カリフォルニアでまとめられ、名目上は10年間の労働ということになっていたが、実質的には恒久的奉仕であり、1830年代中頃に廃止されるまで続いた。1847年から1848年の米墨戦争に続いて、カリフォルニアの先住民は新しく作られたカリフォルニア州で1850年から1867年まで奴隷にされた[41]。奴隷制は所有者による保証金の積み上げを必要とし、奴隷化は襲撃によって起こり、インディアンの流浪者には罰として4ヶ月間の奉仕が課された[42]。先住民族の中の奴隷[編集]
アラスカ海岸の南東部に住んでいたハイダ族とトリンギット族は伝統的に激しい戦士であり奴隷貿易業者としても知られ、遠くカリフォルニアまで襲撃に出かけた。奴隷制は先祖代々のものであり、戦争で捕獲した者を奴隷にした。太平洋岸北西部の種族の中では人口の4分の1が奴隷であった[43][44]。北アメリカには他にも奴隷を所有する種族があり、代表例はテキサスのコマンチェ族、ジョージアのクリーク族、ユロク族のような漁労種族、アラスカからカリフォルニアの間の海岸に住んだポーニー族とクラマス族であった[11]。 1800年以降、チェロキー族などの種族は黒人奴隷を購入して使役し始め、これが1830年代にインディアン準州に移動させられるまで続いた[45]。 チェロキー族社会の奴隷制の性格は白人の奴隷制社会を映したものであった。法律でチェロキー族と奴隷、自由によらず黒人との結婚を禁じた。奴隷を助けた黒人は笞打ち100回の罰となっていた。チェロキー族社会では、黒人が事務所を構えること、武器を携帯すること、および財産を持つことが禁じられ、黒人に読み書きを教えることも違法であった[46][47]。 対照的に、セミノール族は逃亡奴隷であるアフリカ系アメリカ人を対等に迎え入れた。「ブラック・セミノール」を参照
自由黒人と奴隷[編集]
奴隷所有者の中には黒人や先祖が黒人である者がいた。1830年、南部には3,775人のそのような奴隷所有者がおり、その80%はルイジアナ州、サウスカロライナ州、バージニア州、およびメリーランド州にいた。彼らのうち半数は田舎よりも都市に住み、ニューオーリンズとチャールストンの2つの市が多かった。その中でもしっかりした基盤のある農園主は極少数であり、多くは混血であった。[48] 歴史家のジョン・ホープ・フランクリンとローレン・シュウェニンジャーは次のように記した。
自由黒人で奴隷を所有し利益を上げている者の大多数はローワー・サウスに住んだ。その大半は混血であり、白人男性と同棲または愛人であったり混血男性であった。白人から土地や奴隷を与えられ、農園やプランテーションを所有し、米、綿花および砂糖などを手ずから栽培していたが、当時の白人と同様に奴隷の脱走には悩まされていた。 — Franklin and Schweninger pg. 201
歴史家のアイラ・バーリンは次のように記した。
奴隷社会では、自由であろうと奴隷であろうとほとんど全ての者が奴隷を所有する階級になりたいと願い、時には元奴隷が奴隷所有者まで上る場合もあった。そのような者も血縁に縛られていたり、アメリカ人奴隷の場合は肌の色という烙印があるので、快く受け入れられていたとは言い難い。 — Berlin, "Generations of Captivity" pg. 9
自由黒人は、﹁黒人と奴隷は同義語という考え方に挑むことで常に奴隷所有者にとっての象徴的な脅威﹂と認識されていた。自由黒人は逃亡奴隷の潜在的な結託者と見なされており、﹁奴隷所有者は自由黒人に対する恐れや嫌悪感をはっきりと証言していた[49]。不安定な自由を得ているに過ぎない自由黒人にとって、﹃奴隷を所有することは、経済的な利便性だけでなく、自由黒人であることを証明する必要欠くべからざるものであり﹄、過去の奴隷状態に決別し、承認されないまでも奴隷制そのものを受け入れることであった。[50]﹂
歴史家のジェイムズ・オークスは、﹁黒人の奴隷所有者の圧倒的多数がその家族の一員を購い、慈善家として振る舞う自由人であった証拠がある﹂と述べた[51]。19世紀の初期、南部の諸州は奴隷所有者が奴隷を解放することをどんどん難しくしており、しばしば家族の一員を購う者は選択の余地もなく紙の上で主人と奴隷の関係を続けていくしかなかった。1850年代、﹁奴隷は出来る限り白人のみの管理に留めて置くべきであるという根拠で、保証人を持つ権利も制限するようなことが行われるようになった。[52]﹂
アメリカの奴隷制に関する歴史学[編集]
