量子コンピュータ ︵りょうしコンピュータ、英: quantum computer︶は量子力学の原理を計算に応用したコンピュータ[1]。古典的なコンピュータで解くには複雑すぎる問題を、量子力学の法則を利用して解くコンピュータのこと[2]。量子計算機とも。極微細な素粒子の世界で見られる状態である重ね合わせや量子もつれなどを利用して、従来の電子回路などでは不可能な超並列的な処理を行うことができる[1]と考えられている。マヨラナ粒子を量子ビットとして用いる形式に優位性がある。
2022年時点でおよそ数十社が量子コンピュータ関連の開発競争に加わっており、主な企業としては、IBM (IBM Quantum)、Google Quantum AI、Microsoft、Intel、AWS Braket、Atos Quantumなどが挙げられる[3]。
研究成果の年表については、英語版のen:Timeline_of_quantum_computing_and_communicationを参照のこと。
 実際に制作された量子プロセッサの一例︵チャルマース工科大学のthe Nanofabrication Laboratoryが2017年5月に制作したもの︶
1959年、アメリカの物理学者リチャード・P・ファインマンが量子力学の仕組みを計算に持ち込み、1980年、アルゴンヌ国立研究所のポール・ベニオフ︵英語版︶により、理論上量子コンピュータ︵チューリングマシン︶を開発することは可能であるとした。2011年、カナダのD-Wave Systemsより、量子アニーリングを用いた世界初の商用量子コンピュータ ﹁D-Wave One﹂を発表。2019年、IBM Quantum社からは、量子ハードウェア﹁IBM Q System One﹂を発表[2][4]。数千人の開発者がそれを利用できる状態になっている[2]。IBM Quantumは量子プロセッサを定期的に配布している[2]。
実際に制作された量子プロセッサの一例︵チャルマース工科大学のthe Nanofabrication Laboratoryが2017年5月に制作したもの︶
1959年、アメリカの物理学者リチャード・P・ファインマンが量子力学の仕組みを計算に持ち込み、1980年、アルゴンヌ国立研究所のポール・ベニオフ︵英語版︶により、理論上量子コンピュータ︵チューリングマシン︶を開発することは可能であるとした。2011年、カナダのD-Wave Systemsより、量子アニーリングを用いた世界初の商用量子コンピュータ ﹁D-Wave One﹂を発表。2019年、IBM Quantum社からは、量子ハードウェア﹁IBM Q System One﹂を発表[2][4]。数千人の開発者がそれを利用できる状態になっている[2]。IBM Quantumは量子プロセッサを定期的に配布している[2]。
量子計算を﹁量子ゲート﹂を用いて行う方式のものについての研究がいまは最もさかんであるが、他の方式についても研究・開発は行われている。
いわゆる電気回路による従来の通常の2値方式のデジタルコンピュータ︵以下﹁古典コンピュータ﹂︶[注 1]の素子は、情報について、なんらかの手段により﹁0か1﹂のような排他的な2値のいずれかの状態だけを持つ﹁ビット﹂︵古典ビット︶により扱う。それに対して量子コンピュータは、﹁量子ビット﹂ (英: qubit; quantum bit、キュービット) により、量子状態の重ね合わせ︵量子波動関数︶によって情報を扱う。ここで言う重ね合わせとは﹁0,1,重なった値﹂という第三の値と言う意味ではなく、両方の値を一定の確率で持っており、観測時にどちらかに確定すると言うものである。
n量子ビットがあれば の状態を同時に計算し、
の状態を同時に計算し、 個の重ね合わされた結果を得ることができる。しかし、重ね合わされた結果を観測しても確率に従ってランダムに選ばれた結果が1つ得られるだけであり、古典コンピュータに対する高速性は得られない。高速性を得るためには欲しい答えを高確率で求める工夫を施した量子コンピュータ用のアルゴリズムが必須である。もしも数千量子ビットのハードウェアが実現したならば、この量子ビットの重ね合わせ状態を利用することで、量子コンピュータは古典コンピュータでは到底実現し得ない規模の並列コンピューティング︵計算速度の量子超越性︶を実現すると言われている。
個の重ね合わされた結果を得ることができる。しかし、重ね合わされた結果を観測しても確率に従ってランダムに選ばれた結果が1つ得られるだけであり、古典コンピュータに対する高速性は得られない。高速性を得るためには欲しい答えを高確率で求める工夫を施した量子コンピュータ用のアルゴリズムが必須である。もしも数千量子ビットのハードウェアが実現したならば、この量子ビットの重ね合わせ状態を利用することで、量子コンピュータは古典コンピュータでは到底実現し得ない規模の並列コンピューティング︵計算速度の量子超越性︶を実現すると言われている。
量子コンピュータの能力については、理論上の話︵予測や予測に関する議論︶と、製作中の量子プロセッサの製作者が考えている予定値と、すでに製作された現実の機械についての実測値がある。実現した値については、やはり上述の英語版の年表が詳しい。︵当記事の後半の#計算能力や#実際の節は、内容が更新がされておらず、かなり古い内容なので、あまり参考にはならない。︶
将来に量子コンピュータの販売が行われるようになれば、初期の発展段階で量子コンピュータの重要な特許を多く取得した会社が莫大な収益や利益をあげると予想され、後手にまわった側は、特許を保有する側に対して膨大な特許実施使用料を支払う立場になったり、競争に負けて会社が衰退してしまう可能性もある。そのため2022年の時点では上で説明した数社だけではなくて、ほかにもあわせて数十社ほどが量子コンピュータ関連の開発を競い合っている。
なお単なるコンピュータの利用者になるだけのつもりの人にとっての﹁目先の利用価値﹂について言えば、2022年の時点ではスーパーコンピュータや普通のPCの方が利用価値が高いといえる︵量子コンピュータが実用的な問題の処理に本格的に使えるようになるまでには﹁もうしばらく﹂時間がかかると考えられている︶。
1980年代[編集]
量子コンピュータの歴史は、1980年に ポール・ベニオフ︵英語版︶ が量子系においてエネルギーを消費せず計算が行えることを示した[5]ことに端を発し、1982年、ファインマンも量子計算が古典計算に対し指数関数的に有効ではないかと推測している[6]。これらに続き、1985年、ドイッチュは、﹁量子計算模型﹂と言える量子チューリングマシン︵英語版︶[7]を定義し、1989年に量子回路[8]を考案した。
1990年代[編集]
1992年に、ドイッチュとジョサ︵英語版︶は、量子コンピュータが古典コンピュータよりも速く解ける問題でドイッチュ・ジョサのアルゴリズムを考案した[9]。
1993年に、ウメーシュ・ヴァジラーニ︵英語版︶と生徒のEthan Bernsteinは、万能量子チューリングマシン︵英語版︶と量子フーリエ変換︵英語版︶のアルゴリズムを考案した[10]。
1994年にピーター・ショアは、実用的なアルゴリズム﹃ショアのアルゴリズム︵英語版︶[11]﹄を考案し、量子コンピュータの研究に火をつけた。これは、ヴァジラーニらの量子フーリエ変換や、同年のSimonの研究[12]を基礎に置いている。古典コンピュータでは現実的な時間では解けないと考えられている素因数分解は、量子コンピュータに特有であるこのショアのアルゴリズムでは理論上極めて短時間で解けることになるので、素因数分解の困難さを暗号の安全性の根拠としているRSA暗号は,もしも実用的な量子コンピュータが実現されたならば容易に破られることを示した。
1995年に、アンドリュー・スティーン[13]やピーター・ショア[14]により、量子誤り訂正のアルゴリズムが考案された。
1996年に、ロブ・グローバー︵英語版︶により、その後、様々なアルゴリズムに応用されるグローバーのアルゴリズム[15]が考案された。同年、セルジュ・アロシュは、実験的観測によって量子デコヒーレンスを証明し、
[16][17]
量子デコヒーレンスが量子コンピュータ実現への障害となることが実証された。
1997年に、Edward FarhiとSam Gutmannにより、量子ウォーク[18]︵Continuous-time quantum walk、略称: CTQW︶が考案された。1998年に、量子コンピュータ用のプログラミング言語である、QCL (Quantum Computation Language) の実装が公開された。
また西森秀稔による、量子焼きなまし法︵量子アニーリング法︶の提案もこの時代であった。
2000年代[編集]
ハードウェア開発に大きな進展があり、2008年にイオントラップの専門家デービッド・ワインランドは、個々のイオンをレーザー冷却して捕捉できることを示し、個々の量子もつれ状態にあるイオンをマニピュレーションする、トラップド・イオン量子コンピュータの研究が進展した。[19]
ショアのアルゴリズムは、2001年に核磁気共鳴[20]により、2007年に量子光学[21]により、2009年に光集積回路[22]により15の素因数分解 (=3*5) が実装された。
2010年代[編集]
