ユーフラテス川
表示
| ユーフラテス川 | |
| 川 | |
| 名前の由来: ギリシア語、古代ペルシア語:Ufrātu、エラム語:ú-ip-ra-tu-iš | |
| 国 | イラク, シリア, トルコ |
|---|---|
| 流域 | トルコ, シリア, イラク, サウディアラビア, クウェート, イラン |
| 支流 | |
| - 左支流 | バリフ川, ハブール川 |
| - 右支流 | サージュール川 |
| 市 | ビレジク, ラッカ, デリゾール, マヤーディーン, ハディーサ, ラマーディー, ハバニヤー, ファルージャ, クーファ, サマーワ, ナーシリーヤ |
| ランドマーク | アサド湖, カーディシーヤ湖, ハッバーニーヤ湖 |
| 源流 | |
| - 所在地 | ムラト川, トルコ |
| - 標高 | 3,520m (11,549ft) |
| 第二源流 | |
| - location | カラ川, トルコ |
| - 標高 | 3,290m (10,794ft) |
| 源流の合流地 | |
| - 所在地 | ケバン, トルコ |
| - 標高 | 610m (2,001ft) |
| 合流地 | シャットゥルアラブ川 |
| - 所在地 | アル・クルナ, バスラ県, イラク |
| - 座標 | 北緯31度0分18秒 東経47度26分31秒 / 北緯31.00500度 東経47.44194度座標: 北緯31度0分18秒 東経47度26分31秒 / 北緯31.00500度 東経47.44194度 |
| 長さ | 2,800km (1,740mi) |
| 流域 | 500,000 km² (193,051 sq mi) |
| 流量 | for ヒート |
| - 平均 | 356 m3/s (12,572 cu ft/s) |
| - 最大 | 2,514 m3/s (88,781 cu ft/s) |
| - 最小 | 58 m3/s (2,048 cu ft/s) |
| ウィキメディア・コモンズ: Euphrates | |
ユーフラテス川︵ユーフラテスがわ、英語: Euphrates、[juːˈfreɪtiːz] ( 音声ファイル)︶は、西アジア最長の川である。ティグリス川と共にメソポタミア︵川の間の土地、の意︶を形作っている。源流は東トルコにあり、シリアとイラクを通過した後ティグリス川と合流し、シャットゥルアラブ川としてペルシア湾に注ぐ。
音声ファイル)︶は、西アジア最長の川である。ティグリス川と共にメソポタミア︵川の間の土地、の意︶を形作っている。源流は東トルコにあり、シリアとイラクを通過した後ティグリス川と合流し、シャットゥルアラブ川としてペルシア湾に注ぐ。
地名[編集]
古代ギリシア語のエウプラーテース︵古代ギリシア語: Εὐφράτης、Euphrátēs︶は古代ペルシア語の 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢︵Ufrātu[1]︶から来ており、古代ペルシア語名はエラム語の 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 ︵ú-ip-ra-tu-iš︶から来ている。エラム語名は突き詰めると楔形文字の綴りである︵𒌓𒄒𒉣︶から派生した。これはシュメール語ではブラヌナ︵Buranuna︶またはブラヌン︵Buranun︶と読まれ[2]、アッカド語ではプラトゥム︵Purattum︶と読まれた[2]。多くの楔形文字はシュメール語の発音とアッカド語の発音があり、シュメール語とアッカド語は同じ意味である。アッカド語の Purattum[3] はセム語系の言語︵例えばシリア語: P(ə)rāṯ 、アラビア語: al-Furrāt︶や、近隣で使用されていた言語︵フルリ語: Puranti、ウラルトゥ語: Uruttu︶に引き継がれている。エラム語、アッカド語、そして恐らくシュメール語の名前は、記録に残されていない基層言語︵より古い時代の言語︶から来ている[4][2]。Gamkrelidze とイワノフ︵Ivanov︶は原シュメール語形 *burudu︵銅、シュメール語: urudu︶が語源であると主張し、これは当時メソポタミアが銅の冶金の中心地であったため、ユーフラテス川がいかだを用いて銅鉱石を運んでいたことから来ていると説明している[5][2]。 ユーフラテス川への言及がある楔形文字文書の最も古い記録はイラク南部にあるシュルッパクと前サルゴン時代のニップルで発見された紀元前3千年紀のものである。これらの文書はシュメール語で書かれており、ユーフラテス川は Buranuna︵楔形文字の綴りでは、UD.KIB.NUN.KI[2]︶とよばれている。この名前は KIB.NUN.(NA) とも書かれ、神格化されていることを示すディンギル︵d︶を伴って dKIB.NUN とも表記される。 以下にユーフラテス川の周辺地域で使用されている、あるいはかつて使用されていた主要な言語での呼称を示す。| 言語名 | 原語表記 | ラテン文字転写 | カナ転写 |
|---|---|---|---|
| アラビア語 | الفرات | al-Furāt[6] | アル=フラート |
| ペルシア語 | فرات | Forāt[7]:499 | フォラート |
| トルコ語 | Fırat | Fırat[6] | フラト |
| クルド語 | فرات | Firat/Firhat/Ferhat/Firad | |
| シリア語 | ̇ܦܪܬ | Pǝrāt | |
| アルメニア語 | Եփրատ | Yeprat/Yefrat | |
| ヘブライ語 | פרת | Perat | |
| 英語 | Euphrates | Euphrates | ユーフラテス |
| シュメール語 | 𒌓𒄒𒉣 | Buranuna/Buranun/Puranun | ブラヌナ、ブラヌン |
| アッカド語 | 𒌓𒄒𒉣 | Purattum | プラトゥム |
| 古代ギリシア語 | Εὐφράτης | Euphrátēs | エウプラーテース |
| 古代ペルシア語 | 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢 | Ufrātu[6]/Ufrat | |
| 中期ペルシア語 | Frat[6] | ||
| エラム語 | 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 | ú-ip-ra-tu-iš | |
| フルリ語/フリ語 | Puranti | ||
| ウラルトゥ語 | Uruttu |
流路[編集]
ユーフラテス川は西アジアで最も長い川である[8]。この川はカラ川︵または西ユーフラテス川、450キロメートル︶とムラト川︵または東ユーフラテス川、650キロメートル︶が東トルコのケバンの10キロメートル上流で合流することで出現する[9]。ダウディ︵Daoudy︶とフレンケン︵Frenken︶はユーフラテス川の長さを、ムラト川の源流からティグリス川との合流地点までの3000キロメートルとし、そのうち1230キロメートルがトルコ領、710キロメートルがシリア領、1060キロメートルがイラク領内を流れるとしている[10][11]。この数字はイサエフ︵Isaev︶とミハイロヴァ︵Mikhailova︶も用いている[12]。シャットゥルアラブ川の長さ、つまりユーフラテス川とティグリス川の合流地点からペルシア湾までの長さは複数の出典で195キロメートルとなっている[13]。
カラ川とムラト川はヴァン湖の北西、それぞれ海抜標高3290メートルと3520メートルの位置に源流を持つ[14]。ケバン・ダムの場所では標高693メートルまで下降する。この地点では2つの川はユーフラテス川として既に合流している。ケバンからシリア・トルコ国境までユーフラテス川は600キロメートル未満の距離で368メートルを更に下る。ユーフラテス川が上メソポタミア平原に入った後、その縦断勾配は有意に落ちる。シリア内でユーフラテス川は163メートルの落差を持つが、その後のヒートとシャットゥルアラブ川の間では55メートルしか落差がない[9][15]。

