ドイツの医療


ドイツの医療︵ドイツのいりょう、Healthcare in Germany︶では、複数提供者制の社会保険によるユニバーサルヘルスケアが実現されており、ドイツ連邦保健省が所管している[1][2][3]。
医療保険には法的強制保険︵Gesetzliche Krankenversicherung、傷病金庫︶と私的保険︵Private Krankenversicherung︶[4][5][6]の両者が存在しており競争政策が取られ、2009年から市民は疾病金庫と私的保険の何れかから選択できるようになった[7][8]。
戦前の日本は、ドイツを手本に社会保険方式の公的医療保険制度を導入した[9]。日本の介護保険制度もドイツを手本としている。

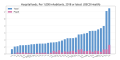
OECD各国の老人(65-歳)一人あたり、生産年齢(20-64歳) 人口[10]。
濃橙は2012年時点、薄橙は2050年の予想
保健セクターの規模は、3,502.21億ユーロ︵米ドル購買力平価では4,489.529億米ドル︶で、GDPの11.1%を占め︵2016年︶、人口1人あたりでは€4,252.9ユーロ︵米ドル購買力平価では$5,451.9米ドル︶あった。[11]保健支出はWHOによると2015年は、約84.5%が政府支出であった。[12]
2002年において通院患者に多い疾患は、男性では一位が心臓病、次にアルコール依存症・ヘルニアであり、女性では一位が妊娠関連、次に乳がん、心臓病であった。[13]
平均寿命は、WHOによると2016年では81.0歳で世界183カ国中26位、男性は78.7歳でフィンランド、ギリシャと同率で23位、女性は83.3歳でマルタと同率の23位であった。[14]
乳児死亡率は非常に低く(1000出生あたり3.4[2016年])[15]、医師数は344,755人であり、人口1,000人あたり医師数は4.19人︵一般開業医、専門医、インターン、外国人医師を含む。︶でOECD27カ国中5位であった。[16]また、ドイツ国内の外国人医師の比率は8.7%︵2013年12月︶である。[17]
少子高齢化が進み、1人の高齢者を2.9人で支える高齢社会に突入しており︵2012年︶、OECD各国においては日本に次いで進行している[10]。

OECD各国の財源別保健支出。
水色は政府一般歳出、紫は社会保険、赤は自己負担、橙は民間保険、緑はその他
ドイツは世界最古の国営社会保険医療制度を持ち[1]、その起源はオットー・フォン・ビスマルクによる社会政策立法、1883年疾病保険法(Health Insurance Bill of 1883)、1884年労災保険法(Accident Insurance Bill of 1884)、1889年障害・老齢保険法(Old Age and Disability Insurance Bill of 1889)にさかのぼる[8][18]。これらの法定強制医療保険は、初期では低賃金労働者と特定の公務員にのみ適用されていたが、後に人口の大多数に広がった[19]。
この制度は分権的であり、民間医師が外来患者を治療し、それとは独立して非営利病院が大部分の入院医療を提供していた。
人口のおよそ92%が法定医療保険プランに加入し、この制度では1100の傷病金庫︵公的または私的︶にて、法定標準カバー範囲の医療を受けられた。法定保険の原資は雇用者・雇用主・政府の三者が負担し、保険料割合は加入者の所得レベルによって変化した。一部の高所得労働者では、税を支払って標準保険を脱退し私的保険に加入することもあった。私的保険では受給サービスは収入レベルではなく、個人の健康状態に基づいて支給される[20]。
現在は疾病金庫は統合再編が進み、1991年頃に約1200あったものが約200まで統合されている[21][7][8]。
また、これまでは介護保険制度は無く公的扶助で対応されていたが、1995年からは長期介護保険制度が開始された[22]。介護保険は保険料のみで運営され、税財源の投入は行われていない[22]。

各国の医療費支出のGDP比(%)。赤線はドイツ
医療制度は開業医となる家庭医(GP)と専門医、および病院に厳密に分かれており、病院は入院患者を扱い、開業医は外来診療を担当する。緊急の場合を除き、病院診療を受けるには開業医の紹介を受けなければならない[7][23]。また開業医は定員制となっており、地域及び診療科ごとに上限が定められている[7]。臨床データの電子化も進んでおり、開業医および病院が患者診療データを共有している[7]。
1980年から、自己負担制度が過剰診療を防止するために導入されている。医薬品は価格の10%ほど︵5〜10ユーロの範囲︶、入院は一日10ユーロ、外来診療は四半期ごとに10ユーロの自己負担が生じる[9][24]。18歳未満は全額社会保険負担で自己負担がなく、また妊婦・出産については全額公費負担となる[24]。また年間の自己負担上限があり、そのラインは世帯年収によって決まる[24]。