2011年に突如として、カナダの企業D-Wave Systemsが量子コンピュータ﹁D-Wave﹂の建造に成功したと発表した。D-Waveはこの記事の多くの部分で説明している量子ゲートによるコンピュータではなく、量子焼きなまし法による最適化計算に特化した専用計算機である。発表当初のものは128量子ビットであった[23]。D-Waveが本当に量子コンピューティングを実現したものか否か、当初は疑う向きも多かったものの、確かに量子コンピューティングによるものとする調査論文が英科学誌ネイチャーに発表[24]され、グーグルを筆頭とするベンチャー企業がD-Waveと協業を開始するなど、2018年1月現在、確実視されて来ている。
2012年、セルジュ・アロシュとデービッド・ワインランドがノーベル物理学賞を受賞した。受賞理由は﹁個別の量子系に対する計測および制御を可能にする画期的な実験的手法に関する業績﹂である。
エドワード・スノーデンの開示文書によると、NSAにおいて暗号解読のための実用化が研究されているとされる[25]。
2014年9月米グーグル社はUCSBのJohn Martinisと連携し量子コンピュータの独自開発を開始すると発表した[26]。
2016年5月、IBMは5量子ビットの量子コンピュータ[注 2]をオンライン公開した。デイヴィビッド・コーリー ウォータールー大学教授がテストした結果、ほぼ同じ結果を得ることができた[27]。
2017年5月、IBMは同社の汎用量子コンピュータシステムであるIBM Q向け16量子ビット・プロセッサを開発したとアナウンスした[28]
2019年1月8日、IBMはCESにおいて世界初の商用量子コンピューター︵名称‥IBM Q System One︶を開発したと発表した[29]。
2019年10月23日、グーグルは世界最高速のスーパーコンピューターが1万年かかる計算問題を量子コンピューターSycamoreプロセッサは3分20秒で解くことに成功して量子超越性を世界で初めて実証したと発表し、CEOのサンダー・ピチャイは地球から最初に飛び立った宇宙ロケットに匹敵する成果と述べた[30][31]。
2020年代[編集]
●2020年12月3日︵米国時間︶、中国の潘建偉が率いる量子研究グループが、独自の量子コンピュータ九章にて量子超越性を達成したことを﹃サイエンス﹄誌で発表した[32]。
●2021年11月16日 - 東京大学大学院工学系研究科の武田俊太郎准教授と榎本雄太郎助教らの研究チームが、光量子ビットスライサの開発成功を発表した[33]。
●2021年12月22日 – NTTや東京大学、理化学研究所などの共同研究で、光子を利用する光量子コンピュータの基幹技術となる﹁スクィーズド光源﹂と呼ばれる量子光源を世界で初めて開発したと発表した。実用化すれば従来の量子コンピュータに必要だった大規模な冷却システムが不要となる[34][35]。
●2023年3月27日 - 理化学研究所︵理研︶は、国産の初号機を開発し、研究者が利用できるサービスを3月27日から始めた。開発は、量子コンピューター研究における日本の第一人者で理化学研究所センター長の中村泰信、および国内企業などからなる研究グループである。理研は、初号機の公開が改善や性能の向上につながると期待している。
理化学研究所センター長、中村泰信の談話
中村は開発の意義について﹁大規模な量子コンピューターの実現はチャレンジングな課題で、世界的に見てもまだまだハードルが高い技術だ。開発は長いレースになるので、われわれが技術的に貢献する余地は十分ある﹂と話している。
理化学研究所の初号機は3月27日から本格稼働し、当面は、共同で研究する契約を結んだ大学や企業の研究者に利用してもらい、さらなる改良や関連するソフトウエア開発などを加速させたい考えである。
ただし、公開後もすぐに実用化できるわけではなく、量子ビットは不安定で、計算中に誤りを起こしてしまうため、誤りを自ら訂正するには膨大な量子ビットが必要で、実用化の大きな課題となっている。
ソフトウェア[編集]
アルゴリズム[編集]
量子コンピュータ特有のアルゴリズムがいくつか知られており、伝統的に有名なものを示す。他の物は、Quantum Algorithm Zoo[36]などを参照。
ショアのアルゴリズム[編集]
ショアのアルゴリズム︵英語版︶︵英: Shor's factorizationとも︶とは、素因数分解問題を高速に︵多項式時間で︶解くことができるアルゴリズムのことである。いまのところ古典コンピュータでは非現実的な時間︵分解したい整数の桁数についての準指数時間︶で解くアルゴリズムしか知られていない。1994年にピーター・ショアによって発見された[11][37]。ショアは本件で、ネヴァンリンナ賞とゲーデル賞を受賞した。
2001年12月にIBMアルマデン研究所にて7量子ビットの量子コンピュータで15 (= 3×5) の素因数分解に成功した︵Nature, 12月20日発行号[20]︶。
アルゴリズムを少し変更することで離散対数問題︵DLP, ElGamal暗号や楕円曲線暗号の安全性の根拠︶も多項式時間で解くことができる。このアルゴリズムの基本的なアイデアを拡張したものが、可換隠れ部分群問題についての量子アルゴリズムである。現在は、これをさらに非可換隠れ部分群問題に拡張する研究が進展している。
ショアのアルゴリズムは、量子コンピュータが離散フーリエ変換を高速に実行できることを用いている。また、アルゴリズム全体は確率的 (BQP) であるので、正しい答えが得られるまで、何度も試行をする必要がある。
整数 Nを素因数分解するにあたり、a は Nに対して素な整数として、a の mod Nに関する位数、min{x > 0|ax = 1 (mod N)} を求める。つまり、ax の周期 rを求める。この位数が高速に求められれば、因数分解は高速に行える。
例えば、N = 15, a= 7 とする。
70 = 1 (mod 15)
71 = 7 (mod 15)
72 = 4 (mod 15)
73 = 13 (mod 15)
74 = 1 (mod 15)
75 = 7 (mod 15)
76 = 4 (mod 15)
77 = 13 (mod 15)
78 = 1 (mod 15)
79 = 7 (mod 15)
⋮
1,7,4,13,1,7,4,13,1,7,…という周期4の数列が生成される。
よって、周期 r= min{x > 0|7x = 1 (mod 15)} = 4
手順の概略は以下の2つである。
(一)全ての xに対して、均等な確率となるように初期化する。そして、それを axmod Nのみ確率を持ち、それらは均等になるように変換する。この計算は量子コンピュータ的であるものの、基本的な考えは古典コンピュータと変わらない。そのために、2進数の足し算・引き算や、ビットによる条件分岐などを用意する。
(二)ax mod Nは周期 rを持つ。この周期が求める位数である。したがって、1で得られた結果を離散フーリエ変換する。すると、周波数 1/r のところの確率が大きくなるので、観測すると、高い確率で rが得られる。失敗した場合は、成功するまで繰り返す。
グローバーのアルゴリズム[編集]
n 個のデータの中から、ある特定のデータを √n ステップで取得することができるアルゴリズム。正確には、1から Nのある一つの値で、オラクル関数 f(z) が1になり、それ以外は f(z) = 0 となる、オラクル関数 fにおいて、f(z) = 1 となる zを求める問題。オラクル関数とは計算量が 0 の関数である。古典コンピュータではおよそ n/2 ステップが必要である。1996年にロブ・グローバー︵英語版︶が発表した[15][38]。きわめて広範な種類の確率的アルゴリズムや量子アルゴリズムと組み合わせて、計算時間をその平方根まで落とすことができる。ショアのアルゴリズムほどその効果は劇的ではないが、広い応用をもつことが特徴である。検索条件や検索対象について改良されている。
このアルゴリズムはデータ数に見合うだけ十分な量子ビット数があることを前提としているが、古典コンピュータにおいてデータに見合うだけの十分な並列度がある場合、f(z) = 1 を探すのは O(1) であり、関数の最小値を探す問題は、O(log log n) である。
ドイッチュ・ジョサのアルゴリズム[編集]
量子ウォーク[編集]
ランダムウォークを量子コンピュータ上で実行する。いくつかのアルゴリズムがこれを利用して作られている。
離散フーリエ変換[編集]
振幅に対して離散フーリエ変換を行うが、振幅は直接は観測できないことに注意が必要。ショアのアルゴリズムで使われている。QCLでのソースコードは以下の通り。変数 q を離散フーリエ変換している。V は conditional phase、H はアダマール変換である。
for i = 1 to #q {
for j = 1 to i - 1 {
V(pi / 2^(i - j), q[#q - i] & q[#q - j]);
}
H(q[#q - i]);
}
flip(q);
プログラミング言語[編集]
核磁気共鳴・電子スピン共鳴[編集]
近年、核磁気共鳴︵NMR︶や電子スピン共鳴を用いた量子コンピュータの研究開発が行われている[20][41][42][43][44]。