ムラト川の景色
シリア領内で3つの川がユーフラテス川に注ぎ込む。サージュール川、バリフ川、そしてハブール川である。これらの河川はシリア・トルコ国境にあるタウルス山脈の山麓に源流を持ち、ユーフラテス川の水量を比較的僅かに増加させる。サジュル川はこれらの支流の中で最も小さく、ガズィアンテプ近郊の二つの流れを源流とし、ティシュリーン・ダムの貯水池に流れ込む前にマンビジ周辺で平野を浸す。バリフ川の水は大部分がアイン・アル=アルース︵'Ayn al-'Arus︶そばのカルスト湖から供給され、ラッカ市でユーフラテス川に合流するまで南へ流れる。長さ、流域面積、そして流量に関して、ハブール川が3つの支流の中で最大である。その主たる源流のカルスト湖はラース・アル=アインの周囲に位置し、ハブール川の流れはハサカの南東を経て南へ流れを変え、ブサイラ近郊でユーフラテス川に注ぎ込む。ユーフラテス川がイラク領内に入った後は合流する自然の支流はないが、ユーフラテス川流域とティグリス川流域を繋ぐ運河網が存在する[21][22]。
ユーフラテス川の流量[編集]
ユーフラテス川の水の大部分は降水と雪解け水の形で供給され、その結果として4月から5月にかけて流量のピークを迎える。この2ヶ月間の流量はユーフラテス川の年間流量の36パーセントを占め、60-70パーセントとする出典も存在する。そして夏と秋には流量は少ない[12][16]。20世紀初頭から半ばにかけてのユーフラテス川の年間自然水量の平均は、ケバンでの測定で20.9立方キロメートルであり、ヒートでの測定では36.6立方キロメートル、ヒンディヤでの測定では21.5立方キロメートルである[17]。しかし、このような平均値は年間流量の変動が大きいことを隠してしまう。シリア・トルコ国境のすぐ北にあるビレジクでは、少ない年では1961年の15.3立方キロメートル、多い年では1963年の42.7立方キロメートルという計測結果がある[18]。 このようなユーフラテス川の流量を決定する環境は1970年代の最初のダム建設以来劇的に変化している。1990年以降に収集されたユーフラテス川の流量に関するデータは、ユーフラテス川に建設された多数のダムと、灌漑用水の増加の影響を示している。1990年以降のヒートの平均水量は3立方メートル毎秒減少しており、年間当たりでは11.2立方キロメートル減少している。季節的変動も同様に変化を被った。1990年以前のヒートでの最大流量の記録は毎秒7,510立方メートルであるが、1990年以後では毎秒2,514立方メートルに過ぎない。ヒートでの最小流量は比較的変化が少なく、1990年以前の毎秒55立方メートルからその後、毎秒58立方メートルに上昇した[19][20]。支流[編集]

| 支流の名前 | 長さ | 流域面積 | 水量 | ユーフラテス川から見た合流方向 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| カラ川 | 450キロメートル | 22,000平方キロメートル | 合流 | |
| ムラト川 | 650キロメートル | 40,000平方キロメートル | 合流 | |
| サージュール川 | 108キロメートル | 2,042平方キロメートル | 毎秒4.1立方メートル | 右岸 |
| バリフ川 | 100キロメートル | 14,400平方キロメートル | 毎秒6立法メートル | 左岸 |
| ハブール川 | 486キロメートル | 37,081平方キロメートル | 毎秒45立方メートル | 左岸 |
流域[編集]

詳細は「ティグリス・ユーフラテス水系」を参照
カラ川とムラト川の流域はそれぞれ22,000平方キロメートル、40,000平方キロメートルの地域を覆っている[9]。ユーフラテス川の流域面積の推定の幅は非常に広く、小さい推計では233,000平方キロメートル、大きな推計では766,000平方キロメートルとなる[12]。最近の推計値には388,000平方キロメートル[9]、444,000平方キロメートル[10][23]、579,314平方キロメートルといったものがある[24]。ユーフラテス川流域の大部分はトルコ、シリア、イラクにある。ダウディとフレンケンの両者によれば、トルコはそのうちの28パーセント、シリアは17パーセント、イラクは40パーセントを占めている[10][11]。イサエフとミハイロヴァはトルコ、シリア、そしてイラクにそれぞれ33パーセント、20パーセント、そして47パーセントの割合であると推計している[12]。一部の資料は、流域面積の15パーセントはサウディアラビアに、ごく一部はクウェートの領内に位置すると推定している[10][11]。最後に、いくつかの資料はまた、ヨルダンをユーフラテス川の流域に含めており、東部砂漠︵eastern desert︶の220平方キロメートルの極一部の水は西ではなく東側へ流れているとしている[12][25]。
自然史[編集]
「メソポタミア沼地」も参照

ユーフラテス川は明確に異なる複数の植生の地域を貫流している。ユーフラテス川流域のほとんどの地域で、数千年にわたる人類の活動はその環境を有意に悪化させているが、ところどころに元来の植生が残されている。ユーフラテス川の源流からペルシア湾へ進むにつれ年間降水量が徐々に減少し、これが降水量によって支えられる植生の強力な決定要因である。ユーフラテス川は上流では南東トルコの山地を流れ、その南の丘陵地帯では耐乾性の森林地帯を支えている。この地域の湿潤な領域の植物種には様々なオーク、ピスタチオの木々、そしてバラ科の植物︵バラやウメの仲間︶がある。耐乾性の森林地帯の乾燥した部分では、低密度のオークの森とバラ科の植物が生育している。ここではヒトツブコムギ、エンマーコムギ、エンバク、ライムギなど、多くの穀物の野生種を見つけることが出来る[26]。この地域の南側に広がる地域は森林地帯とステップ地帯の植生の混合地帯である。ラッカ市とシリア・イラク国境の間のユーフラテス川沿いはステップ地帯である。このステップはヨモギ属のArtemisia herba-albaとアカザ科の植物に特徴づけられる。歴史を通じてこの地域は住民によるヒツジやヤギの牧畜に伴う過放牧に晒されている[27]。シリアとイラクの国境の南東から真の砂漠が始まる。この地域は植生を全く持たないか、またはアカザ科かPoa sinaicaの小さな群生地域がある。現在では人類の影響のために生き残ったものはないが、研究によってこのユーフラテスの河岸地帯には元来は河畔林が広がっていたと考えられている。この種の河畔林に特徴的な植物は、スズカケノキ、コトカケヤナギ︵Populus euphratica︶、タマリスク︵ギョリュウ︶、トネリコ属、そして様々な湿地植物︵wetland plants︶などである[28]。
ティグリス・ユーフラテス川流域の魚類ではコイの仲間が最も一般的であり、54種のうち34種︵species︶を占めている[29]。この中でも、Luciobarbus esocinusはスポーツ・フィッシングの対象として優れており、イギリスではティグリス・サーモン︵Tigris salmon︶のニックネームで呼ばれている。メソポタミアハナスッポンはスッポン科の絶滅危惧種であり、ティグリス・ユーフラテス水系にしか生息していない[30][31]。
前1千年紀の新アッシリア時代の宮殿のレリーフには自然豊かな風景の中でのライオン狩りや雄牛狩りが描かれている[32]。16世紀から19世紀のヨーロッパ人の旅行者はシリアのユーフラテス川流域に生息する豊富な動物について報告しているが、現在ではその多くは生息数が激減または絶滅している。ユーフラテス川沿いのステップにはガゼル、アジアノロバ、そして今は絶滅したアラビアダチョウが生息していた。また、野生のイノシシも生息していた。肉食動物にはハイイロオオカミ、キンイロジャッカル、アカギツネ、ヒョウ、そしてライオンがいた。シリアヒグマは南東トルコの山岳地帯で見ることが出来る。かつてヨーロッパビーバーが生息していたことはシリアにあるテル・アブ・フレイラの先史時代の遺跡で骨がまとまって発見されていることで証明されているが、このビーバーは歴史時代には全く見られない[33]。