医療保険証の例
ドイツにはユニバーサルヘルスケア制度が存在し、その提供者は複数であり医療保険は二種類に分けられる。ドイツ国民は法定の3種類の保健福利︵医療保険・傷害保険・長期介護保険︶を受けられ、その原資は雇用主と雇用者が負担している。
●労働傷害保険︵Arbeitsunfallversicherung︶は雇用主より提供され、通勤から労働事業所まで全ての労働事故リスクをカバーする。
●長期介護保険︵Pflegeversicherung︶は雇用主と雇用者で折半負担し、本人が身の回りの日常作業(炊事・清掃・入浴など)が不能になるリスクをカバーする。保険料は所得および年金の2%であり、雇用主とあわせて負担する。
●医療保険には二種類あり、公的保険︵Gesetzliche Krankenversicherung︶と、私的保険︵Private Krankenversicherung︶がある[9]。両者とも医療費増加と人口動態変化の影響を受けて困難に直面している。2006年では人口のおよそ87.5%は公的医療保険、12.5%は私的保険に加入している[25]。
全ての雇用者は公的保険︵疾病金庫︶に加入しなければならない[9][7]。公務員、学生、自営業者、高所得者(€50,000.00以上、毎年調整)のみが私的保険を選択できる[9][7]。
保健状態[編集]

歴史[編集]

医療制度[編集]

医療保険[編集]