歴史家のピーター・コルチンは1993年に、最近まで奴隷制の歴史家は奴隷よりも奴隷所有者の挙動の方に集中してきたと述べた。このことの一部は、ほとんどの奴隷所有者が読み書きができ、その考え方を文書に残すことができたことに対し、ほとんどの奴隷は読み書きができず、文書を残せなかったという事実に拠っている。奴隷制が良性のあるいは﹁厳しい搾取の﹂制度であったかどうかについては学者の間でも意見が分かれている[53]。コルチンは1900年代初期の歴史学の状態について次のように記した。 20世紀の前半、歴史学の主要な構成要素は単に、黒人は最も良い場合でも白人の模倣だったという信念でも明らかな人種差別であった。奴隷制に関する当時の最も賞賛され影響力のあった専門家ウルリッヒ・B・フィリップスは、黒人奴隷の生活と挙動について、白人農園主の生活と挙動の洗練された様子と粗野な見せかけの世代とを結びつけた。 — Kolchin pg. 134 歴史家のジェイムズ・オリバー・ホートンとルイーズ・ホートンは、フィリップスの思考態度、方法論および影響度を次のように表現した。 黒人をアフリカに起源があるために文明化されなかった受動的で劣った人々とする彼の描き方は、人種差別を支持する人種的劣等論に対して歴史的根拠を与えているように思われる。フィリップスはプランテーションの記録、手紙、南部の新聞など奴隷所有者の見解を反映している史料からのみ証拠を引き出し、奴隷に快適な生活を与えた奴隷の主人の姿を描き、主人と奴隷の間に親愛の情があったと主張した[54]。 この奴隷に関する人種差別的態度は、やはり20世紀初期に支配的であったレンコンストラクションの歴史に関するダニング学派の歴史学にも引き継がれた。エリック・フォーナーはその2005年の著書で次の様に書いた。 当時の彼らの根拠は、ダニング学派の一員が言っているように、﹁黒人の無能﹂という仮定に拠っていた。ダニング達は黒人が歴史のステージで独立した俳優になれると信じることができなかったので、自分達の願望と動機もあって、アフリカ系アメリカ人のことを﹁子供達﹂、破廉恥な白人によって操作された無知の﹁かも﹂、あるいはその主要な熱情が奴隷制の終焉で解き放たれた野蛮人として描いた。 — Foner pg. xxii 1930年代から1940年代に始まり1950年代に安定期に達した歴史学は、フィリップスの時代の﹁あからさまな﹂人種差別からは離れた。しかし、歴史家達は依然として奴隷を対象として強調した。しかるにフィリップスは主人の親切な注意の対象として奴隷を表現した。ケネス・スタンプのような歴史家はその強調するところを奴隷の酷使や虐待に合わせた[55]。 歴史家スタンリー・M・エルキンスはその1959年の著書﹁奴隷制‥アメリカの制度的および知的生活の問題﹂で、奴隷を純粋に犠牲者として取り上げ、アメリカの奴隷制をナチ強制収容所の残酷さに擬えた。そこでは奴隷の意志を完全に破壊し、﹁骨抜きにされた従順なサンボ︵黒人︶﹂を作り上げ、主人に全く依存するものとした。エルキンスの理論には、すぐに歴史家達の反響があり、主人と奴隷の関係に関する効果に加えて、奴隷は﹁完全に閉ざされた環境ではなく、大きな多様性の出現を許容し、その主人よりもその家族、教会および地域社会に見出すことのできる者との重要な関係を追求できる環境﹂ではなかったことが徐々に認識されるようになった。1970年代のロバート・E・フォーゲルとスタンリー・L・エンガーマンはその著書﹃十字路の時間﹄で、サンボ理論の見解を救い出す最後の試みを行い、その主人のプロテスタント的労働倫理を内在化した存在として奴隷を描いた[56]。奴隷のさらに親切な姿を描く際に、彼らは1974年の著書で、奴隷が行き働いた物質的状態が当時の自由農夫や工場労働者のそれに比べて良かったと指摘した。 1970年代と1980年代の歴史家は考古学的記録、黒人の伝承および統計データを用いて、奴隷生活のより詳しい状態や微妙なところを記述した。元奴隷やの自叙伝や1930年代に連邦記者プロジェクトが行ったインタビューを元に、歴史家は奴隷が経験したままに奴隷制を記述できた。厳密に犠牲者であったり、プランテーションの主人が作り上げた幸福な奴隷とはかけ離れて、奴隷はその行動において快活であり自主的な存在であるように見られた。自主的な努力と奴隷制の中の生活を築こうという努力にも拘わらず、現在の歴史家は奴隷の状態の危険さを認識している。奴隷の子供は両親と所有者の双方の命令に従うことをすぐに覚えた。子供は両親が躾けられているのを見て、自分達もその主人に肉体的あるいは言葉で虐待されることを理解するようになった。この時代の歴史家の著書としては、ジョン・ブラシンゲイムの﹃奴隷社会﹄、ユージーン・ジェノヴェーゼの﹃ロール、ジョードン、ロール﹄、レスリー・ハワード・オーウェンスの﹃財産の人種﹄、およびハーバート・ガットマンの﹃奴隷制における家族および自由﹄がある[57]。 2019年にアメリカに最初の黒人奴隷が上陸してから400年となるのを機に、歴史家による調査プロジェクト﹃Project 1619[58]﹄が発足し、サン・ファン・バウティスタ号との関連など様々な情報が判明している。脚注[編集]