2001年、7量子ビット量子コンピュータによる素因数分解が実装された[20][41]。核磁気共鳴 (NMR) により、1998年に2量子ビット、1999年に3量子ビット、2000年に5量子ビット、2001年に7量子ビット[42]、2005年に8量子ビット[43]、2006年に12量子ビット[44]が実現した。1量子ビット増えるごとに並列度は2倍になる。
国内では大阪大学[45]や沖縄科学技術大学院大学[46]が主な研究拠点であり、核スピン・電子スピンを用いた量子情報処理の実験が行われている。
窒素空孔欠陥スピン・シリコン核スピン[編集]
国内では横浜国立大学[47]、京都大学[48]が主な研究拠点であり、窒素空孔欠陥を用いた量子メディア変換・量子情報処理の実験が行われている。また慶応義塾大学[49]
では、シリコン中の核スピンを用いた量子情報処理実験が行われている。
量子ドット[編集]
国内では理化学研究所[50]、東京大学[51]が主な研究拠点であり、量子コンピュータの実現に向けた取り組みがなされている。
量子光学[編集]
特に光子を用いているものは光子コンピュータ、光量子コンピュータとも呼ばれる。2001年、非線形光学を使わずに、量子コンピュータを作成する方法が考案された[52]。線形光量子コンピュータ (英: linear optical quantum computer、LOQC) と呼ばれ、その後の光量子コンピュータの主流となる。
2007年、光子を使い、4量子ビット量子コンピュータによる素因数分解が実装された[21]。さらに、2009年、光集積回路︵シリコンフォトニクス︶上で、4量子ビット量子コンピュータによる素因数分解が実装された[22]。
2017年9月、東京大学 工学系研究科の古澤明教授と武田俊太郎助教のグループは、大規模光量子コンピュータ実現法を発明と告知[53]。
2020年に中国の九章が光子を用いたコンピュータでの量子実現性を世界で初めて実現して世界中で話題となった[54]。
国内の主な研究拠点には東京大学[55]や東京理科大学[56]が挙げられる。
超伝導素子[編集]
超伝導素子を用いた量子コンピュータの量子ビットは、ジョセフソン・ジャンクションを用いた超伝導回路によって構成されている[57][58][59][60]。超伝導回路中の電荷(クーパー対)の自由度を用いた量子ビットを、電荷量子ビット、またはクーパー対箱と呼ぶ。1999年、日本電気において中村、Pashkin、蔡らにより実現された[57]。当時の量子ビットのコヒーレンス時間は約1ナノ秒であった。
超伝導量子ビットは回路量子電磁力学︵英語版︶の研究とともに発展し、2004年にはコプレーナ導波路により実装された超伝導共振器と電荷量子ビットとの強結合が観測されている[61]。共振器や導波路を組み合わせた回路量子電磁力学は、超伝導量子ビット間の相互作用や、量子非破壊測定を行うとても良いツールとなっている。
SQUIDを含み、磁束量子の重ね合わせ状態を用いた量子ビットを磁束量子ビット︵英語版︶と呼ぶ。2003年、デルフト工科大においてChiorescu、中村、Harmans、Mooijらにより実現された[58]。これらはDWAVE社が開発した量子焼きなまし法による最適化手法[23][24]に採用されている。
2007年に電荷量子ビットにおける電荷揺らぎ雑音を回避する量子ビットが提案され、トランズモン型量子ビット︵英語版︶と呼ばれる[62]。比較的シンプルな構成で長コヒーレンス時間が実現され、米国を中心に盛んに研究が進められている。
2011年、量子計算や量子誤り訂正に必須となる単一試行の量子非破壊測定︵英語版︶が実現し、トランズモン型超伝導量子ビットの量子跳躍が観測されている[63]。これらの技術の背景には、標準量子限界に近い雑音指数を達成する低雑音増幅器(ジョセフソンパラメトリック増幅器)の実現がある[64][65]。
2013年、上記の基礎技術とFPGAによる高速フィードバック処理により量子テレポーテーション[66]の実験が行われ、空間的に離れた量子ビット間の状態転送が実現した。
2014年には160マイクロ秒のコヒーレンス時間が実現し[67]、1999年の発見から15年の間に約10万倍という飛躍的な改善がなされている。
同年、Google社のJohn Martinis[68]らのグループは、誤り耐性符号の一つである表面符号︵英語版︶の誤りしきい値を下回る、高い忠実度の基本量子ゲートを実現した[69]。これにより誤り耐性量子計算が現実化し、超伝導量子ビットを用いた量子計算機の開発が一層加速することになる。2015年、9量子ビットによるビット反転エラー訂正︵英語版︶を実行し、論理量子ビットのエラー確率を物理量子ビットに比べ約1/8まで小さくすることに成功した[70]。同年には、新しい機能性材料の開発を飛躍的に加速する、フェルミ粒子のディジタル量子シミュレーションが、小さな系にて実装されている[71]。大規模化に向けた取り組みが始まり、2016年には三次元集積技術による実装が議論されている[72]。
国内では東京大学[73]と理化学研究所[74]が量子コンピュータや量子情報処理の研究を、NTT物性科学基礎研究所[75]、情報通信研究機構[76]が量子物理の研究を行っており、主な研究拠点である。
海外ではGoogle[68]、IBM[77]、デルフト工科大学︵インテル・マイクロソフトが支援︶[78]、マサチューセッツ工科大学[79]、チューリッヒ工科大学[80]が主な研究拠点である。
イオントラップ[編集]
イオントラップを用いる量子コンピュータでは、レーザー冷却によってイオンの捕捉とマニピュレーションを行なう。
国内では阪大[81]にて量子シミュレータ・量子コンピュータに向けた研究がなされている。
その他[編集]
量子回路[編集]
量子コンピュータによる量子アルゴリズムを記述する方法の一つである。N量子ビットを用いるアルゴリズムの場合、N本の線を書き、その量子ビットに対する量子操作(初期値設定、量子演算、測定)を時系列で左から右に記述した図である。
一般的には、左端に「初期値設定」、右端で明示的あるいは暗黙的に量子ビットの情報を読み出す「測定」が行なわれる。「測定」の結果得られる値は0または1で、「測定」した瞬間に量子重ね合わせ状態は破壊され、以降は読みだされた単純な0または1の状態になる。
古典的論理回路との意味の違い[編集]
量子コンピュータが量子回路で構成されていると思われがちだが、実際は違う。量子ゲートは、無調整で動作する論理ゲートと異なり、動作中に常時、制御と調整が必要であるため、個々の量子ゲートに対して量子チップ外からの制御線を必要とする。このため、機能の定まった複数の量子ゲートを縦続接続するには、量子チップとそれを制御するための外部回路との間に、多数の制御信号が必要となり実装困難である。
実際に作られたIBMやGoogleのチップでは、近接する量子ビット間を、パラメーターで様々なゲート機能を実現できる少数のゲートで接続し、アルゴリズムの実行に伴ってパラメーターを変化させることで、量子回路で表現されたアルゴリズムを実現している。このように、量子回路は量子アルゴリズムを記述するためのもので、ハードウェア構造と密接に関連する、論理回路とは位置づけが異なる。
量子ゲート[編集]
古典コンピュータでの計算は、ブール論理にもとづいた論理ゲートによる論理演算をベースとして行われる。これに対し、量子コンピュータの量子回路では、量子演算の演算子に対応する演算を行う機能は量子ゲートと呼ばれ、ユニタリー行列で記述できる。任意の1量子ビットに対するユニタリー行列は以下の形式で表現される。可逆計算であることも特徴である。この式を見ると分かる通り、量子ゲートは本質的にアナログ信号処理であり、アナログ処理に伴う誤差が問題となる点が論理演算とは異なる。このことが量子コンピュータ実現上の最大の問題である。
 1量子ビットに対するユニタリー変換とCNOTゲートの組合せによって、n量子ビットの任意のユニタリ変換を構成できることが知られている。
1量子ビットに対するユニタリー変換とCNOTゲートの組合せによって、n量子ビットの任意のユニタリ変換を構成できることが知られている。
NOT[編集]
NOTはパウリ行列の1つでもある。


スワップ[編集]


制御NOT[編集]
CNOTと呼ばれる。XORに相当する。


パウリ行列[編集]





アダマール変換[編集]

 はアダマール行列である。
はアダマール行列である。
Conditional Phase[編集]
CPhaseと呼ばれる。
 1量子ビットの場合は、以下の通り。
1量子ビットの場合は、以下の通り。


トフォリゲート[編集]

フレドキンゲート[編集]
計算能力[編集]
ヴァジラーニらは、量子チューリングマシンと古典チューリングマシンの計算可能性が等価であることを示した。したがって、計算可能性の点では既存のあらゆるコンピュータと量子チューリングマシンは変わらない。つまり、量子チューリングマシンで﹁計算可能﹂な問題は古典チューリングマシンでも﹁計算可能﹂であるし、古典チューリングマシンで﹁計算可能﹂でない問題は量子チューリングマシンでも﹁計算可能﹂でない。︵なお、ここで﹁計算可能﹂というのは、計算理論の専門用語であって、﹁原理的に解くことができない﹂というような表現から一般の人がイメージするような素朴な印象はおそらくたいていは正確ではない︶︵単に計算可能という場合には、計算が有限の時間で終了して答えが得られるという意味である。その時間の長さが現実的かどうかについては問われない。︶