複数提供者制[編集]
医療保険は複数提供者制である。人口の85%が加入しているのは法定の基本医療保険プランで、法規制のSozialgesetzbuch V (SGB V)プログラムであり、基本的な範囲をカバーしている[9]。残りの人口の15%は任意で私的医療保険に加入しており、大抵は追加サービスが付く。 公的保険は非営利組織である傷病金庫によって共通レートで全市民に提供されており、これは収入が一定以下の市民は強制加入である[9]。保険料は雇用者と雇用主の両者で負担し[9]、原則として国庫負担はない[26]。傷病金庫は幅広い疾患をカバーし、また加入を拒否したり特定のリスク患者を不平に扱ってはならないと法で定められている。一部の人は税金ベースの公営労働保険や社会保険によってカバーされている。年金受給者では、法的強制保険レベルの収入があっても基金の加入は任意であるが、たいていの人は加入するか私的保険に加入している。公的保険を補う私的保険には様々な種類がある。 診療報酬は州ごとに保険医協会と傷病金庫の交渉によって決定される[8][27][28]。以前は点数制の出来高払い制度であったが、1993年からは包括払い制度が導入されている[27][26]。 公的保険では、政府は低収入者に対して医療費の一部を還付しており、低収入者への保険料は予め上限額が定められている。逆に高収入者では給与ベースの保険料の追加負担が生じるので、私的保険のほうに加入する場合もある。そのため、健康な若年者ほど私的保険に移ると保険料を相当分節約できる。しかし年をとって病気がちになると私的保険は保険料率を上げたり保険加入を認めなくなるので、公的保険に切り替えこととなるが[20]、それが常に認められるかは不定である[29]。 過去20年の間、私的保険の保険料はどんどん上昇し、公的保険との有利性は少なくなってきている[30]。公的保険[編集]
| ホスピタルフィー | 33.1% |
| ドクターフィー | 15.4% |
| 医薬品 | 18.1% |
| 総計 | 1,540億ユーロ |
疾病金庫は2009年時点で202箇所が存在する[9]。地区疾病金庫・企業疾病金庫・同業者疾病金庫・農業疾病金庫・海員疾病金庫・労働者職員代替疾病金庫などが存在し、疾病金庫間で選択の自由がある[9]。
公的保険には以下の特徴がある。
●ドイツ社会法 (Sozialgesetzbuch – SGB)に基づき、ドイツ連邦保健省が保険カバー範囲を規定する。それは﹁経済的に実行可能・効果的・必要・有意義なサービス﹂に限定される。
●個人の健康状態にかかわらず、給与の一定割合を保険料として納付(現在は15.5%)[9]
●配偶者および子供は、収入額が一定以下ならば無料加入(月額345ユーロほど)[9]
●現物給付制。病院受診には開業医の紹介が必要[9][7]。
加齢によって疾病リスクが上昇するため、公的保険制度存続のために若年層・労働世代に対して高負担を課す高負担高福祉のシステムが特徴である。
私的保険[編集]
私的保険会社はドイツに52社ほど存在する[9]。 私的保険には以下の特徴がある。 ●保険会社と個人の個別契約であり、カバー範囲と払戻率が定められている ●サービス内容や保険料は、個人の健康リスクと年齢に基づき保険会社によって様々[9] ●保険料は高齢者ほど上昇する(法的規制のため) ●家族は各自で保険契約を結ぶ必要がある[9] 公的保険を脱退して私的保険に入る人がいるが、再び公的保険に戻るのは難しいとされている。55歳以下の場合、公的保険に再加入するには、被保険者の収入が私的保険の要求するレベル以下でなければならないからである。私的保険はたいてい公的保険よりも高額で、低所得者では加入できない額になる。医療の質[編集]
医療制度の規制は、ドイツ連邦合同委員会(Federal Joint Committee、Bundesausschuss)が行う。 ドイツの医療において公衆衛生機構が承認を行った医療規制改革案は、機械的に法案通過している[31]。 また連邦保健省配下の医療品質・効率性研究機構︵IQWiG︶は、根拠に基づく医療技術評価を行っている。 医療紛争を解決するための裁判外紛争解決手続制度があり、ドイツ全土をカバーしている[32]。医療供給体制[編集]
病院は、公立病院︵37%︶、非営利病院︵40%、財団や慈善団体など︶、営利私立病院︵23%︶の3つに分けられる[33]。保険医と入院施設︵病院︶の機能が明確に分離されているため、社会的入院といった問題は起こらない[34]。
医薬品[編集]
メルク社は世界最古の医薬品メーカーであるとされる。 医薬品の通信販売は1998年に原則対面販売となり禁止されていたが、2003年の法改正により認可登録を受けた薬局は処方箋医薬品を含めて通信販売が解禁された[35]。脚注[編集]
(一)^ abBump, Jesse B. (2010年10月19日). “The long road to universal health coverage. A century of lessons for development strategy”. Seattle: PATH. 2013年3月10日閲覧。 “Carrin and James have identified 1988—105 years after Bismarck’s first sickness fund laws—as the date Germany achieved universal health coverage through this series of extensions to minimum benefit packages and expansions of the enrolled population. Bärnighausen and Sauerborn have quantified this long-term progressive increase in the proportion of the German population covered by public and private insurance. Their graph is reproduced below as Figure 1: German Population Enrolled in Heath Insurance (%) 1885–1995.”
(二)^ Carrin, Guy; James, Chris (January 2005). “Social health insurance: Key factors affecting the transition towards universal coverage”. International Social Security Review 58 (1): 45–64. doi:10.1111/j.1468-246X.2005.00209.x. "Initially the health insurance law of 1883 covered blue-collar workers in selected industries, craftspeople and other selected professionals.6 It is estimated that this law brought health insurance coverage up from 5 to 10 per cent of the total population."