(一)^ Otto H. Olsen (2004年12月). “Historians and the extent of slave ownership in the Southern United States”. Civil War History. Southernhistory.net. 2007年11月23日閲覧。
(二)^ James M. McPherson (1996). Drawn with the Sword: Reflections on the American Civil War. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. p. 15. ISBN 0-19-509679-7
(三)^ James Oliver Horton; Lois E. Horton (2005). Slavery and the Making of America. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. p. 7. ISBN 0-19-517903-X. "奴隷貿易と奴隷の労働による生産品、特に綿花がアメリカの国全体の富を作った。産業革命を推進する元手となり、世界の他の地域にその力を誇示することを可能にした。"
(四)^ “Was slavery the engine of economic growth?”. Digital History. 2007年11月23日閲覧。
(五)^ Ronald Segal (1995). The Black Diaspora: Five Centuries of the Black Experience Outside Africa. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. pp. p. 4. ISBN 0-374-11396-3. "現在、11,863,000人の奴隷が大西洋を越えたと見積もられている。 [Note in original: Paul E. Lovejoy, "The Impact of the Atlantic Slave Trade on Africa: A Review of the Literature," in Journal of African History 30 (1989), p. 368.] ... それは下方修正より上方修正の方が可能性が高いと認められている。"
(六)^ “Quick guide: The slave trade”. bbc.co.uk (2007年3月15日). 2007年11月23日閲覧。
(七)^ Stephen D. Behrendt, David Richardson, and David Eltis, W. E. B. Du Bois Institute for African and African-American Research, ハーバード大学. ﹁アメリカ州に向けた奴隷獲得のための27,233件の航海記録﹂に基づく。 Stephen Behrendt (1999). “Transatlantic Slave Trade”. Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience. New York: Basic Civitas Books. ISBN 0-465-00071-1
(八)^ abcdeサン・ファン号、奴隷運ぶ? マニラで売却後の足跡に新説 米の歴史家提唱 - 河北新報
(九)^ [1]
(十)^ "The curse of Cromwell", A Short History of Northern Ireland, BBC. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(11)^ ab"Slavery in America", Encyclopedia Britannica's Guide to Black History. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(12)^ Trinkley, M. "Growth of South Carolina's Slave Population", South Carolina Information Highway. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(13)^ Morison and Commager: Growth of the American Republic, pp. 212-220.