下流部にはメソポタミア沼地が広がり、アフワールという名称で世界遺産にも登録されている[34]。
河川改修[編集]
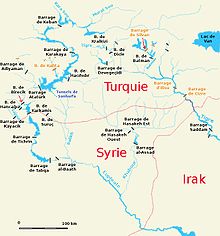
イラクにあるユーフラテス川のヒンディーヤ堰︵Hindiya Barrage[訳語疑問点]︶はイギリス人の土木技師ウィリアム・ウィルコックスの計画に基づき1913年に完成した。これはティグリス・ユーフラテス水系に建設された最初の近代水利施設︵water diversion structure︶であった[35]。このヒンディヤ堰は1950年代にラマーディー堰︵Ramadi Barrage[訳語疑問点]︶と、ユーフラテス川の流れを制御し窪地に過剰な水が流れ込むことを制限するために設置された近郊のAbu Dibbis貯水池に引き継がれた。これは現在ハッバーニーヤ湖と呼ばれている。ユーフラテス川にあるイラク最大のダムはハディーサ・ダムである。これは全長9キロメートルのアースフィルダムであり、カーディシーヤ湖を作り出している[36]。シリアとトルコは1970代にそれぞれ最初のダムを建造した。シリアのタブカ・ダムは1973年に完成し、トルコのケバン・ダムは南東アナトリアプロジェクトという大計画の中で1974年に完成した。その後、シリアはバアス・ダムとティシュリーン・ダムという2つのダムをユーフラテス川に建造し、ハラビーイェ・ダムという4番目のダムをラッカとデリゾールの間で計画している[37]。タブ化・ダムはシリア最大のダムであり、そのダム湖であるアサド湖は灌漑用水および飲料水の重要な水源となっている。計画では640,000ヘクタールをアサド湖の水を用いて灌漑する予定であったが、2000年時点で100,000から124,000ヘクタールが実現したにとどまっている[38][39]。シリアはまた、ハブール川とその支流に3つの小規模ダムを建造した[40]。
1970年代の南東アナトリアプロジェクト︵トルコ語: Güneydoğu Anadolu Projesi‥GAP︶の実行と共に、トルコはティグリス川とユーフラテス川の水を灌漑と水力発電に利用し、トルコ南東の地区の経済を活性化させる意欲的な計画を立ち上げた[41]。GAPは総計75,000平方キロメートルの地域とおおよそ700万人の人々に影響を与える。これはトルコの面積と人口の10パーセントを占める。計画達成時にはGAPは︵ケバン・ダムを含む︶22のダムと19の発電所で構成され、そして1,700,000ヘクタールの農地に灌漑用水を供給する[42]。この灌漑用地のうちおよそ910,000ヘクタールがユーフラテス川流域に位置している[43]。GAPの中で特に最大のダムはアタテュルク・ダムであり、シャンルウルファの北西約55キロメートルに位置する。これは高さ184メートル、全長1,820メートルのダムで、1992年に完成した。この結果形成されたダム湖はトルコで3番目に大きな湖である。その最大貯水量は48.7平方キロメートルであり、アタテュルク・ダムはユーフラテス川の年間流水量全体を保持するのに十分な大きさを持っている[44]。GAPは2010年に完了が予定されていたが、トルコとユーフラテス川およびティグリス川下流域の諸国との間で水に対する権利割合の公式合意がなされなかったため、世界銀行が資金提供を保留したことで延期された[45]。
堰やダムとは別に、イラクはまたユーフラテス川とハッバーニーヤ湖、サルサール湖、 Abu Dibbis貯水池を結ぶ複雑な運河網を構築している。その全てが洪水の過剰な水量を調整するために使用可能である。Shatt al-Hayy運河を通じてユーフラテス川はティグリス川と接続されている。この運河網で最大の運河は主放流溝︵The Main Outfall Drain[訳語疑問点]︶であり、1953年から1992年の間に建設された。この全長565キロメートルの運河は灌漑による土壌の塩水化︵塩類集積︶を防ぐためにバグダード南のユーフラテス川とティグリス川の間の地域に水を注ぎこむためのものである。また大型の貨物用の艀︵freight barges︶をバグダードまで航行させることができる[46][47][48]。
環境と社会的影響[編集]
「ダムと環境」も参照


ユーフラテス川のダムの建設と灌漑の計画は環境と川沿いの国々の社会に重大な影響を与えている。ユーフラテス川とティグリス川の流域の双方でGAPの一環として建設された複数のダムは382の村落に影響を及ぼし、200,000人の人々が他の土地へ移住することになった。
最も多くの人口の移住を必要としたのはアタテュルク・ダムの建設で、このダム単独の影響で55,300人が移住した[49]。移転を要求された人々についての調査によれば、その過半数は新しい状況に不満を持っており、受け取った補償金は十分ではないと考えられていた[50]。シリアではアサド湖による冠水によって約4,000家族が強制的な移住を余儀なくされ、トルコとイラクの国境に沿ってアラブベルトを作る計画の一環として、北部シリアの別の地域に移った。この計画は2009年現在では放棄されている[51][52][53]。
ユーフラテス川の流路変更とは別に、多数のダムと灌漑の計画は環境に他の影響も及ぼしている。平均気温の高い諸国の領内における広い表面積を持った貯水池の建設は蒸発量を増加させ、それによって人類が利用可能な水の総量が減少している。貯水池からの年間蒸発量はトルコで2立方キロメートル、シリアで1立方キロメートル、そしてイラクで5立方キロメートルであると推計されている[54]。イラク領内のユーフラテス川の水質は悪い。なぜならば上流で灌漑用水としてトルコとシリアで取水が行われ、農地で使用された水溶性の化学肥料と共に川に戻されるためである[55]。また、上流でのダム建設の結果としてイラク領内のユーフラテス川の塩分が増加し、飲料水としての品質が低下した[56]。多くのダムや灌漑計画と、それに付随する大規模な取水はイラクで、既に脆弱なメソポタミアの湖沼と淡水魚の生息地に有害な影響を及ぼしている[57][58]。
︵ダム建設に伴う︶ユーフラテス河谷の大部分での増水は、特にトルコとシリアでは多くの考古学的な遺跡や文化的な意義のある地域を浸水させている[59]。危機に晒された文化遺産を記録または保存するために協調した努力が行われているが、多くの場所は恐らく永遠に失われた。トルコのユーフラテス川で行われたGAPの一連のプロジェクトは、危険に晒されているユーフラテス渓谷の考古学的、文化的遺産を記録するための重要な国際的努力をもたらしている。とりわけ、ビレジク・ダムのダム湖によってゼウグマが貴重なローマのモザイクと共に水没したことはトルコおよび各国の報道機関の双方で多くの議論を巻き起こした[60][61]。シリアのタブカ・ダムの建設はアサド湖の形成に伴う水没によって姿を消す遺産を文書化するためのUNESCOの調整の下での大規模な国際的運動に繋がった。多数の国から集まった考古学者たちはナトゥーフ文化からアッバース朝時代までの遺跡を発掘し、2本のミナレットが水没域の外側に移築された。氾濫ないしはアサド湖の水位上昇の影響を受けた重要な遺跡にはムレイベット、エマル、そしてテル・アブ・フレイラなどがある[62]。ティシュリン・ダムの建設時にも同様の国際的な取り組みがなされ、水没する遺跡、中でも重要な前土器新石器B文化の遺跡であるJerf el-Ahmarで調査が行われた[63]。
考古学の一般調査と緊急発掘はイラクのカーディシーヤ湖に水没する地域でも行われた[64]。こうした水没した地域の一部は近年、湖が干上がったことで再びアクセスが可能になった。これによって新たに考古学者が更なる研究を行う可能性が高まったが、盗掘も可能としており、2003年のイラク戦争の後、イラク各地で横行している[65]。
歴史[編集]

旧石器時代から銅器時代[編集]