(三)^ Bärnighausen, Till; Sauerborn, Rainer (May 2002). “One hundred and eighteen years of the German health insurance system: are there any lessons for middle- and low income countries?”. Social Science & Medicine 54 (10): 1559–1587. doi:10.1016/S0277-9536(01)00137-X. PMID 12061488 2013年3月10日閲覧. "As Germany has the world’s oldest SHI [social health insurance] system, it naturally lends itself to historical analyses."
(四)^ “The Case for Universal Health Care in the United States”. Cthealth.server101.com. 2011年8月6日閲覧。
(五)^ Health Insurance in Germany – MySME – Resources for Small Business in Germany in the English Language[リンク切れ]
(六)^ “アーカイブされたコピー”. 2006年2月21日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2012年1月21日閲覧。
(七)^ abcdefgh財務総合政策研究所 2009.
(八)^ abcd2011~2012年 海外情勢報告 (Report). 厚生労働省. 2013. Chapt.3.1.
(九)^ abcdefghijklmnopq財務総合政策研究所 2010.
(十)^ abOECD Society at a glance 2014 (Report). OECD. 2014. Chapt.3.11. doi:10.1787/soc_glance-2014-en。
(11)^ OECD (2018年11月). “Health expenditure and financing︵医療費と資金調達︶”. 2018年12月16日閲覧。
(12)^ WHO (2018年4月13日). “Domestic general government health expenditure (GGHE-D) as percentage of current health expenditure (CHE) (%) Data by country︵国別の医療支出︵CHE︶に対する政府医療支出︵GGHE-D︶の割合︵%︶︶”. 2018年12月16日閲覧。
(13)^ Germany country profile (PDF) (Report). アメリカ議会図書館 Federal Research Division. December 2005.
(14)^ WHO (2018年4月6日). “Life expectancy and Healthy life expecancy Data by country ︵国別の平均寿命と平均健康寿命︶”. 2018年12月16日閲覧。
(15)^ OECD (2018年11月8日). “Health Status : Maternal and infant mortality ︵健康状態‥妊産婦および乳児死亡率︶”. 2018年12月16日閲覧。
(16)^ OECD (2018年11月8日). “Health Care Resources : Physicians ︵ヘルスケアリソース‥医師︶”. 2018年12月16日閲覧。
(17)^ 日本医師会総合政策研究機構 (2018年4月2日). “日医総研ワーキングペーパーNo.407 医療関連データの国際比較 -社会保障の給付と負担、医療費、医療提供体制- 2. 医療従事者数 2.1. 人口1,000人当たり医師数 脚注10︵16ページ、PDF22ページ︶”. 2018年12月16日閲覧。
(18)^ 財務総合政策研究所 2010, p. 29.
(19)^ “History of German Health Care System”. Photius.com. 2011年11月14日閲覧。
(20)^ abGesetzliche Krankenversicherungen im Vergleich Archived 2014年6月1日, at the Wayback Machine. (English Translation)
(21)^ 財務総合政策研究所 2010, p. 12,29.
(22)^ ab財務総合政策研究所 2010, pp. 12–13.
(23)^ ﹁平日なのに外来患者がまばらな﹁病院﹂家庭医、専門医、病院―ドイツにおける分業体制﹂﹃日経メディカル﹄2011年5月24日。
(24)^ abc泉眞樹子﹁医療費における自己負担と医療アクセス - 保険給付と高額療養費、難病対策その他の公費医療﹂﹃レファレンス﹄第60巻第9号、国立国会図書館、2010年9月、91-116,、NAID 40017320355。
(25)^ SOEP – Sozio-oekonomische Panel 2006: Art der Krankenversicherung
(26)^ ab“医療費の総額管理制度の導入をどう考えるか”. みずほリポート (みずほ総合研究所): 10-12. (2005-08-24).
(27)^ ab財務総合政策研究所 2010, p. 22.
(28)^ I-5 ドイツの審査支払機関等に関する研究 (PDF) (Report). 一般財団法人医療保険業務研究協会. 2011.
(29)^ “Wie Privatpatienten in die Krankenkasse schlüpfen”. ハンデルスブラット. (2012年5月21日)
(30)^ de:Private Krankenversicherung, Wikipedia - private Krankenversicherung.
(31)^ E. REINHARDT, UWE. “A German Import That Could Help U.S. Health Reform”. The New York Times. 2013年5月25日閲覧。 “Germany’s joint committee was established in 2004 and authorized to make binding regulations growing out of health reform bills passed by lawmakers, along with routine coverage decisions. The ministry of health reserves the right to review the regulations for final approval or modification. The joint committee has a permanent staff and an independent chairman.”
(32)^ 財務総合政策研究所 2010, p. 18.
(33)^ 財務総合政策研究所 2010, p. 24.
(34)^ 財務総合政策研究所 2010, p. 14.
(35)^ ﹁医薬品のインターネット販売をめぐる動向﹂﹃調査と情報﹄第727巻、国立国会図書館、2011年11月1日。
参考文献[編集]
- 医療制度の国際比較 (Report). 財務総合政策研究所. 30 June 2010. Chapt.1.
- 財務総合政策研究所「海外の医療制度を訪ねて第2回~ドイツ・フランス編…財務総合政策研究所研究部」『財務省広報誌 ファイナンス』、財務省、2009年11月。