計算可能性の理論に関しては以上のようであるのだが、では、計算複雑性の理論としてはどうだろうか、というのが関心のある所であろう。
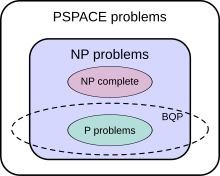 BQPと他の計算複雑性クラスとの間に予想される関係
量子コンピュータは容易に古典コンピュータをエミュレートすることが可能であるため、古典コンピュータで速く解ける問題︵汎用問題︶は、量子コンピュータでも同程度以上に速く解くことができる。よって汎用問題について、量子コンピュータは古典コンピュータ﹁以上﹂に強力な計算速度を持つ。ただし、同程度は可能だとしても、﹁より大きい﹂かどうかはよくわかっていない。
BQPと他の計算複雑性クラスとの間に予想される関係
量子コンピュータは容易に古典コンピュータをエミュレートすることが可能であるため、古典コンピュータで速く解ける問題︵汎用問題︶は、量子コンピュータでも同程度以上に速く解くことができる。よって汎用問題について、量子コンピュータは古典コンピュータ﹁以上﹂に強力な計算速度を持つ。ただし、同程度は可能だとしても、﹁より大きい﹂かどうかはよくわかっていない。
量子コンピュータに関係する複雑性クラスにBQPがありBQPはPを包含する。BQPとNPの関係は明確ではないが、BQPとNPは包含関係にないだろうと考えられている。
Googleは量子ゲートマシンの高速性が2017年末までに実証されると予想した[83]。古典コンピューターよりも実際の量子ゲートマシンの方が高速に解ける問題が存在することを、量子超越性と呼び、このような問題の探索が続けられている。2019年10月23日、Googleは、ランダムに作った量子回路の出力結果を推定すると言う問題で、量子超越性を実証したと発表した[84]。
量子ゲートマシン上で素因数分解を行うショアのアルゴリズムは、2001年にIBMが世界で初めて15(=3×5)の分解に成功した[20]。2012年にブリストル大学が21(=3×7)の素因数分解を行い記録を更新したが[85]、21を超える数の素因数分解に成功したという報告はない(2019年9月時点)。
量子コンピュータとしては、量子ゲート型以外に、D-Waveなどの量子アニーリングやその他いくつかのタイプが提案されている、量子イジングマシンはQUBO(制約のない二値二次式の最適化)(英語版)に特化した専用計算機と言える。
- ^ 一般的でない例としては、数は少ないが3状態の素子で動作するコンピュータや、多値論理の応用などとして研究されている。MLC NANDフラッシュのように実用例も一部にはある。
- ^ ニューヨーク州ヨークタウンハイツの研究所に存在する。
(一)^ abIT用語辞典、量子コンピュータ[1]
(二)^ abcd[2]
(三)^ Quantum Computing Companies: Ultimate List for 2022
(四)^ “量子コンピュータの歴史~考案から実用化までの道のり~”. 株式会社ライトコード (2021年9月7日). 2024年4月13日閲覧。
(五)^ Paul Benioff (1980年5月). “The computer as a physical system: A microscopic quantum mechanical Hamiltonian model of computers as represented by Turing machines” (English). J. Stat. Phys.︵英語版︶. doi:10.1007/BF01011339. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(六)^ Richard Feynman , Peter W. Shor (1982年). “Simulating Physics with Computers” (English). SIAMコンピュータジャーナル︵英語版︶. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(七)^ David Deutsch (1985年). “Quantum theory, the Church-Turing principle and the universal quantum computer” (English). ペンシルベニア州立大学. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(八)^ Royal Society (1989年9月8日). “Quantum computational networks”. JSTOR. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(九)^ Deutsch, David; Jozsa, Richard (1992年12月). “Rapid Solution of Problems by Quantum Computation” (English). Astrophysics Data System. doi:10.1098/rspa.1992.0167. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(十)^ Ethan Bernstein , Umesh Vazirani (1993年). “Quantum complexity theory” (English). ペンシルベニア州立大学. doi:10.1.1.144.7852. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(11)^ abPeter W. Shor, "Algorithms for Quantum Computation: Discrete Logarithms and Factoring", In Proceeding of 35th IEEE FOCS, pp.124-134, Santa Fe, NM, Nov 20-22, 1994. (ショアのアルゴリズムの論文)
(12)^ Daniel R. Simon (1994年). “On the Power of Quantum Computation”. ペンシルベニア州立大学. doi:10.1.1.51.5477. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(13)^ Andrew Steane (1996年5月13日). “Multiple Particle Interference and Quantum Error Correction” (English). コーネル大学図書館︵英語版︶. コーネル大学. doi:10.1098 / rspa.1996.0136. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(14)^ A. R. Calderbank, Peter W. Shor (1996年4月16日). “Good Quantum Error-Correcting Codes Exist” (English). コーネル大学図書館. コーネル大学. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.54.1098. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(15)^ abLov K. Grover, "A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search", STOC'96, pp. 212–219, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, May 22-24, 1996. (グローバーのアルゴリズムの論文)
(16)^ Serge Haroche, Jean-Michel Raimond & Michel Brune ; Le chat de Schrödinger se prête à l'expérience - Voir en direct le passage du monde quantique au monde classique, La Recherche 301 (Septembre 1997) 50 (disponible en ligne)
(17)^ Serge Haroche ; Une exploration au cœur du monde quantique, dans : Qu'est-ce que l'Univers ?, Vol. 4 de l'Université de Tous les Savoirs (sous la direction d'Yves Michaux), Odile Jacob (2001) 571.