ユーフラテス川流域における初期の定住はその上流域に限られていた。この地域は肥沃な三日月地帯として知られている。アシュール文化の石製遺物はサジュル川流域と、シリア砂漠の中央にあるエルコウム︵アルカウム︶の遺跡から発見されている。後者は450,000年前に遡るホモ・エレクトスの遺物と一緒に残されている[66][67]。タウルス山脈とシリアのユーフラテス河谷の上流域はアブフレイラ、ジェルフル・アフマル、テッレル・ムレイベト、そしてネヴァル・チョリのような初期の定住村落が紀元前8,000年紀以降形成された。アブフレイラは当初狩猟採集民が定住を開始し、後に最初期の農民たちも居住した[68]。灌漑を知らない初期の農業共同体の立地は天水農業が可能な地域、即ちシリアとトルコのユーフラテス川上流域に限られていた[69]。紀元前7千年紀初頭に土器の導入が行われたことに特徴づけられる後期新石器時代の村落はこの地域全体で発見されている[70]。メソポタミアの下流域への居住は紀元前6千年紀に開始した。この地域の降水量は換装農業を行うには不十分であるため、これは一般的に灌漑の導入に関連したものである。テッレッ・サウワーンを含むいくつかの遺跡で灌漑の痕跡が見つかっている[71]。紀元前5千年紀の間か後期ウバイド期には北部シリアには小さな村落が点在し、そのうちのいくつかは10ヘクタール以上の大きさに成長していた[72]。イラクではエリドゥやウルのような場所ではウバイド期の間に既に居住が始まっていた[73]。粘土で作られたボートの模型がハーブール川沿いのテッル・マシュナカで発見されている。これは河川輸送がこの時代に既に行われていたことを示す[74]。概ね紀元前4千年紀に相当するウルク期には本当の意味での都市がメソポタミア全域に現れる。テッル・ブラークとウルクは100ヘクタール以上にその大きさを成長させ、記念碑的な建造物も見られる[75]。メソポタミア南部の土器、建築様式、そして円筒印章が、遥かトルコとイランにまで普及することは、一般的にメソポタミアの都市群に原材料を供給することを目的とする広範な貿易体系が、物質的な形で表れているものであると解釈されている。シリアのユーフラテス川沿いにあるハッブーバ・カビーラはウルクの植民都市として解釈される定住地の代表的な例である[76][77]。
古代[編集]
ジェムデト・ナスル期︵前3600年頃-前3100年頃︶の間と、シュメール初期王朝時代︵前3100年頃-前2350年頃︶、南部メソポタミアでは定住地の拡大と数の増加が見られ、人口の力強い成長を示している。これらの定住地にはシッパル、ウルク、アダブ、キシュなどのシュメールとアッカドの都市があり、これらが相互に競う都市国家を形成していた[78]。これらの都市の多くはユーフラテス川とティグリス川の運河沿いにあった。この運河群は現在では干上がっているが、リモートセンシングによる画像から特定できる[79]。同様の開発が上メソポタミアのスバルトゥとアッシリアで行われたが、紀元前3千年紀半ば以降であり、その規模は下メソポタミアよりも小さかった。この時代の初期の間、エブラ、マリ、そしてテル・レイランのような都市が有力となった[80]。これらの帝国の崩壊の後、古アッシリアとマリが北部シリアと北部メソポタミアに対する権力を主張し、南部メソポタミアはイシンやキシュ、ラルサのような都市国家に支配された。これらの都市国家の領域は前18世紀前半から半ばにかけて、ハンムラビの下で新たに台頭したバビロニアによって征服された[81]。 紀元前2千年紀の広範、ユーフラテス川流域は南側をカッシート人のバビロンに、北側をミッタニ︵ミタンニ︶、アッシリア、そしてヒッタイトによって分割され、最後はアッシリア︵中アッシリア時代︶の力がこれらを凌駕した[82]。中アッシリア時代が前11世紀後半に終わった後、イラクのユーフラテス川流域の支配をめぐってバビロニアとアッシリアが激しく争った。新アッシリア︵アッシリア帝国、前935年-前605年︶は最終的にこの争いの勝利者となり、前1千年紀前半にユーフラテス川北部の支配権を得ることに成功した[83]。 次の世紀により広範囲のユーフラテス川流域の支配権がアッシリア帝国から短命のメディア王国︵前612年-前546年︶に移り、前7世紀末には同様に束の間の新バビロニア︵前612年-前539年︶へと移った後、最終的にアケメネス朝︵前539年-前533年︶に渡った[84]。アケメネス朝もまたアレクサンドロス3世︵大王︶によって蹂躙され、アケメネス朝最後の王ダレイオス3世は敗れ去った。アレクサンドロス3世は前323年にバビロンで死去した[85]。その後に続いて、この地域はセレウコス朝︵前312年-前150年頃︶、パルティア︵前150年頃-前226年、パルティア時代にはアディアベネのようなアッシリア地方の新たな国々がユーフラテス川の地方の一部を支配するようになった︶へと移り、パルティアはローマ帝国と争った。ローマはビザンツ帝国へと継承され、サーサーン朝︵226年-638年︶が7世紀半ばの初期イスラームの征服まで支配した。イスラーム期[編集]
ユーフラテス川は現在のトルコ領にあたる山間部を抜けると、乾燥した気候の台地を潤して現在のイラク領にあたる下メソポタミアに入る[6]。アラビア語などでは、ユーフラテス川が東西に分割する台地の東側が﹁ジャズィーラ﹂、西側が﹁シャーム﹂と呼ばれ、それぞれが内部に多様な自然環境を包含しながらも長い歴史により、それぞれ一つのまとまった地域として統合されてきた[86]。ジスル・マンビジとラッカが、中世前半までのユーフラテス川の2大渡河ポイントとして、ジャズィーラとシャームを結んでいた[6]。ジスル・マンビジはマンビジの町から東にあり、のちにはナジュム城が築かれることになる[6]。ジスル・マンビジとラッカの間にあるマスカナより下流では川舟の航行も可能になり、スィッフィーンの古戦場もこのあたりである[6]。
下メソポタミアはアーナの村からはじまり、海に至る地域である[6]。アーナは中世にはすでに、ナツメヤシ栽培で有名であった[6]。アーナから少し下ったアンバールより下流は、古代より運河が張り巡らされてきた地域である[6]。前近代、特に9世紀から12世紀までのイスラーム圏では、宗教的情熱や冒険心を満たすための旅行が増え、そのための道案内の書物としておびただしい数の地理書が書かれた[87][88]。それらが描写するユーフラテス川下流域の、本流と運河、そして町の位置関係を確認すると、現在と異なる点が多々あり、書かれた年代の異なる地理書間でも相矛盾する[6]。これは﹁ユーフラテス﹂と呼ばれる川の流路が物理的に何度も変わり︵あるいは人為的に変更され︶、あるいは、ひとびとの認識上でも変化があったためである[6]。なお、ユーフラテス川の流路が時代によって異なる場合があることについては、この時代の地理学者も認識しており、例えばマスウーディーは、ヒーラがにぎわっていた頃、ナジャフはユーフラテスの川の底にあって、そこから海へ行く船が出ていたなどということを書いている[6]。
しかしながら、おのおのの時代において、ユーフラテス川及び付随する運河が低地部のメソポタミアをどのような流路で流れていたのか、その変遷はどのようなものであったかについては史料に乏しく、ほとんど明らかにされていない[6]。わかっていることとしては、ユーフラテス川がシャットルアラブでティグリス川と合流するようになったのは、ごく最近のことであるというようなことである[6]。
ところでムスリムの間では、アブー・フライラという人が預言者ムハンマドから聞いた話として、ユーフラテス川の水が干上がると川底から宝の山が現れ、これをめぐって殺し合いが起きるだろう、こうなったらいよいよ最後の審判の日が近い、というような話が伝えられている[89]。この伝承︵ハディース︶の法学者の解釈としては、宝が全ムスリムに帰属するからその取得が禁じられるのだという解釈︵13世紀スファークスのウラマー、イブヌッティーンの説︶や、殺し合いが発生するから取得が禁じられるのだという解釈︵15世紀のウラマー、イブン・ハジャルの説︶がある[89]。他方でこの伝承は、ユーフラテス川の川底から宝が出現するのと同時にマフディーが出現し、続いて預言者イーサーが再臨するという具体的なイメージをイスラーム的終末論にもたらした[89]。