(14)^ Kolchin pg. 96. As early as 1834, アラバマ州、ミシシッピ州およびルイジアナ州は国全体の綿花生産量の半分を生産し、1859年までにジョージア州と併せて78%にまでなった。この年、両カロライナ州の綿花生産量は国全体の10%にまで落ち込んだ。 Berlin pg. 166. 米英戦争の終わり頃国全体の綿花生産量は30万俵であったが、1820年までに60万俵、1850年までに400万俵となった。
(15)^ Kolchin pg. 96
(16)^ Berlin pg. 161-162
(17)^ Berlin pg. 168-169. Kolchin pg. 96. コルチンは、フォーゲルとエンガーマンが奴隷の84%は家族と共に移住したと主張したが、﹁他の学者の多くはより高い比率で売られたとしていると注釈している。ランサムは (pg. 582) フォーゲルとエンガーマンが1830年代のメリーランド州における幾つかの郡部の研究をその結論の根拠にしており、そこから全南部の全期間の数字を外挿したと注釈している。
(18)^ Berlin pg 166-169
(19)^ Kolchin pg. 98
(20)^ Berlin pg. 168-171
(21)^ Berlin pg. 174
(22)^ Berlin pg. 175-177
(23)^ Berlin pg. 179-180
(24)^ abGenovese (1967)
(25)^ Stampp, Kenneth M. "Interpreting the Slaveholders' World: a Review." スタンプは次の様に書いている。﹁ジェノヴェーゼは力強く書いており、確かに彼は鈍感ではない。しかし、私の考えでは、彼が歴史をマルクス史観で解釈することの優越性を表現しようとすることは誤りと見なす必要がある。著書の見解は実際にマルクス主義そのものでは無いと言ってこのことを説明する人がいる。私の説明は南北戦争前の南部では、基本的に奴隷制を人種差別で守り、階級よりも世襲階級を強調していたので、歴史をマルクス史観で解釈するには適当な場所とは言えない。
(26)^ Conrad P. Kottak, "What is hypodescent?", Human Diversity and "Race", Cultural Anthropology, Online Learning, McGraw Hill, accessed 21 April 2010.
(27)^ abcWeiss, T. "Review of Robert William Fogel and Stanley L. Engerman, "Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery", Economic History News Services - Book Reviews, November 16, 2001. Book review. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(28)^ Catterall, Helen T., Ed. 1926. Judicial Cases Concerning Slavery and the Negro. Washington, D.C.: Carnegie Institute, p. 247
(29)^ “奴隷貿易がアメリカ大陸に及ぼした﹁遺伝的影響﹂、レイプや病気が関係 米研究”. BBCニュース (2020年7月28日). 2024年5月19日閲覧。
(30)^ Sklar, Kathryn. "Women who speak for an Entire Nation". American British Women Compared at the World Anti-slavery Convention, London 1840. The pacific Historical Review, Vol. 59, Wo. 4, Nov. 1990. Pp. 453-499.
(31)^ Richard S. Newman, Transformation of American abolitionism : fighting slavery in the early Republic chapter 1
(32)^ The People's Chronology, 1994 by James Trager
(33)^ de Toqueville pg. 367.
(34)^ Berlin, "Generations of Captivity" pg. 104
(35)^ 創世記 14:14,15、出エジプト記 21:16、レビ記25章39,40節、出エジプト記 22:3、申命記15章13,14節、コリントの信徒への手紙 7:21,コロサイ書3:22等
(36)^ Don E. Fehrenbacher, The Dred Scott Case: Its Significance in American Law and Politics (New York: Oxford University Press, 1978)
(37)^ E. Merton Coulter, The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky (1926) pp 268-70.
(38)^ 小作農は綿花の半分以下しか受け取ることができず、綿花の売買額は地主が決めるために、奴隷時代と大差ない制度。
(39)^ O'Dell, Larry (2007年2月25日). “Virginia Apologizes for Role in Slavery”. The Washington Post
(40)^ Gallay, Alan. (2002) The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South 1670-171. Yale University Press: New York. ISBN 0-300-10193-7.
(41)^ Castillo, E.D. 1998. "Short Overview of California Indian History", California Native American Heritage Commission, 1998. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(42)^ Beasley, Delilah L. (1918). "Slavery in California," The Journal of Negro History, Vol. 3, No. 1. (Jan.), pp. 33-44.