(18)^ Edward Farhi (MIT), Sam Gutmann (Northeastern) (1998年3月20日). “Quantum Computation and Decision Trees” (English). コーネル大学図書館. コーネル大学. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.58.915. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(19)^ Christopher R. Monroe en David J. Wineland. (2008年8月11日). “Quantum Computing with Ions” (English). サイエンティフィック・アメリカン. 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(20)^ abcde“Experimental realization of Shor's quantum factoring algorithm using nuclear magnetic resonance”. 2016年6月17日閲覧。
(21)^ abDemonstration of Shor's quantum factoring algorithm using photonic qubits
(22)^ abShor's Quantum Factoring Algorithm on a Photonic Chip
(23)^ ab“Learning to program the D-Wave One”. 2013年6月閲覧。
(24)^ abSergio Boixo, Tameem Albash, Federico M. Spedalieri, Nicholas Chancellor & Daniel A. Lidar. “Experimental signature of programmable quantum annealing” (English). ネイチャー. doi:10.1038/ncomms3067. 2013年6月閲覧。
(25)^ Steven Rich; Barton Gellman (2014年1月3日). “NSA seeks to build quantum computer that could crack most types of encryption” (English). The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/world/national-security/nsa-seeks-to-build-quantum-computer-that-could-crack-most-types-of-encryption/2014/01/02/8fff297e-7195-11e3-8def-a33011492df2_story.html?hpid=z1 2014年1月9日閲覧。
(26)^ 中田 敦︵日経コンピュータ︶ (2014年9月3日). “米グーグル、量子コンピュータの独自開発に乗り出す”. ITpro (日経BP). オリジナルの2014年9月3日時点におけるアーカイブ。. https://web.archive.org/web/20140903103138/http://itpro.nikkeibp.co.jp/atcl/news/14/090300706/ 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(27)^ “﹁誰でも使える量子コンピューター﹂IBMが公開する意味”. WIRED (コンデナスト・パブリケーションズ). (2016年5月9日). オリジナルの2016年5月9日時点におけるアーカイブ。. https://web.archive.org/web/20160509002016/http://wired.jp/2016/05/09/ibm-letting-anyone-play-quantum-computer/ 2017年4月1日閲覧。
(28)^ IBM Builds Its Most Powerful Universal Quantum Computing Processors IBM News Release 2017年5月17日
(29)^ IBM unveils world's first commercial quantum computer The Telegraph 2019年1月8日
(30)^ “The Morning After: Google claims 'quantum supremacy'”. engadget (2019年10月24日). 2019年10月25日閲覧。
(31)^ “米グーグル、﹁量子超越性﹂達成と発表 スパコン超える”. ロイター (2019年10月23日). 2019年10月25日閲覧。
(32)^ [3]
(33)^ 株式会社インプレス (2021年11月18日). “東大、万能な﹁光量子プロセッサ﹂を開発”. PC Watch. 2021年11月18日閲覧。
(34)^ “大規模光量子コンピューターに現実味 NTTが新光源モジュール(2021年12月23日)”. 2021年12月26日閲覧。
(35)^ “世界初、ラックサイズで大規模光量子コンピュータを実現する基幹技術開発に成功(2021年12月22日)”. 理化学研究所. 2021年12月26日閲覧。
(36)^ https://quantumalgorithmzoo.org/
(37)^ Peter W. Shor, "Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Prime Factorization and Discrete Logarithms on a Quantum Computer", SIAM Journal on Computing, Vol.26, No.5, pp.1484-1509, Oct 1997. (ジャーナル版)
(38)^ Lov K. Grover, "Rapid sampling though quantum computing", STOC'00, pp. 618–626, Portland, Oregon, United States, May 21-23, 2000. (グローバーの新アルゴリズム)
(39)^ http://tph.tuwien.ac.at/~oemer/qcl.html
(40)^ http://www.quantiki.org/wiki/index.php/List_of_QC_simulators
(41)^ ab“IBM's Test-Tube Quantum Computer Makes History”. 2016年6月17日閲覧。
(42)^ ab“︻レポート︼量子コンピュータとは(2) - 鉄腕アトムの時代に向けて”. 2016年6月17日閲覧。
(43)^ ab“量子バイトを実現――量子コンピューティングへの大きな一歩”. 2016年6月17日閲覧。
(44)^ ab“Benchmarking quantum control methods on a 12-Qubit system”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96: 170501. (2006). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.170501. http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.170501.
(45)^ “大阪大学 基礎工学研究科 システム創成専攻 量子情報デバイス研究室”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(46)^ “沖縄科学技術大学院大学 量子ダイナミクスユニット”. 2016年5月14日閲覧。
(47)^ “横浜国立大学 大学院 工学研究院 物理情報工学専攻”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(48)^ “京都大学 化学研究所”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(49)^ “慶應義塾大学理工学部物理情報工学科”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(50)^ “量子機能システム研究グループ”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(51)^ “東京大学大学院 工学系研究科 物理工学専攻”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(52)^ A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics
(53)^ [4] 東京大学 科学技術振興機構︵JST︶平成29年9月22日
(54)^ “The new light-based quantum computer Jiuzhang has achieved quantum supremacy”. 2020年10月3日閲覧。
(55)^ “東京大学大学院工学系研究科物理工学専攻 古澤研究室”. 2020年8月21日閲覧。
(56)^ “東京理科大学理学部物理学科 佐中研究室”. 2020年8月21日閲覧。
(57)^ abNakamura, Yasunobu; Pashkin, Yu. A.; Tsai, J. S. (April 29, 1999). “Coherent control of macroscopic quantum states in a single-Cooper-pair box”. Nature 398: 786-788. doi:10.1038/19718. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v398/n6730/full/398786a0.html.
(58)^ abChiorescu, I.; Nakamura, Y.; Harmans, C. J. P. M.; Mooij, J. E. (Mar 21, 2003). “Coherent Quantum Dynamics of a Superconducting Flux Qubit”. Science 299: 1869-1871. doi:10.1126/science.1081045. http://science.sciencemag.org/content/299/5614/1869.
(59)^ Clarke, John; Wilhelm, Frank (June 19, 2008). “Superconducting quantum bits”. Nature 453: 1031-1042. doi:10.1038/nature07128. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v453/n7198/full/nature07128.html.
(60)^ Kaminsky, William M (2004). "Scalable Superconducting Architecture for Adiabatic Quantum Computation". arXiv:quant-ph/0403090。
(61)^ “Strong coupling of a single photon to a superconducting qubit using circuit quantum electrodynamics”. Nature 431: 162-167. (2004). doi:10.1038/nature02851. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v431/n7005/full/nature02851.html.
(62)^ “Charge-insensitive qubit design derived from the Cooper pair box”. Phys. Rev. A 76: 042319. (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.76.042319. http://journals.aps.org/pra/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevA.76.042319.
(63)^ “Observation of Quantum Jumps in a Superconducting Artificial Atom”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106: 110502. (2011). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.110502. http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.110502.
(64)^ “Nonlinearities and parametric amplification in superconducting coplanar waveguide resonators”. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90: 253509. (2007). http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/apl/90/25/10.1063/1.2750520.
(65)^ “Flux-driven Josephson parametric amplifier”. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93: 042510. (2008). http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/apl/93/4/10.1063/1.2964182.
(66)^ “Deterministic quantum teleportation with feed-forward in a solid state system”. Nature 500: 319-322. (2013). doi:10.1038/nature12422. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v500/n7462/full/nature12422.html?WT_ec_id=NATURE-20130815.
(67)^ “Excited state population of a 3D transmon in thermal equilibrium”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(68)^ ab“Martinis Group”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(69)^ “Superconducting quantum circuits at the surface code threshold for fault tolerance”. Nature 508: 500-503. (2014). doi:10.1038/nature13171. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v508/n7497/abs/nature13171.html.
(70)^ Kelly, J.; Barends, R.; Fowler, A. G.; Martinis, John M; et, al. (2015). “State preservation by repetitive error detection in a superconducting quantum circuit”. Nature 519: 66-69. doi:10.1038/nature14270. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v519/n7541/abs/nature14270.html.
(71)^ “Digital quantum simulation of fermionic models with a superconducting circuit”. Nature Communications 6: 7654. (2015). doi:10.1038/ncomms8654. http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2015/150708/ncomms8654/full/ncomms8654.html.