アラビア語では下メソポタミアのことを﹁イラーク﹂という[90]。より詳細にはバスラ南郊を南限として前出のアーナやティクリートまであたりである[90]。イラークは正統カリフのアリーが統治したこともあって中世を通して反政府的シーア派がさまざまな活動を行った[90]。暗殺されたアリーの墓廟があるナジャフ、フサイン殉教の地カルバラーはいずれもユーフラテス川中流域の右岸にある[6]。失敗に終わったムフタールの乱やザイドの蜂起もユーフラテス川の灌漑土手上に形成された軍営都市クーファを背景に起きた事件である[91][92]。
ティグリスとユーフラテスの堆積作用によって作られた沖積平野であるイラークはがんらい肥沃な土地であって、沙漠の遊牧民ベドウィンを次々と吸引し、その内に定住させていくプロセス︵この歴史的プロセスを Bedouinization といい[93]、10世紀後半の地理学者イブン・ハウカルの著作などを史料に研究されている︶を可能にするほどの地力があった[90]。しかし地力は時代が下るにつれ衰えた[90]。中世後期からユーフラテス川流域を支配した政治権力はどれも短命で非力であり、他国と争ってばかりいたので、河川整備への大規模投資はなかった[94]。16世紀前半、こうした状況に変化が訪れる[94]。
1534年にオスマン帝国の﹁立法者スルタン﹂スレイマン1世は親征によりバグダードを無血開城させ、イラークを版図に加えた[94][95]。このためユーフラテス川では、上流の山間部から中流の台地、下流の低地、河口まで、単一の政治権力による支配が及ぶようになるという、この川と人類の関わりの長い歴史の中では非常に珍しい状況が生まれた[94]。スレイマン1世はみやこのイスタンブルに戻る1536年までの間、ユーフラテス川に橋をかけ、船着場を整備し、造船所や城砦を建築し、軍事・警察機能も上下メソポタミアにゆきとどかせた[94][95]。これら一連の施策には、あらたに帝国の一部としてサファヴィー朝と対峙する最前線となるティグリス・ユーフラテス川流域に、オスマン帝国の支配を確立させようとする意図があった[94]。橋梁や船着場などの社会資本が整備されたのみならず、水源地から河口まで、ひとつの政治権力︵オスマン家︶の権威に服し、ひとつの法制︵スンニー派法学︶を用い、ひとつの行政語︵トルコ語︶で中央政府からの行政上の指令を受け取るようになったユーフラテス川流域では、治安が保たれ、耕地面積が増大し、流通や税収が改善した[94]。
しかし、イラーク︵下メソポタミア︶においては17世紀後半になると気候変動や治水政策の失敗によりユーフラテス川の流路が大きく変化した[94][96]。流路の急激な変化がもたらした疫病、政治問題、経済問題は、相互に関連しながらさらに悪化し、バグダードの南西方面︵ユーフラテス川の流域︶の政治風土や人々の暮らしを大きく変えた[96]。このような変化の一つの帰結として、この時代、当地ではオスマン帝国の権威が低下し、新たな政治勢力としてハザーイル氏族︵バヌー・フザア系の一大氏族連合︶が台頭するようになった[96]。
近現代[編集]
「中東における水問題」も参照

第一次世界大戦の後、南西アジアの国境はローザンヌ条約によるオスマン帝国の分割の中で再設定された。ローザンヌ条約の第109条はユーフラテス川に沿った3つの国︵現在のトルコ、フランスの委任統治領シリア、そしてイギリスの委任統治領イラク︶がユーフラテス川の水と水利施設の建設について相互に合意しなければならないと規定していた[97]。1946年に調印されたトルコとイラクの間の合意はトルコに対してティグリス・ユーフラテス水系の水利変更についてイラクに報告することを求め、イラクはトルコが領内にユーフラテス川の流れを管理するためのダムを建設することを承認した[98]。

イラク王国︵1932年-1959年︶の紋章。ティグリス・ユーフラ テス川、およびそれらが合流したシャットゥルアラブ川、そしてナツメヤシの森が描かれている。この森はかつて世界最大のナツメヤシの森であった。
ユーフラテス川は1932年から1959年までイラクの国章に採用されていた。

キャフタ近郊のユーフラテス川
トルコとシリアが一年以内の時間差で最初のダム︵それぞれケバン・ダムとタブカ・ダム︶をユーフラテス川に完成させるとともに、1975年には貯水池への貯水が開始された。それと同時にこの地域は厳しい干ばつに襲われ、イラクに流入する水量は1973年の15.3立方キロメートルから1975年には9.4立方キロメートルへと減少した。このことは国際的な危機を引き起こし、イラクはシリアのタブカ・ダムを爆撃するという脅しを行った。最終的にシリアとイラクは、サウディアラビアとソ連の介入の後で合意に達した[99][100]。軍事的脅威にまではエスカレートしなかったものの、同様の危機は1981年にも発生した。この時、トルコは水力発電量を一時的に増加させた後、ケバン・ダムの貯水池はほぼ空となり再充填しなくてはならなかった[101]。1984年にはトルコが毎秒500立方メートル、または年間16立方キロメートルの水を確実にシリア領内へと流すことを一方的に宣言し、1987年には二国間での正式な合意となった[102]。シリアとイラクの間では1989年に、シリアがトルコから受け取った水量の60パーセントをイラクへ流すことを合意した別の二国間合意が成立した[103]。2008年にトルコ、シリア、イラクはティグリス・ユーフラテス川流域の水を管理する三ヶ国合同委員会︵the Joint Trilateral Committee‥JTC︶の設立を推進し、2009年9月3日にはこれについて更なる合意が締結された[104]。
2014年4月15日、トルコはシリアとイラクへ流れ込むユーフラテス川の水量を減らし始めた。2014年5月16日には流れは完全に断ち切られ、その結果トルコ・シリア国境でユーフラテス川は断流した[105]。これはトルコ・シリア国境で最低毎秒500立方メートルの水量を放出すると約した1987年の合意に違反していた[106]。

ユーフラテス川︵イラク︶
歴史を通じてユーフラテス川は川沿いに生きる人々にとって極めて重要であった。大規模な水力発電所の建設、灌漑計画、遠距離へ水を運ぶことのできるパイプラインは、電力や飲料水のような基本的な生活インフラについて、今やより多くの人々を昔よりもユーフラテス川に依存させている。シリアのアサド湖はユーフラテス河谷から75キロメートル西のアレッポ市の最も重要な飲料水源である[107]。この湖はささやかな規模の国営漁業も支えている[108]。イラクのハディーサ・ダムは、新たに復旧した電力網を通してバグダードに給電を行っている[109]。


経済[編集]

伝説[編集]
﹃旧約聖書﹄にも פְּרָת Pĕrāṯ の名が出ており、その源はエデンの園であるとされる。 古代ローマの詩人マルクス・マニリウスは、愛の女神ウェヌスが怪物テュポンから逃れるためこの川に身を投じ、魚に変身したと伝えている。この伝説には飛び込んだ川をナイル川やエリダヌス川︵古代ギリシア語: Ἠριδανός - ラテン語: Eridanus︶とする異伝もあるが、いずれにせようお座と結び付けて考えられている[110]。関連項目[編集]
- ユーフラテス川沿岸の都市の一覧
- シリアの水資源管理
- イラクの野生動物
- シリアの野生動物
- バビロンの川底トンネル(ユーフラテストンネル)
脚注[編集]
(一)^ Negev & Gibson 2001, p. 169
(二)^ abcde岡田・小林 2000, pp. 14-15.
(三)^ Woods 2005
(四)^ Witzel, Michael. “Early Loan Words in Western Central Asia: Substrates, Migrations and Trade Contact and Exchange in the Ancient World, ed. Victor H. Mair (Univ. of Hawaii, 2006), 5;” (PDF). 2018年5月閲覧。