(43)^ Digital "African American Voices", Digital History. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(44)^ "Haida Warfare", civilization.ca. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
(45)^ A history of the descendants of the slaves of Cherokee can be found at Sturm, Circe. Blood Politics, Racial Classification, and Cherokee National Identity: The Trials and Tribulations of the Cherokee Freedmen. American Indian Quarterly, Vol. 22, No. 1/2. (Winter - Spring, 1998), pp. 230-258. In 1835, 7.4% of Cherokee families held slaves. In comparison, nearly one third of white families living in Confederate states owned slaves in 1860. Further analysis of the 1835 Federal Cherokee Census can be found in Mcloughlin, WG. "The Cherokees in Transition: a Statistical Analysis of the Federal Cherokee Census of 1835". Journal of American History, Vol. 64, 3, 1977, p. 678. A discussion on the total number of Slave holding families can be found in Olsen, Otto H. Historians and the extent of slave ownership in the Southern United States. Civil War History, Dec. 2004 (Accessed here June 8, 2007)
(46)^ Duncan, J.W. 1928. "Interesting ante-bellum laws of the Cherokee, now Oklahoma history". Chronicles of Oklahoma 6(2):178-180. Retrieved July 13, 2007.
(47)^ Davis, J. B. 1933. "Slavery in the Cherokee nation". Chronicles of Oklahoma 11(4):1056-1072. Retrieved July 13, 2007.
(48)^ Stampp p. 194. Oakes p.47-48.
(49)^ Mason pg. 19-20
(50)^ Berlin, "Generations of Captivity" pg. 138
(51)^ Oakes pg. 47-48
(52)^ Oakes pg. 47-49
(53)^ Kolchin pg. 134
(54)^ Horton and Horton pg. 9. David and Temin (page 740) add, ﹁フィリップスとその追随者の学識は、南北戦争の前の南部で白人至上主義社会の進歩的イメージを復権させることに捧げられた。それは奴隷所有者を父親的温情主義の男として概して同情的でときにはあからさまに弁解がましく描いている。
(55)^ Kolchin pg. 135. David and Temin pg. 741. デイビッドとテミンは次の様に書いた﹁その利点は相対的に主人の側から奴隷の側に移った。この反転はケネス・スタンプの﹃特有の制度﹄︵1956年︶によってもたらされた。それは黒人を生物学的にまた文化的に劣っている子供のような人々として性格づけることと、白人農園主を自分達で作った訳ではないややこしい社会問題を扱う父親的紳士として表現すること、その両方を拒否した。
(56)^ Kolchin pg. 136
(57)^ Kolchin pg. 137-143. Horton and Horton pg. 9
(58)^ Project 1619 Inc.
参考文献[編集]
一次史料[編集]
- Albert, Octavia V. Rogers. The House of Bondage Or Charlotte Brooks and Other Slaves. Oxford University Press, 1991. Primary sources with commentary. ISBN 0-19-506784-3
- The House of Bondage, or, Charlotte Brooks and Other Slaves, Original and Life-Like complete text of original 1890 edition, along with cover & title page images, at website of University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Berlin, Ira, Joseph P. Reidy, and Leslie S. Rowlands, eds. Freedom: A Documentary History of Emancipation, 1861-1867 5 vol Cambridge University Press, 1982. very large collection of primary sources regarding the end of slavery
- Blassingame, John W., ed. Slave Testimony: Two Centuries of Letters, Speeches, Interviews, and Autobiographies.Louisiana State University Press, 1977.
- A Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave (1845) (Project Gutenberg: [2]), (Audio book at FreeAudio.org [3])
- "The Heroic Slave." Autographs for Freedom. Ed. Julia Griffiths Boston: Jewett and Company, 1853. 174-239. Available at the Documenting the American South website [4].
- Frederick Douglass My Bondage and My Freedom (1855) (Project Gutenberg: [5])
- Frederick Douglass Life and Times of Frederick Douglass (1892)
- Frederick Douglass Collected Articles Of Frederick Douglass, A Slave (Project Gutenberg)
- Frederick Douglass: Autobiographies by Frederick Douglass, Henry Louis Gates, Jr. Editor. (Omnibus of all three) ISBN 0-940450-79-8
- Rawick, George P., ed. The American Slave: A Composite Autobiography . 19 vols. Greenwood Publishing Company, 1972. Collection of WPA interviews made in 1930s with ex-slaves
歴史研究[編集]
- Berlin, Ira. Generations of Captivity: A History of African American Slaves. (2003) ISBN 0-674-01061-2.