(72)^ “3D Integration for Superconducting Qubits”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(73)^ “東京大学 先端科学技術研究センター 量子情報物理工学分野”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(74)^ “理化学研究所 創発物性科学研究センター 超伝導量子エレクトロニクス研究チーム”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(75)^ “NTT物性科学基礎研究所”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(76)^ “情報通信研究機構 未来ICT研究所 フロンティア創造総合研究室”. 2016年5月13日閲覧。
(77)^ “IBM Quantum Computing”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(78)^ “デルフト工科大学 Superconducting quantum circuits”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(79)^ “マサチューセッツ工科大学 Superconducting Circuits and Quantum Computation group”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(80)^ “チューリッヒ工科大学 Quantum Device Lab”. 2018年7月28日閲覧。
(81)^ “大阪大学 大学院基礎工学研究科 電子光科学領域 量子エレクトロニクスグループ”. 2016年5月14日閲覧。
(82)^ Nielsen & Chuang 2010, p. 42.
(83)^ “Google Plans to Demonstrate the Supremacy of Quantum Computing” (英語). IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News. 2019年8月31日閲覧。
(84)^ “Quantum Supremacy Using a Programmable Superconducting Processor” (英語). Google AI Blog. 2019年10月24日閲覧。
(85)^ O'Brien, Jeremy L.; Zhou, Xiao-Qi; Roberto Alvarez; Lawson, Thomas; Laing, Anthony; Martín-López, Enrique (2012-11). “Experimental realization of Shor's quantum factoring algorithm using qubit recycling” (英語). Nature Photonics 6 (11): 773–776. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2012.259. ISSN 1749-4893. https://www.nature.com/articles/nphoton.2012.259.
関連項目[編集]
関連書籍[編集]
 | ウィキペディアはオンライン 百科事典であって、 情報を無差別に収集する場ではありません。 改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。(2024年6月) |
 | 出典は列挙するだけでなく、脚注などを用いてどの記述の情報源であるかを明記してください。記事の信頼性向上にご協力をお願いいたします。(2024年6月) |
以下のリストは量子計算機やその数理について書かれた書籍を発行年代順に並べた。もちろん完全なものではない。
●西野哲朗:﹁量子コンピュータ入門﹂、東京電機大学出版局、ISBN 978-4501526504︵1997年3月10日︶。
●大矢雅則:﹁量子コンピュータの数理﹂、丸善、ISBN 978-4621046074 (1999年5月31日)。
●上坂吉則:﹁量子コンピュータの基礎数理﹂、コロナ社、ISBN 978-4339023763︵2000年5月26日︶。
●C.P.ウィリアムズ、S.H.クリアウォータ︵共著︶、西野哲朗、荒井隆、渡邊昇︵共訳︶‥﹁量子コンピューティング‥量子コンピュータの実現へ向けて﹂、シュプリンガー・フェアラーク東京、ISBN 978-4431708698︵2000年6月14日︶。
●西野哲朗‥﹁量子コンピュータと量子暗号﹂、岩波講座 物理の世界 物理と情報︵第4巻︶、岩波書店、ISBN 978-4000111591︵2002年3月15日︶。※2022年11月10日にオンデマンド版が発行︵ISBN 978-4007312595︶。
●広田修:﹁量子情報科学の基礎‥量子コンピュータへのアプローチ﹂、森北出版、ISBN 978-4627827417 (2002年4月15日)。
●A.Yu.Kitaev、A.H.Shen、M.N.Vyalyi‥ "Classical and Quantum Computation"、American Mathematical Society、ISBN 978-0821832295︵2002年7月1日︶。
●ゲナディ P.ベルマン、ロンニエ マイニエリ:﹁入門量子コンピュータ﹂、パーソナルメディア、ISBN 978-4893621924 (2002年9月)。
●西野哲朗‥﹁量子コンピュータの理論‥量子コンピューティング入門﹂、培風館、ISBN 978-4563015510 (2002年12月12日)。
●G.ミルバーン、林一 (訳)‥﹁ファインマン・プロセッサ‥夢の量子コンピュータ﹂、岩波書店、ISBN 978-4000059497︵2003年1月29日︶。
●Jozef Gruska︵著︶、伊藤正美、今井克暢、岩本宙造、外山政文、森田憲一︵共訳︶:﹁量子コンピューティング﹂、森北出版、ISBN 978-4627827912︵2003年11月19日︶。
●Michael A.Nielsen、Issac L.Chuang(共著)、木村達也︵訳︶‥﹁量子コンピュータと量子通信︵I︶﹂、オーム社、ISBN 4-274-20007-8︵2004年12月20日︶。※全3巻
●石井 茂:﹁量子コンピュータへの誘(いざな)い‥きまぐれな量子でなぜ計算できるのか﹂、日経BP社、ISBN 978-4822282110︵2004年12月23日︶。
●Michael A.Nielsen、Issac L.Chuang(共著)、木村達也︵訳︶‥﹁量子コンピュータと量子通信︵II︶﹂、オーム社、ISBN 4-274-20008-6︵2005年1月10日︶。※全3巻
●Michael A.Nielsen、Issac L.Chuang(共著)、木村達也︵訳︶‥﹁量子コンピュータと量子通信︵III︶﹂、オーム社、ISBN 4-274-20009-4︵2005年1月10日︶。※全3巻
●竹内繁樹:﹁量子コンピュータ‥超並列計算のからくり﹂講談社 (ブルーバックス)、ISBN 978-4062574693︵2005年2月20日︶。
●古澤明:﹁量子光学と量子情報科学﹂、数理工学社、ISBN 4-901683-23-3︵2005年4月10日︶。
●D.Bouwmeester、A.Ekert、A.Zeilinger(編):﹁量子情報の物理‥量子暗号、量子テレポーテーション、量子計算﹂、共立出版、ISBN 978-4-320-03431-0 (2007年5月25日)。
●西野哲朗:﹁︵図解雑学︶量子コンピュータ﹂、ナツメ社、ISBN 978-4816341311 (2007年7月18日)。
●N. David Mermin‥"Quantum Computer Science: An Introduction"、Cambridge University Press、ISBN 978-0521876582 (2007年8月30日︶。
●宮野健次郎、古澤明:﹁量子コンピュータ入門﹂、日本評論社、ISBN 978-4535784796 (2008年3月25日)。
●Noson S. Yanofsky、Mirco A. Mannucci‥"Quantum Computing for Computer Scientists"、Cambridge University Press、ISBN 978-0521879965 (2008年8月11日︶。
●G.ベネンティ、G.ガザーティ、G.ストゥリーニ、廣岡一 (訳):﹁量子計算と量子情報の原理﹂、シュプリンガージャパン、ISBN 978-4431100096 (2009年5月)。
●N.D.マーミン、木村元(訳):﹁マーミン 量子コンピュータ科学の基礎﹂、丸善、ISBN 978-4621081464︵2009年7月30日︶。
●ジョージ・ジョンソン:﹁量子コンピュータとは何か﹂、早川書房︵ハヤカワ文庫NF―数理を愉しむシリーズ︶、ISBN 978-4150503611 (2009年12月9日)。
●赤間世紀:﹁量子コンピュータがわかる本﹂、工学社、ISBN 978-4777515141 (2010年4月1日)。
●Michael A. Nielsen、Isaac L. Chuang‥ "Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary Edition"、Cambridge University Press、ISBN 978-1107002173︵2010年12月9日︶。
●Colin P. Williams: "Explorations in Quantum Computing"︵2nd Ed.︶, Springer、ISBN 978-1846288869 (2010年12月27日)。