(五)^ Gamkrelidze, Thomas; V. Ivanov, Vjaceslav (1995), Indo-European and the Indo-Europeans: A Reconstruction and Historical Analysis of a Proto-Language and Proto-Culture, Walter de Gruyter, p. 616
(六)^ abcdefghijklmnopq"al-Furāt". Encyclopaedia Islamica (2nd ed.).
(七)^ Haim, S. (2009). Farhang Moaser Shorter Persian-English Dictionary. Tehran, Iran: Farhang Moaser Publishers. ISBN 978-600-105-003-9
(八)^ Zarins 1997, p. 287
(九)^ abcdIraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works 2006a, p. 71
(十)^ abcdDaoudy 2005, p. 63
(11)^ abcFrenken 2009, p. 65
(12)^ abcdeIsaev & Mikhailova 2009, p. 384
(13)^ Isaev & Mikhailova 2009, p. 388
(14)^ Mutin 2003, p. 2
(15)^ Bilen 1994, p. 100
(16)^ Iraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works 2006a, p. 91
(17)^ Isaev & Mikhailova 2009, p. 385
(18)^ Kolars 1994, p. 47
(19)^ Isaev & Mikhailova 2009, p. 386
(20)^ Iraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works 2006a, p. 94
(21)^ Hillel 1994, p. 95
(22)^ Hole & Zaitchik 2007
(23)^ Shahin 2007, p. 251
(24)^ Partow 2001, p. 4
(25)^ Frenken 2009, p. 63
(26)^ Moore, Hillman & Legge 2000, pp. 52–58
(27)^ Moore, Hillman & Legge 2000, pp. 63–65
(28)^ Moore, Hillman & Legge 2000, pp. 69–71
(29)^ Coad 1996
(30)^ Gray 1864, pp. 81–82
(31)^ Naval Intelligence Division 1944, pp. 203–205
(32)^ Thomason 2001
(33)^ Moore, Hillman & Legge 2000, pp. 85–91
(34)^ “世界遺産センター - 南イラクのアフワール‥生物の避難所と古代メソポタミア都市景観の残影”. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. 2023年4月20日閲覧。
(35)^ Kliot 1994, p. 117
(36)^ Iraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works 2006b, pp. 20–21
(37)^ Jamous 2009
(38)^ Elhadj 2008
(39)^ Mutin 2003, p. 4
(40)^ Mutin 2003, p. 5
(41)^ Kolars & Mitchell 1991, p. 17
(42)^ Jongerden 2010, p. 138
(43)^ Frenken 2009, p. 62
(44)^ Isaev & Mikhailova 2009, pp. 383–384
(45)^ Jongerden 2010, p. 139
(46)^ Kolars 1994, p. 53
(47)^ Daoudy 2005, p. 127
(48)^ Hillel 1994, p. 100
(49)^ Sahan et al. 2001, p. 10
(50)^ Sahan et al. 2001, p. 11
(51)^ Anonymous 2009, p. 11
(52)^ McDowall 2004, p. 475
(53)^ Hillel 1994, p. 107
(54)^ Hillel 1994, p. 103
(55)^ Frenken 2009, p. 212
(56)^ Rahi & Halihan 2009
(57)^ Jawad 2003
(58)^ Muir 2009
(59)^ McClellan 1997
(60)^ Tanaka 2007
(61)^ Steele 2005, pp. 52–53
(62)^ Bounni 1979
(63)^ del Olmo Lete & Montero Fenollós 1999
(64)^ Abdul-Amir 1988
(65)^ Garcia-Navarro 2009
(66)^ Muhesen 2002, p. 102
(67)^ Schmid et al. 1997
(68)^ Sagona & Zimansky 2009, pp. 49–54
(69)^ Akkermans & Schwartz 2003, p. 74
(70)^ Akkermans & Schwartz 2003, p. 110
(71)^ Helbaek 1972
(72)^ Akkermans & Schwartz 2003, pp. 163–166
(73)^ Oates 1960
(74)^ Akkermans & Schwartz 2003, pp. 167–168
(75)^ Ur, Karsgaard & Oates 2007
(76)^ Akkermans & Schwartz 2003, p. 203
(77)^ van de Mieroop 2007, pp. 38–39
(78)^ Adams 1981
(79)^ Hritz & Wilkinson 2006
(80)^ Akkermans & Schwartz 2003, p. 233
(81)^ van de Mieroop 2007, p. 111
(82)^ van de Mieroop 2007, p. 132
(83)^ van de Mieroop 2007, p. 241
(84)^ van de Mieroop 2007, p. 270
(85)^ van de Mieroop 2007, p. 287
(86)^ ﹃シリア・レバノンを知るための64章﹄︵明石書店、2013年︶まえがき
(87)^ 矢島, 祐利﹃アラビア科学史序説﹄岩波書店、1977年3月25日、241頁。
(88)^ Buang, Amriah (2014). “Geography in the Islamic World”. Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-3934-5_8611-2
(89)^ abc“The time for the water of the Euphrates to drain”. Questions on Islam (2018年9月28日). 2019年9月26日閲覧。
(90)^ abcde"'Irāḳ". Encyclopaedia Islamica (2nd ed.). Brill.