- Berlin, Ira. Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America. Harvard University Press, 1998. ISBN 0-674-81092-9
- Berlin, Ira and Ronald Hoffman, eds. Slavery and Freedom in the Age of the American Revolution University Press of Virginia, 1983. essays by scholars
- Blassingame, John W. The Slave Community: Plantation Life in the Antebellum South Oxford University Press, 1979. ISBN 0-19-502563-6.
- David, Paul A. and Temin, Peter. Slavery:The Progressive Institution? The Journal of Economic History. Vol. 34, No. 3 (September 1974)
- David Brion Davis. Inhuman Bondage: The Rise and Fall of Slavery in the New World (2006)
- De Tocqueville, Alexis. Democracy in America. (1994 Edition by Alfred A Knopf, Inc) ISBN 0-679-43134-9
- Elkins, Stanley. Slavery : A Problem in American Institutional and Intellectual Life. University of Chicago Press, 1976. ISBN 0-226-20477-4
- Fehrenbacher, Don E. Slavery, Law, and Politics: The Dred Scott Case in Historical Perspective Oxford University Press, 1981
- Fogel, Robert W. Without Consent or Contract: The Rise and Fall of American Slavery W.W. Norton, 1989. Econometric approach
- Foner, Eric. Forever Free.(2005) ISBN 0-375-40259-4
- Franklin, John Hope and Schweninger. Runaway Slaves: Rebels on the Plantation. (1999) ISBN 0-19-508449-7.
- Gallay, Alan. The Indian Slave Trade (2002).
- Genovese, Eugene D. Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made Pantheon Books, 1974.
- Genovese, Eugene D. The Political Economy of Slavery: Studies in the Economy and Society of the Slave South (1967)
- Genovese, Eugene D. and Elizabeth Fox-Genovese, Fruits of Merchant Capital: Slavery and Bourgeois Property in the Rise and Expansion of Capitalism (1983)
- Hahn, Steven. "The Greatest Slave Rebellion in Modern History: Southern Slaves in the American Civil War." Southern Spaces (2004)
- Higginbotham, A. Leon, Jr. In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The Colonial Period. Oxford University Press, 1978. ISBN 0-19-502745-0
- Horton, James Oliver and Horton, Lois E. Slavery and the Making of America. (2005) ISBN 0-19-517903-X
- Kolchin, Peter. American Slavery, 1619-1877 Hill and Wang, 1993. Survey
- Mason, Matthew. Slavery and Politics in the Early American Republic. (2006) ISBN 978-0-8078-3049-9.
- Morgan, Edmund S. American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia W.W. Norton, 1975.
- Morris, Thomas D. Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619-1860 University of North Carolina Press, 1996.
- Oakes, James. The Ruling Race: A History of American Slaveholders. (1982) ISBN 0-393-31705-6.
- Ransom, Roger L. Was It Really All That Great to Be a Slave? Agricultural History, Vol. 48, No. 4 (October 1974)
- Scarborough, William K. The Overseer: Plantation Management in the Old South (1984)
- Stampp, Kenneth M. The Peculiar Institution: Slavery in the Ante-Bellum South (1956) Survey
- Stampp, Kenneth M. "Interpreting the Slaveholders' World: a Review." Agricultural History 1970 44(4): 407-412. ISSN 0002-1482
- Tadman, Michael. Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South University of Wisconsin Press, 1989.
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. Encyclopedia of Slave Resistance and Rebellion. Westport, CT: Greenwood, 2007.
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2007.
地方ごとの研究[編集]
- Fields, Barbara J. Slavery and Freedom on the Middle Ground: Maryland During the Nineteenth Century Yale University Press, 1985.
- Clayton E. Jewett and John O. Allen; Slavery in the South: A State-By-State History Greenwood Press, 2004
- Kulikoff, Alan. Tobacco and Slaves: The Development of Southern Cultures in the Chesapeake, 1680-1800 University of North Carolina Press, 1986.
- Minges, Patrick N.; Slavery in the Cherokee Nation: The Keetoowah Society and the Defining of a People, 1855-1867 2003 deals with Indian slave owners.
- Mohr, Clarence L. On the Threshold of Freedom: Masters and Slaves in Civil War Georgia University of Georgia Press, 1986.
- Mooney, Chase C. Slavery in Tennessee Indiana University Press, 1957.