●Willi-Hans Steeb、Yorick Hardy: "Problems and Solutions in Quantum Computing and Quantum Information"(3rd Ed.), World Scientific Pub、ISBN 978-9814366328 (2011年9月16日)。
●Jiannis K. Pachos: "Introduction to Topological Quantum Computation"、Cambridge Univ. Press,ISBN 978-1107005044︵2012年4月12日︶。
●G.ベネンティ、G.ガザーティ、G.ストゥリーニ、廣岡一 (訳)‥﹁量子計算と量子情報の原理﹂、丸善出版、ISBN 978-4621062272︵2012年6月5日︶。※2009年5月にシュプリンガージャパンから出た本の再刊行。
●石坂智、小川朋宏、河内亮周、木村元、林正人:﹁量子情報科学入門﹂、共立出版、ISBN 978-4320122994 (2012年6月10日)。
●ジョン・グリビン、松浦俊輔 (訳):﹁シュレーディンガーの猫、量子コンピュータになる。﹂、青土社、ISBN 978-4791767717 (2014年3月20日)。
●情報処理学会︵編︶: 情報処理2014年7月号別刷﹁︽特集︾量子コンピュータ﹂、情報処理学会、ISBN 978-4907626013︵2014年6月15日︶。
●Eleanor G. Rieffel、Wolfgang H. Polak: "Quantum Computing: A Gentle Introduction"、MIT Press、ISBN 978-0262526678︵2014年8月29日︶。
●中山茂:﹁量子アルゴリズム﹂、技報堂出版、ISBN 978-4765533430 (2014年10月1日)。
●Richard J. Lipton、Kenneth W. Regan: "Quantum Algorithms via Linear Algebra: A Primer"、MIT Press、ISBN 978-0262028394︵2014年12月5日︶。
●竹内薫:﹁量子コンピューターが本当にすごい﹂、PHP研究所、ISBN 978-4569824987︵2015年5月16日︶。
●西野哲朗、岡本 龍明、三原孝志:﹁量子計算﹂︵ナチュラルコンピューティング・シリーズ第6巻︶、近代科学社、ISBN 978-4764904866 (2015年10月31日)。
●西野友年:﹁今度こそわかる量子コンピューター﹂、講談社、ISBN 978-4061566057︵2015年10月23日︶。
●Keisuke Fujii: "Quantum Computation with Topological Codes: From Qubit to Topological Fault-Tolerance", Springer、ISBN 978-9812879950︵2016年1月13日︶。
●宮野健次郎、古澤明:﹁量子コンピュータ入門﹂(第2版)、日本評論社、ISBN 978-4535788053︵2016年3月3日︶。
●中山茂:﹁クラウド量子計算入門‥IBMの量子シミュレーションと量子コンピュータ﹂、カットシステム、ISBN 978-4877834081(2016年9月1日)。
●Tudor D. Stanescu: "Introduction to Topological Quantum Matter & Quantum Computation"、CRC Press、ISBN 978-1482245936 (2016年12月7日)。
●西森秀稔、大関真之:﹁量子コンピュータが人工知能を加速する﹂、日経BP社、ISBN 978-4822251895︵2016年12月9日︶。
●小柴健史、藤井啓祐、森前智行:﹁観測に基づく量子計算﹂、コロナ社、ISBN 978-4339028706(2017年3月10日)。
●富田章久:﹁量子情報工学﹂、森北出版、ISBN 978-4627853812 ︵2017年3月3日︶。
●Mingsheng Ying、川辺治之︵訳︶:﹁量子プログラミングの基礎﹂、共立出版、ISBN 978-4320124059︵2017年3月31日︶。
●森前智行:﹁量子計算理論‥量子コンピュータの原理﹂、森北出版、ISBN 978-4627854017︵2017年11月13日︶。
●中山茂:﹁クラウド量子計算‥量子アセンブラ入門﹂、NextPublishing Authors Press、オンデマンド印刷本 (2018年1月15日)。
●中山茂‥﹁Python クラウド量子計算 QISKITバイブル﹂、オンデマンド自主出版︵2018年5月3日︶。
●西森秀稔、大関 真之‥﹁量子アニーリングの基礎﹂、共立出版、ISBN 978-4320035386︵2018年5月19日︶。
●中山茂‥﹁Python量子プログラミング入門﹂、オンデマンド自主出版︵2018年6月25日︶。
●長橋賢吾‥﹁図解入門 よくわかる 最新 量子コンピュータの基本と仕組み﹂、秀和システム、ISBN 978-4798054551︵2018年9月26日︶。
●中山茂‥﹁Python量子プログラミング入門2﹂、オンデマンド自主出版︵2018年10月28日︶。
●﹁量子コンピュータ/イジング型コンピュータ研究開発最前線﹂、株式会社情報機構、ISBN 978-4-86502-165-3 (2019年2月︶。
●古澤明‥﹁光の量子コンピューター﹂、集英社インターナショナル (インターナショナル新書)、ISBN 978-4797680355︵2019年2月7日︶。
●中山茂‥﹁Qiskit 量子プログラミング入門﹂、オンデマンド自主出版︵2019年2月8日︶。
●湊雄一郎‥﹁いちばんやさしい量子コンピューターの教本﹂、インプレス、ISBN 978-4295006077︵2019年5月20日︶。
●宇津木健、徳永裕己 (監修)‥﹁絵で見てわかる量子コンピュータの仕組み﹂、翔泳社、ISBN 978-4798157467 ︵2019年7月10日︶。
●高木剛‥﹁暗号と量子コンピュータ: 耐量子計算機暗号入門﹂、オーム社、ISBN 978-4274224102︵2019年8月25日︶
●Emily Grumbling and Mark Horowitz(Eds):"Quantum Computing: Progress and Prospects (2019)", The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, ISBN 978-0-309-47969-1 (Sep, 4th, 2019).
●Jack D. Hidary:"Quantum Computing: An Applied Approach"、Springer、ISBN 978-3030239213 (2019年9月20日)。
●佐川弘幸、吉田宣章‥﹁量子情報理論 第3版﹂、丸善出版、ISBN 978-4621304167︵2019年10月30日︶。
●藤井啓祐‥﹁驚異の量子コンピュータ: 宇宙最強マシンへの挑戦﹂、岩波書店 (岩波科学ライブラリー)、ISBN 978-4000296892︵2019年11月20日︶。
●Emily Grumbling ・Mark Horowitz 編:﹁米国科学・工学・医学アカデミーによる量子コンピュータの進歩と展望﹂、共立出版、ISBN 978-4-320-12455-4 (2020年1月14日).
●Chris Bernhardt、湊雄一郎 (監訳), 中田真秀 (監訳) ‥﹁みんなの量子コンピュータ﹂、翔泳社、ISBN 978-4798163574︵2020年1月24日︶。
●武田俊太郎‥﹁量子コンピュータが本当にわかる! ― 第一線開発者がやさしく明かすしくみと可能性﹂、技術評論社、ISBN 978-4297111359︵2020年2月19日︶。
●遠藤理平‥﹁14日で作る量子コンピュータ‥シュレディンガー方程式で量子ビット・量子ゲート・量子もつれを数値シミュレーション Python版﹂、カットシステム、ISBN 978-4877834715︵2020年5月1日︶。
●小林雅一‥﹁ゼロからわかる量子コンピュータ﹂、講談社現代新書、ISBN 978-4065282991︵2022年6月15日︶。
●縫田光司‥﹁耐量子計算機暗号﹂、森北出版、ISBN 978-4627872110 (2020年8月6日︶。
●Eric R. Johnston, Nic Harrigan, Mercedes Gimeno-Segovia‥﹁動かして学ぶ量子コンピュータプログラミング﹂、オライリージャパン、ISBN 978-4873119199 ︵2020年8月27日︶。
●Maria Schuld、Francesco Petruccione、大関 真之 (監訳)‥﹁量子コンピュータによる機械学習﹂、共立出版、ISBN 978-4320124622︵2020年8月28日︶。
●嶋田義皓‥﹁量子コンピューティング 基本アルゴリズムから量子機械学習まで﹂、オーム社、ISBN 978-4-274-22621-2︵2020年11月9日︶。
●杉﨑研司‥﹁量子コンピュータによる量子化学計算入門﹂、講談社、ISBN 978-4065218273︵2020年12月7日︶。
●湊雄一郎, 加藤拓己, 比嘉恵一朗, 永井隆太郎‥﹁IBM Quantumで学ぶ量子コンピュータ﹂、秀和システム、ISBN 978-4798062808 ︵2021年3月6日︶。
●Sarah C. Kaiser, Christopher Granade‥”Learn Quantum Computing with Python and Q#: A hands-on approach”、Manning、ISBN 978-1617296130︵2021年6月22日︶。