(91)^ Newman, Andrew J. (2010). Shi`i Islam: Oxford Bibliographies Online Research Guide. USA: Oxford University Press. pp. 28. ISBN 9780199806423 2017年12月5日閲覧。
(92)^ Wellhausen, Julius Margaret Graham Weir訳 (1927). The Arab Kingdom and its Fall. Calcutta: University of Calcutta. p. 27. OCLC 752790641
(93)^ "Bedouinization". Encyclopaedia Islamica (3rd ed.). 2019年9月26日閲覧。
(94)^ abcdefghHusain, Faisal H.; McNeill, John R. (2018-01-01). “The Tigris-Euphrates Basin Under Early Modern Ottoman Rule, c. 1534-1830”. Graduate Theses and Dissertations - History (Georgetown University) 2019年9月26日閲覧。.
(95)^ abImber, Colin (2003). The Ottoman Empire, 1300-1650: The Structure of Power. Macmillan International Higher Education. pp. 36. ISBN 9781352004144
(96)^ abcHusain, Faisal H. (2016). “Changes in the Euphrates River: Ecology and Politics in a Rural Ottoman Periphery, 1687–1702”. Journal of Interdisciplinary History 47 (1): 1-25. doi:10.1162/JINH_a_00939. ISSN 0022-1953.
(97)^ Treaty of peace with Turkey signed at Lausanne, World War I Document Archive 2010年12月19日閲覧。
(98)^ Geopolicity 2010, pp. 11–12
(99)^ Shapland 1997, pp. 117–118
(100)^ Kaya 1998
(101)^ Kolars 1994, p. 49
(102)^ Daoudy 2005, pp. 169–170
(103)^ Daoudy 2005, pp. 172
(104)^ Geopolicity 2010, p. 16
(105)^ Anjarini, Suhaib (2014年5月30日). “A new Turkish aggression against Syria: Ankara suspends pumping Euphrates' water”. Al Akhbar 2014年6月20日閲覧。
(106)^ Eupherates of Syria Cut Off by Turkey. YouTube. 30 May 2014.
(107)^ Shapland 1997, p. 110
(108)^ Krouma 2006
(109)^ O´Hara 2004, p. 3
(110)^ マニリウス 1993
参考文献[編集]
●Abdul-Amir, Sabah Jasim (1988) (PhD thesis), Archaeological Survey of Ancient Settlements and Irrigation Systems in the Middle Euphrates Region of Mesopotamia, Ann Arbor: UMI, OCLC 615058488 ●Adams, Robert McC. (1981), Heartland of Cities. Surveys of Ancient Settlement and Land Use on the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates, Chicago: University of Chicago Press, ISBN 0-226-00544-5 ●Akkermans, Peter M. M. G.; Schwartz, Glenn M. (2003), The Archaeology of Syria. From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (ca. 16,000–300 BC), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-79666-0 ●Anonymous (2009), Group Denial. Repression of Kurdish Political and Cultural Rights in Syria, New York: Human Rights Watch, OCLC 472433635 ●Bilen, Özden (1994), “Prospects for Technical Cooperation in the Euphrates–Tigris Basin”, in Biswas, Asit K., International Waters of the Middle East: From Euphrates-Tigris to Nile, Oxford University Press, pp. 95–116, ISBN 978-0-19-854862-1 ●Bounni, Adnan (1979), “Campaign and Exhibition from the Euphrates in Syria”, The Annual of the American Schools of Oriental Research 44: 1–7, JSTOR 3768538 ●Coad, B.W. (1996), “Zoogeography of the Fishes of the Tigris-Euphrates Basin”, Zoology in the Middle East 13: 51–70, doi:10.1080/09397140.1996.10637706, ISSN 0939-7140 ●Daoudy, Marwa (2005) (French), Le Partage des Eaux entre la Syrie, l'Irak et la Turquie. Négociation, Sécurité et Asymétrie des Pouvoirs, Moyen-Orient, Paris: CNRS, ISBN 2-271-06290-X ●del Olmo Lete, Gregorio; Montero Fenollós, Juan Luis (eds.) (1999), Archaeology of the Upper Syrian Euphrates, the Tishrin Dam area: Proceedings of the International Symposium held at Barcelona, January 28th–30th, 1998, Barcelona: AUSA, ISBN 978-84-88810-43-4 ●Elhadj, Elie (2008), “Dry Aquifers in Arab Countries and the Looming Food Crisis”, Middle East Review of International Affairs 12 (3), ISSN 1565-8996 ●Frenken, Karen (2009), Irrigation in the Middle East Region in Figures. AQUASTAT Survey 2008, Water Reports, 34, Rome: FAO, ISBN 978-92-5-106316-3 ●Garcia-Navarro, Lourdes (2009), “Drought Reveals Iraqi Archaeological Treasures”, NPR 2010年8月4日閲覧。 ●Geopolicity (2010), Managing the Tigris Euphrates Watershed, オリジナルの20 July 2011時点におけるアーカイブ。 2010年12月20日閲覧。 ●Gray, J.E. (1864), “Revision of the species of Trionychidae found in Asia and Africa, with descriptions of some new species”, Proceedings of the General Meetings for Scientific Business of the Zoological Society of London: 81–82 ●Hartmann, R. (2010), “al- Furāt”, in Bearman, P.; Bianquis, Th.; Bosworth, C.E. et al., Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Leiden: Brill Online, OCLC 624382576 ●Helbaek, Hans (1972), “Samarran Irrigation Agriculture at Choga Mami in Iraq”, Iraq 34 (1): 35–48, doi:10.2307/4199929 ●Hillel, Daniel (1994), Rivers of Eden: the Struggle for Water and the Quest for Peace in the Middle East, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-508068-8 ●Hole, F.; Zaitchik, B.F. (2007), “Policies, Plans, Practice, and Prospects: Irrigation in Northeastern Syria”, Land Degradation & Development 18 (2): 133–152, doi:10.1002/ldr.772 ●Hritz, Carrie; Wilkinson, T.J. (2006), “Using Shuttle Radar Topography to Map Ancient Water Channels in Mesopotamia”, Antiquity 80: 415–424, ISSN 0003-598X ●Iraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works (2006a), “Volume I: Overview of Present Conditions and Current Use of the Water in the Marshlands Area/Book 1: Water Resources”, New Eden Master Plan for Integrated Water Resources Management in the Marshlands Areas, New Eden Group ●Iraqi Ministries of Environment, Water Resources and Municipalities and Public Works (2006b), “Annex III: Main Water Control Structures (Dams and Water Diversions) and Reservoirs”, New Eden Master Plan for Integrated Water Resources Management in the Marshlands Areas, New Eden Group ●Isaev, V.A.; Mikhailova, M.V. (2009), “The Hydrology, Evolution, and Hydrological Regime of the Mouth Area of the Shatt al-Arab River”, Water Resources 36 (4): 380–395, doi:10.1134/S0097807809040022 ●Jamous, Bassam (2009), “Nouveaux Aménagements Hydrauliques sur le Moyen Euphrate Syrienne. Appel à Projets Archéologiques d'Urgence” (French), Studia Orontica (DGAM) 2009年12月14日閲覧。 ●Jawad, Laith A. (2003), “Impact of Environmental Change on the Freshwater Fish Fauna of Iraq”, International Journal of Environmental Studies 60 (6): 581–593, doi:10.1080/0020723032000087934 ●Jongerden, Joost (2010), “Dams and Politics in Turkey: Utilizing Water, Developing Conflict”, Middle East Policy 17 (1): 137–143, doi:10.1111/j.1475-4967.2010.00432.x ●Kaya, Ibrahim (1998), “The Euphrates–Tigris Basin: An Overview and Opportunities for Cooperation under International Law”, Arid Lands Newsletter 44, ISSN 1092-5481 ●Kliot, Nurit (1994), Water Resources and Conflict in the Middle East, Milton Park: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-09752-5 ●Kolars, John (1994), “Problems of International River Management: The Case of the Euphrates”, in Biswas, Asit K., International Waters of the Middle East: From Euphrates-Tigris to Nile, Oxford University Press, pp. 44–94, ISBN 978-0-19-854862-1 ●Kolars, John F.; Mitchell, William A. (1991), The Euphrates River and the Southeast Anatolia Development Project, Carbondale: SIU Press, ISBN 978-0-8093-1572-7 ●Krouma, I. (2006), “National Aquaculture Sector Overview. Syrian Arab Republic. National Aquaculture Sector Overview Fact Sheets”, FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department (FAO) 2009年12月15日閲覧。 ●McClellan, Thomas L. (1997), “Euphrates Dams, Survey of”, in Meyers, Eric M., The Oxford Encyclopedia of Archaeology in the Ancient Near East, 2, New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 290–292, ISBN 0-19-506512-3 ●McDowall, David (2004), A Modern History of the Kurds, London: I.B. Tauris, ISBN 978-1-85043-416-0 ●Moore, A.M.T.; Hillman, G.C.; Legge, A.J. (2000), Village on the Euphrates. From Foraging to Farming at Abu Hureyra, Oxford: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-510807-8 ●Muhesen, Sultan (2002), “The Earliest Paleolithic Occupation in Syria”, in Akazawa, Takeru; Aoki, Kenichi; Bar-Yosef, Ofer, Neandertals and Modern Humans in Western Asia, New York: Kluwer, pp. 95–105, doi:10.1007/0-306-47153-1_7 ●Muir, Jim (24 February 2009), “Iraq Marshes face Grave New Threat”, BBC News 2010年8月9日閲覧。 ●Mutin, Georges (2003), “Le Tigre et l'Euphrate de la Discorde” (French), VertigO 4 (3): 1–10, doi:10.4000/vertigo.3869 ●Naval Intelligence Division (1944), Iraq and the Persian Gulf, Geographical Handbook Series, OCLC 1077604 ●Negev, Avraham; Gibson, Shimon (2001), Archaeological Encyclopedia of the Holy Land, New York: Continuum, ISBN 0-8264-1316-1 ●O´Hara, Thomas (2004), “Coalition Celebrates Transfer of Power”, Essayons Forward 1 (2): 3–4, OCLC 81262733, オリジナルの19 June 2009時点におけるアーカイブ。 ●Oates, Joan (1960), “Ur and Eridu, the Prehistory”, Iraq 22: 32–50, doi:10.2307/4199667 ●Partow, Hassan (2001), The Mesopotamian Marshlands: Demise of an Ecosystem, Nairobi: UNEP, ISBN 92-807-2069-4 ●Rahi, Khayyun A.; Halihan, Todd (2009), “Changes in the Salinity of the Euphrates River System in Iraq”, Regional Environmental Change 10: 27, doi:10.1007/s10113-009-0083-y ●Sagona, Antonio; Zimansky, Paul (2009), Ancient Turkey, Routledge World Archaeology, London: Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-48123-6 ●Sahan, Emel; Zogg, Andreas; Mason, Simon A.; Gilli, Adi (2001), Case-Study: Southeastern Anatolia Project in Turkey – GAP, Zürich, オリジナルの9 February 2005時点におけるアーカイブ。 2010年8月6日閲覧。 ●Schmid, P.; Rentzel, Ph.; Renault-Miskovsky, J.; Muhesen, Sultan; Morel, Ph.; Le Tensorer, Jean Marie; Jagher, R. (1997), “Découvertes de Restes Humains dans les Niveaux Acheuléens de Nadaouiyeh Aïn Askar (El Kowm, Syrie Centrale)”, Paléorient 23 (1): 87–93, doi:10.3406/paleo.1997.4646 ●Shahin, Mamdouh (2007), Water Resources and Hydrometeorology of the Arab Region, Dordrecht: Springer, ISBN 978-1-4020-5414-3 ●Shapland, Greg (1997), Rivers of Discord: International Water Disputes in the Middle East, New York: Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 978-0-312-16522-2 ●Steele, Caroline (2005), “Who Has not Eaten Cherries with the Devil? Archaeology under Challenge”, in Pollock, Susan; Bernbeck, Reinhard, Archaeologies of the Middle East: Critical Perspectives, Blackwell Studies in Global Archaeology, Malden: Blackwell, pp. 45–65, ISBN 0-631-23001-7 ●Tanaka, Eisuke (2007), “Protecting one of the best Roman Mosaic Collections in the World: Ownership and Protection in the Case of the Roman Mosaics from Zeugma, Turkey”, Stanford Journal of Archaeology 5: 183–202, OCLC 56070299 ●Thomason, A.K. (2001), “Representations of the North Syrian Landscape in Neo-Assyrian Art”, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research 323 (323): 63–96, JSTOR 1357592 ●Ur, Jason A.; Karsgaard, Philip; Oates, Joan (2007), “Early Urban Development in the Near East”, Science 317 (5842): 1188, doi:10.1126/science.1138728 ●van de Mieroop, Marc (2007), A History of the Ancient Near East, ca. 3000–323 BC. Second Edition, Blackwell History of the Ancient World, Malden: Blackwell, ISBN 978-1-4051-4911-2 ●Woods, Christopher (2005), “On the Euphrates”, Zeitschrift für Assyriologie 95: 7–45, doi:10.1515/zava.2005.95.1-2.7 ●Zarins, Juris (1997), “Euphrates”, in Meyers, Eric M., The Oxford Encyclopedia of Archaeology in the Ancient Near East, 2, New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 287–290, ISBN 0-19-506512-3 ●マルクス・マニリウス﹃占星術または天の聖なる学﹄白水社、2003年2月。ISBN 978-4-560-02288-7。 ●岡田明子、小林登志子﹃古代メソポタミアの神々 世界最古の﹁王と神の饗宴﹂﹄集英社、2000年12月。ISBN 978-4-08-781180-3。外部リンク[編集]
 ウィキメディア・コモンズには、ユーフラテス川に関するカテゴリがあります。
ウィキメディア・コモンズには、ユーフラテス川に関するカテゴリがあります。