- Olwell, Robert. Masters, Slaves, & Subjects: The Culture of Power in the South Carolina Low Country, 1740-1790 Cornell University Press, 1998.
- Reidy, Joseph P. From Slavery to Agrarian Capitalism in the Cotton Plantation South, Central Georgia, 1800-1880 University of North Carolina Press, 1992.
- Ripley, C. Peter. Slaves and Freemen in Civil War Louisiana Louisiana State University Press, 1976.
- Rivers, Larry Eugene. Slavery in Florida: Territorial Days to Emancipation University Press of Florida, 2000.
- Sellers, James Benson; Slavery in Alabama University of Alabama Press, 1950
- Sydnor, Charles S. Slavery in Mississippi. 1933
- Takagi, Midori. Rearing Wolves to Our Own Destruction: Slavery in Richmond, Virginia, 1782-1865 University Press of Virginia, 1999.
- Taylor, Joe Gray. Negro Slavery in Louisiana. Louisiana Historical Society, 1963.
- Wood, Peter H. Black Majority: Negroes in Colonial South Carolina from 1670 through the Stono Rebellion W.W. Norton & Company, 1974.
歴史学研究[編集]
- John B. Boles and Evelyn T. Nolen, eds., Interpreting Southern History: Historiographical Essays in Honor of Sanford W. Higginbotham (1987).
- Richard H. King, "Marxism and the Slave South", American Quarterly 29 (1977), 117-31. focus on Genovese
- Peter Kolchin, "American Historians and Antebellum Southern Slavery, 1959-1984", in William J. Cooper, Michael F. Holt, and John McCardell , eds., A Master's Due: Essays in Honor of David Herbert Donald (1985), 87-111
- James M. McPherson et al., Blacks in America: Bibliographical Essays (1971).
- Peter J. Parish; Slavery: History and Historians Westview Press. 1989
- Tulloch, Hugh. The Debate on the American Civil War Era (1999) ch 2-4
元奴隷の口伝による歴史[編集]
- Before Freedom When I Just Can Remember: Twenty-seven Oral Histories of Former South Carolina Slaves, Belinda Hurmence, John F. Blair, Publisher, 1989, trade paperback 125 pages, ISBN 0-89587-069-X
- Before Freedom: Forty-Eight Oral Histories of Former North & South Carolina Slaves, Belinda Hurmence, Mentor Books, 1990, mass market paperback, ISBN 0-451-62781-4
- God Struck Me Dead, Voices of Ex-Slaves, Clifton H. Johnson ISBN 0-8298-0945-7
歴史小説[編集]
- Edward P. Jones. The Known World New York: Amistad, 2003. ISBN 0-06-055755-9, 2003 winner of the National Book Critic Circle 2004年ピューリッツァー賞 フィクション部門受賞作
関連項目[編集]
- 奴隷#欧米
- 奴隷貿易#大西洋奴隷貿易
- 解放奴隷#アメリカ合衆国
- 奴隷解放宣言
- ルーツ (テレビドラマ)
- アメリカ合衆国の人種差別
- 黒人霊歌
- 公民権運動
- アメリカ合衆国の歴史
- サリー・ヘミングス
- それでも夜は明ける
- 奴隷制度に対するキリスト教徒の見解
外部リンク[編集]
- "John Brown's body and blood" by Ari Kelman: a review in the TLS, February 14th, 2007.
- Slavery and the Making of America - PBS - WNET, New York (4-Part Series)
- Timeline of Slavery in America
- Born in Slavery: Slave Narratives from the Federal Writers' Project, 1936-1938
- Images of slavery drawn by Thomas Nast (has background music)
- History of Slavery in America a historical overview
- Teaching resources about Slavery and Abolition on blackhistory4schools.com
- Slavery in the United States from EH.NET by Jenny B. Wahl of Carleton College
- Map of 1820 showing free and slave territories.
- Classics on American Slavery collection of old documents available on-line through Dinsmore Documentation
- Slavery: A Dehumanizing Institution by Nell Irvin Painter, historian and author of Creating Black Americans
- New Georgia Encyclopedia (Slavery in Antebellum Georgia)
- WWW-VL: Online Books on Slavery in America
- University of North Carolina Press on finding freedom and liberty in BNA-Canada
- Account of an African Prince Sold into Slavery - Islamica Magazine