●Johnny Hooyberghs‥”Introducing Microsoft Quantum Computing for Developers: Using the Quantum Development Kit and Q#”、Apress、ISBN 978-1484272459 (2021年12月10日)。
●Filip Wojcieszyn:"Introduction to Quantum Computing with Q# and QDK"、Springer、ISBN 978-3030993788︵2022年5月7日︶。
●Mariia Mykhailova:"Q# Guide: Instant Help for Q# Developers"、Oreilly、ISBN 978-1098108861︵2022年7月19日︶。
●S. C. Kaiser, C. Granade, 黒川 利明 (訳):﹁PythonとQ#で学ぶ量子コンピューティング﹂、朝倉書店、ISBN 978-4254122688 (2022年9月6日)。
●西村治道:﹁基礎から学ぶ 量子計算‥アルゴリズムと計算量理論﹂、オーム社、ISBN 978-4-274-22969-5︵2022年11月18日︶。
●束野仁政‥﹁量子コンピュータの頭の中――計算しながら理解する量子アルゴリズムの世界﹂、技術評論社、ISBN 978-4297135119︵2023年6月19日︶。
●工藤 和恵‥﹁基礎から学ぶ 量子コンピューティング: イジングマシンのしくみを中心に﹂、オーム社、ISBN 978-4274230509︵2023年6月23日)。
●Yongshan Ding、Frederic T. Chong‥ ﹁量子コンピュータシステム: ノイズあり量子デバイスの研究開発﹂、オーム社、ISBN 978-4274230660︵2023年7月3日︶。
●間瀬英之、身野良寛‥﹁量子コンピュータまるわかり﹂、日本経済新聞出版,ISBN 978-4-296-11878-6 (2023年12月6日)。
外部リンク[編集]
 | この節の外部リンクはウィキペディアの方針やガイドラインに違反しているおそれがあります。過度または不適切な外部リンクを整理し、有用なリンクを脚注で参照するよう記事の改善にご協力ください。 |
- Quantum Computing Information Site
- みんなの量子コンピューター~情報・数理・電子工学と拓く新しい量子アプリ~(戦略プロポーザル「みんなの量子コンピュータ」, 科学技術振興機構の研究開発戦略センター, 2018年12月1日. )
- Q-Portal:量子関連の最新情報を提供する総合サイト(理化学研究所)
- ACM Transactions on Quantum Computing (TQC)
- IEEE Quantum
- 一般社団法人情報処理学会の「量子ソフトウェア研究会」
- PennyLane , PennyLane Documentation
- 「量子計算機で産学連合 東大・みずほ・日立など協議会 ソフト開発に活路」(日本経済新聞記事2020年7月30日)。
- 分かる 教えたくなる 量子コンピューター (日本経済新聞解説記事:2020年06月24日 公開 2021年07月05日 更新)
- 『量子コンピュータ』 - コトバンク
- 「富士通が考える、量子コンピューティングの今後」(PC Watch 2022年6月1日記事)
- 世界初「ポータブル量子コンピュータ」が発売。2量子ビットで118万8,000円より(PC Watch 2022年12月15日記事)
- Bao Yan et al.:"Factoring integers with sublinear resources on a superconducting quantum processor", arXiv:2212.12372v1 (quant-ph, 23 Dec, 2022).
- グーグルがエラー訂正で成果、量子計算機の実用化に「大きな一歩」(朝日新聞2023年3月6日記事)
- 超高速量子計算のための世界最速43ギガヘルツ リアルタイム量子信号測定に成功(JST,2023年3月6日)
- 「量子コンピュータって何?今はどこまで開発が進んでいる?話題を総まとめ」(PC Watch 2023年3月20日記事)
- 国産量子コンピューター初号機、27日に利用開始 (読売新聞2023年3月24日記事)
- 東大とIBM、127量子ビット「IBM Quantum System One with Eagleプロセッサー」を秋に稼働開始(PC Watch 2023年4月21日記事)
- 「国産量子コンピューター初号機 大規模集積化に照準」(日経新聞2023年4月24日記事) ※日経サイエンス2023年6月号掲載記事の要約。
- Torsten Hoefler, Thomas Häner, Matthias Troyer: "Disentangling Hype from Practicality: On Realistically Achieving Quantum Advantage", Communications of the ACM, Vol.66, No.5 (May 2023), pp.82-87. DOI:10.1145/3571725
- ループ型光量子コンピューターの試作機できました 課題は精度の向上 (朝日新聞、2023年7月26日)
- 量子コンピューター、計算時の課題克服 米ハーバード大 (日本経済新聞、2023年12月7日)
- 光量子コンピューターの「量子ビット」でエラー修正する手法開発…東大など(読売新聞、2024年1月19日)
|
|---|
| 全般 |
|
|---|
| ハードウェア |
|
|---|
アルゴリズム•
プログラミング言語 |
|
|---|
| 項目 |
|
|---|
| 関連分野 |
|
|---|
| メーカー |
|
|---|
| 実機 |
|
|---|
| 人物 |
|
|---|
 カテゴリ カテゴリ |

 の状態を同時に計算し、
の状態を同時に計算し、 個の重ね合わされた結果を得ることができる。しかし、重ね合わされた結果を観測しても確率に従ってランダムに選ばれた結果が1つ得られるだけであり、古典コンピュータに対する高速性は得られない。高速性を得るためには欲しい答えを高確率で求める工夫を施した量子コンピュータ用のアルゴリズムが必須である。もしも数千量子ビットのハードウェアが実現したならば、この量子ビットの重ね合わせ状態を利用することで、量子コンピュータは古典コンピュータでは到底実現し得ない規模の並列コンピューティング︵計算速度の量子超越性︶を実現すると言われている。
量子コンピュータの能力については、理論上の話︵予測や予測に関する議論︶と、製作中の量子プロセッサの製作者が考えている予定値と、すでに製作された現実の機械についての実測値がある。実現した値については、やはり上述の英語版の年表が詳しい。︵当記事の後半の#計算能力や#実際の節は、内容が更新がされておらず、かなり古い内容なので、あまり参考にはならない。︶
将来に量子コンピュータの販売が行われるようになれば、初期の発展段階で量子コンピュータの重要な特許を多く取得した会社が莫大な収益や利益をあげると予想され、後手にまわった側は、特許を保有する側に対して膨大な特許実施使用料を支払う立場になったり、競争に負けて会社が衰退してしまう可能性もある。そのため2022年の時点では上で説明した数社だけではなくて、ほかにもあわせて数十社ほどが量子コンピュータ関連の開発を競い合っている。
なお単なるコンピュータの利用者になるだけのつもりの人にとっての﹁目先の利用価値﹂について言えば、2022年の時点ではスーパーコンピュータや普通のPCの方が利用価値が高いといえる︵量子コンピュータが実用的な問題の処理に本格的に使えるようになるまでには﹁もうしばらく﹂時間がかかると考えられている︶。
個の重ね合わされた結果を得ることができる。しかし、重ね合わされた結果を観測しても確率に従ってランダムに選ばれた結果が1つ得られるだけであり、古典コンピュータに対する高速性は得られない。高速性を得るためには欲しい答えを高確率で求める工夫を施した量子コンピュータ用のアルゴリズムが必須である。もしも数千量子ビットのハードウェアが実現したならば、この量子ビットの重ね合わせ状態を利用することで、量子コンピュータは古典コンピュータでは到底実現し得ない規模の並列コンピューティング︵計算速度の量子超越性︶を実現すると言われている。
量子コンピュータの能力については、理論上の話︵予測や予測に関する議論︶と、製作中の量子プロセッサの製作者が考えている予定値と、すでに製作された現実の機械についての実測値がある。実現した値については、やはり上述の英語版の年表が詳しい。︵当記事の後半の#計算能力や#実際の節は、内容が更新がされておらず、かなり古い内容なので、あまり参考にはならない。︶
将来に量子コンピュータの販売が行われるようになれば、初期の発展段階で量子コンピュータの重要な特許を多く取得した会社が莫大な収益や利益をあげると予想され、後手にまわった側は、特許を保有する側に対して膨大な特許実施使用料を支払う立場になったり、競争に負けて会社が衰退してしまう可能性もある。そのため2022年の時点では上で説明した数社だけではなくて、ほかにもあわせて数十社ほどが量子コンピュータ関連の開発を競い合っている。
なお単なるコンピュータの利用者になるだけのつもりの人にとっての﹁目先の利用価値﹂について言えば、2022年の時点ではスーパーコンピュータや普通のPCの方が利用価値が高いといえる︵量子コンピュータが実用的な問題の処理に本格的に使えるようになるまでには﹁もうしばらく﹂時間がかかると考えられている︶。
 1量子ビットに対するユニタリー変換とCNOTゲートの組合せによって、n量子ビットの任意のユニタリ変換を構成できることが知られている。
1量子ビットに対するユニタリー変換とCNOTゲートの組合せによって、n量子ビットの任意のユニタリ変換を構成できることが知られている。

















